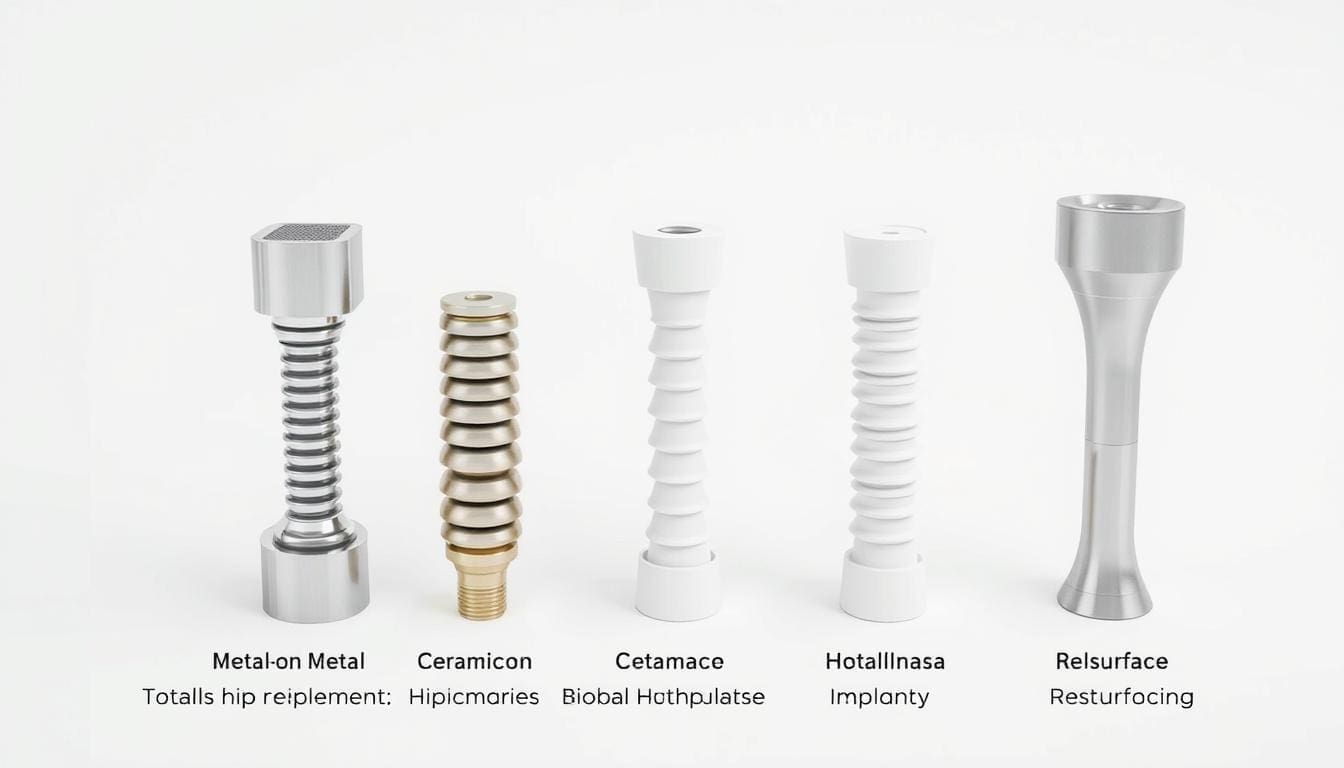
Choosing the right hip replacement solution is key for long-term comfort and mobility. At Liv Hospital, we know picking the right option can be tough. That’s why we’re here to help you understand the five main types of artificial hip materials used in surgeries.
Our team is all about giving you top-notch care with the latest tech. We’ll look at the differences between these implants, their benefits, and how to pick the best one for you.
Key Takeaways
- Knowing the different hip implant types is vital for making a smart choice.
- Liv Hospital’s experts are here to offer personalized care and advice every step of the way.
- The five common hip implant types vary in materials, durability, and fit.
- Things like your age, lifestyle, and health play a big role in picking the right implant.
- Keeping up with new hip replacement tech is key for the best results.
Understanding Hip Implant Devices and Their Purpose

Hip joints can get damaged beyond repair. Hip implant devices offer a good solution to fix this. They help restore mobility and reduce pain.
What Are Hip Implant Devices?
Hip implant devices, or hip prostheses, replace or repair damaged hip joints. They are made to work like the natural hip, improving life for those who have surgery.
Components of a Hip Replacement System
A hip replacement system has key parts like the acetabular cup, femoral head, and stem. The acetabular cup goes into the pelvis. The femoral head and stem go into the femur. Together, they help the hip move smoothly and reduce pain.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Acetabular Cup | Implanted into the pelvis | Replaces the natural hip socket |
| Femoral Head | Articulates with the acetabular cup | Replicates the ball of the hip joint |
| Stem | Implanted into the femur | Provides stability and support |
Who Needs Hip Implants?
Hip implants are for those with severe hip damage or arthritis. This can make moving hard and hurt. The choice to have surgery depends on age, activity level, and medical needs. Younger patients might need stronger implants for more activity, while older ones might want easier recovery implants.
Choosing the right hip implant is a big decision. It depends on the patient’s condition and lifestyle. Knowing about hip implant devices helps patients make better choices.
The Evolution of Hip Replacement Technology
Hip replacement technology has seen huge progress over the years. Advances in materials and design have greatly improved outcomes for patients. This evolution is driven by the goal to enhance patient satisfaction and extend implant life.
Historical Development
The idea of hip replacement started in the late 19th century. But, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that it became a reality. Early attempts used ivory and metal, but they failed due to compatibility and durability issues.
The 1960s brought a big change with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement. It helped implants stay in place better. The 1970s and 1980s saw more progress with new materials and designs. This included ceramic and polyethylene components.
Recent Advancements in Materials and Design
Recently, hip replacement technology has kept improving. This is thanks to better materials and surgical techniques. Modern implants are made to last longer, with features like highly cross-linked polyethylene and advanced ceramic materials.
Now, we have different types of hip implants. These include metal-on-polyethylene, ceramic-on-ceramic, metal-on-metal, ceramic-on-polyethylene, and dual mobility designs. Each has its own benefits and possible downsides.
Metal-on-Polyethylene Hip Implants
Metal-on-polyethylene hip implants have been a key part of hip replacement surgery for many years. They help patients move better and feel less pain. These implants are made to work like the natural hip joint.
Design and Material Composition
These implants have a metal femoral head and a polyethylene liner. The metal is strong and safe for the body, made from alloys like cobalt-chromium or titanium. The polyethylene liner is special, designed to last longer and reduce wear.
Advantages and Limitations
One big plus of these implants is their durability and long-term performance. The metal is strong, and the polyethylene liner cuts down on friction. But, there are downsides. The polyethylene can wear out, causing osteolysis or bone loss. Also, some people might react to the metal, leading to tissue problems.
Typical Longevity and Performance
The life span of these implants depends on several things, like the patient’s age and activity level. Generally, they can last 15 to 20 years or more with good care. New materials and designs have made them even better.
Prosthetic hip implants can be either cemented or cementless. Cemented implants use a special cement for stability. Cementless implants rely on bone growth for attachment. The choice depends on the patient’s needs.
Ceramic-on-Ceramic Hip Implants
Ceramic-on-ceramic hip implants are special because of their materials and benefits. They are made to last a long time for people getting hip surgery.
Design and Material Properties
These implants are all ceramic, which is very hard and doesn’t wear down easily. This is good for people who can’t handle metal because it reduces metal debris risks.
The ceramics are made to be strong and move smoothly, just like a real hip. This helps them last longer and move better.
Advantages and Limitations
Ceramic-on-ceramic implants are durable and don’t wear down much. They’re also safe for people who react badly to metal. They’re great for young, active people who need a strong hip replacement.
But, they can break more easily than other implants. They might also make squeaking or other noises because of the ceramic parts.
Key Benefits:
- High durability and resistance to wear
- Low risk of adverse reactions to metal debris
- Suitable for younger, more active patients
Long-term Durability
Ceramic-on-ceramic implants are made to last a long time, up to 30 years. New ceramic technology makes them stronger and more reliable. They’re a good choice for the long haul.
Research shows they work well for a long time if the surgery is done right. They have low rates of needing to be replaced.
Metal-on-Metal Hip Implants
Metal-on-metal hip implants have been a focus in orthopedic surgery. They are durable but come with risks. We look at their design, benefits, and drawbacks to understand their place in hip surgery.
Design and Material Composition
Metal-on-metal implants are made of cobalt and chromium alloys. They were chosen for their strength and low wear rate. This design aims to reduce dislocation risk and offer more movement.
Key components of these implants include:
- The acetabular cup
- The femoral head
- The stem
Together, these parts aim to mimic the natural hip joint movement.
Advantages and Possible Risks
Metal-on-metal implants are durable, making them good for active patients. But, they also have risks. These include:
- Metallosis: metal ions in the blood and tissue.
- Adverse local tissue reactions (ALTR): inflammation and tissue damage.
These issues have made doctors rethink using these implants.
Current Status in Clinical Practice
The use of metal-on-metal implants has dropped a lot due to risks. New materials and designs have come out. Now, guidelines help pick the right patients and watch over those with these implants.
Choosing hip implants depends on the patient’s age, activity, and health needs. Sometimes, other options might be better.
Ceramic-on-Polyethylene Hip Implants
Ceramic-on-polyethylene hip implants are a big step forward in hip replacement tech. They are known for their durability and performance. This makes them a top choice for surgeons and patients.
Design and Material Innovations
These implants mix ceramic and polyethylene materials. The ceramic part is hard and wears down less. The polyethylene liner is soft and helps prevent the implant from breaking. Together, they make a strong and reliable implant for daily activities.
Key Features:
- Reduced wear and tear due to the ceramic component
- Lower risk of implant fracture
- Improved longevity and performance
Why They Represent Over 50% of Current Cases
Ceramic-on-polyethylene implants are now used in over 50% of hip replacements. Surgeons choose them for their balance of durability and performance. For more on hip replacement, check out hip replacement resources.
| Implant Type | Material | Longevity |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic-on-Polyethylene | Ceramic head, Polyethylene liner | 15-20 years |
| Metal-on-Polyethylene | Metal head, Polyethylene liner | 10-15 years |
| Ceramic-on-Ceramic | Ceramic head, Ceramic liner | 20-25 years |
Expected Longevity and Performance
Ceramic-on-polyethylene implants last 15 to 20 years. This depends on the patient’s age, activity level, and surgery. They offer a smooth joint for better movement and quality of life.
We see ceramic-on-polyethylene implants as a major leap in hip replacement tech. They offer a strong and lasting solution for hip arthritis and other hip issues.
Dual Mobility Hip Implant Devices
Dual mobility hip implants are a big step forward in joint replacement tech. They give patients better stability and more movement. These implants tackle the problems of old hip replacement systems, like dislocation risks and limited movement.
Unique Design Features
The dual mobility design has two moving parts. One is between the femoral head and a mobile polyethylene liner. The other is between the liner’s outer surface and the acetabular cup. This setup boosts mobility and cuts down on wear on the implant parts. The dual mobility concept is great for those at risk of dislocation or needing more movement for daily tasks.
Stability and Range of Motion Benefits
Dual mobility hip implants offer improved stability and a wide range of motion. This is key for young, active people or those with a history of hip dislocation. The design lowers the chance of impingement and dislocation, common issues with traditional hip replacements.
Ideal Candidates for This Design
Dual mobility hip implants are best for those at high risk of dislocation, with hip instability, or needing lots of mobility. They’re also good for revision surgeries where stability is a big concern. Choosing a dual mobility implant depends on the patient’s health, activity level, and hip condition.
| Patient Profile | Benefits of Dual Mobility Implants |
|---|---|
| Young, active patients | Enhanced stability and range of motion |
| Patients with a history of hip dislocation | Reduced risk of dislocation |
| Revision surgery patients | Improved stability in complex cases |
Fixation Methods for Hip Implant Devices
Understanding the different ways to fix hip implant devices is key for both doctors and patients. The right choice can greatly affect the success of hip replacement surgery and how well a patient recovers.
Cemented Fixation: Process and Benefits
Cemented fixation uses special cement to hold the hip implant in place. This method has been used for many years and is known for its immediate stability.
The cement used is usually made from polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). It fills the space between the implant and the bone, creating a strong bond. One big plus of cemented fixation is that it allows patients to bear weight right after surgery, thanks to the cement’s stability.
This method is often chosen for older patients or those with weaker bones. But, it might not be the best for younger, more active patients because the cement can loosen over time.
Cementless Fixation: Osseointegration
Cementless fixation uses the body’s natural process of osseointegration. This means the bone grows onto or into the implant, holding it in place. This method is gaining popularity because it can last a long time.
Cementless implants have a porous surface or are coated to help bone growth. The success of this method depends on the patient’s bone quality and the implant’s design.
One big advantage of cementless fixation is its long-term stability. The bone continues to grow into the implant over time. But, it might take longer to recover compared to cemented fixation.
Hybrid Fixation Approaches
Hybrid fixation combines elements of both cemented and cementless fixation. For example, a cementless acetabular component might be paired with a cemented femoral stem.
Hybrid fixation aims to offer the best of both worlds. It provides immediate stability and also promotes long-term osseointegration. The choice of hybrid fixation depends on the patient’s anatomy and the surgeon’s preference.
How Fixation Method Affects Recovery
The fixation method used can greatly affect how a patient recovers. Factors like the patient’s age, bone quality, and activity level play a role in choosing the fixation method.
| Fixation Method | Immediate Stability | Long-term Durability | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cemented | High | Moderate | Shorter |
| Cementless | Moderate | High | Longer |
| Hybrid | High | High | Variable |
In the end, the right fixation method should match the patient’s needs. This means considering their specific condition and lifestyle.
Materials Science in Modern Hip Implants
New materials have greatly improved hip implants. Today’s hip replacements use different materials. Each is chosen for its special properties that help the implant work well and last long.
Metals: Cobalt-Chromium Alloys and Titanium
Metals are key in making hip implants. Cobalt-Chromium alloys and Titanium are most used. Cobalt-Chromium alloys are strong and wear-resistant, great for the moving parts of implants.
Titanium is chosen for its ability to bond with bone and resist corrosion. It’s used for parts that don’t move as much.
Advanced Ceramics
Advanced ceramics are now a top choice for the moving parts of hip implants. They are very resistant to wear and safe for the body. Ceramic-on-ceramic implants have shown to be effective, but they can break if hit hard.
Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene
Highly cross-linked polyethylene is a big step forward in hip implant materials. It’s made to last longer and reduce wear. This makes implants less likely to loosen or cause bone loss.
Biocompatibility Considerations
It’s very important that hip implant materials don’t harm the body. They must be safe and not cause bad reactions. Metals and ceramics are tested a lot to make sure they’re safe.
| Material | Key Properties | Typical Use in Hip Implants |
|---|---|---|
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloys | High wear resistance, strength | Bearing surfaces |
| Titanium | Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance | Stem, non-bearing components |
| Advanced Ceramics | Exceptional wear resistance, biocompatibility | Bearing surfaces |
| Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene | Improved wear resistance, durability | Bearing surfaces, liners |
Selecting the Right Hip Implant Device
Choosing a hip implant device is a big decision. We look at the patient’s health and lifestyle. This helps us pick the best option for them.
Age-Based Considerations
Age is important when picking a hip implant. Younger people need stronger implants because they’re more active. Older people might prefer implants with less risk of problems.
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research showed ceramic-on-ceramic implants are good for the young. They last long and wear less.
Activity Level Assessment
How active a patient is also matters. Active people need implants that can handle more stress.
| Activity Level | Recommended Implant Type |
|---|---|
| High | Ceramic-on-Ceramic or Metal-on-Metal |
| Moderate | Ceramic-on-Polyethylene |
| Low | Metal-on-Polyethylene |
Medical Factors and Contraindications
Some medical conditions affect implant choice. For example, those with metal allergies might need ceramic or other non-metal implants.
“The choice of hip implant device should be tailored to the individual patient’s needs, taking into account their medical history, lifestyle, and personal preferences.” – Dr. an Orthopaedic Surgeon
The Surgeon’s Role in Device Selection
The surgeon’s skill is key in picking the right implant. They look at the patient’s needs and suggest the best option.
We consider age, activity level, and medical history to find the best implants. This ensures the best results and a better life for our patients.
Conclusion
Choosing the right hip implant is very important. It greatly affects the success of hip replacement surgery. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest advancements in hip replacement to help our patients. This way, they get the best care possible.
Understanding the different types of hip implants is key. This includes their materials, design, and how they are fixed in place. Knowing this helps patients make better choices for their surgery.
Our team is dedicated to top-notch healthcare for all patients, including those from abroad. We think knowing about hip implant devices is essential for a good surgery and quick recovery. If you’re thinking about hip replacement or just want more info, we’re here to help.
We focus on personalized care and the latest hip implant technology. Our goal is to help our patients get the best results and improve their quality of life.
FAQ
What are the main types of hip implant devices?
Hip implant devices come in several types. These include metal-on-polyethylene, ceramic-on-ceramic, and metal-on-metal. There are also ceramic-on-polyethylene and dual mobility implants. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks.
How do I choose the right hip implant device for my needs?
Choosing the right hip implant depends on several factors. These include your age, how active you are, and your medical history. Your surgeon will also play a big role in making this decision.
What are the components of a hip replacement system?
A hip replacement system has three main parts. These are the acetabular cup, femoral head, and stem. Together, they help restore the hip’s natural movement and function.
What are the benefits of ceramic-on-ceramic hip implants?
Ceramic-on-ceramic implants are very durable. They resist wear and tear well. This makes them a favorite among patients. They also have a lower risk of metallosis compared to metal-on-metal implants.
What is the difference between cemented and cementless fixation methods?
Cemented fixation uses bone cement to hold the implant in place. Cementless fixation, on the other hand, relies on bone growth onto the implant. The choice depends on the patient’s bone quality and other factors.
Are metal-on-metal hip implants used today?
Metal-on-metal implants were once common but are now less used. This is due to concerns over metallosis and other risks. We carefully consider each case to decide if they are suitable.
How long do hip implants typically last?
Hip implants can last for 20-30 years or more. This depends on the implant type, materials, and patient factors. Proper care and maintenance are key to their longevity.
What are the advantages of dual mobility hip implant devices?
Dual mobility implants offer better stability and range of motion. They are good for patients with certain hip conditions. They also reduce the risk of dislocation and other complications.
How do I know if I’m a candidate for hip replacement surgery?
Hip replacement is recommended for severe hip damage or arthritis. If conservative treatments haven’t worked, surgery might be an option. Our surgeons will assess your condition to advise on the best treatment.
What materials are used in modern hip implants?
Modern implants are made from metals like cobalt-chromium and titanium, and advanced ceramics. Highly cross-linked polyethylene is also used. The material choice depends on the implant type and patient needs.


































