NBA star Kevin Durant’s devastating Achilles tendon injury in 2019 shocked the sports world. It showed how serious such injuries are for athletes. Knowing the difference between a torn and strained Achilles tendon is key for treatment and recovery. A torn tendon means a lot of downtime, but a strained one might let you get back sooner.
It’s important to understand the signs and symptoms of Achilles tendon injuries. Both torn and strained tendons can hurt and feel uncomfortable. But, the injury’s severity and how it feels can tell you how bad it is.
Key Takeaways
- Distinguishing between a torn and strained Achilles tendon is vital for the right treatment.
- Achilles tendon injuries can greatly affect athletes and others.
- Knowing the signs and symptoms helps figure out how serious the injury is.
- Getting a proper diagnosis is key for a good recovery and getting back to activities.
- Ignoring Achilles tendon injuries can cause more problems.
Understanding the Achilles Tendon Anatomy
Knowing how the Achilles tendon works is key to avoiding and treating injuries. This tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It’s vital for walking, running, and jumping.
Function and Importance of the Achilles Tendon
The Achilles tendon helps the calf muscles push the heel down. This is important for standing on tiptoes and walking upstairs. It’s also key for pushing off the ground when we walk.
This tendon is under a lot of stress, which makes it prone to injuries. It’s essential for our mobility and balance. Without it, we can’t move as well or do everyday activities.
Common Causes of Achilles Tendon Injuries
Achilles tendon injuries happen for many reasons. Overuse is a big one, causing small tears and swelling. Starting to exercise too hard too fast can also lead to injuries.
Other reasons include poor training habits and not warming up or cooling down right. Wearing the wrong shoes can also cause problems.
| Cause | Description | Prevention Strategy |
| Overuse | Repetitive stress leading to micro-tears | Gradual increase in activity level |
| Sudden Intensity Increase | Rapid change in physical activity level | Structured training programs |
| Poor Training Habits | Inadequate warm-up or cool-down | Proper training techniques |
Knowing why injuries happen helps us prevent them. It’s important for everyone to understand the risks of Achilles tendon injuries.
Torn vs Strained Achilles: Key Differences
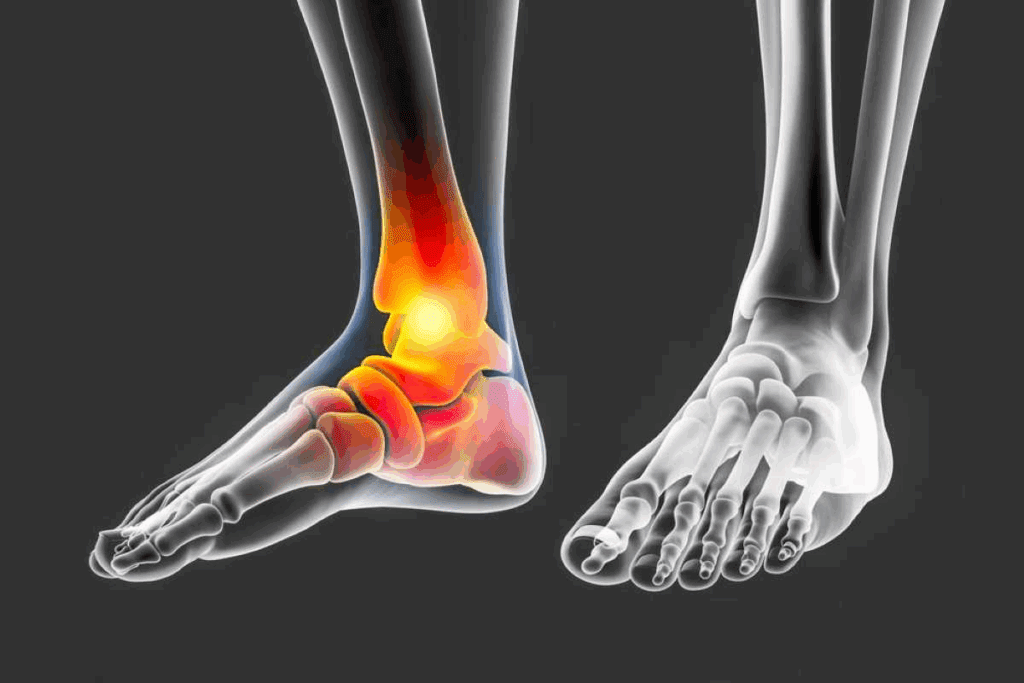
It’s important to know the difference between a torn and strained Achilles tendon. This knowledge helps in getting the right treatment. The Achilles tendon is key to our movement, and injuries can really affect our lives.
Injuries to the Achilles tendon can be mild or severe. The treatment depends on the injury’s severity. Getting a correct diagnosis is key for proper care.
What Constitutes a Strain
A strain happens when the Achilles tendon stretches too far, causing small tears. This injury is often called a “pull” or “stretch.” It can happen from sudden activity, not warming up, or bad training.
Signs of a strained Achilles tendon include pain, stiffness, and trouble moving. The severity of the strain can vary. Treatment usually includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), plus physical therapy to make the tendon stronger.
What Defines a Tear or Rupture
A tear or rupture is a more serious injury where the tendon is partially or completely broken. This injury is marked by sudden, sharp pain and might sound like a “pop” or “snap.”
Tears can be partial or complete, with complete ones being worse. Treatment for a torn Achilles tendon often needs more serious steps. This might include surgery, keeping the tendon in place, or a mix of both, followed by a rehab program.
“The key to effective treatment is understanding the extent of the injury and tailoring the approach.” -An Orthopedic Specialist
Grading System for Achilles Injuries
Achilles tendon injuries are graded from 1 to 3. Grade 1 is a mild strain, and Grade 3 is a severe tear or rupture. This system helps doctors figure out how bad the injury is and plan the best treatment.
- Grade 1: Mild strain with minimal pain and no significant loss of function.
- Grade 2: Moderate strain with noticeable pain and some loss of function.
- Grade 3: Severe tear or rupture with significant pain and loss of function.
Knowing the grading system is vital for diagnosis and treatment. It helps doctors make the right decisions for care.
Risk Factors for Achilles Tendon Injuries
The risk of Achilles tendon injuries is influenced by many factors. These include age, lifestyle, and health. Knowing these factors helps prevent and diagnose injuries early.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age is a big risk factor for Achilles tendon injuries. The risk grows with age, mainly between 30 and 50. Middle-aged men are more likely to get Achilles tendon ruptures than others. For example, Kevin Durant’s injury shows the risk for athletes in this age group.
Men are more likely to get Achilles tendon injuries than women. This is because men often do more intense sports.
Athletic Activities with Higher Risk
Some sports increase the risk of Achilles tendon injuries. Sports like basketball, soccer, and tennis are risky because they involve running, jumping, and quick changes of direction. Athletes in these sports should be careful and take preventive steps.
How hard and often you train also matters. Sudden increases in training load without rest can cause injuries like Achilles tendonitis.
Medical Conditions that Increase Vulnerability
Some medical conditions make you more likely to get Achilles tendon injuries. For example, people with diabetes, hypertension, and obesity are at higher risk. This is because these conditions can lead to poor circulation and more stress on tendons.
Also, some medicines, like fluoroquinolone antibiotics and corticosteroids, can increase the risk of tendon injuries, including the Achilles tendon.
Immediate Signs of an Achilles Tendon Injury
When an Achilles tendon injury happens, you’ll notice some key signs right away. Knowing these signs helps you figure out what to do next.
The Moment of Injury: What It Feels Like
An Achilles tendon injury feels unique. People often say it feels like a sharp pain or a kick in the back of the leg. You might also feel your ankle wobble or feel weak.
Sudden Pain in the Achilles Tendon
Pain in the Achilles tendon is a big sign of injury. This pain is sharp and usually feels right above the heel. It might hurt all the time or only when you move your ankle.
Audible Popping or Snapping Sounds
At times, you might hear a popping or snapping sound when it happens. This loud “pop” can mean a serious injury.
Key immediate signs to watch for include:
- Sudden, severe pain in the back of the leg
- A feeling of being kicked or struck
- Inability to stand on tiptoe or push off the ground with the affected leg
- Audible popping or snapping sounds
- Swelling or bruising around the Achilles tendon
If you notice any of these signs, get medical help right away. This helps avoid more damage and ensures you get the right treatment.
Pain Characteristics: Torn vs Strained Achilles
The pain from Achilles tendon injuries can be quite different, depending on if it’s torn or strained. Knowing these differences is key to figuring out how serious the injury is and when to see a doctor.
Location and Intensity of Pain
The pain’s location and how bad it is can tell you if it’s a torn or strained tendon. A strained tendon usually hurts in one spot, feeling like a dull ache or stiffness. This pain often happens after resting or when starting to move.
A torn tendon, on the other hand, causes sudden, sharp pain. This pain is usually at the back of the ankle and can be so bad it makes it hard to stand or walk.
Pain During Rest vs Activity
The way pain acts during rest and activity can also give clues. For a strained tendon, pain might feel better as you move, but it can come back or get worse after stopping.
But a torn tendon’s pain stays the same, whether you’re moving or resting. The pain might change in intensity based on how active you are.
Pain Progression Over Time
Watching how pain changes over time can also help. A strained tendon’s pain might get better with rest and care, but it can get worse if it doesn’t heal right.
A torn tendon’s pain might seem to get better, but that doesn’t mean it’s healed. It could mean the pain is changing or other problems are starting.
| Pain Characteristic | Strained Achilles | Torn Achilles |
| Location of Pain | Localized to the area of inflammation | Localized to the back of the ankle |
| Intensity of Pain | Dull ache or stiffness | Sudden, severe sharp or stabbing pain |
| Pain During Activity | May decrease with activity, worsen after | Persists during activity and at rest |
| Pain Progression | Gradually improves with rest, can worsen without proper care | Initial severe pain may subside, potentially leading to chronic pain or complications |
Visual and Physical Symptoms of Achilles Injuries
Achilles tendon injuries show clear signs that help tell if it’s a strain or a tear. Knowing these signs is key to figuring out how bad the injury is and what to do next.
Swelling Patterns in Tears vs Strains
Swelling is a common sign of Achilles tendon injuries. A strain usually causes swelling in one spot, which isn’t too bad. But, a tear or rupture makes swelling spread all along the tendon.
Comparison of Swelling Patterns
| Symptom | Strain | Tear/Rupture |
| Swelling Location | Localized | Extensive, along the tendon |
| Swelling Severity | Less pronounced | More pronounced |
Bruising as an Indicator of Severity
Bruising is a sign of how serious an Achilles tendon injury is. It happens when blood leaks into the tissue around the injury. Strains might not show much bruising, but tears or ruptures can cause a lot, spreading to the heel or ankle.
Skin and Tissue Changes Around the Injury
The skin and tissue around an Achilles injury can change in ways that hint at the injury’s nature. Strains might just look a bit inflamed. But, tears or ruptures can cause big changes like discoloration, swelling, and even a visible gap in the tendon.
It’s essential to monitor these symptoms closely and seek medical attention if they worsen or if there’s significant impairment of function.
Functional Limitations After Achilles Injuries
After an Achilles injury, people often face big challenges in their daily lives and sports. These issues depend on how bad the injury is, whether it’s a strain or a tear.
Differences in Range of Motion
One big problem after an Achilles injury is less movement. People with a strained Achilles might not move as much as those with a torn one. A tear really limits how far you can bend your foot up or down.
Range of Motion Comparison:
| Movement | Strained Achilles | Torn Achilles |
| Dorsiflexion | Moderately Limited | Significantly Limited |
| Plantarflexion | Mildly Limited | Severely Limited |
Weight-Bearing Capabilities
Being able to stand on your feet is also a big issue after an Achilles injury. A strained Achilles might hurt but you can stand. But a torn Achilles makes it hard or impossible to stand on the hurt leg.
Difficulties with Walking and Standing
Walking and standing get really hard after an Achilles injury. How hard it is depends on how bad the injury is. For example, someone with a torn Achilles might feel a lot of pain and wobble while walking or standing. They might need to use crutches.
The table below shows the big challenges with strained and torn Achilles tendons:
| Activity | Strained Achilles | Torn Achilles |
| Walking | Painful but possible | Difficult or impossible |
| Standing | Manageable with discomfort | Challenging due to instability |
| Range of Motion | Mild to moderate limitation | Significant limitation |
Self-Assessment Tests for Achilles Injuries

Self-assessment tests for Achilles injuries can give you clues before you see a doctor. These tests are not a full diagnosis but can show how serious the injury might be.
The Thompson Test (Calf Squeeze Test)
The Thompson Test, or Calf Squeeze Test, is a simple way to check the Achilles tendon. Here’s how to do it:
- Lie on your stomach with your feet hanging off the bed.
- Have someone squeeze your calf muscle.
- If your foot doesn’t flex, it could mean a ruptured tendon.
This test is good because it doesn’t stress the tendon more.
Single Leg Heel Raise Test
The Single Leg Heel Raise Test is another tool to check the Achilles tendon. Here’s how to do it:
- Stand on one leg.
- Slowly raise your heel off the ground.
- If it’s hard or hurts, it might be an injury.
Limitations of Self-Diagnosis
Self-assessment tests are helpful but have limits. They might not always show the injury’s full picture. Always see a doctor for a real diagnosis and treatment plan. For more on Achilles tendon injuries, visit The Foot Institute.
| Test | Description | Indication |
| Thompson Test | Squeeze calf muscle while lying on stomach | Lack of foot flexion may indicate rupture |
| Single Leg Heel Raise | Stand on one leg and raise heel | Difficulty or pain may indicate injury |
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Severe Achilles injuries need quick medical help to avoid lasting damage. Knowing when to get help is key for a good recovery.
Red Flag Symptoms Requiring Emergency Care
Some signs of Achilles injuries mean you should see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe pain or swelling in the Achilles tendon area
- Audible popping or snapping sounds at the time of injury
- Inability to stand on tiptoes or walk
- Significant bruising or discoloration around the Achilles tendon
- Deformity or a palpable gap in the tendon
If you notice any of these signs, get medical help fast. A study in a Journal shows early treatment helps a lot.
Complications of Untreated Achilles Injuries
Not getting medical help for severe Achilles injuries can cause problems. These include:
- Chronic pain and weakness
- Increased risk of re-injury
- Prolonged recovery time
- Potential for the injury to become chronic
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons warns, “Ignoring treatment for Achilles tendon injuries can lead to long-term problems.”
Knowing when to get medical help is important for treating Achilles injuries. Spotting red flag symptoms and understanding complications helps you recover faster.
Professional Diagnosis of Achilles Injuries
Diagnosing Achilles tendon injuries involves a mix of clinical checks and imaging studies. Doctors use different methods to figure out the injury’s severity and type. This is key to finding the best treatment.
Physical Examination Techniques
A detailed physical check is the first step in diagnosing Achilles tendon injuries. Healthcare providers use several methods to check the tendon’s condition, including:
- Palpation to find tender spots
- Checking range of motion and strength
- Specific tests like the Thompson test (calf squeeze test)
These physical checks help doctors find out if there’s an Achilles tendon injury and how severe it is.
Imaging Studies: MRI, Ultrasound, and X-rays
Imaging studies are key in confirming the diagnosis and seeing how bad the injury is. The most used imaging tools are:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Gives detailed images of soft tissues, like tendons, making it great for finding tears and tendinopathy.
- Ultrasound: Offers live images and is good for checking tendon structure and finding tears or inflammation.
- X-rays: Not as good for soft tissue, but X-rays can help rule out bone problems.
Each imaging tool has its own benefits, and the choice depends on the situation and what’s needed.
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
When diagnosing Achilles tendon injuries, it’s important to think about other conditions that might look or happen with these injuries. Other possible diagnoses include:
- Calf strains or tears
- Ankle sprains
- Other heel pain causes, like plantar fasciitis
A thorough diagnostic process ensures patients get the right diagnosis and treatment plan.
Partial vs Complete Achilles Tears
Achilles tendon injuries can range from partial tears to complete ruptures. Knowing the difference is key for the right treatment and recovery.
Symptoms Specific to Partial Tears
Partial Achilles tears can be tricky because they don’t always stop you from moving. You might feel:
- Pain and stiffness in the Achilles tendon area, mainly after you’ve been active
- Swelling or thickening of the tendon
- A feeling of weakness when pushing off with the affected leg
These symptoms can sneak up on you, getting worse over time. They might be treated with rest and other non-surgical methods first.
Signs of a Complete Rupture
A complete rupture is a serious injury. It’s marked by:
- A sudden, sharp pain in the lower leg
- An audible snap or pop at the time of injury
- Significant difficulty or inability to stand on tiptoes or push off with the affected leg
This injury needs quick medical attention because it severely damages the tendon fibers.
Prognosis Differences
The outlook for partial Achilles tears and complete ruptures is quite different. Partial tears might heal with rest and physical therapy. But, they can turn into complete ruptures if not treated right.
Complete ruptures, being more severe, often need surgery. Their recovery takes longer, and the rehab is tougher.
In short, telling partial from complete Achilles tears is critical for the right treatment. While partial tears might be treated without surgery, complete ruptures usually need more aggressive care to fix and prevent more problems.
Achilles Tendonitis vs Tear: Distinguishing Features
Telling the difference between Achilles tendonitis and a tear can be tricky. Tendonitis is when the tendon gets inflamed, often from too much use or strain. An Achilles tear, on the other hand, means the tendon fibers have partially or fully ruptured.
Chronic vs Acute Symptoms
Tendonitis usually starts with chronic symptoms like pain and stiffness that grow over time. These symptoms often show up in the morning or after rest. An Achilles tear, by contrast, comes with sudden, severe pain and might even sound like a snap.
Chronic symptoms are typical of tendonitis. The pain builds up over time, and you might see swelling and warmth around the tendon.
Pain Patterns and Progression
The pain from tendonitis is usually spread out and might feel like it’s just above the heel. It gets worse with activity but can get better with rest. If ignored, it can stick around. A tear, on the other hand, causes sharp pain right at the tear site, leading to a big drop in strength and function.
Pain progression is a big difference too. Tendonitis pain can change with how active you are, but a tear’s pain is immediate and intense.
Risk of Progression from Tendonitis to Tear
There’s a worry that tendonitis could turn into a tear if not treated right. Long-term inflammation and tendon wear can make it weak and prone to rupture. So, it’s key to treat tendonitis early with rest, physical therapy, and sometimes medicine.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of Achilles tendonitis can prevent progression to a tear.
- Proper management includes a combination of rest, rehabilitation, and potentially medication to reduce inflammation.
- Understanding the risk factors and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of progressing from tendonitis to a more severe injury.
Treatment Approaches for Strained Achilles
Treating a strained Achilles tendon requires a mix of conservative management and physical therapy. Knowing these methods is key to a full recovery and avoiding more harm.
Conservative Management Strategies
For Achilles tendon strains, the first step is usually conservative management. This method aims to lessen pain, reduce swelling, and help the tendon heal. It includes:
- Rest and Ice: Allowing the tendon to heal and using ice to cut down swelling.
- Compression: Applying compression bandages to lessen swelling.
- Elevation: Raising the affected leg to reduce swelling.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Using over-the-counter drugs like ibuprofen to ease pain and swelling.
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons says, “The first steps in treating Achilles tendon strains often include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with NSAIDs for pain relief.”
Physical Therapy Protocols
Physical therapy is vital in rehabilitating Achilles tendon strains. A good physical therapy program can improve strength, flexibility, and function. It may include:
| Therapy Type | Description | Benefits |
| Stretching Exercises | Targets the calf muscles and Achilles tendon | Makes the tendon more flexible and less stiff |
| Strengthening Exercises | Works on the calf and ankle muscles | Boosts strength and stability |
| Eccentric Training | Slow, controlled movements to strengthen the tendon | Helps the tendon heal and get stronger |
Recovery Timeline for Strains
The time it takes to recover from an Achilles tendon strain varies. Mild strains might heal in a few weeks, while severe ones can take months. It’s important to be patient and stick to the treatment plan for proper healing.
A study in a Journal found, “A structured rehab program with progressive strengthening exercises can greatly improve outcomes for patients with Achilles tendon strains.”
Treatment Options for Torn Achilles Tendons
When it comes to a torn Achilles tendon, you have two main choices: non-surgical or surgical treatment. The right option depends on the tear’s severity, your health, and how active you are.
Non-Surgical vs Surgical Management
Non-surgical treatment means wearing a cast or boot to let the tendon heal naturally. This method is often picked for older patients or those with minor tears. Surgical treatment, on the other hand, involves surgery to fix the tendon. It might offer a stronger repair and quicker recovery.
Comparison of Non-Surgical and Surgical Management
| Treatment Aspect | Non-Surgical | Surgical |
| Immobilization | Cast or walking boot for 6-8 weeks | Initial immobilization, followed by rehabilitation |
| Rehabilitation Duration | Typically longer, 6-9 months | Generally shorter, 4-6 months |
| Risk of Re-rupture | Higher risk | Lower risk with proper rehabilitation |
| Return to Activity | Slower return | Faster return to sports and activity |
Factors Influencing Treatment Decisions
Many things affect whether you’ll have surgery or not. Your age, how active you are, and your health are key. For example, younger, more active people might choose surgery for a stronger repair and quicker comeback.
Post-Treatment Rehabilitation
Rehab is important after treatment, whether it’s surgery or not. It involves physical therapy to strengthen the ankle. A good rehab plan can help avoid future problems and ensure you fully recover.
Rehabilitation Protocols might include exercises for ankle mobility, calf muscle strength, and balance. The exact plan depends on your treatment type.
Long-Term Consequences of Misdiagnosed Achilles Injuries
Achilles injuries that are not correctly diagnosed can greatly affect a person’s life and sports abilities. These misdiagnoses can lead to serious long-term health issues. They can also impact a person’s overall well-being and sports performance.
Chronic Pain and Weakness
One major issue with misdiagnosed Achilles injuries is chronic pain and weakness. If not treated right, these injuries can cause ongoing pain. This pain can make daily tasks and sports hard.
For example, athletes like Kevin Durant have faced the tough side of Achilles injuries. This shows how critical it is to get a correct diagnosis and treatment.
Chronic pain can make simple tasks hard. Also, the Achilles tendon’s weakness can harm the ankle’s stability and function. This makes the condition worse.
Increased Risk of Re-injury
Misdiagnosed Achilles injuries also raise the chance of getting hurt again. If the first injury isn’t fixed right, the tendon might not heal well. This makes it more likely to get hurt again.
This cycle of injury and re-injury can make it hard to fully recover. For athletes, it means being out of their sport for a long time. This can hurt their career and performance.
Impact on Athletic Performance
The effect of misdiagnosed Achilles injuries on sports performance is huge. Athletes with these injuries often see their performance drop. This is because of chronic pain, weakness, and the risk of getting hurt again.
For athletes, this can mean changing their training or not being able to compete at the same level. The mental impact of this situation is also big. The fear of getting hurt again can lower an athlete’s confidence and performance.
| Consequence | Description | Impact on Athletes |
| Chronic Pain | Persistent pain due to improper healing | Affects daily activities and athletic performance |
| Increased Risk of Re-injury | Weakened tendon prone to further damage | Prolonged absence from sports, career impact |
| Athletic Performance Decline | Reduced capability due to pain and weakness | Career longevity and performance level affected |
Conclusion
Knowing the difference between a torn and strained Achilles tendon is key for proper treatment and healing. We’ve looked at the tendon’s anatomy, injury causes, and the main differences between strains and tears.
A torn vs strained Achilles summary shows clear symptoms and treatment needs. Strains cause pain and stiffness, while tears lead to sharp pain and loss of function. Getting a correct diagnosis is vital for the right treatment.
Getting the right diagnosis and treatment is important for recovery. Whether it’s non-surgical care for strains or surgery for tears, early and proper care helps. It helps restore function and lowers the chance of long-term problems.
Recognizing injury signs and getting medical help is the first step to recovery. It helps people get back to their usual activities.
FAQ
What are the common signs of an Achilles tendon rupture?
Signs include sudden pain, a popping sound, swelling, and bruising. You might also find it hard to walk or stand.
How can I differentiate between a torn and strained Achilles tendon?
A torn tendon hurts more, swells more, and limits movement. A strain hurts during activity, but a tear hurts even when you’re not moving.
What are the risk factors for Achilles tendon injuries?
Risks include age, gender, and sports that involve running or jumping. Certain health issues like tendonitis or arthritis also increase the risk.
Can I self-diagnose an Achilles tendon injury?
Self-tests like the Thompson Test can help. But, getting a doctor’s opinion is best for a sure diagnosis.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for an Achilles injury?
Get help right away for severe pain, swelling, or trouble walking. Watch for red flags like more pain, swelling, or instability.
How do medical professionals diagnose Achilles tendon injuries?
Doctors use physical exams, MRI or ultrasound, and rule out other conditions to diagnose.
What is the difference between Achilles tendonitis and a tear?
Tendonitis is chronic inflammation and pain. A tear is sudden, severe pain and limited mobility.
What are the treatment options for a strained Achilles tendon?
Treatment includes conservative management, physical therapy, and a slow return to activity.
How are torn Achilles tendons treated?
Treatment depends on the injury’s severity. It might be non-surgical or surgical.
What are the long-term consequences of misdiagnosed or improperly treated Achilles injuries?
Misdiagnosis or bad treatment can cause chronic pain, weakness, and a higher risk of injury. It can also affect sports performance.
How can I prevent Achilles tendon injuries?
Prevent injuries by gradually increasing exercise, warming up, cooling down, and addressing risk factors like overuse.
What is the recovery timeline for Achilles tendon strains?
Recovery time varies by injury severity. It usually takes weeks of conservative treatment and physical therapy.
Can Achilles tendonitis progress to a tear?
Yes, tendonitis can lead to a tear if not treated properly.
How do I know if I have a partial or complete Achilles tear?
A partial tear hurts and limits movement. A complete rupture has severe symptoms, including a noticeable gap in the tendon and trouble walking.
References
- Shamrock, A. G. (2023). Achilles tendon rupture. In StatPearls. Retrieved August 16, 2023, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430844/



































