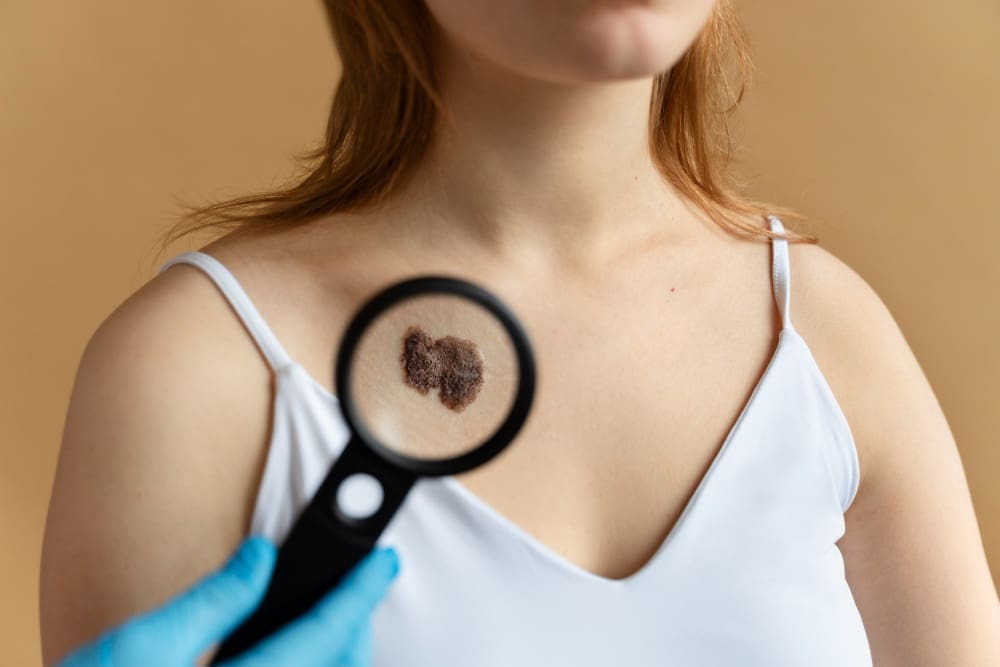
At Liv Hospital, we know skin cancer surgery can be scary, even more so when it’s on the face. Our care is top-notch and patient-centered. We use the newest surgical techniques to ensure the best results for both health and looks.
We use different surgical ways to safely and quickly get rid of skin cancers. Surgical excision is a common choice. It removes the tumor and some healthy tissue around it to lower the chance of it coming back.
For face lesions or when it keeps coming back, Mohs micrographic surgery is often the go-to. It saves healthy tissue and boosts cure rates.
Key Takeaways
- Effective surgical methods are available for basal cell carcinoma removal.
- Surgical excision and Mohs micrographic surgery are commonly used techniques.
- Removing the tumor with a margin of healthy tissue minimizes recurrence risk.
- Our surgeons prioritize both cure and cosmetic outcome.
- Liv Hospital provides internationally recognized, patient-focused care.
Understanding Basal Cell Carcinoma
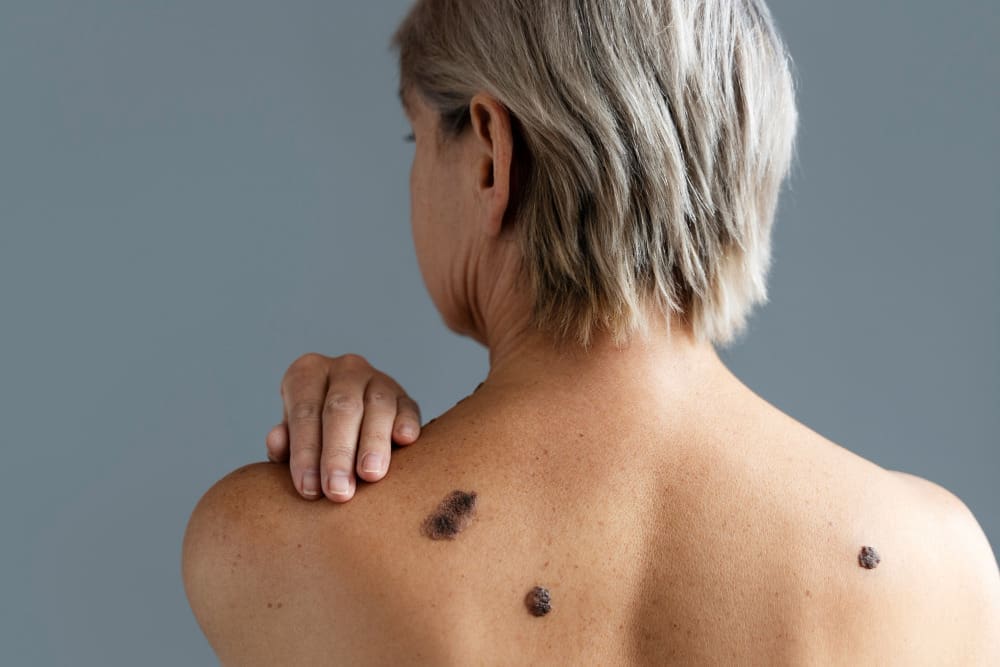
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that starts in the basal cell layer. It’s important to know about it to manage it well. We’ll look at what it is, where it often shows up, and what makes you more likely to get it.
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin cancer. It happens when abnormal cells grow in the basal layer of the skin. It’s a type of non-melanoma skin cancer, which is usually treatable if caught early.
Key characteristics of BCC include:
- Slow growth rate
- Rarely metastasizes
- Can cause local destruction of surrounding tissue if left untreated
Common Locations and Appearance
Basal cell carcinoma often shows up on sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, neck, and hands. It can look different, but common signs include:
- A shiny or pearly bump
- A flat, flesh-colored or brown scar-like lesion
- A sore that bleeds or oozes
A study in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology shows how important it is to spot these signs early.
“Basal cell carcinoma is a common and treatable form of skin cancer, but it requires prompt attention to prevent local destruction and disfigurement.”
Risk Factors for Developing BCC
There are several things that can make you more likely to get basal cell carcinoma. Knowing these can help prevent and catch it early.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| UV Exposure | Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds |
| Fair Skin | Individuals with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are more susceptible |
| Family History | A family history of skin cancer, specially BCC |
| Age | Risk increases with age, typically appearing in individuals over 50 |
| Previous Skin Cancer | Having had skin cancer previously increases the risk of developing BCC |
Knowing about these risk factors and what basal cell carcinoma looks like can help patients understand their diagnosis and treatment options better.
Diagnosing Basal Cell Carcinoma
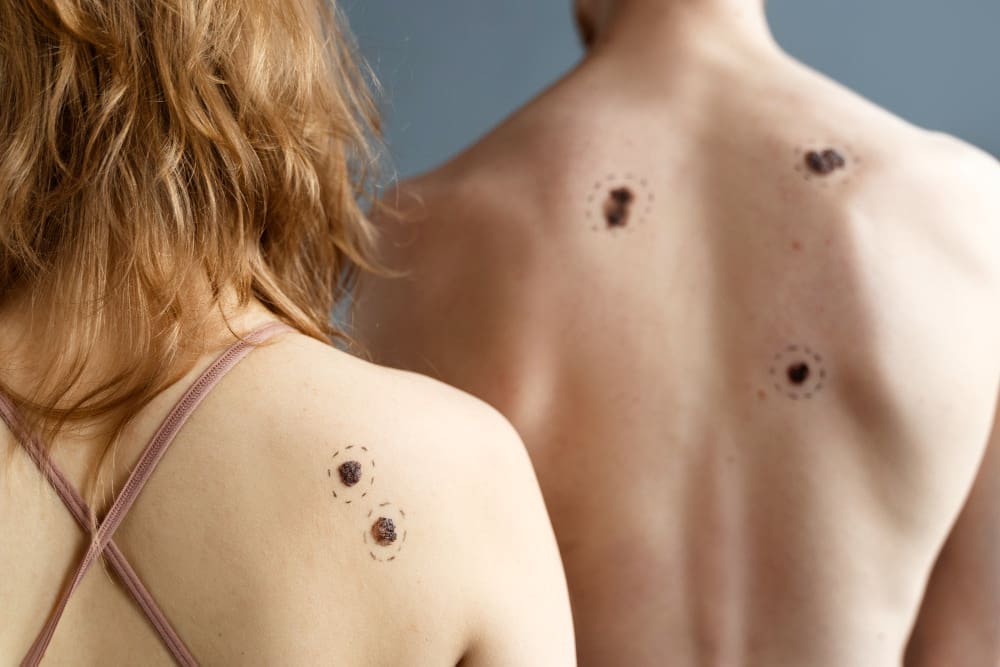
To find basal cell carcinoma, doctors use a few steps. They look at the skin, do biopsies, and check how far the cancer has spread. This way, they can make sure the treatment works well.
Visual Examination and Symptoms
Doctors start by looking at the skin. They look for signs like shiny bumps or red patches. If you see anything strange, it’s important to see a dermatologist.
Biopsy Procedures
If a doctor thinks it might be basal cell carcinoma, they do a biopsy. There are a few ways to do this, like shaving or cutting out a piece of skin. The method depends on the tumor’s size and where it is.
Staging and Assessment
After the biopsy confirms basal cell carcinoma, doctors check how big it is and if it has spread. Even though it rarely spreads, knowing this helps plan the best treatment.
| Diagnostic Step | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Examination | Initial assessment of skin changes | Identify possible basal cell carcinoma |
| Biopsy | Removing tissue for a closer look | Make sure it’s cancer |
| Staging | Checking how big and spread the cancer is | Plan the best treatment |
Factors Affecting Treatment Selection
Choosing the right treatment for basal cell carcinoma depends on several key factors. We look at these elements to find the best treatment for each patient.
Size and Location of the Tumor
The size and where the tumor is located are big factors. Larger tumors or those in sensitive areas, like the face, need careful treatment.
Tumors near the eyes or nose need special attention. We consider the tumor’s size and where it is to pick the right treatment.
Tumor Subtype and Aggressiveness
The type and how aggressive the tumor is also matter. Some types, like morpheaform or infiltrative BCC, are more aggressive. They might need treatments like Mohs micrographic surgery.
We look at the tumor’s type to understand its behavior. This helps us tailor the treatment to meet its specific needs.
Patient’s Overall Health
A patient’s health and medical history are important too. Certain health conditions or medications can affect treatment choices.
For example, patients on blood thinners might need to stop before surgery. We check each patient’s health to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Cosmetic Considerations
Cosmetic concerns are also important, mainly for tumors in visible areas. We aim to remove the tumor effectively while keeping the appearance in mind.
| Factor | Consideration | Impact on Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor Size | Larger tumors require more extensive treatment | May necessitate Mohs surgery or wider excision margins |
| Tumor Location | Cosmetically sensitive areas require precise treatment | May involve techniques like Mohs surgery for better tissue preservation |
| Tumor Subtype | Aggressive subtypes require more aggressive treatment | May require Mohs surgery or other advanced treatments |
| Patient’s Health | Health conditions may affect treatment choices | May require adjustments to treatment plan, such as altering medication |
By carefully looking at these factors, we can create a treatment plan that meets each patient’s needs.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Removal: Surgical Excision
Surgical excision is a common and effective way to treat basal cell carcinoma. It involves removing the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. This method is chosen because it has a high success rate and allows for checking the removed tissue for cancer cells.
Standard Excision Procedure
The standard excision procedure for basal cell carcinoma has several steps. First, the area is numbed with local anesthesia to reduce pain. Then, the surgeon carefully removes the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. The size of the removed tissue depends on the tumor’s size and location.
Key steps in the standard excision procedure include:
- Administering local anesthesia to numb the area
- Removing the tumor with a margin of healthy tissue
- Closing the wound using appropriate techniques
- Examining the removed tissue to ensure clear margins
Determining Appropriate Margins
Choosing the right margins is key to prevent the tumor from coming back. The size of the margin depends on the tumor’s size, location, and type. For example, bigger or more aggressive tumors need wider margins.
The goal is to remove the tumor completely while keeping as much healthy tissue as possible. This is important, as it helps in preserving the appearance of sensitive areas like the face.
Wound Closure Techniques
After removing the tumor, the wound must be closed. The method used depends on the wound’s size and location. Techniques include simple closure, skin grafting, and flap reconstruction.
Wound closure techniques:
- Simple closure for small wounds
- Skin grafting for larger wounds
- Flap reconstruction for complex or facial wounds
Success Rates and Recurrence Risk
The success rate for removing basal cell carcinoma through surgery is usually high, with cure rates over 90%. But, there’s a chance the cancer could come back, mainly if the margins are not clear of cancer cells.
Factors influencing success rates and recurrence risk include:
- Tumor size and location
- Margin status
- Tumor subtype and aggressiveness
It’s important to have regular follow-ups to watch for any signs of the cancer coming back.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery for Precision Removal
Mohs micrographic surgery is a top choice for treating basal cell carcinoma. It’s great for keeping as much tissue as possible. This method is perfect for areas that are hard to treat or keep looking good.
How Mohs Surgery Works
Mohs surgery removes cancer layer by layer. Each layer is checked under a microscope right away. This keeps going until all cancer is gone, saving healthy tissue.
We do Mohs surgery in a special place. This lets us check the tissue as we go. It helps us cure more cases than other methods.
Benefits for Facial and Recurring BCCs
Mohs surgery is great for face BCCs and those that come back. It’s very precise, which means less healthy tissue is lost. This is key for keeping the face looking good.
Checking every part of the tumor helps us get rid of all cancer cells. This lowers the chance of it coming back.
Tissue Preservation Advantages
Mohs surgery is good at saving healthy tissue. It removes cancer bit by bit and checks each piece. This is super helpful for areas where keeping tissue is very important.
When Mohs Is the Preferred Option
Mohs surgery is best for big, aggressive, or tricky-to-treat BCCs. It’s also good for BCCs that keep coming back. Or those that are hard to define.
We suggest Mohs for those who want the best chance of getting rid of cancer. It’s also for those who care a lot about how they look after treatment. Mohs surgery is a top choice for effective treatment that keeps the area looking good.
Less Invasive Removal Methods for Superficial BCCs
We use less invasive methods to treat superficial basal cell carcinomas. This means patients get effective treatments with fewer side effects and quicker recovery times.
Curettage and Electrodessication
Curettage and electrodessication are common for superficial BCCs. First, a curette scrapes away the tumor. Then, electrodessication kills any remaining cancer cells. This combination makes the treatment more effective.
This method is simple and can be done on an outpatient basis. But, it’s important to have regular check-ups to watch for any signs of the cancer coming back.
Cryotherapy (Freezing)
Cryotherapy freezes the tumor with liquid nitrogen, killing the cancer cells. It’s relatively painless and doesn’t require surgery. This makes it great for superficial BCCs.
The procedure is quick and done in a doctor’s office. Afterward, the area might blister or swell. It’s key to follow the care instructions to heal properly.
Topical Treatments and Immunotherapy
For some superficial BCCs, topical treatments like imiquimod cream or 5-fluorouracil work well. These creams boost the immune system to fight or kill the cancer cells. Topical treatments are a good choice for those who don’t want surgery.
Immunotherapy, like imiquimod, changes how the immune system fights cancer. It’s applied directly to the skin. This makes it a good option for treating superficial BCCs without surgery.
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) uses a light-sensitive medication and light to destroy cancer cells. PDT is great for treating superficial BCCs in areas that are sensitive to appearance.
| Treatment Method | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Curettage and Electrodessication | Scraping away the tumor followed by electrodessication | Effective, simple, outpatient procedure |
| Cryotherapy | Freezing the tumor with liquid nitrogen | Painless, no surgical incisions |
| Topical Treatments | Applying creams to stimulate the immune system or kill cancer cells | Non-surgical, good for cosmetically sensitive areas |
| Photodynamic Therapy | Applying light-sensitive medication followed by specific light exposure | Effective for cosmetically sensitive areas, non-invasive |
Excision Depth: Basal Cell vs. Squamous Cell Carcinoma
It’s important to know how deep to cut for basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Surgeons need to remove the tumor completely while keeping healthy tissue. This is key for effective treatment.
Standard Depth Guidelines for BCC
For BCC, doctors usually remove the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. They go as deep as the subcutaneous fat layer. This method helps prevent the tumor from coming back.
Why SCC Requires Deeper Excision
SCC needs a deeper cut than BCC. SCC can grow deeper into the skin and tissues. So, removing more tissue is needed to ensure all cancer is gone. This helps lower the chance of the cancer coming back or spreading.
Reaching the Subcutaneous Fat Layer
Both BCC and SCC aim to reach the subcutaneous fat layer. This layer acts as a natural boundary. It helps ensure the tumor is fully removed. But, the exact depth depends on the tumor’s size and where it is.
Histological Confirmation of Clear Margins
After cutting out the tumor, it’s vital to check the tissue under a microscope. This confirms that no cancer cells are left behind. This step is important for both BCC and SCC. It makes sure the tumor is fully removed and reduces the need for more surgery.
Special Considerations for Facial Skin Cancer Removal
Removing skin cancer from the face is a delicate task. It needs to treat the cancer well while keeping the face looking natural. This is a complex process that requires a lot of skill and care.
Techniques for Different Facial Areas
Each part of the face needs its own special way to remove skin cancer. The skin around the eyes, nose, and mouth is very delicate. We use precise surgical methods to avoid scars and keep these areas working right.
For the forehead and cheeks, we often use standard excision techniques. But for more sensitive areas, Mohs micrographic surgery is better. It removes cancer cells carefully while keeping healthy tissue.
Preserving Aesthetic Appearance
Keeping the patient’s face looking good is very important to us. We know that scars or changes in appearance can affect someone’s mood. So, we try to use methods that leave as little scar as possible.
To do this, we might use advanced reconstructive techniques after removing the cancer. These can include skin grafts, local flaps, or other surgeries. Our goal is to make the face look as natural as possible again.
Reconstructive Options After Facial BCC Removal
There are many ways to rebuild the face after removing BCC. The choice depends on the size and location of the cancer, the patient’s health, and what they want. We talk to patients to find the best plan for them, which might include several surgeries.
- Skin grafting to cover larger areas
- Local flaps to repair adjacent tissue
- Complex reconstructive surgery for extensive areas
Recovery Timeline for Facial Procedures
The time it takes to recover from facial surgery varies. It depends on how big the surgery was and the methods used. Patients usually see swelling and bruising at first, but these go away as they heal.
We give our patients clear instructions on how to care for themselves after surgery. We also schedule follow-up visits to check on their healing and answer any questions or concerns.
The Outpatient Experience and Recovery Process
Understanding the recovery process is key when having basal cell carcinoma removed as an outpatient. We make sure our patients know what to expect during and after the procedure.
What to Expect During an Outpatient Procedure
During an outpatient procedure for basal cell carcinoma removal, you’ll be in a comfortable and safe environment. Our medical team will use local anesthesia to numb the area. This way, you won’t feel pain during the procedure.
The surgery involves removing the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. This ensures all cancer cells are removed.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After the procedure, you’ll be taken to a recovery area. Our staff will watch over you for a short time. You might feel some discomfort, swelling, or bleeding.
These symptoms can be managed with pain medication and cold compresses. It’s important to have someone with you to drive you home and stay for a few hours.
Wound Care and Scar Management
Proper wound care is essential for healing and reducing scar appearance. We’ll give you detailed instructions on wound care. This includes keeping it clean and dry and using topical ointments as directed.
We might also recommend scar management techniques. These include silicone gel or sheeting to improve scar appearance over time.
Follow-up Appointments and Monitoring
Follow-up appointments are key for monitoring healing and checking for recurrence. We schedule these based on your healing progress and case specifics.
At these visits, we check the wound’s healing, remove sutures or staples, and give ongoing care instructions.
Conclusion
Removing basal cell carcinoma requires different surgical methods. These include surgical excision and Mohs micrographic surgery. The right treatment depends on the tumor’s size, location, type, and how aggressive it is. It also depends on the patient’s health.
We talked about the surgical options for basal cell carcinoma. It’s important to reduce the risk of the cancer coming back and keep the skin looking good. How well someone recovers from surgery depends on the procedure and their health.
It’s key to follow up after surgery to watch for any signs of cancer coming back. This helps address any problems or concerns. Knowing about the different skin cancer surgeries helps patients make better choices about their treatment.
At our institution, we aim to give top-notch healthcare to everyone, including international patients. Our team works hard to make sure patients get the best care for removing basal cell carcinoma.
FAQ
What is the standard treatment for basal cell carcinoma removal?
The usual treatment for basal cell carcinoma is surgery. This can be either excision or Mohs micrographic surgery. The choice depends on the tumor’s size, location, and how aggressive it is.
How deep do they cut for basal cell carcinoma?
For basal cell carcinoma, doctors remove the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. They go down to the subcutaneous fat layer. This helps lower the chance of the tumor coming back.
What is the difference in excision depth between basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma usually needs a shallower cut than squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma often needs a deeper cut because it can grow more aggressively.
How is Mohs micrographic surgery different from standard surgical excision?
Mohs surgery is a precise method. It removes the tumor layer by layer. Each layer is checked under a microscope. This method saves more tissue and has lower recurrence rates, which is good for facial and recurring lesions.
What are the less invasive removal methods for superficial basal cell carcinomas?
For superficial basal cell carcinomas, there are less invasive options. These include curettage and electrodessication, cryotherapy, topical treatments, immunotherapy, and photodynamic therapy. These methods are good for superficial BCCs and are more conservative.
How is skin cancer removed from the face, and what are the considerations?
Removing skin cancer from the face is done carefully to keep the face looking good. The method used depends on where the cancer is. After removal, there are options to minimize scarring and improve how the face looks.
What can I expect during an outpatient procedure for basal cell carcinoma removal?
During an outpatient procedure, the surgical team will guide you. They will help with immediate care after the procedure. You’ll get instructions on how to care for your wound and manage scars to help with recovery.
How do they remove basal cell skin cancer, and what are the success rates?
Basal cell skin cancer is usually removed by surgery or Mohs surgery. These methods have high success rates and low recurrence risks. Proper treatment and follow-up care are key to success.
What is the role of histological confirmation in basal cell carcinoma removal?
Histological confirmation is very important. It involves checking the removed tissue under a microscope. This ensures that all tumor cells are removed and the margins are clear.
What are the factors that influence the choice of treatment for basal cell carcinoma?
Several factors influence treatment choices for basal cell carcinoma. These include the tumor’s size, location, subtype, and aggressiveness. The patient’s health and cosmetic concerns are also considered. These factors help determine the best treatment approach.
What is the standard treatment for basal cell carcinoma removal?
The usual treatment for basal cell carcinoma is surgery. This can be either excision or Mohs micrographic surgery. The choice depends on the tumor’s size, location, and how aggressive it is.
How deep do they cut for basal cell carcinoma?
For basal cell carcinoma, doctors remove the tumor and some healthy tissue around it. They go down to the subcutaneous fat layer. This helps lower the chance of the tumor coming back.
What is the difference in excision depth between basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma usually needs a shallower cut than squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma often needs a deeper cut because it can grow more aggressively.
How is Mohs micrographic surgery different from standard surgical excision?
Mohs surgery is a precise method. It removes the tumor layer by layer. Each layer is checked under a microscope. This method saves more tissue and has lower recurrence rates, which is good for facial and recurring lesions.
What are the less invasive removal methods for superficial basal cell carcinomas?
For superficial basal cell carcinomas, there are less invasive options. These include curettage and electrodessication, cryotherapy, topical treatments, immunotherapy, and photodynamic therapy. These methods are good for superficial BCCs and are more conservative.
How is skin cancer removed from the face, and what are the considerations?
Removing skin cancer from the face is done carefully to keep the face looking good. The method used depends on where the cancer is. After removal, there are options to minimize scarring and improve how the face looks.
What can I expect during an outpatient procedure for basal cell carcinoma removal?
During an outpatient procedure, the surgical team will guide you. They will help with immediate care after the procedure. You’ll get instructions on how to care for your wound and manage scars to help with recovery.
How do they remove basal cell skin cancer, and what are the success rates?
Basal cell skin cancer is usually removed by surgery or Mohs surgery. These methods have high success rates and low recurrence risks. Proper treatment and follow-up care are key to success.
What is the role of histological confirmation in basal cell carcinoma removal?
Histological confirmation is very important. It involves checking the removed tissue under a microscope. This ensures that all tumor cells are removed and the margins are clear.
What are the factors that influence the choice of treatment for basal cell carcinoma?
Several factors influence treatment choices for basal cell carcinoma. These include the tumor’s size, location, subtype, and aggressiveness. The patient’s health and cosmetic concerns are also considered. These factors help determine the best treatment approach.
References
Skin Cancer Foundation. Mohs Surgery. https://www.skincancer.org/treatment-resources/mohs-surgery/
MD. The Process of Mohs Surgery: A Step-by-Step Guide. https://www.johnvinemd.com/process-of-mohs-surgery/



































