The tibial tuberosity is a key spot in the knee. It’s found on the front part of the upper tibia. It holds the patellar ligament, linking the patella to the tibia.
Knowing about the tibial tuberosity is very important. It’s key in treating knee problems like Osgood-Schlatter disease. It helps move the knee and is easy to feel during exams.
Key Takeaways
- The tibial tuberosity is a bony prominence on the anterior aspect of the proximal tibia.
- It serves as the attachment site for the patellar ligament.
- The tibial tuberosity plays a critical role in knee extension.
- It is a significant landmark in clinical examinations.
- Understanding the tibial tuberosity is essential in orthopedic and musculoskeletal medicine.
The Anatomy of the Tibial Tuberosity
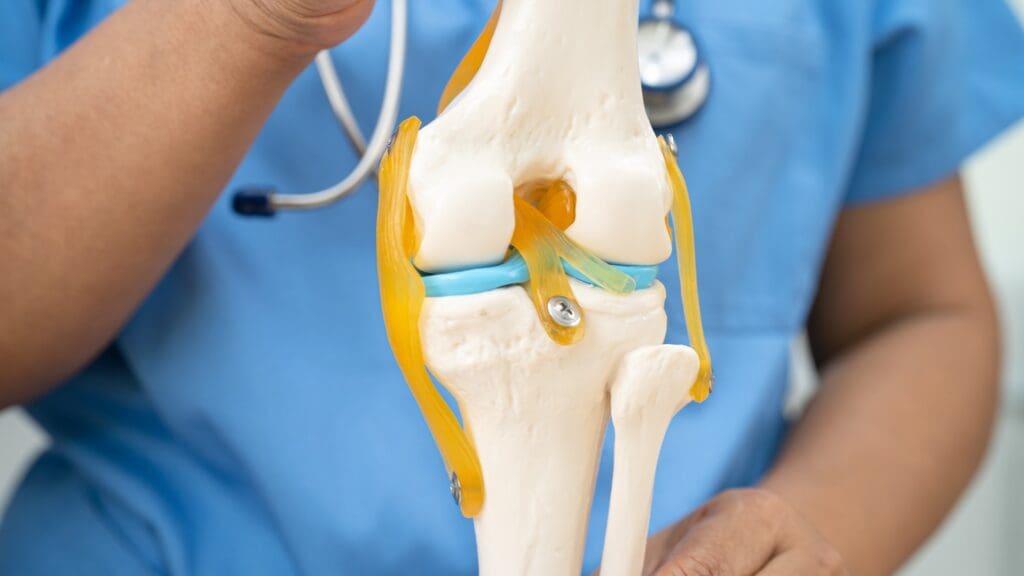
The tibial tuberosity is on the front of the tibia. It’s key for knee extension and stability. We’ll dive into its anatomy, including its definition, structure, and variations.
Definition and Basic Structure
The tibial tuberosity is a bony bump on the tibia. It’s where the patellar ligament attaches. This area is important for the quadriceps muscle to extend the knee.
The patellar ligament links the patella to the tibial tuberosity. Its strength is essential for knee movement.
Anatomical Variations
There are different shapes and sizes of the tibial tuberosity. These differences can affect its prominence. They also play a role in conditions like Osgood-Schlatter disease.
The size and shape of the tibial tuberosity vary among people. These differences can be based on how prominent and oriented the tuberosity is. Below is a table that outlines these variations:
| Variation Type | Description | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Prominence | Minimally elevated tuberosity | Less susceptible to Osgood-Schlatter disease |
| Moderate Prominence | Moderately elevated tuberosity | Moderate risk of Osgood-Schlatter disease |
| Marked Prominence | Significantly elevated tuberosity | Higher risk of Osgood-Schlatter disease |
Knowing the anatomy of the tibial tuberosity is key for diagnosis and treatment. We’ve seen how its variations can affect its function and risk of certain conditions.
Terminology and Nomenclature
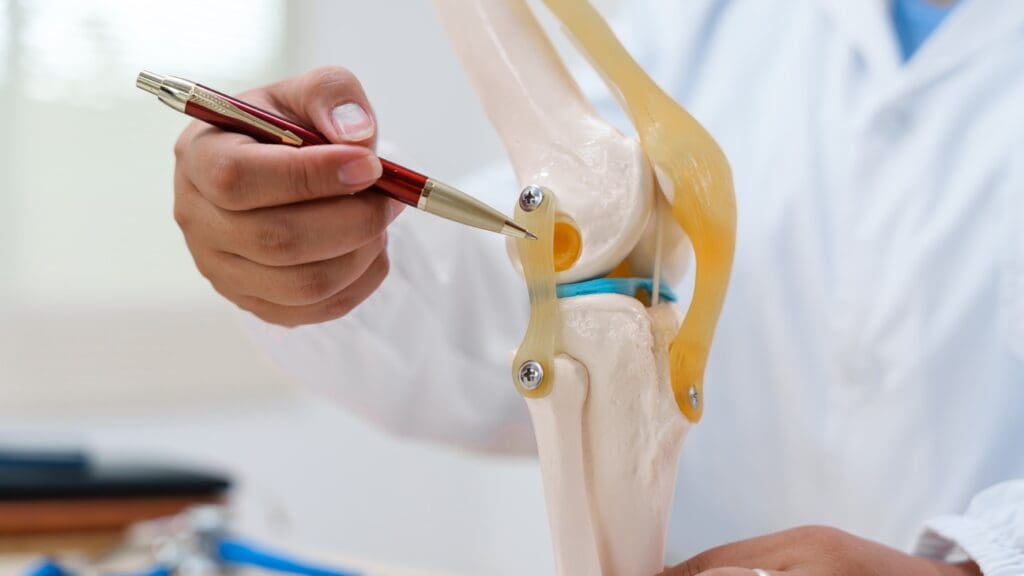
It’s important to know the different names for the tibial tuberosity in healthcare. This part of the body is key in studies and treatments. It has many names, showing its big role in health.
Various Terms for the Tibial Tuberosity
The tibial tuberosity is called many things in medical books. You might see it as “tibial tubercle,” “tuberositas tibiae,” or “anterior tibial tuberosity.” These names are used a lot, but they might mean slightly different things.
Key Terms and Their Usage:
| Term | Description | Context of Use |
|---|---|---|
| Tibial Tuberosity | A bony prominence on the tibia | General anatomical reference |
| Tibial Tubercle | Specifically refers to the attachment site of the patellar ligament | Orthopedic and clinical contexts |
| Tuberositas Tibiae | Latin term for tibial tuberosity | Anatomical and medical literature |
Historical Context of Terminology
The names for the tibial tuberosity have changed over years. This change came from studies and treatments. “Tuberositas tibiae” was once common in books, but “tibial tubercle” is now more used in medical fields.
Knowing the history of these names helps us understand the tibial tuberosity better. It’s key for doctors to talk clearly and for patients to grasp their health issues and treatments.
Precise Location of the Tibia Tuberosity
Knowing where the tibial tuberosity is located is key for both study and medical use. It’s a major landmark on the front of the upper tibia, just before the knee. It’s easy to feel when you touch the leg below the kneecap.
Topographical Landmarks
The tibial tuberosity sticks out and can be felt on the front of the leg, just below the kneecap. This topographical landmark is important for finding where the patellar ligament attaches. This ligament links the kneecap to the tibia.
To find the tibial tuberosity, follow the patellar ligament down from the kneecap. It’s at the end of this ligament, where it meets the tibia. This spot is important for both finding and treating problems.
Relation to Surrounding Structures
The tibial tuberosity is near many important structures for the knee. The patellar ligament, which connects to the tibial tuberosity, helps extend the knee. It carries force from the quadriceps muscles to the tibia.
The quadriceps muscles on the thigh front help extend the knee through the patellar ligament. The tibial tuberosity is a key point for this action. It helps with actions like standing up or climbing stairs.
It’s vital to understand how the tibial tuberosity works with these structures. This knowledge helps diagnose and treat knee issues like Osgood-Schlatter disease or tibial tuberosity fractures.
The Lateral Tibial Tubercle and Related Structures
The lateral tibial tubercle is often less talked about than the tibial tuberosity. Yet, it has its own set of characteristics and roles. It is a bony bump on the outside of the upper tibia, separate from the tibial tuberosity.
Distinguishing Features from the Tibial Tuberosity
The lateral tibial tubercle is different from the tibial tuberosity in both location and function. While the tibial tuberosity is on the front of the tibia, the lateral tibial tubercle is on the side. This difference is key to understanding their unique roles.
The lateral tibial tubercle is where muscles and ligaments attach, helping keep the knee stable. Its position allows it to help with the tibia’s rotational movements.
Functional Significance
The lateral tibial tubercle plays a big role in knee stability and movement. It’s where muscles and ligaments attach, affecting the knee’s biomechanics.
The role of the lateral tibial tubercle in knee function is often overlooked. Yet, it’s essential for the lower limb’s movement. Knowing its role can help us understand knee injuries and conditions better.
Development of the Tibial Tuberosity
The tibial tuberosity starts to form early in a baby’s development. It keeps changing as the person grows up. This process is complex and involves many stages.
Embryological Development
The tibial tuberosity grows from a part of the tibia called the tibial apophysis. This growth center is important for the upper part of the tibia. Abnormalities in this process can lead to various clinical conditions.
This early stage is key to understanding the tibial tuberosity’s anatomy and related health issues. It involves the work of many growth centers. This shapes the tibial tuberosity’s structure and function.
Growth and Ossification
Ossification of the tibial tuberosity happens in childhood and adolescence. The rate and pattern of ossification can vary among individuals. Genetics and environment play a role in this process.
As it ossifies, the tibial tuberosity becomes a key spot for the patellar ligament. It’s vital for knee extension and lower limb function. Knowing how it grows and ossifies helps in diagnosing and treating conditions like Osgood-Schlatter disease.
It’s important to watch the tibial tuberosity’s growth, mainly during fast growth periods. This helps prevent and manage any issues that might arise.
Functional Significance of the Tibial Tuberosity
Understanding the tibial tuberosity’s role is key to seeing its importance in knee movement. It is a vital spot for the patellar ligament, which helps extend the knee.
Role in Knee Extension
The tibial tuberosity is essential for knee extension. It’s where the patellar ligament attaches, connecting the patella to the tibia. This connection lets the quadriceps muscle group straighten the knee. The tibial tuberosity’s health is critical for effective knee extension.
When the quadriceps muscle contracts, it pulls the patellar ligament. This action pushes on the tibial tuberosity, helping the knee extend. This is important for actions like standing up or kicking a ball.
Biomechanical Importance
The tibial tuberosity’s role goes beyond knee extension. It also helps transmit forces from the quadriceps to the tibia, aiding in knee movement. It acts as a lever, boosting the mechanical advantage of the quadriceps.
The tibial tuberosity’s design and location make it strong against stress and strain. Its biomechanical importance is clear in maintaining knee stability and enabling various movements.
In summary, the tibial tuberosity is a vital part of the knee. It’s key for knee extension and has a big role in knee biomechanics. Its function as a ligament attachment point highlights its importance in both anatomy and medicine.
Muscular and Ligamentous Attachments
It’s important to know how muscles and ligaments attach to the tibial tuberosity. This area is key for the patellar ligament, which is part of the quadriceps mechanism.
The Patellar Ligament Connection
The patellar ligament links the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It’s vital for knee extension. This ligament helps move forces from the quadriceps to the tibia.
The patellar ligament is a big part of the quadriceps mechanism. This mechanism includes the quadriceps, patella, and patellar ligament. Together, they help extend the knee.
Quadriceps Mechanism
The quadriceps mechanism is key for knee function. The patellar ligament connects the quadriceps to the tibial tuberosity. When the quadriceps contract, they pull the patella, which then pulls the patellar ligament, extending the knee.
The main parts of the quadriceps mechanism are:
- The quadriceps femoris muscle group
- The patella
- The patellar ligament
- The tibial tuberosity
Knowing about these parts and how they work is key to understanding the tibial tuberosity’s role. The tibial tuberosity’s job as the patellar ligament’s attachment point shows its importance in knee mechanics.
The tibial tuberosity’s role in the quadriceps mechanism is vital for knee extension and lower limb function.
Clinical Conditions Affecting the Tibial Tuberosity
Many conditions can harm the tibial tuberosity, causing knee pain and problems. Knowing about these issues is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease mainly hits teens, when they grow fast. It makes the tibial tuberosity swell and hurt, right below the knee. This happens because of too much stress on the patellar ligament. Symptoms include tenderness and swelling over the tibial tuberosity, pain during activities like jumping and running, and sometimes limping. Doctors usually suggest rest, ice, and stretching to help.
Fractures and Avulsions
Fractures and avulsions of the tibial tuberosity can happen, mostly in young people. These injuries come from sudden muscle contraction or direct hits to the area. Avulsion fractures, where the tibial tuberosity is pulled away from the tibia, are more common in younger individuals. Treatment might include a cast for minor fractures or surgery for bigger ones.
Inflammatory and Degenerative Conditions
Inflammatory and degenerative issues can also trouble the tibial tuberosity. For example, inflammation of the patellar ligament or bursitis can cause pain and swelling. Also, wear and tear from age or overuse can lead to long-term pain and trouble. Finding the root cause is vital for the right treatment, which might include physical therapy, meds, or other steps.
Conclusion
The tibial tuberosity is key to knee extension and linked to many health issues. We’ve looked closely at it, from what it is and where it is to its role in knee function and health problems.
Knowing about the tibial tuberosity is vital for doctors and patients. At Liv Hospital, we aim to offer top-notch care for issues related to this area.
In short, the tibial tuberosity is a vital part of our body that needs a deep understanding. We hope this article has given you a clear view of its importance in medicine.
FAQ
Where is the tibial tuberosity located?
The tibial tuberosity is found on the front part of the upper tibia, just below the knee.
What is the function of the tibial tuberosity?
It acts as a point for the patellar ligament to attach. This is key for straightening the knee.
What is the difference between the tibial tuberosity and the lateral tibial tubercle?
The tibial tuberosity is on the front of the upper tibia. The lateral tibial tubercle is on the side. They both have important roles.
What is Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is an inflammation of the tibial tuberosity. It’s caused by stress and strain, common in teens.
What are the clinical implications of anatomical variations in the tibial tuberosity?
Variations in the tibial tuberosity can make some people more prone to Osgood-Schlatter disease. This is important in medical settings.
How does the tibial tuberosity develop?
It develops from the tibial apophysis during early development. Its bone formation happens in childhood and adolescence.
What is the role of the patellar ligament in knee extension?
The patellar ligament helps the quadriceps muscle group extend the knee. This is how we straighten our knee.
What conditions can affect the tibial tuberosity beside Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Other than Osgood-Schlatter disease, the tibial tuberosity can suffer from fractures, avulsions, and other conditions. These can cause pain and make it hard to move.
Why is understanding the terminology related to the tibial tuberosity important?
Knowing the terms like “tibial tubercle” and “tuberositas tibiae” helps doctors and patients talk clearly. It’s key for good communication in healthcare.
Where is the tibial tuberosity located?
The tibial tuberosity is found on the front part of the upper tibia, just below the knee.
What is the function of the tibial tuberosity?
It acts as a point for the patellar ligament to attach. This is key for straightening the knee.
What is the difference between the tibial tuberosity and the lateral tibial tubercle?
The tibial tuberosity is on the front of the upper tibia. The lateral tibial tubercle is on the side. They both have important roles.
What is Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Osgood-Schlatter disease is an inflammation of the tibial tuberosity. It’s caused by stress and strain, common in teens.
What are the clinical implications of anatomical variations in the tibial tuberosity?
Variations in the tibial tuberosity can make some people more prone to Osgood-Schlatter disease. This is important in medical settings.
How does the tibial tuberosity develop?
It develops from the tibial apophysis during early development. Its bone formation happens in childhood and adolescence.
What is the role of the patellar ligament in knee extension?
The patellar ligament helps the quadriceps muscle group extend the knee. This is how we straighten our knee.
What conditions can affect the tibial tuberosity beside Osgood-Schlatter disease?
Other than Osgood-Schlatter disease, the tibial tuberosity can suffer from fractures, avulsions, and other conditions. These can cause pain and make it hard to move.
Why is understanding the terminology related to the tibial tuberosity important?
Knowing the terms like “tibial tubercle” and “tuberositas tibiae” helps doctors and patients talk clearly. It’s key for good communication in healthcare.
References
Kenhub. Tibial tuberosity: location, anatomy and function. https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/tibial-tuberosity



































