Thalassemia is a blood disorder that affects how red blood cells carry oxygen. It’s passed down from parents to their kids through genes. Early detection is key to managing its health issues. Discover 12 key signs of thalassemia and symptoms you shouldn’t ignore for early diagnosis.
At LivHospital, we know how vital it is to spot thalassemia symptoms. Our focus is on you, ensuring top-notch care for all thalassemia types. This article will cover the 12 key signs you shouldn’t ignore, helping you know when to see a doctor.
Key Takeaways
- Thalassemia is an inherited condition affecting hemoglobin production.
- Early detection is critical for managing thalassemia-related health concerns.
- LivHospital offers advanced care for thalassemia patients.
- Recognizing the symptoms is key for timely medical help.
- There are 12 key signs of thalassemia you should know.
Understanding Thalassemia: A Brief Overview

Thalassemia is a genetic disorder that affects how the body makes hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is key for carrying oxygen in red blood cells. Without enough hemoglobin, people with thalassemia face anemia and other health issues.
What Causes Thalassemia?
Thalassemia comes from genetic changes passed down from parents. These changes affect how red blood cells make hemoglobin. It’s more common in areas where malaria used to be a big problem, as it helps those with thalassemia survive.
Thalassemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. This means a child needs two mutated genes to have the condition. Carriers, with one normal and one mutated gene, usually don’t show severe symptoms but can pass the mutated gene to their kids.
Types of Thalassemia and Their Severity
Thalassemia comes in two main types: Alpha and Beta. The type and how severe it is depend on which hemoglobin chain is affected and how many genes are mutated.
- Alpha Thalassemia: This happens when there’s a problem with one or more of the four genes for alpha-globin. The severity depends on how many genes are affected.
- Beta Thalassemia: It’s caused by mutations in the two genes for beta-globin. Beta thalassemia major, or Cooley’s anemia, is the most serious form and requires constant blood transfusions.
The severity of thalassemia can range from mild to severe. Knowing the type and severity helps in managing the condition better.
How Thalassemia Affects Your Blood and Body
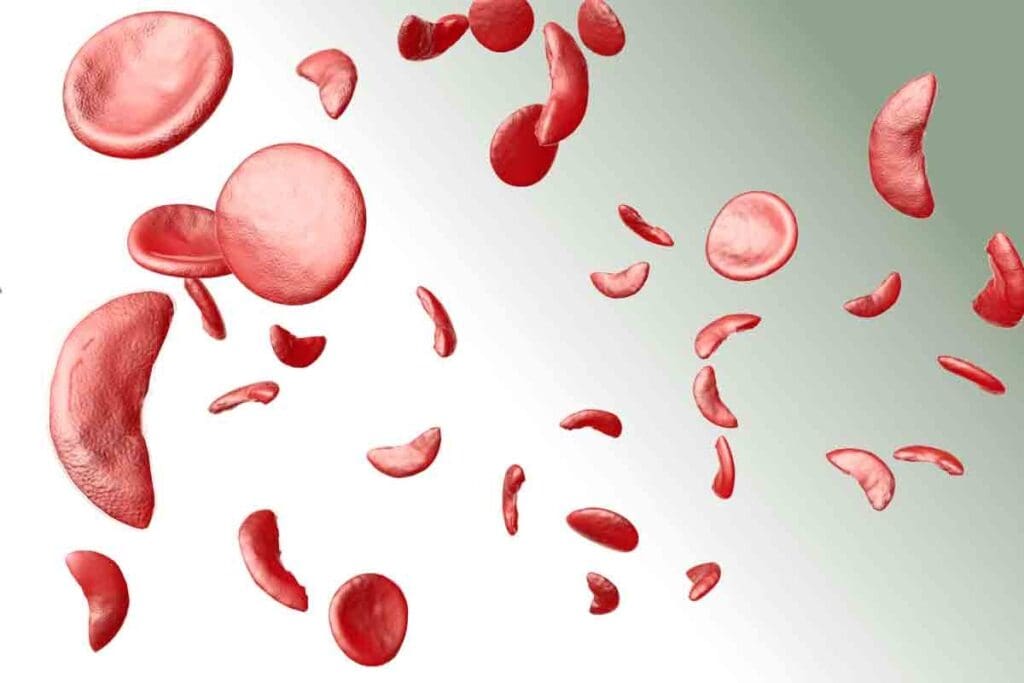
Thalassemia is a genetic disorder that affects how your body makes hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is key for red blood cells to carry oxygen. This oxygen is vital for your body’s tissues and organs to work right.
With thalassemia, your body can’t make enough normal hemoglobin. This causes anemia and health problems because red blood cells can’t carry oxygen well.
The Role of Hemoglobin in Thalassemia
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. In thalassemia, genetic mutations mess up hemoglobin production. This means less or no hemoglobin, leading to anemia and other issues.
The severity of thalassemia depends on how much hemoglobin is made. Severe cases can cause serious health problems like deep anemia, fatigue, and more.
Impact on Red Blood Cells and Oxygen Transport
Thalassemia affects red blood cells in two ways. It messes up how red blood cells are made and makes them last shorter. This also adds to anemia.
Because of thalassemia, your body can’t transport oxygen well. This can cause symptoms like tiredness, weakness, and shortness of breath. Your body’s tissues and organs might not get enough oxygen, leading to problems like poor growth in kids and organ damage.
| Aspect | Normal Condition | Thalassemia Condition |
| Hemoglobin Production | Normal production of hemoglobin | Reduced or absent production of hemoglobin |
| Red Blood Cell Function | Effective oxygen transport | Ineffective oxygen transport due to abnormal hemoglobin |
| Health Implications | No significant anemia or related issues | Anemia, fatigue, weakness, and potentially organ damage |
The 12 Key Signs of Thalassemia to Watch For
Thalassemia symptoms can vary from mild to severe. It’s important to recognize these signs early for proper treatment. Here are the 12 key signs to look out for.
Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
One common symptom is persistent fatigue and weakness. This happens because of low hemoglobin levels. Hemoglobin carries oxygen to the body’s tissues and organs.
Without enough hemoglobin, the body doesn’t get enough oxygen. This leads to tiredness and weakness.
Pale or Yellowish Skin (Jaundice)
People with thalassemia may have pale or yellowish skin. This is called jaundice. It’s caused by the breakdown of red blood cells.
This breakdown leads to a buildup of bilirubin. The skin and eyes may turn yellow.
Shortness of Breath and Dizziness
Shortness of breath and dizziness are also symptoms. These happen because the body lacks healthy red blood cells. This means it doesn’t get enough oxygen.
People may feel out of breath easily. They might also feel dizzy because their brain isn’t getting enough oxygen.
Dark Urine
Dark urine is another sign of thalassemia. It happens when red blood cells break down. This causes urine to look darker than usual.
This is because more bilirubin is being passed through the urine.
To understand thalassemia symptoms better, let’s look at a summary of the 12 key signs in the following table:
| Symptom | Description |
| 1. Persistent Fatigue | Feeling tired and weak due to low hemoglobin levels. |
| 2. Pale or Yellowish Skin | Jaundice caused by the breakdown of red blood cells. |
| 3. Shortness of Breath | Difficulty breathing due to insufficient oxygen supply. |
| 4. Dark Urine | Urine appears darker due to increased bilirubin levels. |
| 5. Enlarged Spleen | The spleen becomes enlarged due to excessive red blood cell destruction. |
| 6. Bone Deformities | Bone changes occur due to bone marrow expansion. |
| 7. Growth and Development Delays | Children may experience delayed growth and development. |
| 8. Poor Appetite | Reduced appetite can be a symptom, particular in children. |
| 9. Dizziness | Feeling dizzy due to inadequate oxygen supply to the brain. |
| 10. Cold Hands and Feet | Poor circulation can cause hands and feet to feel cold. |
| 11. Headaches | Frequent headaches can occur due to anemia. |
| 12. Fast Heartbeat | The heart beats faster to compensate for low oxygen levels. |
Knowing these symptoms can help identify thalassemia early. If you or someone you know shows several of these signs, see a doctor. They can diagnose and treat the condition properly.
Recognizing Mild Thalassemia Symptoms
It’s important to spot mild thalassemia symptoms early. This condition, also known as thalassemia minor, has signs that are easy to miss. We’ll look at these signs and how to tell them apart from other illnesses.
Subtle Signs That Are Often Overlooked
Mild thalassemia symptoms can be very subtle. Some people might feel mild fatigue or slight pallor. These could be seen as just stress or a minor illness. But, they might actually point to a problem with making red blood cells.
In alpha-thalassemia, having one missing gene copy usually means no symptoms. But, these people can pass the disease to their kids. Knowing about genes is key for planning families.
When Mild Symptoms Mimic Other Conditions
The signs of mild thalassemia can look like other health issues. For example, mild anemia, fatigue, or weakness might seem like iron or vitamin deficiencies. Doctors need to think about thalassemia, too, when they see these symptoms, mainly in areas where thalassemia is common.
Knowing the thalassemia signs and symptoms is critical. A full diagnosis includes blood tests and genetic checks to find out if someone has thalassemia.
Understanding mild thalassemia symptoms is key for both patients and doctors. Spotting these signs early can lead to better care and a better life for those with thalassemia minor.
Severe Thalassemia: Critical Symptoms That Require Attention
Severe thalassemia brings serious symptoms that can really hurt someone’s life quality. These symptoms are not just annoying; they can be deadly if not treated right.
Bone Deformities and Facial Changes
Bone deformities, mainly in the face and skull, are big problems with severe thalassemia. Bone marrow expansion from making more red blood cells can cause distinctive facial changes and other bone issues. These changes can really change how someone looks and affects their health a lot.
Enlarged Spleen and Abdominal Issues
Severe thalassemia also makes the spleen get bigger, known as splenomegaly. This happens because the spleen works harder to clean out bad red blood cells. A big spleen can cause belly pain, discomfort, and other problems like infections and anemia.
Growth and Development Delays
Children with severe thalassemia often grow and develop slower. The disease can mess with growth hormones and body development, causing late puberty and other growth issues. It’s key to get regular medical check-ups to help manage these problems and support normal growth.
Living with severe thalassemia is tough for patients and their families. It’s vital to work with doctors to handle symptoms and avoid serious problems.
Thalassemia Symptoms in Children
It’s important to spot thalassemia symptoms in kids early. This genetic disorder affects how the body makes hemoglobin. We’ll look at the signs to watch for and how it can affect a child’s growth.
Early Warning Signs in Infants (0-2 years)
In babies, thalassemia symptoms can show up in the first two years. Some babies might show signs right at birth. Others might develop them later. Look out for these early signs:
- Pale or yellowish skin due to anemia
- Poor feeding and failure to gain weight at a normal rate
- Enlarged spleen or liver
- Dark urine
These signs mean the baby might not be making enough healthy red blood cells. This is a key sign of thalassemia.
Poor Feeding and Slowed Development
Kids with thalassemia might not eat well because of anemia. This can slow down their growth and development. It’s important for parents to watch their child’s eating and growth closely. If they notice anything off, they should talk to a doctor.
Some signs of slow development include:
- Failure to gain weight or height at a normal rate
- Delayed milestones, such as sitting, standing, or walking
- Fatigue and weakness
Delayed Puberty and Growth Issues
As kids with thalassemia get older, they might hit puberty later. Thalassemia can mess with growth hormones, causing delays. It’s key to have a doctor check on this regularly.
| Age Group | Common Symptoms | Potential Complications |
| 0-2 years | Pale skin, poor feeding, enlarged spleen | Anemia, failure to thrive |
| 2-12 years | Fatigue, slowed growth, delayed development | Growth hormone deficiencies, delayed puberty |
| Teenage years | Delayed puberty, anemia, fatigue | Osteoporosis, heart complications |
Knowing these symptoms and possible problems helps parents get the right care for their kids. This ensures they get the support they need for good health and growth.
How Thalassemia Manifests in Adults
Adults with thalassemia face unique symptoms that affect their daily life. We need to know about the complications like late symptoms, metabolic problems, and bone issues.
Late-Onset Symptoms
Some adults with thalassemia show symptoms later in life. These can include:
- Dark urine from red blood cell breakdown
- Fatigue and weakness from anemia
- Shortness of breath and dizziness from poor oxygen delivery
These symptoms start off mild but can get worse. It’s key to get regular check-ups and care.
Metabolic Complications
Thalassemia can cause metabolic issues in adults, such as:
- Iron overload from blood transfusions, harming the heart, liver, and glands
- Diabetes and other gland problems from iron in the pancreas and glands
Dealing with these issues needs a detailed plan. This includes blood tests, scans, and chelation therapy to lower iron.
Osteoporosis and Bone Problems
Osteoporosis and bone issues are common in adults with thalassemia. These problems come from:
- Bone marrow expansion for anemia, causing bone deformities
- Hormonal deficiencies, like hypogonadism, affecting bone density
To tackle bone problems, adults with thalassemia might need bone scans, hormone therapy, and other treatments. These help keep bones strong.
In summary, thalassemia in adults brings a variety of symptoms and complications. Understanding these helps people with thalassemia and their doctors create better treatment plans. This way, they can live a better life.
Thalassemia Anemia Symptoms: Understanding the Connection
It’s important to know how thalassemia and anemia are linked. Thalassemia is a genetic disorder that affects how the body makes hemoglobin. This often leads to anemia, which is when there aren’t enough red blood cells or hemoglobin.
Chronic Tiredness and Pallor
Chronic tiredness is a main symptom of thalassemia anemia. This happens because the body can’t carry enough oxygen to its tissues and organs. This tiredness can really affect your daily life and how well you feel.
People with thalassemia anemia also might look pale. This is because they have fewer red blood cells.
Chronic tiredness and weakness are more than just symptoms. They can really limit how well you can do everyday things. It’s important to think about these when we’re diagnosing and treating thalassemia anemia.
Differentiating from Other Types of Anemia
It’s important to tell thalassemia anemia apart from other types of anemia. Unlike iron-deficiency anemia, which can be treated with iron, thalassemia anemia needs a different treatment. This focuses on managing the genetic condition itself.
To tell thalassemia anemia apart, doctors look at the patient’s genetic history and how severe the anemia is. They also check for other symptoms of thalassemia. Tests like genetic testing and blood analyses help make a correct diagnosis.
Accurate diagnosis is key to good treatment. By understanding what makes thalassemia anemia different, doctors can create better treatment plans.
It’s important to spot thalassemia anemia symptoms early. Knowing the link between thalassemia and anemia helps people get help if they’re feeling very tired or weak for a long time.
Clinical Manifestations: Alpha vs. Beta Thalassemia
It’s important to know the signs of alpha and beta thalassemia for the right treatment. Thalassemia is a genetic disorder that affects how the body makes hemoglobin. It’s mainly split into alpha and beta thalassemia, based on the globin chain involved.
Alpha thalassemia happens when there’s a problem with the genes for alpha-globin chains. Beta thalassemia is caused by mutations in the genes for beta-globin chains. These differences lead to different symptoms.
Unique Symptoms of Alpha Thalassemia
Alpha thalassemia can be mild or severe, depending on the genes affected. If one or two genes are affected, people might not show symptoms or have mild anemia. But, if three or four genes are affected, it can cause severe anemia, known as Hemoglobin H disease or Hydrops Fetalis.
Symptoms of alpha thalassemia include feeling tired, looking pale, and having trouble breathing. In severe cases, like Hemoglobin H disease, patients may have serious anemia, jaundice, and a big spleen.
Distinctive Signs of Beta Thalassemia
Beta thalassemia’s severity also varies. The major form, Cooley’s anemia, is the most severe. Symptoms include severe anemia, pale or yellowish skin, big spleen and liver, and bone problems. People with beta thalassemia intermedia have milder symptoms, while those with beta thalassemia minor might not show symptoms or have mild anemia.
Beta thalassemia major often starts in the first two years of life. Children may not grow well, get sick often, and have severe anemia that needs regular blood transfusions.
Thalassemia Major vs. Thalassemia Minor Presentations
Knowing the difference between thalassemia major and minor is key for treatment. Thalassemia major, whether alpha or beta, has severe anemia and symptoms. It needs regular transfusions and might need other treatments like iron chelation therapy.
Thalassemia minor is milder, with some people having mild anemia. It’s often found during routine blood tests.
Healthcare providers need to understand these differences to give the right treatment. This is true for both alpha and beta thalassemia, and whether it’s major or minor.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Suspected Thalassemia
Knowing when to see a doctor for thalassemia is key. Early signs and symptoms can lead to quick diagnosis and treatment. This can greatly improve life for those with the condition.
Red Flags That Require Immediate Care
Some symptoms need immediate doctor visits. Look out for severe fatigue, pale or yellowish skin, shortness of breath, or dark urine. If you have a family history of thalassemia and show symptoms, get medical help right away.
Specific red flags include:
- Severe anemia symptoms
- Significant enlargement of the spleen
- Bone deformities or facial changes
- Delayed growth or development in children
Preparing for Your Doctor’s Appointment
Getting ready for your doctor’s visit is smart. Write down your symptoms, when they started, and how they’ve changed. Mention any family history of thalassemia or other health issues. Bringing past medical records or test results is also a good idea.
To prepare effectively:
- Gather your medical history
- List your symptoms and their duration
- Write down any questions you have for your doctor
- Bring a family member or friend for support
Diagnostic Tests and What to Expect
Tests for thalassemia usually include blood tests for anemia and abnormal hemoglobin. A complete blood count (CBC) can spot anemia. Hemoglobin electrophoresis can pinpoint the thalassemia type. Genetic testing might also be suggested to find the cause.
Your doctor will do a physical check-up and ask about your health history. They might then order tests based on what they find. Knowing about these tests can help you understand your diagnosis and treatment better.
Conclusion: Living with Thalassemia and Managing Symptoms
Knowing the signs and symptoms of thalassemia is key for early diagnosis and treatment. The right treatment lets people live full, active lives. A care plan that includes blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and folic acid is essential.
In some cases, a bone marrow or stem cell transplant might be needed. This shows that managing thalassemia symptoms is a team effort.
Living with thalassemia means being proactive about your health. Spotting signs like fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath early is important. This helps manage symptoms and prevents complications.
We stress the need for a team approach in managing thalassemia symptoms. Working with healthcare providers helps create a treatment plan that fits your needs. This teamwork is vital for a fulfilling life with thalassemia.
FAQ
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2022). Guidelines for the management of α-thalassaemia.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK602223/
What are the common symptoms of thalassemia?
Symptoms of thalassemia include feeling very tired and skin that looks pale or yellowish. You might also have shortness of breath and dark urine. In severe cases, it can cause bone deformities, an enlarged spleen, and slow growth.
How do I know if I have thalassemia?
Doctors use blood tests to find thalassemia. These tests check hemoglobin levels and look for genetic mutations. If you’re always tired or your skin looks pale, see a doctor for a diagnosis.
What is the difference between alpha and beta thalassemia?
Alpha thalassemia happens when there’s a problem with the genes for alpha-globin. Beta thalassemia is caused by issues with the genes for beta-globin. The symptoms and how severe it is can differ between the two.
Can thalassemia be mild?
Yes, some types of thalassemia, like thalassemia minor, can be mild. They might not need constant medical care. But, it’s important to keep an eye on it to avoid problems.
How does thalassemia affect children?
Babies with thalassemia might not eat well or grow as they should. Kids can face delayed puberty and growth issues if it’s not treated right.
What are the symptoms of thalassemia in adults?
Adults might see symptoms later, like metabolic problems and bone issues. It’s key to see a doctor regularly to manage these issues.
How is thalassemia-related anemia different from other types of anemia?
Thalassemia anemia comes from a genetic problem with hemoglobin. Other anemias might be from iron or vitamin lack. Knowing the cause is important for treatment.
When should I seek medical attention for suspected thalassemia?
If you’re tired all the time, your skin is pale, or you have trouble breathing, see a doctor. Also, if you have a family history of thalassemia, get checked out.
What diagnostic tests are used to confirm thalassemia?
Tests for thalassemia include blood work like a complete blood count (CBC) and hemoglobin electrophoresis. Genetic tests also look for mutations in hemoglobin genes.
Can thalassemia be managed with treatment?
Yes, thalassemia can be managed with treatment. This includes blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and other care. Working with a healthcare team is key to a good treatment plan.