Get facts about lasix kidney scan, results, normal/abnormal findings, and how to interpret images for health. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch, patient-focused care in renal scans. We help both patients and doctors with the newest in nuclear medicine renography.
A Lasix kidney scan is a test that uses a special dye and Lasix to check kidney function. It also finds blockages in urine flow. This test is key for checking how well the kidneys are working.
We use this advanced test to give the best care. We help patients understand their scan results and what they mean.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the purpose and significance of a Lasix kidney scan.
- Learn how renography helps in diagnosing kidney issues.
- Discover the role of radiotracers and Lasix in renal scans.
- Find out how this test detects obstructions and evaluates kidney function.
- Get insights into the importance of renal scan results and interpretation.
The Fundamentals of Lasix Kidney Scan Procedures
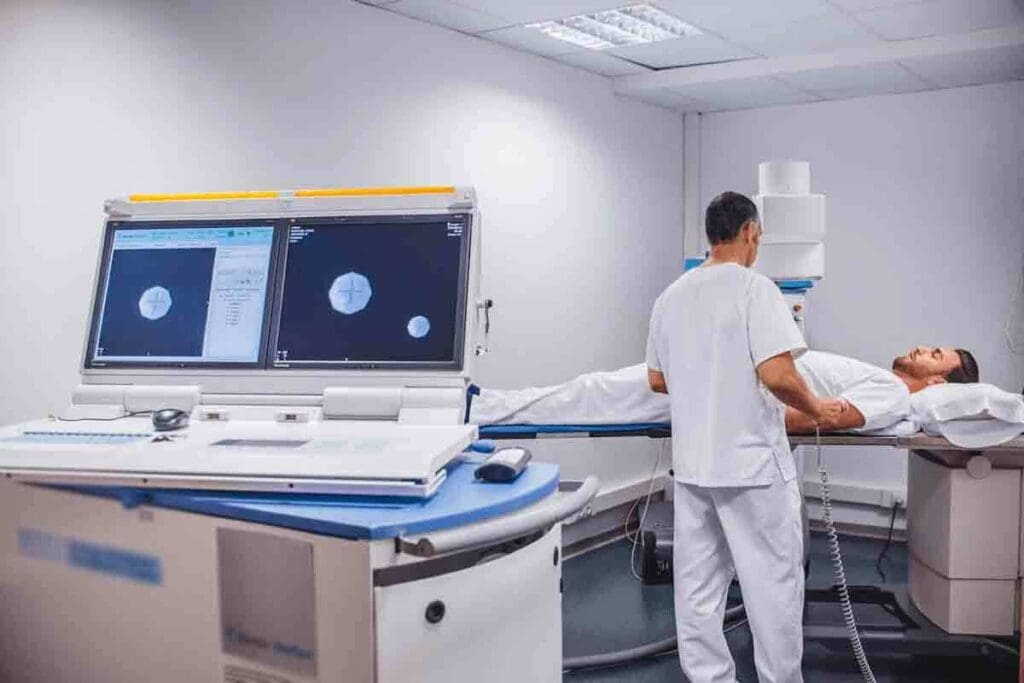
A Lasix kidney scan, also known as a renal scan with Lasix, is a test that checks how well your kidneys work. It uses a tiny bit of radioactive material, or radiotracer, injected into your blood. This material goes to your kidneys, letting a special camera take pictures of how they function and drain urine.
Definition and Medical Purpose
The Lasix kidney scan checks if your kidneys can work and drain urine well. It uses furosemide, a medicine that makes you pee more, to see how your kidneys do. Doctors use this scan to learn about your kidney health, spot problems like blockages or damage, and find out if your kidneys are working right.
How Furosemide Enhances Diagnostic Accuracy
Furosemide, or Lasix, is given during the scan to make your kidneys pee more. This helps doctors see how well your kidneys can handle this extra work. By watching how your kidneys react to furosemide, doctors can find out if there are any issues. This makes the scan more accurate in showing how your kidneys are doing.
The table below shows what the Lasix kidney scan procedure does and how furosemide helps:
| Procedure Component | Description | Role of Furosemide |
| Radiotracer Injection | A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the bloodstream. | Not applicable |
| Furosemide Administration | Furosemide is given to stimulate urine production. | Enhances diagnostic accuracy by challenging kidney function. |
| Imaging | A special camera captures images of kidney function and drainage. | Helps assess kidney response to increased urine production. |
Knowing how the Lasix kidney scan works helps patients understand its importance in checking kidney health. Furosemide is key in making the scan more accurate by testing how well your kidneys can handle more urine.
Nuclear Medicine Technology Behind Renal Scintigraphy

Nuclear medicine technology is key in renal scintigraphy. It helps doctors check how well kidneys work. This method uses tiny amounts of radioactive materials, called radiotracers, to see how kidneys function.
Radiotracers and Their Function in Kidney Imaging
Radiotracers are special compounds that target kidney functions. When given to a patient, they release gamma rays. A gamma camera then picks up these rays, creating images that show how kidneys work.
There are different radiotracers for different kidney functions. For example, Tc-DTPA checks how well kidneys filter blood. On the other hand, Tc-MAG3 looks at how kidneys remove waste. The right radiotracer depends on what the doctor wants to know.
The Science of Detecting Kidney Activity
Renal scintigraphy uses science to see how kidneys work. A gamma camera picks up the gamma rays from the radiotracer. This info is then used to make moving pictures of kidney function.
The data from renal scintigraphy can give exact numbers about kidney function. Doctors can see how each kidney works and how fast the radiotracer leaves the kidneys.
| Radiotracer | Primary Use | Key Characteristics |
| Tc-DTPA | GFR assessment | Excreted mainly by glomerular filtration |
| Tc-MAG3 | Tubular secretion and drainage assessment | High extraction fraction, good for assessing renal function in patients with impaired kidney function |
| Tc-DMSA | Renal cortical imaging | Binds to renal cortex, useful for detecting cortical scars and anomalies |
What to Expect During Your Lasix Kidney Scan
If you’re getting a Lasix kidney scan, knowing what to expect can ease your worries. We’ll walk you through each step, from getting ready to aftercare. This way, you’ll feel comfortable and know what’s happening every step of the way.
Patient Preparation Guidelines
To get the best results from your scan, you need to prepare. Drink lots of water before the test to stay hydrated. You might also need to stop taking some medicines that could affect the scan.
On the day of the scan, wear loose, comfy clothes. Avoid jewelry or clothes with metal to prevent interference. You’ll also sign a consent form after the procedure is explained to you.
| Preparation Step | Description |
| Hydration | Drink plenty of water before the test to ensure you’re well-hydrated. |
| Medication Adjustment | Stop taking certain medications as advised by your healthcare provider. |
| Comfortable Clothing | Wear comfortable clothing without metal parts. |
The Step-by-Step Scanning Process
The scan starts with a small injection of radioactive material into your arm. This makes your kidneys show up on the scan. Then, you’ll lie on a table while images are taken at different times.
Next, you’ll get an injection of Lasix to see how your kidneys work. More images will be taken to check how your kidneys respond. The whole process usually takes about an hour and a half.
Post-Procedure Care and Safety
After the scan, you can usually go back to your normal routine unless told not to. The radioactive material leaves your body in a few hours. Drinking lots of water helps get rid of it faster.
Some people might feel a bit dizzy or have an allergic reaction to Lasix. If you notice any strange symptoms, call your doctor right away.
Your scan results will be checked by a specialist. Your doctor will then talk to you about what they found. This information will help decide what to do next in your care.
Decoding Renography: Understanding Time-Activity Curves
Renography curves are key to checking how well the kidneys drain and their health. They show kidney function over time. This helps doctors spot and track kidney problems.
The Three Phases of a Renogram
A renogram has three phases. Each phase gives different information about kidney function. The first phase shows how the radiotracer first enters the kidney.
The second phase shows how well the kidney takes the radiotracer from the blood. The third phase shows how well the kidney gets rid of the radiotracer in urine.
Understanding these phases is key to reading renography curves correctly. Doctors look at each phase’s curve to check kidney health and find problems.
How Specialists Interpret Curve Patterns
Doctors look at the shape and details of each phase’s curve. A normal curve shows quick uptake and then fast clearance, meaning healthy kidneys.
But abnormal curves can mean kidney issues. For example, a curve that peaks late or clears slowly might show a blockage in the urinary tract.
| Phase | Normal Curve Characteristics | Abnormal Curve Indications |
| Perfusion Phase | Rapid initial uptake | Delayed or reduced uptake |
| Uptake Phase | Peak activity within a few minutes | Prolonged time to peak activity |
| Excretion Phase | Prompt clearance of radiotracer | Delayed clearance, indicating possible obstruction |
By studying these curves, doctors can understand kidney function. They can spot issues like blockages or swelling. Reading these curves is complex and requires a lot of knowledge about the kidneys.
Normal Renal Scan with Lasix Results: Hallmarks of Healthy Kidney Function
Understanding a normal renal scan with Lasix results is key to knowing if your kidneys are healthy. A normal scan shows how well your kidneys are working.
Symmetric Uptake and Activity Patterns
A normal scan shows both kidneys working the same. This is seen in how evenly the kidneys take in the radiotracer. It means the kidneys are healthy.
The kidneys should quickly get rid of the radiotracer. This is shown in time-activity curves. These curves show how fast the kidneys process and get rid of the tracer.
Optimal Excretion Times and Clearance Rates
Normal scans with Lasix show fast waste removal, usually in 10-20 minutes. This shows the kidneys are working well. The Lasix test checks how well the kidneys handle a diuretic by making more urine.
- Normal excretion times: less than 10-20 minutes
- Efficient clearance of radiotracer
- Appropriate response to Lasix challenge
A healthy kidney response to Lasix is a big increase in urine flow. This helps clear the radiotracer from the kidneys. It’s a sign of good urine flow.
Visual Characteristics of Normal Renograms
Normal renograms show kidney function over time. They have:
- A quick start of radiotracer uptake
- A peak followed by a slow drop as it’s excreted
- Even curves for both kidneys, showing balanced function
These signs, along with scan data, give a full view of kidney health. Doctors use this to confirm healthy kidneys and find any problems.
Identifying Abnormal Renal Scan Results: Key Diagnostic Indicators
When looking at Lasix kidney scan results, spotting abnormal patterns is key. These signs can point to various kidney problems. It’s vital for doctors to know these signs well.
Delayed Washout: The Primary Sign of Obstruction
Delayed washout is a major sign of an abnormal renal scan. It means there’s a blockage in the urinary tract. This blockage slows down the urine flow and the radiotracer’s removal from the kidney.
Studies show that delayed washout is a key sign of obstructive uropathy. Learn more about it here.
- Delayed washout indicates possible obstruction
- Obstruction can harm the kidneys if not treated
- Measuring how much is affected helps understand the problem
Asymmetric Function and Its Clinical Significance
Asymmetric function between the two kidneys is another sign of trouble. It might mean one kidney is sick or blocked. It’s important to compare both kidneys’ functions to spot any differences.
An asymmetric function can point to serious issues that need more checking.
Quantitative Measurements in Abnormal Scans
Quantitative measurements are very important in abnormal renal scans. They include things like how well each kidney works and how fast waste is removed. Doctors use these numbers to figure out how bad the kidney problem is and what to do next.
- Differential renal function shows how each kidney is doing
- Clearance rates tell us how well kidneys remove waste
- These numbers help doctors decide on treatment and care
DTPA Scanning: Quantifying Glomerular Filtration Rate
DTPA renal scanning is a detailed test to measure GFR, which shows how well the kidneys work. It helps us check kidney health and function in different situations.
Technical Aspects of DTPA Renal Scanning
DTPA (Diethylene Triamine Pentaacetate) is a special medicine used in this test. It’s mixed with Technetium-99m (Tc-99m) and given to the patient. This mix is filtered by the kidneys, and how fast it’s cleared is tracked.
The steps of DTPA renal scanning include:
- Administration of Tc-99m DTPA
- Dynamic imaging using a gamma camera
- Measurement of DTPA clearance rate
This method gives us a precise GFR reading. This is key for spotting and tracking kidney problems.
Clinical Interpretation of GFR Measurements
GFR readings from DTPA scans are vital for kidney health checks. A normal GFR changes with age, sex, and size, usually between 90 to 120 mL/min/1.73m. If the GFR is off, it means the kidneys are not working properly.
| GFR (mL/min/1.73m2) | Kidney Function Status |
| >90 | Normal |
| 60-89 | Mildly decreased |
| 30-59 | Moderately decreased |
| 15-29 | Severely decreased |
| Kidney failure |
Understanding GFR readings helps us diagnose kidney diseases, track how they progress, and see if treatments work. These measurements guide our decisions for patient care.
Diagnostic Variations: Renalgram, Kidney Scintigraphy, and Nuclear Renal Scans
It’s important to know the differences between renalgram, kidney scintigraphy, and nuclear renal scans. These terms are used in renal imaging but each has its own method and use.
Terminology Differences in Renal Imaging
Renal imaging uses many diagnostic methods, each with its own name. A renalgram shows kidney function over time, often from nuclear medicine studies. Kidney scintigraphy uses radiotracers to see kidney function and structure. Nuclear renal scans use nuclear medicine to check kidney function.
The main difference is in what they show. Renalgrams focus on function. Kidney scintigraphy and nuclear renal scans show both function and structure. Knowing these differences helps doctors understand results better and make good decisions.
Selecting the Appropriate Diagnostic Technique
Choosing the right test depends on the patient’s condition and what we need to know. For example, a Lasix renogram is good for checking kidney function with obstruction. But for detailed anatomy, CT or MRI might be better.
We look at many things when picking a test. We consider the patient’s history, the suspected problem, and if we need to see the function or structure. Knowing each test’s strengths and weaknesses helps us choose the best one for each patient.
- Renalgram: Useful for assessing kidney function over time.
- Kidney Scintigraphy: Provides both functional and anatomical information.
- Nuclear Renal Scans: Offers a detailed assessment of kidney function using nuclear medicine technology.
By understanding these differences and choosing the right test, we can make sure patients get the right diagnosis and treatment for kidney problems.
The Lasix Renogram: Specialized Assessment for Urinary Tract Obstruction
The Lasix renogram is a key tool for finding urinary tract blockages. It uses Lasix (furosemide) to test the kidneys’ collecting system. This test shows if there’s a blockage and how bad it is.
How Lasix Challenges the Collecting System
Lasix makes the kidneys produce more urine during a renogram. This test helps find blockages in the urinary tract. A gamma camera takes images to see how the radiotracer moves through the kidneys and tract.
Lasix helps tell if a blockage is causing the urinary tract to swell. In a normal kidney, Lasix quickly clears the radiotracer from the renal pelvis. But if there’s an obstruction, it takes much longer.
Interpreting T1/2 Values in Lasix Renograms
The T1/2 value is a key part of the Lasix renogram. It shows how long it takes for the radiotracer to leave the renal pelvis after Lasix. A T1/2 under 10 minutes means no blockage. Between 10-20 minutes is uncertain, and over 20 minutes means there’s a big blockage.
| T1/2 Value (minutes) | Interpretation |
| < 10 | Normal, no significant obstruction |
| 10-20 | Equivocal, further evaluation may be needed |
| > 20 | Significant obstruction |
Understanding T1/2 values needs careful thought. It depends on the patient’s hydration, kidney health, and the renogram’s details. By looking at T1/2 values and other tests, doctors can accurately diagnose and treat urinary tract blockages.
Clinical Applications of Lasix Nuclear Renal Scans
Lasix nuclear renal scans are key in nephrology. They give deep insights into kidney function and diseases. This helps doctors diagnose and treat kidney issues.
Diagnosing Hydronephrosis and Obstruction
Lasix scans are mainly used to find hydronephrosis and blockages. Hydronephrosis is when the kidney swells due to a blockage. These scans help doctors see how bad the blockage is and what to do next.
A study in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine says Lasix scans are great for finding and managing blockages. They give important information on how well the kidneys work and drain.
“The Lasix renogram has become an essential diagnostic tool in our clinical practice, enabling us to accurately diagnose and manage patients with suspected urinary tract obstruction.” – A top Nephrologist
Evaluating Split Renal Function
Lasix scans also check how each kidney works. This is key for patients with kidney disease or after surgery. Doctors use this info to decide the best treatment.
| Kidney | Function (%) | Clearance Rate (ml/min) |
| Left Kidney | 55 | 120 |
| Right Kidney | 45 | 100 |
Post-Surgical Monitoring and Follow-up
After surgery, Lasix scans are very important. They help doctors see if treatment is working and watch for problems. This is true for kidney transplants or surgery for blockages.
In summary, Lasix scans are very useful. They help find problems like hydronephrosis and blockages. They also check how the kidneys work and help after surgery. These scans help doctors give the best care to patients.
Limitations, Risks, and Alternatives to Renal Scanning
Renal scanning is a key tool in diagnosing kidney issues. Yet, it has its own set of limitations and risks. It has greatly helped in the field of nephrology, but it’s not perfect.
Radiation Exposure Considerations
One major concern with renal scanning is the radiation it involves. It uses small amounts of radioactive materials to check kidney function. While the dose is usually safe, there are risks involved.
It’s important to balance the benefits of renal scanning with the risks of radiation. This is true, mainly for patients who need to have scans often. Keeping the radiation dose as low as possible is key.
“The risk of radiation-induced harm is generally considered to be low for most patients undergoing renal scans. Yet, it’s vital to think about the need for repeated scans and look for other ways to diagnose when we can.” – a Nuclear Medicine Specialist
Patient Contraindications and Special Populations
Some patients face higher risks with renal scanning. This includes pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, and those with severe kidney disease.
| Patient Group | Considerations |
| Pregnant Women | Risk of radiation exposure to the fetus; alternative methods preferred when possible. |
| Breastfeeding Mothers | Potential for radioactive material to be secreted in breast milk; temporary cessation of breastfeeding may be advised. |
| Severe Kidney Disease | Impaired renal function may affect the clearance of radiotracers; careful interpretation of scan results is necessary. |
Complementary Diagnostic Approaches
In some cases, other tests might be better. These include ultrasound, CT scans, MRI, and more non-invasive tests.
- Ultrasound for assessing kidney size and detecting obstruction
- CT scans for detailed anatomical information
- MRI for evaluating kidney function and vascular anatomy
By looking at these alternatives and the limits of renal scanning, doctors can choose the best test for each patient.
Conclusion: The Critical Role of Lasix Kidney Scans in Modern Nephrology
Lasix kidney scans are key in modern nephrology. They give vital info for treatment plans. These scans use furosemide to check kidney function and find blockages.
These scans help us diagnose and manage kidney diseases well. They give insights for better treatment plans. This improves patients’ lives and health.
Lasix kidney scans are essential for accurate diagnosis. They help us give top-notch care to those with kidney disease. This leads to better health for our patients in the long run.
FAQ
What is a Lasix kidney scan, and how does it work?
A Lasix kidney scan, also known as a renal scan with Lasix, is a test to check kidney function. It uses a special dye and the diuretic Lasix. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the blood. Then, a gamma camera tracks it as it moves through the kidneys.
What is the purpose of using Lasix during a renal scan?
Lasix is used in a renal scan to test the kidneys. It makes the kidneys work harder by increasing urine production. This helps doctors see how well the kidneys function and find any blockages.
How do I prepare for a Lasix kidney scan?
To get ready for a Lasix kidney scan, drink lots of water. Don’t eat a big meal before it. Tell your doctor about any medicines you’re taking. They’ll give you specific instructions based on your situation.
What are the normal results of a renal scan with Lasix?
Normal results show both kidneys working well. They should clear the dye quickly and evenly. The curves from the scan will look normal, showing healthy kidneys.
What does an abnormal renal scan with Lasix indicate?
An abnormal scan might show one kidney working slower or not at all. It could mean there’s a blockage or damage. These signs need more tests to figure out what’s wrong.
How is DTPA scanning used in renal imaging?
DTPA scanning measures how well the kidneys filter waste. It uses a special dye to check the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This helps doctors see if the kidneys are working right.
What are the clinical applications of Lasix nuclear renal scans?
Lasix scans help find blockages and check how well each kidney works. They’re also used after surgery to see how the kidneys are healing. These scans help doctors make treatment plans.
Are there any limitations or risks associated with renal scanning?
Yes, renal scans use some radiation. Some people might not be able to have them because of kidney problems or allergies. Doctors might use other tests, like an ultrasound or an MR,I instead.
How is a Lasix renogram interpreted?
A Lasix renogram is read by looking at the curves from the scan. These curves show how the kidneys handle Lasix. Doctors look for certain patterns to find problems and check kidney function.
What is the significance of T1/2 values in Lasix renograms?
T1/2 values show how long it takes for the dye to leave the kidneys after Lasix. If it takes too long, it might mean there’s a blockage. Normal values mean the kidneys are working fine.
References
- Taylor, A. T., Nally, J., Aurell, M., et al. (2018). SNMMI Procedure Standard / EANM Practice Guideline for Diuretic Renal Scintigraphy in Adults With Suspected Upper Urinary Tract Obstruction. Seminars in Nuclear Medicine, 48(4), S1-S35. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6020824/
- Banks, K. P. (2022). Diuretic Renal Scintigraphy Protocol Considerations. Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology, 50(4), 309–315. https://tech.snmjournals.org/content/50/4/309























