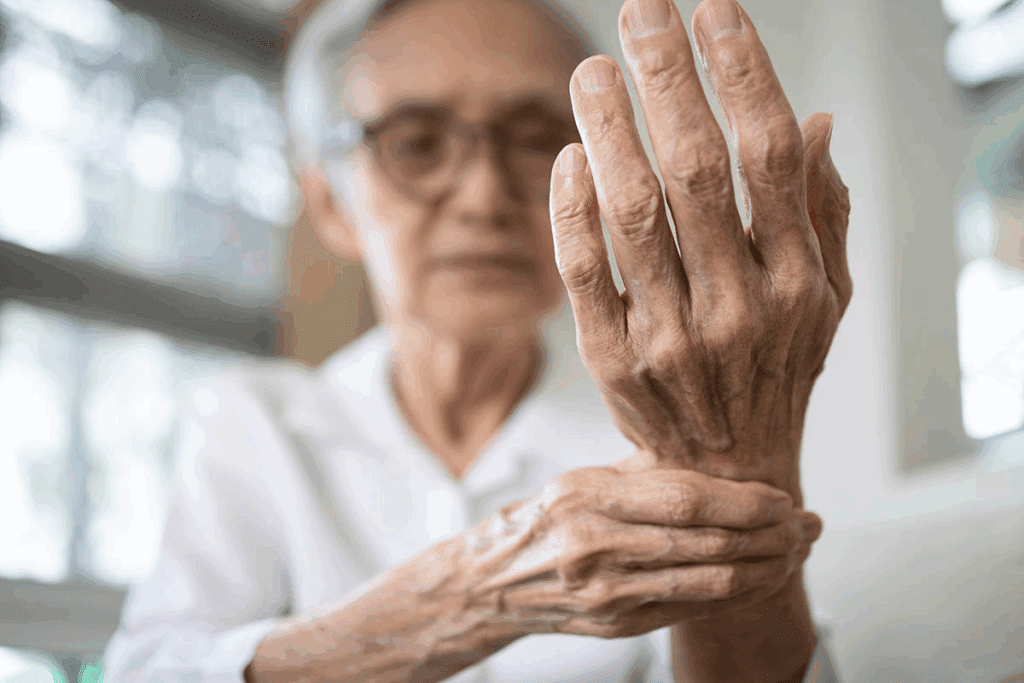
Did you know millions of people worldwide suffer from tendonitis and arthritis? They often wonder if one can turn into the other. Inflammation and joint pain are common in both, leading to concerns about their connection. Is your tendonitis dangerous? Learn the Critical warning signs of tendonitis turning into arthritis. Must read now.
We look into the link between tendonitis and arthritis. We cover their causes, symptoms, and treatments. Tendonitis, marked by tendon inflammation, can lead to more serious joint problems if not treated right. Understanding the link between these conditions is key for prevention and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Tendonitis and arthritis are distinct but related conditions.
- Chronic tendonitis can potentially lead to arthritis if left untreated.
- Understanding the causes and symptoms is key for effective management.
- Treatment options vary, focusing on reducing inflammation and pain.
- Prevention strategies can help lower the risk of both conditions.
Understanding Tendonitis: Causes and Symptoms
Tendonitis is a common condition that can affect anyone, no matter their activity level or age. It happens when tendons, which connect muscles to bones, get inflamed. This inflammation can cause pain and make daily activities hard.
What is Tendonitis?
Tendonitis is when a tendon gets inflamed or irritated. Tendons help us move by linking muscles to bones. When they get inflamed, it can hurt a lot and make it hard to move.
Common Causes of Tendonitis
Tendonitis often comes from doing the same thing over and over again. This can be from typing, sports, or manual work. Other reasons include:
- Direct injury to the tendon
- Aging, as tendons become less flexible and more prone to injury over time
- Poor posture or biomechanics
- Certain diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes
Recognizing Tendonitis Symptoms
The signs of tendonitis can differ based on where and how bad it is. Common signs include:
- Pain or tenderness near a joint
- Swelling or redness around the affected tendon
- A grating sensation when moving the affected limb
- Weakness in the affected limb
Spotting these signs early can help stop it from getting worse.
Acute vs. Chronic Tendonitis
Tendonitis can be either acute or chronic. Acute tendonitis is short-term and usually comes from a sudden injury. Chronic tendonitis, though, is long-term and happens from doing the same thing over and over again.
Chronic tendonitis can lead to serious problems like tendon degeneration or rupture if not treated right. Knowing the difference between acute and chronic tendonitis is key for the right treatment and avoiding long-term damage.
Arthritis Explained: Types and Development
Arthritis is a complex condition with many forms. Each type has its own causes and symptoms. Understanding arthritis is key to managing and treating it.
Different Types of Arthritis
There are several types of arthritis, like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis happens when cartilage in joints breaks down, causing pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and can damage joints severely if not treated.
Other types include psoriatic arthritis, linked to psoriasis, and gout, known for sudden, severe pain and swelling. Each type needs a specific treatment plan.
How Arthritis Develops in Joints
Arthritis in joints comes from genetics, environment, and wear and tear. In osteoarthritis, cartilage wears down, causing pain and stiffness. This is because joints start to rub against each other.
Rheumatoid arthritis happens when the immune system attacks the joints’ lining, causing inflammation. This can destroy cartilage and bone. Knowing how arthritis develops helps in preventing it and managing its symptoms.
Risk Factors for Arthritis
Several factors increase the risk of arthritis, including age, genetics, obesity, and past joint injuries. As we get older, the risk of osteoarthritis grows. Genetics also play a big role in rheumatoid arthritis.
- Age
- Genetic predisposition
- Obesity
- Previous joint injuries
Common Symptoms of Arthritis
Arthritis symptoms vary by type but often include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced motion. It can also cause fatigue, fever, and feeling unwell.
Spotting these symptoms early is vital. It helps in getting the right medical care and starting treatment early.
The Relationship Between Inflammation and Joint Disease
Inflammation and joint health are closely linked. This connection affects diseases like tendonitis and arthritis. When inflammation lasts too long, it can harm tissues and worsen diseases.
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a quick response to injury or infection. It causes redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. Chronic inflammation, lasting longer, can damage healthy tissues and organs.
Chronic inflammation can come from many sources. This includes autoimmune disorders, infections, or ongoing tissue damage. It’s a major factor in many joint diseases, like arthritis.
How Inflammation Affects Joint Tissues
Inflammation harms joint tissues, causing pain, stiffness, and less mobility. In tendonitis, it affects tendons, leading to pain and reduced function. In arthritis, it damages the synovium, causing joint damage and degeneration.
Inflammatory Cascades in the Body
The inflammatory process is a complex series of events. When tissues are damaged, immune cells are activated. They release chemical mediators that promote inflammation. This cycle can become chronic if not stopped.
Systemic Effects of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation affects more than just joints. It can harm overall health. It raises the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other conditions. Managing chronic inflammation is key for joint health and overall well-being.
| Condition | Impact of Chronic Inflammation |
| Tendonitis | Persistent pain and impaired tendon function |
| Arthritis | Joint damage, degeneration, and deformity |
| Systemic Health | Increased risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes |
Can Tendonitis Turning into Arthritis? The Medical Perspective
Tendonitis and arthritis are different conditions but can be linked. Recent studies are uncovering how tendonitis might lead to arthritis. It’s important to understand the direct and indirect connections between these two conditions.
Direct vs. Indirect Relationships
Whether tendonitis can directly turn into arthritis is a complex issue. Research shows no direct link, but there’s an indirect one. Chronic tendonitis can damage joints, possibly leading to arthritis.
Chronic inflammation from tendonitis can change how joints work. This can lead to degenerative changes and eventually arthritis.
What Research Shows
Recent studies have uncovered a link between tendonitis and arthritis. They found that people with chronic tendonitis are more likely to get arthritis in the affected joint. This is because of ongoing inflammation and tendon degeneration.
A study in a top rheumatology journal showed a higher osteoarthritis rate in patients with chronic tendonitis.
Expert Medical Opinions
Rheumatologists and orthopedic experts share their views on the tendonitis-arthritis link. They agree that tendonitis itself doesn’t directly become arthritis. But, the chronic inflammation and joint stress from tendonitis can increase the risk of arthritis.
Dr. [Last Name], a well-known rheumatologist, says, “Effective management of tendonitis is key to preventing long-term issues, like arthritis.”
Case Studies and Clinical Observations
Real-world evidence from case studies and clinical observations shows tendonitis can lead to arthritis. For example, athletes with untreated or undertreated tendonitis are at higher risk of arthritis in affected joints. This is due to repetitive strain and chronic inflammation.
A study on professional athletes found that those with chronic tendonitis were more likely to get early-onset osteoarthritis. This highlights the need for early treatment and proper management of tendonitis.
Chronic Tendonitis and Its Long-Term Effects on Joints
When tendonitis turns chronic, it deeply affects joints. It changes how they work and their structure. Chronic tendonitis causes ongoing inflammation and tendon degeneration. This can lead to many problems in the joint.
When Tendonitis Becomes Chronic
Tendonitis turns chronic if the initial inflammation doesn’t go away. This leads to ongoing tendon damage. It happens due to too much strain, not enough rest, or bad biomechanics.
Factors contributing to chronic tendonitis include:
- Repetitive strain or overuse
- Inadequate recovery or rest
- Poor biomechanics or alignment
- Age-related changes in tendon health
Changes in Joint Biomechanics
Chronic tendonitis changes how joints work. The tendons don’t function right, leading to uneven stress on the joint. This can cause more damage.
For example, chronic Achilles tendonitis puts more stress on the ankle. This can cause pain and more injury.
Tendon Degeneration Processes
Tendon degeneration in chronic tendonitis involves complex changes. These changes weaken the tendon, making it more likely to rupture or get hurt again.
| Degeneration Process | Description | Impact on Tendon |
| Collagen fiber disruption | Disruption of the collagen fibers within the tendon | Weakening of tendon structure |
| Increased inflammation | Ongoing inflammatory response | Further degeneration and pain |
| Tendon thickening | Thickening of the tendon due to chronic inflammation | Altered biomechanics and possible injury |
Impact on Surrounding Tissues
Chronic tendonitis also affects tissues around the joint. This includes ligaments, cartilage, and bursae. The changes in biomechanics and inflammation can cause problems like ligament strain, cartilage wear, and bursitis.
Managing chronic tendonitis well is key to avoiding these long-term issues. It helps keep joints healthy.
Common Areas Where Tendonitis and Arthritis Coexist
Tendonitis and arthritis often appear together in different parts of the body. This can lead to discomfort and make it hard to move. Knowing where these issues happen is key for the right treatment.
Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Tendonitis and Arthritis
The shoulder is a common spot for both rotator cuff tendonitis and arthritis. Rotator cuff tendonitis is when the tendons around the shoulder get inflamed. Arthritis makes the joint cartilage wear down. Doing the same overhead movements over and over can make both worse.
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy found a link between rotator cuff tendonitis and shoulder arthritis. Treatment might include physical therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, or surgery.
Knee: Patellar Tendonitis and Osteoarthritis
The knee is another common spot for tendonitis and arthritis. Patellar tendonitis, or jumper’s knee, is when the tendon from the kneecap to the shinbone gets inflamed. Osteoarthritis, a joint disease, can also happen, causing pain and stiffness in the knee.
| Condition | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Patellar Tendonitis | Pain below the kneecap, tenderness, swelling | Rest, ice, physical therapy, bracing |
| Osteoarthritis | Pain, stiffness, limited mobility | Medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes |
Hand and Wrist: De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis and Arthritis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. It causes pain and tenderness. It often happens with arthritis in the hand and wrist, making it hard to use your hands.
“De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is often seen in individuals who perform repetitive tasks involving the thumb and wrist, such as typing or assembly line work.” – American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Ankle and Foot: Achilles Tendonitis and Arthritis
The ankle and foot can also have tendonitis and arthritis together. Achilles tendonitis is when the tendon from the calf to the heel gets inflamed. Arthritis in these areas adds to the pain and stiffness.
A study in the Foot & Ankle International journal found runners and athletes are at high risk for Achilles tendonitis. This can be made worse by arthritis. Treatment includes rest, physical therapy, and sometimes using orthotics.
Risk Factors That Connect Tendonitis and Arthritis
Understanding the link between tendonitis and arthritis involves looking at shared risk factors. Both conditions impact the musculoskeletal system. Certain factors can raise the chance of getting one or both.
Age-Related Factors
Age is a big risk factor for both tendonitis and arthritis. As we get older, our tendons and joints change. Tendons lose flexibility and joints wear out, leading to arthritis. Older adults are more likely to get both conditions due to years of use and past injuries.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetics play a key role in tendonitis and arthritis. People with a family history of musculoskeletal issues are at higher risk. Some genetic markers increase the risk of certain arthritis types, like rheumatoid arthritis. Knowing your genetic risk can help prevent these conditions.
Lifestyle and Occupational Risks
Lifestyle and job choices also impact the risk of tendonitis and arthritis. Repetitive strain injuries, common in some jobs or sports, can cause tendonitis. Jobs or activities that involve heavy lifting or repetitive movements raise arthritis risk. Living a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and proper ergonomics, can reduce these risks.
Previous Joint Injuries
Previous joint injuries are a major risk factor for both conditions. Trauma to a joint can cause chronic inflammation and degeneration, leading to arthritis. Tendonitis can also follow a joint injury, as scar tissue can irritate tendons. Proper rehabilitation after an injury is key to preventing long-term problems.
| Risk Factor | Tendonitis | Arthritis |
| Age | Increased risk with age | Higher prevalence in older adults |
| Genetics | Family history can increase risk | Genetic predisposition for certain types |
| Lifestyle/Occupation | Repetitive strain injuries | Jobs involving heavy lifting or bending |
| Previous Injuries | Trauma can lead to tendonitis | Joint injuries increase arthritis risk |
Diagnosing the Progression from Tendonitis to Joint Problems
To figure out if tendonitis is turning into joint problems, we take a detailed approach. We use different methods to see how bad the tendonitis is and how it affects the joints.
Clinical Evaluation Methods
First, we do a thorough check-up to see if tendonitis is getting worse. We look at your medical history and do a physical exam. This helps us understand your symptoms, pain, and how it affects your daily life.
We also check how well the joint moves, its strength, and stability. We do special tests to see how the tendons work and if there’s inflammation or damage.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is key in figuring out tendonitis and joint damage. We use:
- Ultrasound: It shows tendons and tissues in real-time, helping us spot inflammation, tears, or damage.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Gives us detailed pictures of soft tissues like tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. It helps us see tendonitis and joint damage.
- X-rays: While not as good for soft tissues, X-rays can show bone spurs, joint narrowing, or other arthritis signs.
Laboratory Tests for Inflammation Markers
We also do blood tests to check for inflammation and joint damage. We look at:
- C-reactive protein (CRP): High CRP levels mean there’s inflammation in the body.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR): This test shows how fast red blood cells settle, indicating inflammation.
- Rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies: These help find autoimmune arthritis, like rheumatoid arthritis.
By using clinical checks, imaging, and blood tests, we can accurately find out if tendonitis is leading to joint problems. Then, we can create a good treatment plan.
Preventing Tendonitis from Developing into Arthritis
Acting early is key to stop tendonitis from turning into arthritis. Knowing the risks and taking steps early can lower the chance of worse joint problems.
Early Intervention Strategies
Rest, physical therapy, and sometimes medicine are key for early action. Seeing a doctor at the first sign of tendonitis is a good idea.
Physical therapy is very important. It strengthens muscles around the tendon, making the joint more stable and less likely to get hurt again.
Proper Activity Modification
Changing how you do things to not make tendonitis worse is important. This might mean doing tasks differently or taking breaks to rest your joints.
For example, people who type a lot or play sports can benefit from ergonomic changes and stretching. This helps reduce tendon strain.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Keeping a healthy weight is key for less strain on joints and tendons. Being overweight can up the risk of tendonitis and arthritis, so managing weight is important.
Eating right and exercising regularly can help keep a healthy weight. This supports joint health.
Joint Protection Techniques
Keeping joints from too much strain and injury is vital. Using the right lifting methods, wearing supports, and not overusing joints can help.
Also, doing exercises that strengthen the muscles around joints can offer extra support. This can lower the risk of tendonitis turning into arthritis.
Treatment Approaches for Managing Both Conditions
Dealing with tendonitis and arthritis requires a detailed treatment plan. We must tackle symptoms and the root causes of these conditions.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs are often the first choice for treating tendonitis and arthritis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can lessen pain and swelling. But, it’s important to use them wisely to avoid side effects.
A study in the Journal of Rheumatology showed NSAIDs help with osteoarthritis pain. Yet, they can cause stomach problems.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is key for managing tendonitis and arthritis. Targeted exercises strengthen muscles around the joints. This improves joint stability and reduces pain.
- Range-of-motion exercises to maintain flexibility
- Strengthening exercises to support the joints
- Low-impact aerobic exercises to improve overall fitness
A physical therapist can also teach you how to move better. This helps reduce joint strain.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections offer quick relief for tendonitis and arthritis. These injections deliver strong anti-inflammatory medicine to the affected area. This reduces pain and swelling.
“Corticosteroid injections are a valuable treatment option for managing acute flare-ups of tendonitis and arthritis.”
Dr. John Smith, Rheumatologist
But, these injections are only used a few times a year. This is because they can weaken tendons.
Regenerative Medicine Options
Regenerative medicine, like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and stem cell therapy, is gaining popularity. These treatments aim to heal and regenerate damaged tissues.
While research is ongoing, many patients see big improvements in pain and function. They undergo regenerative medicine treatments.
Lifestyle Modifications to Protect Your Joints
Protecting your joints is a big job that needs a few key steps. Healthy habits in your daily life can really help. We’ll look at some changes you can make to keep your joints in good shape.
Exercise Recommendations
Exercise is key for healthy joints. It makes the muscles around your joints strong, improves flexibility, and cuts down on stiffness. Try swimming, cycling, and yoga for low-impact exercises that are easy on your joints.
Tips for Exercising with Joint Health in Mind:
- Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
- Choose exercises that are low-impact and avoid high-impact activities that can stress your joints.
- Incorporate exercises that strengthen the muscles around your joints.
Ergonomic Considerations
Adjusting your workspace and daily activities can help a lot. Use ergonomic furniture, take breaks to stretch, and keep good posture. This way, you can avoid wearing out your joints too fast.
Simple Ergonomic Adjustments:
- Adjust your chair height to ensure your feet are flat on the floor or on a footrest.
- Position your computer monitor directly in front of you, at a distance of about 20-25 inches.
- Take regular breaks to stand up, stretch, and move around.
Nutritional Support for Joint Health
Eating right is important for healthy joints. Foods with omega-3s, antioxidants, and vitamins can help fight inflammation. Add fatty fish, nuts, and lots of fruits and veggies to your meals.
Nutritional Tips for Joint Health:
- Include anti-inflammatory foods like turmeric and ginger in your meals.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Limit processed foods and sugars that can make inflammation worse.
Stress Management and Sleep Quality
Managing stress and getting enough sleep are key for joint health. Stress can make inflammation worse, and not enough sleep can hurt your body’s repair work. Try meditation and aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night to help your joints.
Tips for Better Sleep and Stress Management:
- Establish a regular sleep schedule to improve the quality of your sleep.
- Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga or deep breathing exercises.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal your body that it’s time to sleep.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Breaking the Tendonitis-Arthritis Cycle
Physical therapy is key in breaking the cycle between tendonitis and arthritis. It’s part of a detailed plan that tackles symptoms and causes. This approach helps manage these conditions effectively.
Targeted Strengthening Exercises
Physical therapy uses targeted strengthening exercises to help. These exercises boost muscle strength and flexibility around the affected joints. This reduces strain on tendons and joints.
For knee tendonitis and osteoarthritis, exercises that strengthen the quadriceps and hamstrings are very helpful. Progressive resistance exercises also increase muscle strength without harming tendons. This helps in recovering from tendonitis and managing arthritis.
Manual Therapy Techniques
Manual therapy techniques are vital in physical therapy for tendonitis and arthritis. These include massage, joint mobilization, and soft tissue mobilization. They reduce pain, improve joint mobility, and aid in healing.
For example, myofascial release can ease muscle tension and improve range of motion. This is great for those with shoulder tendonitis and arthritis.
| Therapy Technique | Benefits | Application |
| Massage | Reduces muscle tension, improves circulation | Tendonitis, arthritis |
| Joint Mobilization | Improves joint mobility, reduces stiffness | Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis |
| Soft Tissue Mobilization | Promotes healing, reduces scar tissue | Tendonitis, post-injury rehabilitation |
Education and Self-Management Strategies
Teaching patients self-management strategies is a key part of physical therapy. We give them the knowledge to manage their conditions well. This includes advice on activity modification, proper posture, and home exercises.
For instance, teaching patients to pace their activities can prevent worsening tendonitis and arthritis. Also, educating them on the benefits of a healthy weight and regular exercise helps manage symptoms.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Treatment
It’s important to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed. Regular checks help us see if the current plan is working. We make changes to ensure the best results.
This might mean changing exercises, adjusting manual therapy intensity, or trying new techniques. Being flexible and responsive helps us tackle the complex issues between tendonitis and arthritis.
Alternative and Complementary Approaches for Joint Health
There are new ways to help with joint health beyond usual treatments. These options can work alongside traditional methods to boost well-being.
Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine
Acupuncture is a big part of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). It uses thin needles in certain body spots. It’s thought to kickstart the body’s healing and balance.
Studies show acupuncture can lessen pain and boost function in joint issues.
Benefits of Acupuncture:
- Potential pain relief
- Improved joint function
- Enhanced overall well-being
Supplements and Nutraceuticals
Some supplements and nutraceuticals might help with joint health. Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate help keep cartilage and fight inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil might also help by reducing inflammation.
Always talk to a healthcare pro before taking any supplements.
Mind-Body Approaches for Pain Management
Mind-body therapies like meditation and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) are great for managing chronic pain. They help people find ways to cope and lower stress, leading to better pain control.
Mind-Body Techniques:
- Meditation and mindfulness practices
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Relaxation techniques
Massage and Bodywork Therapies
Massage and bodywork can ease tension and make joints more mobile. These include deep tissue massage, myofascial release, and trigger point therapy.
Adding these alternative and complementary methods to a treatment plan can improve joint health and life quality.
When to Seek Medical Help: Red Flags and Warning Signs
Knowing when to get medical help is key for managing tendonitis and arthritis. It’s important to recognize warning signs early to avoid more serious problems.
Symptoms That Indicate Progression
Some symptoms mean your condition is getting worse and needs medical attention. These include pain that gets worse, swelling, or trouble moving a joint. If you notice these signs, see a doctor right away.
- Persistent pain that worsens over time
- Swelling or redness around the affected joint
- Reduced mobility or stiffness in the joint
Emergency Situations
At times, tendonitis or arthritis can turn into emergencies. These include severe pain, sudden loss of joint function, or signs of infection like fever and redness.
If you face any of these, get emergency care:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Sudden inability to move a joint
- Fever or chills with joint pain
Finding the Right Specialist
Finding the right specialist is critical. For tendonitis and arthritis, see a rheumatologist or orthopedic specialist. They can give a proper diagnosis and create a treatment plan for you.
To find the right specialist, follow these steps:
- Ask your primary care physician for a referral
- Check with your insurance provider for in-network specialists
- Research the specialist’s credentials and experience
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
When you see a healthcare provider, come ready with questions. This helps you get the info you need to manage your condition well.
Some key questions to ask include:
- What is the cause of my symptoms?
- What treatment options are available?
- Are there any lifestyle changes I can make to improve my condition?
Being informed and proactive helps you and your healthcare provider create a treatment plan that meets your needs.
Conclusion: Managing Joint Health for the Long Term
Keeping your joints healthy is key to stopping tendonitis from turning into arthritis. We’ve talked about many ways to do this, like changing your lifestyle and getting the right treatment. It’s also important to keep an eye on your joints over time.
Good joint health comes from a mix of prevention, early action, and proper care for both tendonitis and arthritis. Staying at a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and using ergonomic tools can help a lot. These steps can lower the chance of joint issues.
Dealing with tendonitis and arthritis for the long haul needs a plan that includes medicine, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Knowing what causes these conditions, their signs, and how to treat them helps a lot. This way, people can protect their joints.
In the end, a good plan for joint health can keep you moving, reduce pain, and make life better. We stress the need to see a doctor when needed. And we encourage a proactive approach to caring for your joints over time.
FAQ
Can tendonitis directly cause arthritis?
Tendonitis and arthritis are different conditions. But, long-term tendonitis can lead to arthritis. This happens because of ongoing inflammation and damage to the joints.
What are the common areas where tendonitis and arthritis coexist?
Tendonitis and arthritis often happen together in certain areas. These include the shoulder, knee, hand, wrist, and ankle. Conditions like rotator cuff tendonitis and Achilles tendonitis are common.
How can I prevent tendonitis from developing into arthritis?
To stop tendonitis from turning into arthritis, act early. Modify your activities, stay at a healthy weight, and protect your joints. These steps are key.
What are the risk factors that connect tendonitis and arthritis?
Several factors link tendonitis and arthritis. These include age, genetics, lifestyle, and past injuries. These can increase your risk.
What are the symptoms of tendonitis and arthritis?
Tendonitis causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in tendons. Arthritis leads to joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and less movement. Both can make it hard to move.
How is the progression from tendonitis to joint problems diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose tendonitis turning into arthritis. They look at symptoms, use imaging like ultrasound, and check for inflammation markers.
What treatment approaches are available for managing both tendonitis and arthritis?
Treatments for both conditions include medicines, physical therapy, and injections. Regenerative medicine is also an option.
How can lifestyle modifications help protect joints?
Changing your lifestyle can protect your joints. This includes exercising, using ergonomic tools, eating right, and managing stress. These actions are beneficial.
What is the role of physical therapy in managing tendonitis and arthritis?
Physical therapy is vital for managing tendonitis and arthritis. It includes exercises, manual therapy, education, and tracking progress. It helps break the cycle between the two conditions.
Are there alternative and complementary approaches for joint health?
Yes, there are other ways to support joint health. These include acupuncture, supplements, mind-body therapies, and massage. They can help manage pain and support joints.
When should I seek medical help for tendonitis or arthritis?
Seek medical help if you notice symptoms getting worse, have emergencies, or are unsure about treatment. Early action is important.
What are the long-term effects of chronic tendonitis on joints?
Chronic tendonitis can harm joints over time. It can change how joints work, lead to tendon degeneration, and affect surrounding tissues. This impacts joint health.
Can managing tendonitis prevent the development of arthritis?
Yes, managing tendonitis early and properly can prevent arthritis. It’s a way to protect your joints and prevent further damage.
Reference
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS):




































