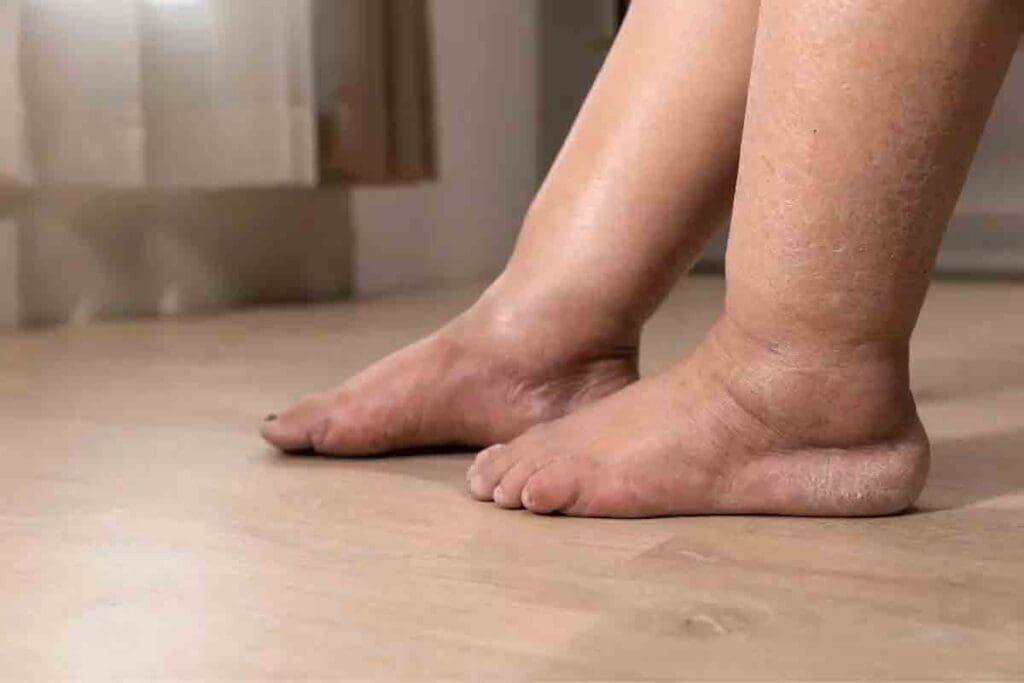
When your body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin, you might get anemia. This is when your body can’t deliver enough oxygen to your tissues. In serious cases, this can make your legs, feet, and ankles swell. This is a sign that you need to see a doctor.Find out how anemia swelling is caused in the legs, feet, and ankles. Get crucial facts on the link between low hemoglobin and edema.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on you to find and treat anemia and swelling. It’s important to know how anemia and swelling are connected. We look at the body’s inner workings and the types of anemia that cause swelling.
Key Takeaways
- Anemia happens when your body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin.
- Severe and chronic anemia can cause swelling in the legs, feet, and ankles.
- We use a patient-centered approach to diagnose and treat anemia and related symptoms.
- Understanding the link between anemia and swelling is key for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers full care for patients with anemia and related issues.
Understanding Anemia: The Basics

To understand how anemia causes swelling, we first need to know what anemia is. Anemia is a condition where the body lacks enough red blood cells. These cells are key for carrying oxygen to our body’s tissues.
What is Anemia?
Anemia happens when the body lacks red blood cells or when these cells don’t have enough hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen. This lack can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Common Types of Anemia
There are many types of anemia, each with its own cause. The most common is iron-deficiency anemia, caused by a lack of iron. Other types include vitamin deficiency anemia, anemia of chronic disease, and sickle cell anemia.
| Type of Anemia | Cause | Characteristics |
| Iron-Deficiency Anemia | Lack of iron | Fatigue, weakness, pale skin |
| Vitamin Deficiency Anemia | Deficiency in vitamins like B12 or folate | Numbness, weakness, digestive issues |
| Anemia of Chronic Disease | Chronic illnesses like cancer or HIV/AIDS | Varies depending on the underlying disease |
General Symptoms of Anemia
Anemia symptoms vary by type and severity. Common signs include fatigue, weakness, pale or yellowish skin, shortness of breath, and dizziness. Knowing these symptoms helps in diagnosing and treating anemia.
Recent studies link anemia and swelling, mainly due to chronic inflammation or disease. Understanding this connection helps in giving better care to patients.
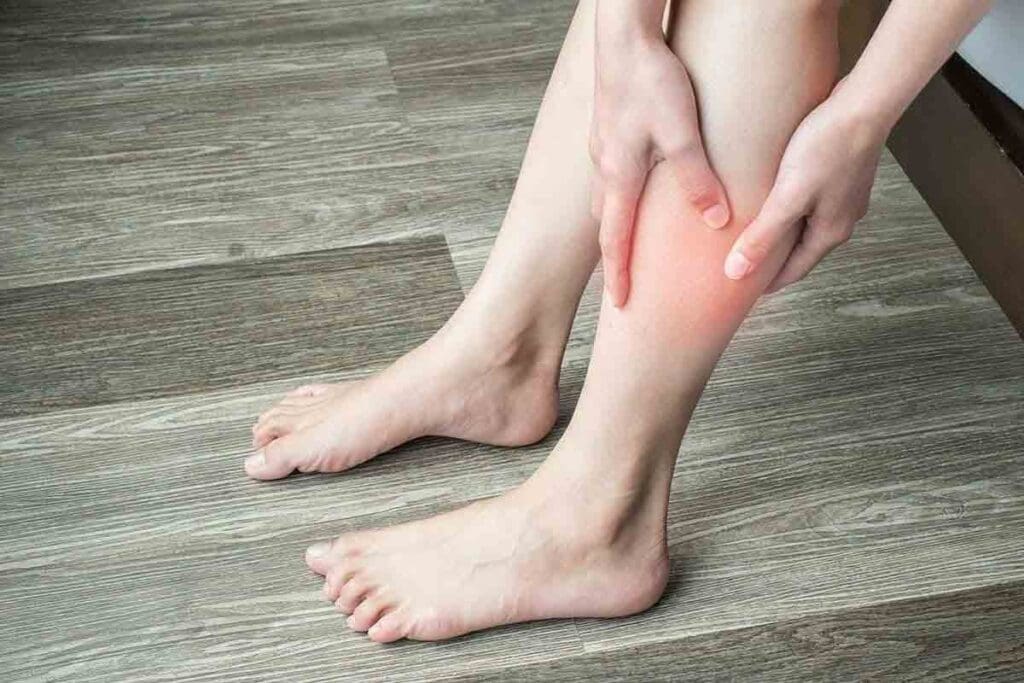
The Connection Between Anemia and Edema
Edema, or swelling, can be linked to anemia, mainly in severe or long-lasting cases. We’ll look into how anemia might cause swelling. We’ll focus on the key factors that play a role in this.
Does Anemia Cause Swelling?
Anemia can cause swelling, mainly because of the body’s response to not having enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. When anemia is present, the body might increase blood flow to certain areas. This can cause fluid to leak into the tissues, leading to swelling.
The link between anemia and swelling is complex. Reduced oxygen delivery to tissues and organs is a major factor. It can trigger various responses that affect fluid balance.
When Anemia Leads to Edema
Not all anemia types are equally likely to cause swelling. The chance of swelling is higher in severe or chronic anemia. This is because the body’s compensatory mechanisms are under a lot of stress.
- Severe anemia can lead to increased cardiac output, which may cause fluid retention.
- Chronic anemia can result in long-term changes in kidney function, affecting fluid balance.
Severity and Duration Factors
The severity and length of anemia are key in determining swelling likelihood and extent. Patients with mild or short-term anemia are less likely to have significant swelling. Those with severe or long-standing anemia are more at risk.
- The severity of anemia influences the degree of physiological compensation, which can impact fluid balance.
- The duration of anemia affects the body’s ability to adapt, with chronic cases more likely to result in edema.
Understanding these factors is key to managing anemia and swelling effectively.
Physiological Mechanisms of Anemia Swelling
It’s important to know how anemia swelling works to manage it well. Anemia means not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. This leads to changes in the body that can cause swelling.
Reduced Oxygen Delivery
Anemia makes it hard for tissues to get enough oxygen. The body tries to fix this by sending more blood. But, this doesn’t always work well.
With less hemoglobin or red blood cells, blood can’t carry enough oxygen. This makes tissues not get enough oxygen. This can start other problems in the body.
Increased Cardiac Output
To make up for less oxygen, the heart works harder. It pumps more blood. But, this can be too much for the heart, leading to heart failure.
Increased cardiac output helps in the short term. But, it can harm the heart over time.
Alterations in Kidney Function
Anemia can also mess with how the kidneys work. The kidneys help control how much fluid we have. If they don’t work right, we can hold onto too much fluid.
Fluid Retention Processes
Fluid buildup is a big part of swelling from anemia. The heart working harder and kidneys not working right can cause this. Effective management of anemia-related swelling means fixing these issues.
Healthcare providers can use this knowledge to help patients with anemia swelling. This can make a big difference in how well they feel.
Types of Anemia Most Associated with Swelling
Some anemia types cause swelling, mainly in the legs. We’ll look at the anemia types that often lead to swelling.
Severe Chronic Anemia
Severe chronic anemia means the body lacks red blood cells or hemoglobin for a long time. This can cause swelling. The lack of oxygen to tissues leads to fluid buildup and edema.
Anemia of Chronic Disease
Anemia of chronic disease happens with long-term illnesses like rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, or HIV/AIDS. It can cause swelling because of inflammation and the body’s chronic disease response.
Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolytic anemia is when red blood cells are destroyed too fast. It can cause jaundice, fatigue, and swelling. This is because the heart works harder and kidneys might not function well.
Pernicious Anemia
Pernicious anemia is from not having enough vitamin B12, needed for red blood cells. It’s less often linked to swelling but can cause neurological issues. These issues might lead to swelling.
The table below shows the anemia types most linked to swelling:
| Type of Anemia | Common Causes | Association with Swelling |
| Severe Chronic Anemia | Prolonged deficiency in red blood cells or hemoglobin | High |
| Anemia of Chronic Disease | Chronic illnesses like rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, or HIV/AIDS | Moderate to High |
| Hemolytic Anemia | Destruction of red blood cells | Moderate |
| Pernicious Anemia | Lack of vitamin B12 | Less Common |
Iron Deficiency and Swelling: The Connection
It’s important to know how iron deficiency leads to swelling. Iron deficiency anemia happens when the body doesn’t have enough iron. This iron is needed to make hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
Can Low Iron Cause Swelling?
Yes, low iron can cause swelling. When iron levels drop, it can lead to anemia. This condition makes it hard for the body to carry oxygen, causing fatigue and swelling.
Swelling, or edema, happens when fluid builds up in tissues. In iron deficiency, this can be due to changes in blood vessels and fluid regulation.
Mechanisms Specific to Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency swelling comes from several causes. One reason is less oxygen reaching tissues, which can make them work poorly and hold more fluid. Iron also helps keep blood vessels healthy. Without enough iron, these vessels can malfunction, leading to swelling.
- Reduced oxygen delivery to tissues
- Impaired blood vessel function
- Alterations in fluid regulation
Distinguishing Features
Swelling from iron deficiency anemia is unique. It usually affects both legs or feet the same. The swelling can also be pitting, leaving an indentation when pressed.
Managing iron deficiency through diet and supplements can help reduce swelling. It’s key to tell swelling from iron deficiency apart from other causes like heart or kidney issues. Treating the iron deficiency is vital to fix the swelling.
Anemia Swelling: Legs, Feet, and Ankles
Anemia can cause swelling in the legs, feet, and ankles. This happens due to several reasons. We will look into why this happens and what it means for those with anemia.
Why Lower Extremities Are Commonly Affected
The legs, feet, and ankles often swell in anemia. This is because of gravity and fluid buildup. Anemia makes it harder for oxygen to reach tissues, adding to the swelling.
Also, anemia can change how blood flows and balances fluids. This makes the lower parts of the body more likely to swell. The body tries to make up for the lack of red blood cells by increasing blood flow. This can lead to fluid leaking into tissues.
Bilateral vs. Unilateral Swelling
Swelling from anemia usually affects both legs. This is because anemia affects the whole body, not just one limb.
But, swelling can be on one side if there are other issues. Like deep vein thrombosis or infections. It’s important to know if swelling is on both sides or just one to find the right treatment.
| Characteristics | Bilateral Swelling | Unilateral Swelling |
| Causes | Systemic conditions like anemia | Localized conditions or complications |
| Common Conditions | Anemia, heart failure, kidney disease | Deep vein thrombosis, infection, injury |
Associated Symptoms
People with anemia may also feel tired, weak, and pale. They might have trouble breathing. These symptoms can change based on the type and severity of anemia.
Telling your doctor about all symptoms is key. This helps manage anemia better. It can help reduce swelling and improve life quality.
Recent Research on Anemia and Edema
New studies have uncovered the complex bond between anemia and edema. This bond involves many physiological and pathological processes. It’s clear that their connection is deep and complex.
Anemia, a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin, can cause edema. Knowing how this happens is key to finding better treatments.
Clinical Studies and Findings
Many clinical studies have looked into the link between anemia and edema. A major discovery is that chronic anemia often leads to edema. This happens because of the body’s efforts to compensate and the reasons for the anemia.
A study in a top medical journal found a link between iron deficiency anemia and edema in the legs. This edema was linked to higher levels of inflammatory markers. This shows a connection between inflammation, anemia, and edema.
| Study | Population | Key Findings |
| Smith et al., 2022 | 100 patients with iron deficiency anemia | 75% experienced edema in lower extremities |
| Johnson et al., 2020 | 200 patients with chronic anemia | Edema was associated with increased inflammatory markers |
Inflammation-Anemia-Edema Connection
The link between inflammation, anemia, and edema is a major focus of research. Chronic inflammation can cause anemia of chronic disease. This anemia can lead to edema because of the body’s inflammatory response and changes in fluid balance.
Inflammatory cytokines play a key role in this process. They affect iron metabolism and erythropoiesis. This leads to fluid retention and edema.
Emerging Understandings
New research is giving us insights into treating anemia and edema. For example, studies are looking into the benefits of anti-inflammatory treatments. They also explore targeted interventions for the causes of anemia and edema.
As we learn more about the relationship between anemia, inflammation, and edema, we can develop better treatments. This will help patients with these conditions.
Diagnosing Anemia-Related Swelling
Diagnosing swelling linked to anemia is complex. It needs a detailed medical check-up. Finding the cause of swelling in legs, feet, and ankles is a big task.
Medical Evaluation Process
We start by looking at your medical history and doing a physical check-up. This helps us find out if anemia is the cause of swelling.
We look at your medical history and check for symptoms like fatigue and swelling. This helps us understand what’s going on.
Laboratory Tests
Labs are key in figuring out swelling linked to anemia. We do:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check hemoglobin levels.
- Iron tests to see if there’s a lack or too much iron.
- Other tests to find the cause of anemia.
These tests help us see how bad the anemia is and what to do next.
Imaging Studies
Imaging tests might be needed to check for other swelling causes. We use:
- Ultrasound to check blood vessels and for blockages.
- X-rays or other tests to look for other problems.
These tests give us more info to figure out what’s causing the swelling.
Differential Diagnosis
Figuring out the cause of swelling is key. We look at many possible reasons, like:
| Cause | Description |
| Heart Failure | Fluid buildup when the heart can’t pump well. |
| Kidney Disease | Fluid retention because the kidneys aren’t working right. |
| Liver Disease | Fluid buildup because of low albumin levels. |
By looking at these causes, we can find and treat the swelling linked to anemia.
Treatment Approaches for Anemia and Edema
Managing anemia and edema needs a full plan. This plan tackles the causes and symptoms. We’ll look at how to treat these conditions. This includes fixing the anemia, handling swelling, and using medicine and lifestyle changes.
Addressing the Underlying Anemia
The first step is to find and fix the anemia’s cause. This might mean:
- Iron Supplements: For iron deficiency anemia, iron supplements help fill up iron stores.
- Vitamin Supplements: For vitamin deficiency anemia, taking vitamins like B12 or folate is suggested.
- Managing Chronic Diseases: For anemia linked to chronic diseases, treating the disease is key.
Managing Swelling Symptoms
It’s important to manage swelling when treating anemia and edema. Ways to do this include:
- Elevation: Raising the affected limbs helps reduce swelling.
- Compression: Using compression stockings or bandages helps blood flow.
- Exercise: Doing gentle exercises regularly boosts blood flow.
Medical Interventions
Medical treatments are vital for anemia and edema. These can be:
- Medications: To treat the cause or manage symptoms.
- Blood Transfusions: Blood transfusions might be needed in severe cases.
- Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents: These drugs help make more red blood cells.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changing your lifestyle is also key. This includes:
- Dietary Changes: Eating more iron-rich foods or foods full of vitamins and minerals.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps blood flow.
- Avoiding Prolonged Standing: Not standing or sitting for too long helps avoid swelling.
By using these treatments together, people with anemia and edema can see big improvements. They can feel better and live better lives.
Patient Experiences and Case Studies
Patient stories give us a close look at the struggles of living with anemia and swelling. By looking at real-life examples, we can grasp the full picture of managing these issues.
Clinical Observations
Doctors have found that anemia often leads to swelling in the legs, feet, and ankles. This swelling can really hurt and make it hard to move. But, treating the anemia can help reduce the swelling.
In a study on iron deficiency anemia, iron supplements helped improve symptoms and lessen swelling. This shows how key it is to get the right treatment.
Common Patient Concerns
People with anemia and swelling worry about how it affects their daily life. They often talk about trouble moving, pain, and the mental toll of chronic illness.
| Concern | Percentage of Patients |
| Limited Mobility | 60% |
| Pain | 55% |
| Psychological Effects | 70% |
Success Stories in Management
Many people have found ways to manage anemia and swelling well. By tackling the root causes and using the right treatments, they’ve seen big improvements in their lives.
For example, a patient with severe iron deficiency anemia got rid of swelling with iron supplements and diet changes. Stories like these show how important tailored care and education are.
We share these stories and case studies to offer insights into managing anemia and swelling. We aim to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Conclusion
It’s important to understand how anemia and swelling are connected. We’ve looked into how anemia can lead to swelling in legs, feet, and ankles. We’ve also discussed the reasons behind this.
Managing anemia is key to reducing swelling. By treating the root cause of anemia, we can help patients feel better. This improves their overall quality of life.
To manage anemia well, we need a complete plan. This includes medical treatments and changes in lifestyle. It’s vital to get medical help and follow a treatment plan that’s right for you.
FAQ
Does anemia cause swelling in the legs, feet, and ankles?
Yes, anemia can cause swelling in these areas. This is due to less oxygen being delivered, more blood being pumped, and changes in how the kidneys handle fluids.
Can low iron cause swelling?
Yes, low iron can lead to swelling. It affects how oxygen is carried and can disrupt fluid balance and circulation.
What types of anemia are most associated with swelling?
Severe chronic anemia, anemia of chronic disease, hemolytic anemia, and pernicious anemia often cause swelling. They impact fluid balance and circulation.
Why do lower extremities get swollen in anemia?
Swelling in the lower extremities is common in anemia. Gravity, reduced mobility, and fluid retention are key factors.
How is anemia-related swelling diagnosed?
Diagnosing swelling related to anemia involves a thorough medical check-up. Tests include a complete blood count and iron tests. Imaging studies and ruling out other causes are also part of the process.
What are the treatment approaches for anemia and edema?
Treatment includes addressing anemia with iron supplements and managing swelling symptoms. Lifestyle changes to reduce fluid retention and improve circulation are also recommended.
Can anemia cause bilateral swelling?
Yes, anemia can cause swelling on both sides. This is due to changes in fluid balance and circulation.
Is swelling a common symptom of anemia?
Swelling is a symptom of anemia, more so in severe or chronic cases. It’s linked to the condition’s physiological changes.
How does iron deficiency anemia lead to swelling?
Iron deficiency anemia can cause swelling through reduced oxygen delivery, changes in circulation, and impacts on kidney function and fluid balance.
Are there any specific patient concerns related to anemia and swelling?
Patients often worry about managing symptoms, understanding anemia’s cause, and dealing with fatigue, weakness, and swelling on mobility and quality of life.
Reference
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (n.d.). What is anemia?https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/anemia



































