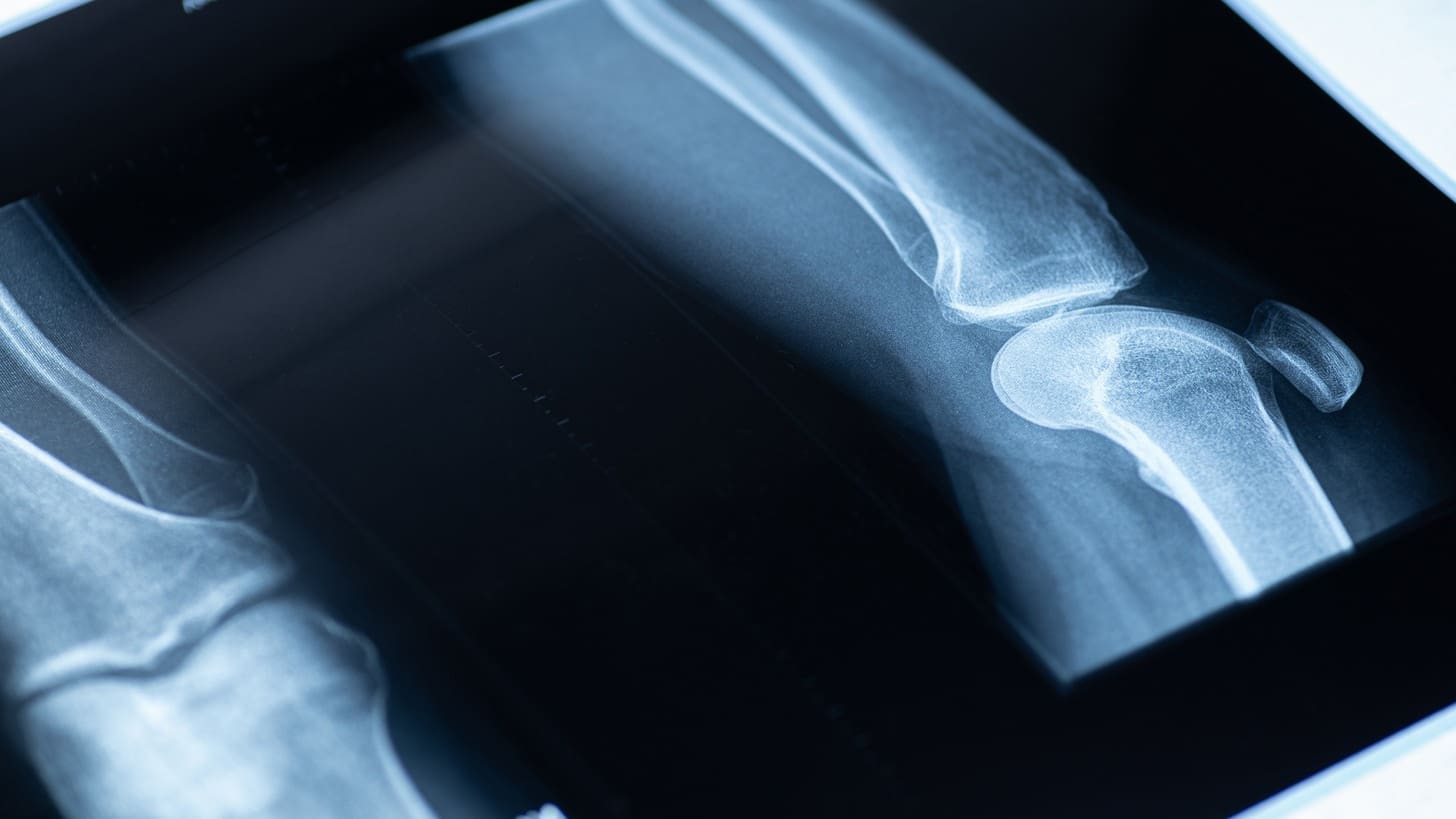
At Liv Hospital, we know how key it is to understand the body’s parts well. The tibial tuberosity, or tibial tubercle, is a key part of the knee. It’s important for how we move.
The tibial tuberosity is found on the front of the tibia. It helps the patellar ligament attach, which is key for bending the knee and moving around.
Knowing where and how the tibial tuberosity works is key for treating knee problems. At Liv Hospital, our team is all about top-notch care that puts patients first.
Key Takeaways
- The tibial tuberosity is a vital spot for the patellar ligament to attach.
- It’s essential for bending the knee and moving around.
- Liv Hospital offers expert orthopedic care with a focus on patient-centered excellence.
- Understanding knee anatomy is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Our team is committed to delivering world-class healthcare services.
Anatomical Overview of the Tibial Tubercle
The tibial tubercle is a key part of the knee. It’s a bony spot on the tibia. It helps the patellar ligament attach, linking the patella to the tibia. This connection is important for extending the knee and keeping it stable.
Definition and Terminology
The tibial tubercle is also called tuberositas tibiae or tuberosidad tibial. These names highlight its role as a bony part of the tibia. Knowing these terms helps doctors and patients talk clearly about knee issues.
The tibial tuberosity anatomyis more than just bones. It’s about how it works with muscles and ligaments. Knowing about the tibial tubercle is key for treating knee problems.
Evolutionary Significance
The evolutionary significance of the tibial tubercle is huge. It helps with movement and knee function in many animals. In humans, it supports walking and running on two legs. Its development is linked to our need for knee stability and weight-bearing activities.
- The tibial tubercle provides a mechanical advantage for knee extension.
- It serves as a critical attachment point for the patellar ligament.
- Its development is closely tied to the overall anatomy of the lower limb.
Understanding the tibial tubercle helps us see how human movement works. It shows how our bodies have adapted to do many physical activities.
Precise Location of the Tibial Tuberosity
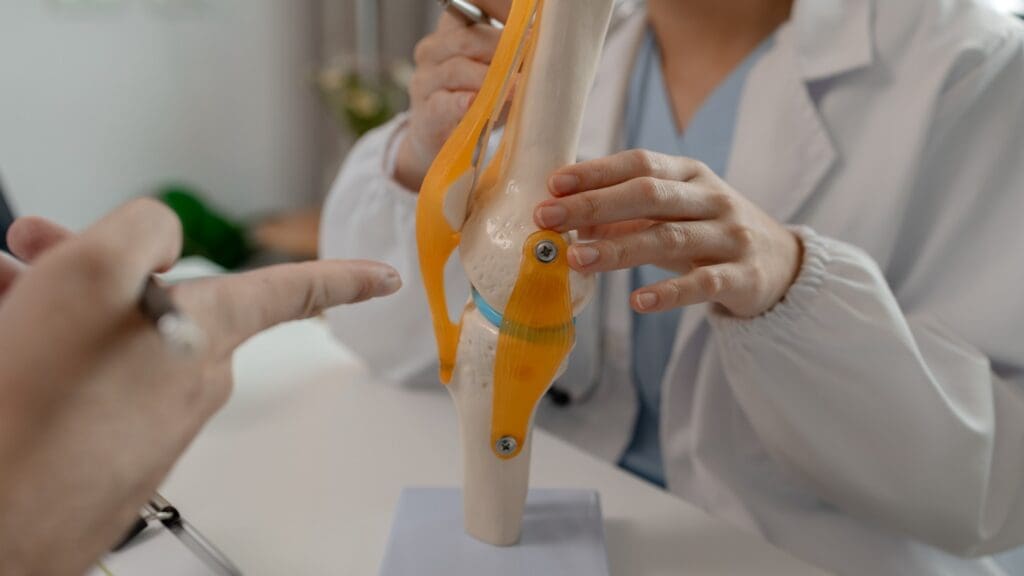
The tibial tuberosity is found on the front part of the upper tibia. It’s where the patellar ligament attaches. This spot is key for understanding how the knee works and for spotting knee problems.
Anterior Proximal Tibia Positioning
The tibial tuberosity is on the front of the upper tibia. It’s easy to feel during a check-up because of its bony bump. You can spot it by its clear bump on the front upper tibia.
Relationship to the Patella and Knee Joint
The tibial tuberosity is near the patella and the knee joint. It’s where the patellar ligament connects the patella to the tibia. This connection helps the knee extend and stay stable. The way the tibial tuberosity lines up with the patella and knee is important for knee movement.
Palpation and External Landmarks
Doctors can find the tibial tuberosity by feeling it. It’s just below the patella, on the front of the leg. By following the patellar ligament down, you can feel the tibial tuberosity’s bump. This landmark helps doctors check for knee issues or injuries.
Development and Growth of the Tibial Tuberosity
The tibial tuberosity grows through many complex steps. These steps are key for its role in knee mechanics. We’ll look at how this important part of the knee forms and grows.
Embryological Formation
The tibial tuberosity starts forming early in development. This early start is vital for its proper growth and function. Research shows its formation is tied to the growth of the lower limb as discussed in recent research.
Growth Patterns During Adolescence
In adolescence, the tibial tuberosity grows a lot. This is a key time for its bone formation. It gets bigger and changes shape to fit the growing knee joint.
Maturation and Ossification Timeline
The tibial tuberosity becomes fully formed by late adolescence. The exact time can differ, but it usually follows a set pattern. Knowing this timeline helps in diagnosing and treating related issues.
| Stage | Description | Age Range |
|---|---|---|
| Embryological Formation | Initial development of the tibial tuberosity | Early fetal development |
| Growth During Adolescence | Ossification and growth of the tuberosity | 10-18 years |
| Maturation | Final ossification and hardening | Late adolescence to early adulthood |
Structural Composition and Variations
The tibial tuberosity is key to the knee’s function. It has different structures that are important for its job. We will look at the bone’s makeup, its tissue, and how it varies among people.
Bone Architecture and Histology
The tibial tuberosity is made mostly of cancellous bone. This type of bone is strong but light. It’s built to handle stress, like the force from the patellar ligament.
Histological Composition: It has lots of collagen fibers for strength. Cells like fibroblasts help keep the tissue healthy and strong.
Anatomical Variations Among Individuals
People’s tibial tuberosities can differ a lot. These differences can change how the knee works.
- Size differences can change how the patellar ligament works.
- Shape differences can affect how stress is spread in the knee.
- Orientation differences can change how the patella moves.
| Variation Type | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Size | Affects patellar ligament leverage |
| Shape | Influences stress distribution |
| Orientation | Impacts patella tracking |
The Lateral Tibial Tubercle and Its Significance
The lateral tibial tubercle is an important part of the knee. It can be different in size and presence among people.
Significance: It can affect how the knee rotates and might change the risk of injuries.
Knowing about the tibial tuberosity’s structure and variations is key for doctors. It helps them understand and treat knee problems better.
Primary Functions of the Tibial Tuberosity
The tibial tuberosity is key to knee movement and stability. It has several important roles that help us move and stay balanced. This part of our body is essential for many knee actions.
Attachment Site for the Patellar Ligament
The tibial tuberosity is where the patellar ligament attaches. This ligament links the patella to the tibia. It helps the quadriceps muscle group push the tibia, which extends the knee.
This connection is vital for knee extension. It makes sure forces are transferred efficiently. This is important for knee mechanics.
Connection to the Quadriceps Muscle Group
The tibial tuberosity is linked to the quadriceps muscle group through the patellar ligament. This link lets the quadriceps muscles push on the tibia. This helps extend the knee.
The quadriceps are important for knee movement. Their connection to the tibial tuberosity is key for walking, running, and jumping.
Role in Knee Extension Mechanics
The tibial tuberosity is important for knee extension. It acts as a leverage point for the patellar ligament. When the quadriceps contract, they pull the patellar ligament, which pulls the tibial tuberosity. This extends the knee.
This mechanism is essential for movement. It helps us do daily activities efficiently.
Contribution to Lower Limb Stability
The tibial tuberosity also helps with lower limb stability. It provides a stable point for the patellar ligament. This stability is important for keeping the knee in line and preventing injuries.
In summary, the tibial tuberosity is vital for knee mechanics and stability. It attaches the patellar ligament, connects to the quadriceps, aids in knee extension, and supports lower limb stability. It’s a key part of our anatomy.
Key Functions of the Tibial Tuberosity:
- Attachment site for the patellar ligament
- Connection to the quadriceps muscle group
- Role in knee extension mechanics
- Contribution to lower limb stability
Biomechanical Importance in Movement
The tibial tuberosity is very important for human movement. It helps the patellar ligament connect the quadriceps to the tibia. This connection is key for knee extension.
Force Transmission During Walking and Running
The tibial tuberosity is key in force transmission during walking and running. It acts like a lever, boosting the force from the quadriceps. This helps in moving efficiently.
This process is vital for keeping the gait stable and moving forward. The tibial tuberosity’s design also helps spread out forces. This reduces injury risks in activities like running.
Prevention of Knee Collapse During Weight-Bearing
The tibial tuberosity helps prevent knee collapse during weight-bearing activities. It provides a stable point for the patellar ligament. This keeps the knee joint stable, even when it’s under load.
This function is key in avoiding injuries and ensuring smooth movement. It’s essential for keeping the knee stable.
Role in Athletic Performance and Jumping
In sports, the tibial tuberosity’s role is even more critical. It’s vital for athletic performance, mainly in jumping and quick changes of direction. Its ability to handle high forces and support powerful knee extensions is essential for athletes.
The strength and development of the tibial tuberosity greatly affect an athlete’s performance. This shows how important this part of the body is in sports medicine and training.
Common Conditions Affecting the Tibial Tubercle
The tibial tubercle can face many issues that affect knee health. These problems can come from growth issues, injuries, or inflammation. They can really change how people live their lives.
Osgood-Schlatter Disease: Causes and Risk Factors
Osgood-Schlatter disease is common in teens. It causes pain and swelling because of inflammation in the patellar tendon. This happens when the tendon is stressed a lot during growth spurts.
Playing sports that involve running and jumping, and growing fast during puberty, increase the risk.
Fractures and Avulsion Injuries
Fractures and avulsion injuries can happen from direct hits or muscle contractions. Avulsion fractures, where the tibial tubercle is pulled away, are common in teens. These injuries can make it hard to move the knee and need quick medical help.
The damage can be mild or severe, needing surgery to fix.
Inflammatory Conditions and Bursitis
Inflammatory conditions like bursitis can also affect the tibial tubercle. Bursitis is when the bursa, a fluid sac, gets inflamed. This can happen from too much motion or pressure. These issues can make the knee hurt and swell, making it hard to move.
Knowing about these conditions helps doctors give the right treatment. They can plan better care by understanding the causes and risks of each problem.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tibial Tuberosity Disorders
Managing tibial tuberosity disorders starts with accurate diagnosis and custom treatment plans. At Liv Hospital, we take a detailed approach to tackle these issues.
Physical Examination Techniques
Our first step is a thorough physical exam. We check symptoms, feel for tenderness, and see how well the knee moves. Physical examination techniques help us understand how serious the problem is and what tests we need next.
Imaging Methods: X-rays, MRI, and Ultrasound
We use different imaging methods to confirm the diagnosis. X-rays show bone issues, while MRI and ultrasound give us clear pictures of soft tissues. This helps us see how far the disorder has spread.
Conservative Treatment Approaches
For many, conservative treatment approaches work well. This includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory drugs. We adjust these treatments to fit each patient’s needs.
Surgical Interventions When Necessary
If other treatments don’t work, surgical interventions might be needed. We might do tibial tuberosity realignment or fix soft tissue injuries. Our skilled surgeons work with patients to find the best solution.
At Liv Hospital, we’re dedicated to top-notch care for tibial tuberosity disorder patients. Our team ensures each patient gets a treatment plan made just for them.
Conclusion
The tibial tuberosity is key in knee anatomy. It helps the patellar ligament attach and aids in knee extension. At Liv Hospital, we know how vital it is for knee health and effective care.
We understand the tibial tuberosity well. This knowledge helps us diagnose and treat knee issues like Osgood-Schlatter disease and fractures. With advanced technology and knowledge, we offer top-notch care for tibial tuberosity problems.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on detailed orthopedic care. We meet each patient’s needs with care and precision. Our goal is to improve our patients’ lives by combining knowledge of knee anatomy with a caring approach.
FAQ
What is the tibial tuberosity, and where is it located?
The tibial tuberosity is a bony part on the front of the tibia, just below the knee. It’s where the patellar ligament attaches.
What is the function of the tibial tuberosity?
It helps extend the knee by passing forces from the quadriceps to the tibia. This is key for straightening the knee and keeping the lower limb stable.
What is Osgood-Schlatter disease, and how does it relate to the tibial tuberosity?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common issue in teens. It causes pain and inflammation at the tibial tuberosity due to repetitive stress.
How is Osgood-Schlatter disease diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose it through physical exams, medical history, and sometimes X-rays or ultrasound to check for other conditions.
What are the treatment options for tibial tuberosity disorders?
Treatments include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and pain management. Surgery might be needed in some cases.
Can the tibial tuberosity be fractured or injured?
Yes, it can fracture or avulse, often in sports injuries or high-energy trauma. This causes pain, swelling, and mobility issues.
How is a tibial tuberosity fracture diagnosed?
Doctors use X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to see the extent of the injury.
What is the role of the lateral tibial tubercle?
The lateral tibial tubercle is a variation of the tibial tuberosity. It can affect knee biomechanics and surrounding structures.
How does the tibial tuberosity contribute to athletic performance?
It’s vital for jumping, running, and quick changes in direction. Its role in knee extension is key for top performance.
Can the tibial tuberosity be affected by inflammatory conditions?
Yes, conditions like bursitis can affect it. This leads to pain, swelling, and mobility issues.
What is the tibial tuberosity, and where is it located?
The tibial tuberosity is a bony part on the front of the tibia, just below the knee. It’s where the patellar ligament attaches.
What is the function of the tibial tuberosity?
It helps extend the knee by passing forces from the quadriceps to the tibia. This is key for straightening the knee and keeping the lower limb stable.
What is Osgood-Schlatter disease, and how does it relate to the tibial tuberosity?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is a common issue in teens. It causes pain and inflammation at the tibial tuberosity due to repetitive stress.
How is Osgood-Schlatter disease diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose it through physical exams, medical history, and sometimes X-rays or ultrasound to check for other conditions.
What are the treatment options for tibial tuberosity disorders?
Treatments include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and pain management. Surgery might be needed in some cases.
Can the tibial tuberosity be fractured or injured?
Yes, it can fracture or avulse, often in sports injuries or high-energy trauma. This causes pain, swelling, and mobility issues.
How is a tibial tuberosity fracture diagnosed?
Doctors use X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to see the extent of the injury.
What is the role of the lateral tibial tubercle?
The lateral tibial tubercle is a variation of the tibial tuberosity. It can affect knee biomechanics and surrounding structures.
How does the tibial tuberosity contribute to athletic performance?
It’s vital for jumping, running, and quick changes in direction. Its role in knee extension is key for top performance.
Can the tibial tuberosity be affected by inflammatory conditions?
Yes, conditions like bursitis can affect it. This leads to pain, swelling, and mobility issues.
References
Kenhub. Tibial tuberosity: location, anatomy and function. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/tibial-tuberosity
































