Bone marrow is a vital, spongy tissue inside bones. It holds stem cells that help make blood cells and store fat. At Liv Hospital, we know how crucial bone marrow is for our health. We aim to offer top-notch healthcare and support for international patients.
There are two types of bone marrow: one makes blood cells, and the other stores fat. Knowing the difference between them helps us understand our bodies better.
Our bones have a complex tissue that’s key to our health. By learning about bone marrow functions and where it’s found, we can see how our bodies stay healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Bone marrow is a spongy tissue that produces blood cells and stores fat.
- There are two types of bone marrow with distinct functions.
- Understanding bone marrow is crucial for overall health.
- Bone marrow contains stem cells essential for health.
- Liv Hospital provides comprehensive support for bone marrow health.
What is Bone Marrow? Understanding the Basics

The human body has a vital tissue called bone marrow. It’s found in bones like hips and thighbones. Bone marrow makes blood cells.
Bone marrow is soft and spongy. It’s filled with cells, blood vessels, and connective tissue. It’s a key organ for our health.
Definition and Composition of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones. It’s made of hematopoietic cells and adipocytes. These cells produce blood and store fat. The type of cells changes with age and location.
It has a network of blood vessels. These include arteries, veins, and capillaries. They bring nutrients and oxygen to the marrow.
| Component | Description | Function |
| Hematopoietic Cells | Cells responsible for producing blood cells | Produce red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets |
| Adipocytes | Cells that store fat | Store energy in the form of fat |
| Blood Vessels | Network of vessels supplying the marrow | Provide nutrients and oxygen |
The Vital Role of Bone Marrow in the Human Body
Bone marrow is key to making blood cells. It produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This is called hematopoiesis.
Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infections, and platelets help blood clot. Bone marrow also stores fat for energy. This makes it vital for our health.
Knowing about bone marrow is important for our health. It helps us understand its role and the importance of bone marrow transplants.
The Two Types of Bone Marrow: An Overview

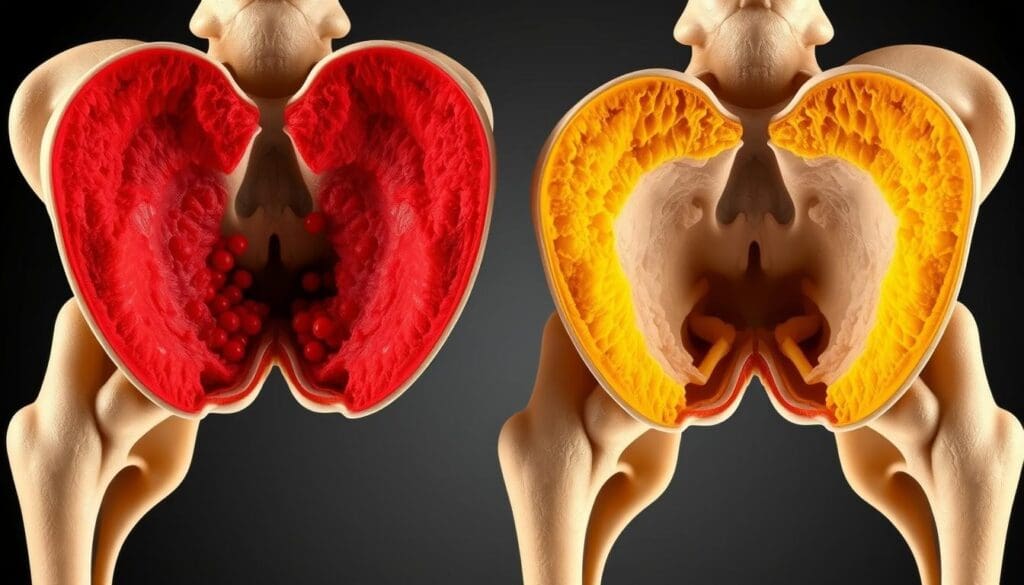
Our bodies have two main types of bone marrow: red and yellow. Each type has its own job and looks different. Knowing about these types helps us understand their importance for our health.
Classification of Bone Marrow Types
Bone marrow is divided into two types. Red bone marrow makes blood cells like red and white blood cells and platelets. Yellow bone marrow, on the other hand, is mostly fat and stores energy.
The names “red” and “yellow” marrow come from their looks. Red marrow has lots of blood vessels to help it make blood cells.
Key Differences at a Glance
Here’s what sets red and yellow bone marrow apart:
- Function: Red marrow makes blood cells, while yellow marrow stores fat.
- Composition: Red marrow is full of cells that make blood, while yellow marrow is mostly fat.
- Location: Red marrow is in the body’s center and some limbs. Yellow marrow is found in long bones.
Knowing these differences helps us see how important bone marrow is for our health.
Red Bone Marrow: The Blood Cell Factory
Red bone marrow is key to our health, making different blood cells. It’s found in bones like the pelvis, vertebrae, and long bones.
Composition and Cellular Structure
Red bone marrow has blood vessels and sinusoids for blood cell flow. It holds hematopoietic stem cells, which turn into all blood cells. These cells become red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
The structure of red bone marrow is complex. It has cells at various stages and stromal cells for support. This setup is crucial for blood cell production.
Hematopoietic Function Explained
The main job of red bone marrow is hematopoiesis, making new blood cells. This process is controlled by growth factors and cytokines. It keeps the body’s blood cell count steady.
Types of Blood Cells Produced
Red bone marrow makes three main blood cell types:
- Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes): Carry oxygen.
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes): Fight infections.
- Platelets (Thrombocytes): Help with blood clotting.
| Blood Cell Type | Function |
| Red Blood Cells | Carry oxygen throughout the body |
| White Blood Cells | Play a key role in the immune system |
| Platelets | Essential for blood clotting |
Yellow Bone Marrow: The Fat Storage Tissue
Yellow bone marrow is a type of bone marrow filled with fat. It looks yellow, unlike red bone marrow. We’ll look at what it’s made of, its main jobs, and why it’s important for our bodies.
Adipose Tissue Composition
Yellow bone marrow is mostly fat cells. These cells help store and release energy. Its yellow color comes from all the fat, making it different from red bone marrow.
The makeup of yellow bone marrow can change with age and health. But its main job stays the same: to hold fat for energy.
Primary Functions of Yellow Marrow
Yellow bone marrow’s main job is to store fat for energy. This is key for keeping our energy levels up, especially when we’re active or hungry.
It also helps keep bones strong and healthy. It feeds the bone and keeps it in good shape.
Metabolic Importance
Yellow bone marrow is important because it stores and releases fat for energy. This helps keep our metabolism balanced and supports our body’s functions.
When we’re very active or don’t eat enough, our body uses the fat in yellow bone marrow for energy. This shows how crucial yellow bone marrow is for our metabolic health.
| Characteristics | Red Bone Marrow | Yellow Bone Marrow |
| Primary Function | Hematopoiesis (blood cell production) | Fat storage |
| Composition | Hematopoietic cells, blood vessels | Adipocytes (fat cells) |
| Location | Mainly in the axial skeleton | Mainly in long bone shafts |
It’s important to know the differences between red and yellow bone marrow. Red bone marrow makes blood cells, while yellow bone marrow is our energy reserve.
Anatomical Locations: Where to Find Each Type
Knowing where bone marrow is in our body is key to understanding its health role. It’s spread out in the skeleton, but its spots change as we age. In adults, red and yellow bone marrow have specific places.
Distribution in the Adult Skeleton
In adults, red bone marrow is mostly in flat bones and long bone ends. Red marrow makes blood cells, a vital process. Yellow bone marrow, full of fat, is in long bone shafts.
“Bone marrow’s spots change with life, adapting to our health needs,” say doctors. This shows how bone marrow is flexible and crucial for health.
Red Marrow Locations in the Axial Skeleton
Red bone marrow is mainly in the axial skeleton. This includes the skull, vertebrae, ribs, and pelvis. These areas have lots of cancellous bone, where red marrow lives. Specifically, red marrow is found in the:
- Pelvis
- Vertebrae
- Ribs
- Sternum
- Skull
These spots are key for making blood cells, like red and white blood cells, and platelets.
Yellow Marrow Predominance in Long Bone Shafts
Yellow bone marrow is mostly in long bone shafts, like the femur and humerus. Its fatty tissue acts as an energy backup. It can turn into red marrow if the body needs more blood cells.
Yellow marrow’s dominance in long bone shafts is a key adult feature. It shows the body’s ability to balance blood making and fat storage, meeting different health needs.
Developmental Changes in Bone Marrow
As we grow from infancy to adulthood, our bone marrow changes a lot. At birth, it’s all red and key to making blood cells. But, as we age, much of it turns into yellow marrow.
Bone Marrow Composition at Birth
At birth, all bone marrow is red and busy making blood cells. This red marrow is vital for creating all blood cells. It’s full of blood vessels and supports blood cell growth.
Age-Related Conversion from Red to Yellow Marrow
As we age, red bone marrow turns to yellow, especially in long bones. This change starts early in childhood and continues into adulthood. By adulthood, much of the red marrow is replaced by yellow, which is mostly fat.
The change from red to yellow marrow isn’t the same everywhere. The bones in our body’s center, like the spine and pelvis, keep more red marrow. Even in adults, these bones have a lot of red marrow.
Factors Influencing Marrow Conversion
Several things affect the change from red to yellow bone marrow. These include:
- Age: The biggest factor, with more change as we get older.
- Demand for Blood Cells: When we need more blood cells, the change slows down or stops.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal shifts can change how fast the marrow converts.
- Health Status: Some health issues can affect the marrow’s type and amount.
Understanding these changes is key to seeing how bone marrow affects our health. The shift from red to yellow marrow is not just a simple change. It’s a body’s way of adapting to its needs.
The Remarkable Adaptability of Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a dynamic tissue that changes to meet the body’s needs. This flexibility is key to keeping the body balanced and responding to different demands. We’ll look at how bone marrow shifts, especially from yellow to red, in emergency situations.
Yellow to Red Marrow Conversion in Emergency Situations
In serious cases like severe anemia or blood loss, the body can switch yellow marrow to red. This switch helps increase blood cell production quickly to meet urgent needs.
Key aspects of this conversion process include:
- The reactivation of hematopoietic stem cells in yellow marrow
- Increased vascularization to support enhanced cellular activity
- Changes in the marrow microenvironment to facilitate blood cell production
Triggers for Marrow Transformation
Several factors can trigger the transformation of yellow marrow to red marrow. These include:
- Severe blood loss or hemorrhage
- Chronic anemia or other conditions leading to increased demand for blood cells
- Certain infections or inflammatory conditions require an enhanced immune response
Clinical Significance of Marrow Adaptability
The ability of bone marrow to adapt has big implications for medicine. Knowing about this adaptability helps in:
| Clinical Application | Description |
| Diagnosis of Marrow Disorders | Assessing the marrow’s ability to respond to stress can aid in diagnosing various hematological conditions. |
| Treatment of Blood-Related Diseases | Knowledge of marrow adaptability can inform treatment strategies for conditions like anemia or leukemia. |
| Bone Marrow Transplantation | Understanding how to optimize marrow function is crucial for the success of bone marrow transplants. |
Bone marrow’s adaptability is crucial for the body’s response to challenges. This ability shows how important bone marrow is for health. It also highlights the complex interactions between different body systems.
Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Red Bone Marrow
Hematopoietic stem cells in red bone marrow create all blood cell types. They keep our blood cell count healthy and strong.
Characteristics of Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Hematopoietic stem cells have special traits. They can self-renew and differentiate into different blood cells. This is key for making red, white blood cells, and platelets.
These cells also rely on their environment, or “niche,” for signals and support. Knowing about these traits helps us understand their role in health and disease.
Differentiation Pathways
The paths hematopoietic stem cells take are complex and controlled. These paths guide them to become specific blood cells. The main paths are:
- Myeloid lineage: making monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and platelets.
- Lymphoid lineage: leading to T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
These paths are key to making blood cells that help with oxygen transport, immune defense, and blood clotting.
Clinical Applications in Transplantation
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation saves lives for blood disorders like leukemia and lymphoma. It replaces a patient’s bad stem cells with healthy ones from a donor.
This treatment has many uses and is growing. Allogeneic transplantation uses donor stem cells, and autologous transplantation uses the patient’s own cells.
Learning about hematopoietic stem cells and their use in transplantation is crucial. It helps improve treatments for blood diseases.
Bone Marrow Examination and Disorders
Bone marrow examination is key in finding and treating blood-related diseases. We’ll look at how doctors check bone marrow, common problems, and the terms used.
Diagnostic Procedures: Aspiration and Biopsy
Doctors use two main methods to check bone marrow: aspiration and biopsy. Bone marrow aspiration takes a liquid sample from the hip or sternum. It helps see how blood cells are made.
A bone marrow biopsy takes a small piece of bone and marrow. It’s important to look at the marrow’s structure and any issues.
Common Bone Marrow Disorders
Bone marrow problems can cause issues like anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma. Anemia happens when the marrow doesn’t make enough red blood cells, causing tiredness and weakness.
Leukemia is a cancer that affects the blood and marrow, causing too many white blood cells.
| Disorder | Description | Common Symptoms |
| Anemia | Low red blood cell count | Fatigue, weakness, pale skin |
| Leukemia | Cancer of the blood and marrow | Fever, weight loss, frequent infections |
| Lymphoma | Cancer of the lymphatic system | Swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats |
Medical Terminology: Medulla Rubra and Related Terms
The term medulla rubra means red bone marrow. Knowing these terms helps doctors diagnose and treat bone marrow issues well.
Other important terms include hematopoiesis, which is blood cell production, and myeloid tissues, related to bone marrow.
Conclusion: The Dual Nature of Bone Marrow
We’ve looked into the complex world of bone marrow, focusing on its two main types: red and yellow. Knowing about the dual nature of bone marrow helps us see its key role in our health.
Bone marrow is more than just tissue; it’s a dynamic part of our body. It’s key for making blood cells and storing fat. Red marrow makes blood cells, while yellow marrow stores fat. The balance between these is vital for our body’s functions.
At Liv Hospital, we understand how important bone marrow health is. We aim to provide top-notch healthcare, supporting patients from around the world. By learning about bone marrow’s functions and disorders, we can better care for our health.
FAQ
What are the two types of bone marrow?
There are two types of bone marrow: red and yellow. Red marrow makes blood cells. Yellow marrow stores fat.
What is the function of red bone marrow?
Red bone marrow makes blood cells. It creates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This process is called hematopoiesis.
Where is red bone marrow located?
Red bone marrow is found in the vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and pelvis. It’s also in the long bones’ upper parts.
What is the primary function of yellow bone marrow?
Yellow bone marrow stores fat. This fat helps the bone function and acts as an energy reserve.
Where is yellow bone marrow predominantly found?
Yellow bone marrow is mainly in the long bones’ shafts. This includes the femur and humerus.
Can bone marrow change its type?
Yes, bone marrow can change. For example, yellow marrow can turn into red marrow when blood cells are needed quickly.
What is the role of hematopoietic stem cells in red bone marrow?
Hematopoietic stem cells in red marrow turn into different blood cells. This includes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
How is bone marrow examined?
Bone marrow is checked through tests like aspiration and biopsy. These tests take a bone marrow sample for analysis.
What are some common bone marrow disorders?
Common disorders include leukemia, anemia, and myelodysplastic syndromes. These affect blood cell production.
What is medulla rubra?
Medulla rubra is another name for red bone marrow. It’s responsible for making blood cells.
How does bone marrow composition change with age?
At birth, bones have red marrow. As we age, yellow marrow replaces some of it. This change happens throughout childhood and adolescence.
What triggers the conversion of yellow to red marrow?
Yellow marrow turns red when blood cell production is needed more. This happens in severe anemia or blood loss.
References
- Małkiewicz, A., Orzechowski, P., & Podgórski, M. (2012). Imaging of physiological changes in bone marrow. Polish Journal of Radiology, 77(4), 45-55. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3529711/