
A painful or swollen wrist might not just be a minor injury. It could signal a serious condition like a blood clot. Liv Hospital is a trusted partner for patients, providing expert care for every symptom.
Symptoms of a blood clot in wrist include swelling, pain, warmth, and color changes. Visible veins can also be a sign. It’s important to catch these symptoms early because they can resemble other issues like sprains.
A blood clot in veins or arteries can cause serious health problems. If you notice any symptoms, get medical help right away.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize the symptoms of a blood clot in the wrist, such as swelling and localized pain.
- Understand that early diagnosis is vital for effective treatment.
- Know that a blood clot can lead to serious health issues if left untreated.
- Seek medical attention promptly if you’re experiencing symptoms.
- Liv Hospital provides trusted care for patients with possible blood clots.
Understanding Blood Clots in the Wrist

Blood clots are more common in the legs, but they can also happen in the wrist. These clots in the wrist are less common but serious. They can cause pain and lead to serious problems. They usually form in the wrist veins due to injury, overuse, surgery, or clotting conditions.
What Is a Blood Clot in the Wrist?
A blood clot in the wrist is a mass of blood cells and proteins in the wrist veins or arteries. It happens when blood clots abnormally, often due to injury or other factors. Blood clots in the wrist can be dangerous if they block blood flow or travel to other parts of the body.
How Common Are Wrist Blood Clots?
Blood clots in the arm or wrist are rare compared to leg clots. They can happen, though, in people with certain health issues or after medical procedures. Risks include trauma, staying immobile, and medical conditions that affect blood clotting.
- Trauma or injury to the wrist
- Prolonged immobilization
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., thrombophilia)
- Use of catheters or pacemakers
DVT in the Wrist: A Special Consideration
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) usually happens in the legs, but it can also occur in the wrist. When it happens in the wrist, it’s less common but just as risky. Prompt medical attention is key if you notice DVT symptoms in your wrist.
Common Blood Clot Symptoms in Wrist
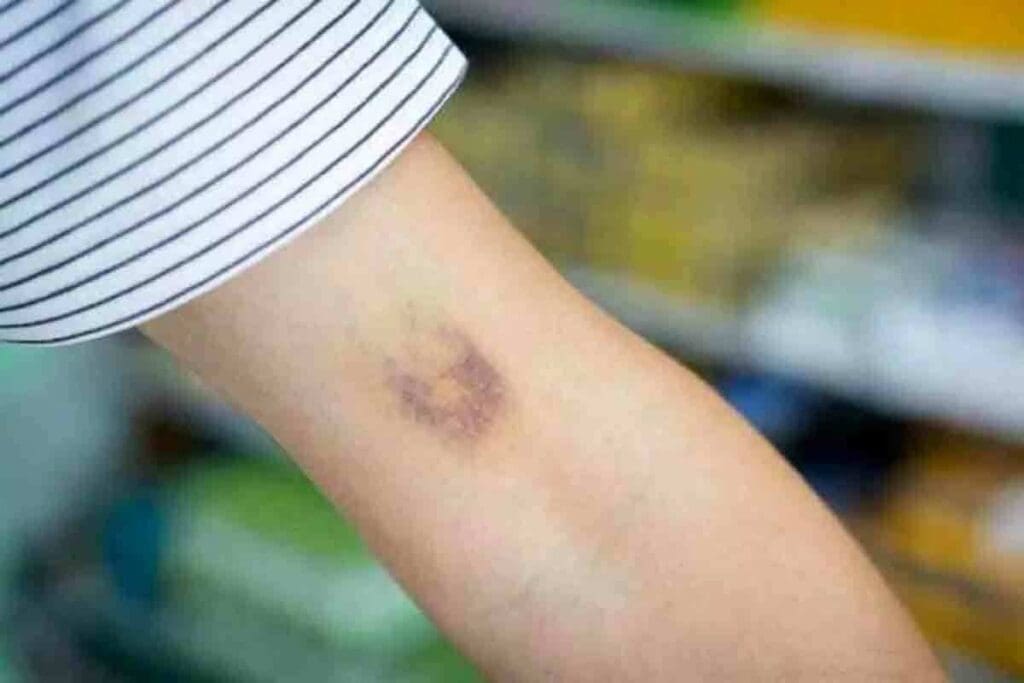
It’s important to know the signs of a blood clot in the wrist. These symptoms can seem minor at first but can become serious if not treated quickly.
Pain and Discomfort
Pain is a key sign of a blood clot in the wrist. The pain can feel like a dull ache or sharp stabbing. It usually happens in the area of the clot and can get worse when you move your wrist or apply pressure.
Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling is another common symptom. It’s caused by inflammation from the clot. Your wrist might look swollen, feel tender, and warm. Sometimes, the swelling can make it hard to move your wrist.
Skin Changes and Temperature
The skin around the clot might change color or feel warmer. This is because of increased blood flow. The skin might also look pale or blue, showing poor circulation.
The symptoms of a blood clot in the wrist can vary. It’s important to notice these signs early to avoid bigger problems.
| Symptom | Description | Severity |
| Pain | Dull ache or sharp pain, often localized | Variable |
| Swelling | Visible swelling, tenderness, warmth | Mild to Severe |
| Skin Changes | Redness, discoloration, warmth, or paleness | Mild to Severe |
Visual Identification of a Blood Clot in Wrist
A blood clot in the wrist can show up in different ways. These signs can be subtle, so it’s important to know what to look for.
Visible Blood Clot Characteristics
A blood clot in the wrist can change how it looks. You might see swelling, redness, or discoloration of the skin. The skin might also feel warm or look slightly bluish because of the clot.
To learn more about blood clots, check out this resource. It explains the difference between blood clots and bruises.
Comparing Normal vs. Clotted Wrist Appearance
Looking at a normal wrist and one with a blood clot shows the differences. A wrist with a clot might have:
- Swelling or puffiness around the wrist area
- Visible veins that are more pronounced or tender
- Skin that is red, warm, or discolored
A normal wrist doesn’t usually show these signs.
| Characteristics | Normal Wrist | Wrist with Blood Clot |
| Swelling | No swelling | Visible swelling |
| Skin Color | Normal skin color | Redness or discoloration |
| Vein Appearance | Normal vein appearance | More pronounced or tender veins |
Changes in Visible Veins
One sign of a blood clot in the wrist is changes in the veins. The veins might look more noticeable or feel tender. Sometimes, the vein can be hard or cord-like because of the clot.
Knowing these signs can help spot a blood clot in the wrist. If you think you have one, getting medical help is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors for Wrist Blood Clots
Blood clots in the wrist can come from many sources. These include injuries, health conditions, and lifestyle choices. Knowing what causes them is key to preventing and treating them.
Trauma and Injury to the Wrist
Getting hurt in the wrist can lead to blood clots. This can happen from:
- Fractures or severe sprains
- Sports injuries, like falls onto the wrist
- Repetitive strain injuries from overuse
When the wrist gets hurt, the body tries to stop bleeding by clotting. But sometimes, this can cause unnecessary or too-large clots, leading to problems.
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Some health issues can make you more likely to get blood clots in the wrist. These include:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Though more common in legs, DVT can happen in the wrist, often in people with catheters or pacemakers.
- Clotting disorders: Conditions like Factor V Leiden or antiphospholipid syndrome can make clotting more likely.
- Cancer: Some cancers can raise clotting risk because they make substances that promote clotting.
Surgical Procedures and Aftereffects
Wrist or arm surgeries can also raise the risk of blood clots. This is because of:
- Being immobile during and after surgery
- The body’s reaction to the surgery
- The use of certain surgical tools like catheters
After surgery, doctors often use anticoagulant meds and encourage early movement to prevent clots.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Our lifestyle and environment also affect our risk of getting wrist blood clots. These include:
- Prolonged immobilization: Long periods of not moving, like on long flights or in bed, can increase clot risk.
- Smoking: Smoking harms blood vessels and raises clotting risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can put more pressure on veins, making clots more likely.
By knowing these causes and risks, we can take steps to prevent them. If symptoms show up, getting medical help can help avoid serious problems from wrist blood clots.
How Blood Clots Form in the Wrist Veins
It’s important to know how blood clots form in wrist veins. This knowledge helps doctors diagnose and treat them quickly. Blood clots in the wrist can cause serious problems if not treated fast.
Anatomy of Wrist Circulation
The wrist has a complex network of veins and arteries. These supply blood to the hand. The veins in the wrist are more likely to clot because of their structure.
The venous anatomy includes both superficial and deep veins. Superficial veins are near the skin, while deep veins are deeper and more likely to clot.
The Clotting Process
Blood clotting happens naturally when there’s an injury. It involves several steps to form a fibrin clot. In the wrist, this can start from trauma or other causes.
The clotting process needs platelets, clotting factors, and fibrinogen. When a vein gets injured, platelets stick to it. Then, a series of chemical reactions creates a clot.
Why Clots Can Develop in the Wrist
Several things can make blood clots form in the wrist. These include trauma, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices.
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Trauma or Injury | Direct injury to the wrist can cause blood clot formation. |
| Medical Conditions | Conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or clotting disorders increase the risk. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Prolonged immobilization or certain medications can contribute to clot formation. |
Knowing these factors is key to preventing and treating blood clots in the wrist.
Diagnosing a Blood Clot in Wrist
Diagnosing a blood clot in the wrist requires a few steps. These include a physical check, imaging tests, and lab tests. It’s important to catch it early because symptoms can be similar to sprains.
Physical Examination Techniques
A doctor will start with a physical check. They look for swelling, redness, and warmth in the wrist. They also check for tenderness and pain when moving or touching the area.
Key physical examination techniques include:
- Inspecting the wrist for visible signs of clotting
- Palpating the wrist to check for tenderness
- Assessing the range of motion and pain upon movement
Imaging Tests and Procedures
To confirm a blood clot, imaging tests are needed. These include:
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to visualize the blood vessels and detect clots.
- Venography: An X-ray test that involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins to visualize the clot.
- MRI or CT scans: These may be used in some cases to provide detailed images of the wrist and surrounding tissues.
Laboratory Blood Tests
Laboratory blood tests help diagnose blood clots. They measure substances in the blood. These tests include:
- D-dimer test: This test measures the levels of D-dimer, a protein fragment produced when a blood clot dissolves.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test can help identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to clot formation.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is key to accurately diagnosing a blood clot in the wrist. Healthcare professionals must consider other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as:
- Wrist sprains or strains
- Tendinitis
- Other vascular conditions
By combining physical examination findings, imaging test results, and laboratory test data, healthcare professionals can make an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Wrist Blood Clots
The main goal of treating a blood clot in the wrist is to stop it from getting bigger or breaking loose. This can cause serious problems. The treatment depends on the clot’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
Anticoagulant Medications
Anticoagulant medications are often the first choice for blood clots in the wrist. They help prevent the clot from growing and stop new clots from forming. Common ones include:
- Warfarin
- Rivaroxaban
- Apixaban
- Dabigatran
These drugs need careful monitoring to avoid bleeding problems.
Thrombolytic Therapy
In severe cases or when there’s a high risk, thrombolytic therapy might be used. This treatment breaks down the clot with drugs. It’s for emergency situations where the clot is a big threat.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery might be needed for some wrist clots. Procedures like thrombectomy remove the clot. Surgery is for cases where other treatments don’t work or are not possible.
Home Care and Recovery
Home care is also important for recovering from a blood clot in the wrist. This includes:
- Elevating the affected arm to reduce swelling
- Applying warm compresses to alleviate pain
- Engaging in gentle exercises as recommended by a healthcare provider
- Monitoring for signs of complications or clot progression
Following your healthcare provider’s advice and going to follow-up appointments is key. This ensures proper healing and any needed treatment changes.
Potential Complications and Seriousness
If a blood clot in the wrist is not treated, it can cause serious problems. These can range from minor damage to life-threatening conditions. The risk to your health is very high.
Short-term Local Complications
At first, a blood clot in the wrist might cause pain, swelling, and stiffness. These symptoms can make everyday tasks hard. Sometimes, the clot can lead to post-thrombotic syndrome, causing long-lasting pain and swelling.
Risk of Clot Migration
A big worry with a blood clot in the wrist is that it might move to other places in your body. This could lead to serious issues like pulmonary embolism. This is when the clot goes to your lungs and can block blood flow, which is very dangerous.
Long-term Vascular Damage
Not treating a blood clot can harm your blood vessels over time. This can lead to chronic venous insufficiency. This makes it hard for veins to return blood to the heart, causing swelling, pain, and skin changes.
Life-Threatening Scenarios
In severe cases, a blood clot in the wrist can be very dangerous. For example, if it breaks loose and goes to your lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism. Getting medical help quickly is key to avoiding these serious problems.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help for a wrist blood clot is key to recovery. A wrist blood clot can cause serious problems if not treated quickly.
Emergency Warning Signs
Certain symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe pain or swelling in the wrist or arm
- Discoloration or paleness of the skin
- Coldness or numbness in the hand or fingers
- Weakness or inability to move the hand or fingers
If you notice any of these signs, get medical help right away. Waiting can cause permanent harm or even be life-threatening.
Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Other symptoms also need attention. These include:
- Mild to moderate pain or discomfort in the wrist
- Swelling or redness around the wrist
- Visible veins or tenderness
Keep an eye on these symptoms and see a doctor if they get worse or don’t go away.
Follow-up Care Guidelines
After treatment, follow-up care is vital. It helps make sure the clot is gone and prevents new ones. This may include:
| Follow-up Care | Description | Frequency |
| Medical Check-ups | Regular visits to monitor clot resolution and overall health | As advised by your doctor |
| Medication Adherence | Taking prescribed anticoagulant medications | As prescribed |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Making necessary changes to reduce risk factors | Ongoing |
Following these guidelines is important for successful treatment and avoiding complications.
Getting medical help quickly is key to treating and preventing problems. If you think you have a blood clot in your wrist, don’t wait to get help.
Conclusion
A blood clot in the wrist is serious if not treated. Knowing the symptoms is key for early action and care.
Blood clots in the wrist can be very painful. They might also lead to serious problems. It’s important to notice the signs and get help fast.
Can you get a blood clot in your wrist? Yes, it’s possible. Knowing the risks and symptoms is vital. Early treatment can help a lot and prevent harm.
With quick medical help and the right treatment, wrist blood clots can be managed. It’s important for people to know their risks. They should also seek help if they notice unusual symptoms.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of a blood clot in the wrist?
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and skin changes. You might also notice temperature changes in the wrist.
Can a blood clot in the wrist be visible?
Yes, sometimes you can see a blood clot. It might look like swelling, redness, or a lump.
What are the risk factors for developing a blood clot in the wrist?
Risk factors include wrist injuries and certain medical conditions. Surgery and long periods of not moving can also increase risk.
How is a blood clot in the wrist diagnosed?
Doctors use physical exams and imaging tests like ultrasound. They also do blood tests and rule out other conditions.
What are the treatment options for a blood clot in the wrist?
Treatment includes medicines to prevent clotting and surgery. Home care helps manage symptoms and prevent problems.
Can a blood clot in the wrist lead to serious complications?
Yes, complications can include local issues and clot movement. Long-term damage and serious problems like pulmonary embolism are also risks.
When should I seek medical attention for a blood clot in the wrist?
Get help right away if you have severe pain, can’t move your wrist, or see signs of clot movement.
Are blood clots in the wrist a form of DVT?
While rare, wrist blood clots are like DVT. They need quick medical care.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent blood clots in the wrist?
Yes, a healthy lifestyle and avoiding long periods of rest can lower risk. Managing health conditions also helps.
What are the signs of clot migration?
Signs include sudden chest pain, trouble breathing, or pain elsewhere. These need immediate medical help.
How can I identify a blood clot in my wrist?
Look for pain, swelling, redness, or warmth. If you notice these, see a doctor for a proper check.
References
- Medical News Today. (2023, December 19). Blood Clot in Arm: Symptoms, Is It Dangerous, Causes, and Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325299








