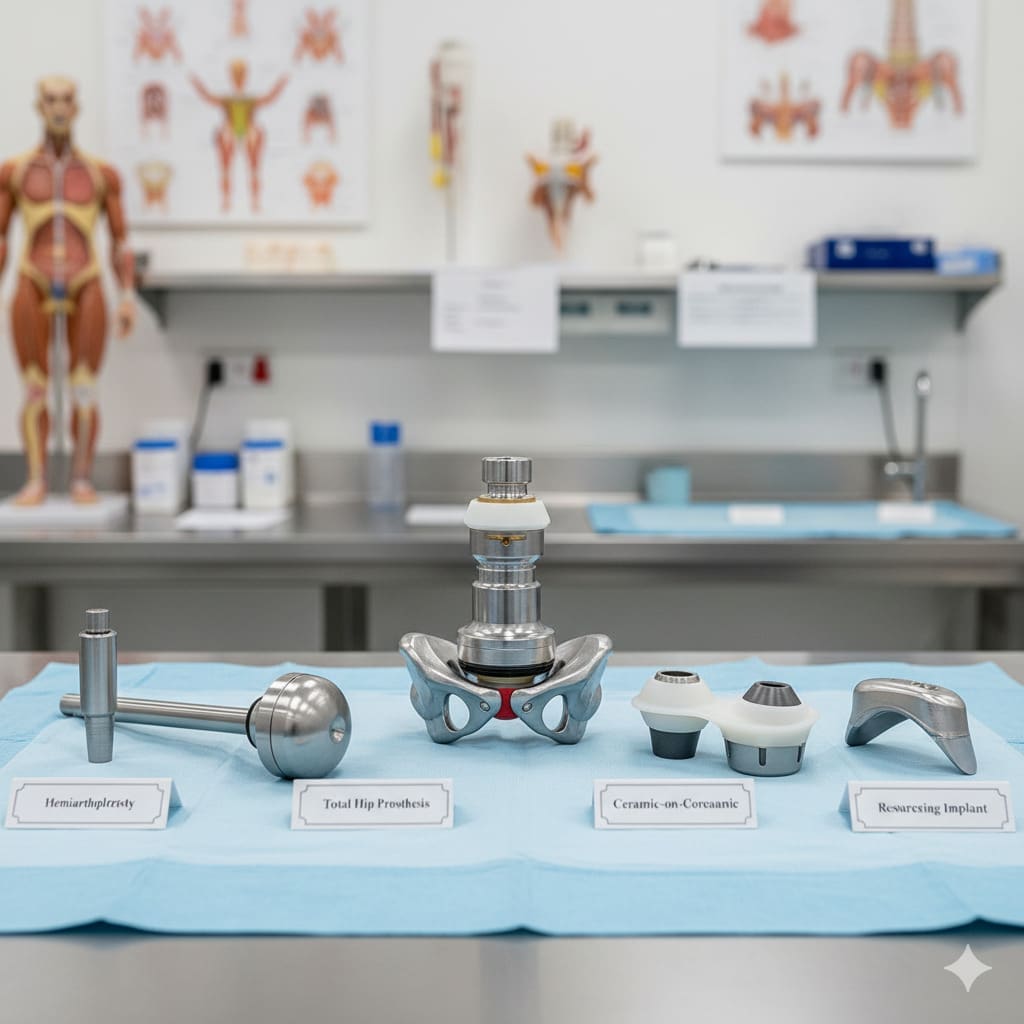
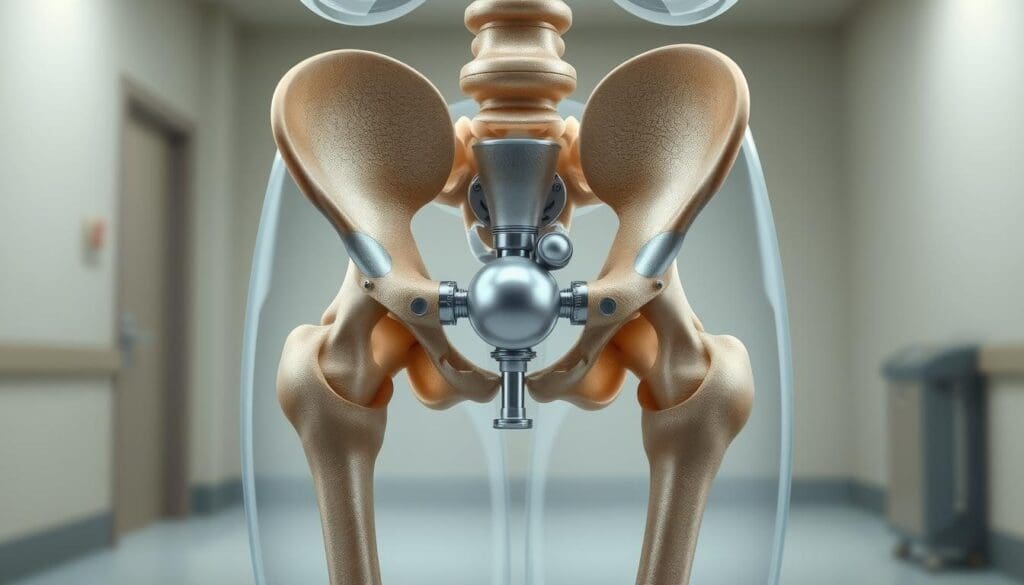
At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to pick the right materials for artificial hip components. Modern hip replacement surgeries need materials that last long, work well together, and perform at their best.
We mix different materials for our hip replacements. We choose them for their strength and to lower the chance of bad reactions.
Our goal is to use the best artificial hip materials available. This is part of our mission to offer top-notch healthcare to everyone, including international patients.
Key Takeaways
- Artificial hip components are made from advanced materials chosen for durability and compatibility.
- The choice of materials is critical for ensuring patient safety and optimal performance.
- Liv Hospital is committed to using the most reliable and up-to-date materials in hip replacement surgeries.
- Our approach is designed to minimize the risk of adverse reactions and ensure long-term success.
- We prioritize patient-centered care, providing complete support for international patients.
The Evolution of Artificial Hip Materials
The journey of artificial hip materials has been long and important. It’s all about making them better and safer for patients. We’ll look at how we’ve moved from simple materials to advanced ones today.
Early Materials and Their Limitations
At first, artificial hips were made from materials that didn’t last long. These early materials caused problems like wear and tear. For example, stainless steel was strong but not always good for the body.
Advancements in Biomedical Engineering
New materials have come from advances in biomedical engineering. Now, we have titanium alloys, cobalt-chromium alloys, and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE). These are better for lasting longer and working well with the body.
Today’s hip replacements have parts made from these new materials. Titanium alloys are used for the stem because they’re strong and safe. UHMWPE is used for the liner because it doesn’t wear down easily.
Understanding the Anatomy of Artificial Hips
Knowing how artificial hip replacements work is key for those thinking about surgery. These devices are made to act like the real hip joint. They help ease pain and make moving easier.
The Four Main Components: Stem, Ball, Cup, and Liner
An artificial hip has four main parts: the stem, ball, cup, and liner. Each part is vital for the hip’s function.
- Stem: The stem goes into the femur, giving the hip a solid base.
- Ball: The ball, or femoral head, sits on top of the stem. It mimics the natural femur head.
- Cup: The cup, or acetabular component, goes into the pelvis. It’s the socket for the artificial joint.
- Liner: Inside the cup, the liner makes the ball move smoothly.
How These Components Work Together
The parts of an artificial hip work together like a real hip. The ball and liner make the joint move smoothly. This reduces wear over time.
We design these parts to work well together. This lets patients move freely and feel less pain. The materials are chosen for their strength, safety, and how well they work.
Design Variations in Modern Prostheses
Today’s artificial hips come in many designs. They meet different patient needs and likes. Some main variations include:
| Design Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material Combinations | Different materials for the ball and liner, like metal-on-polyethylene or ceramic-on-ceramic. | They last longer and wear less. |
| Stem Design | Stems vary in length, shape, and texture for better fit and stability. | They stay in place better and bond with bone. |
| Cup Design | Cups differ in material, size, and how they’re fixed. | They fit better and are less likely to loosen. |
These variations help doctors pick the best hip for each patient. They consider things like age, how active the patient is, and bone quality.
What Are Artificial Hips Made Of: A Complete Overview
The materials in artificial hips are picked for their strength, safety, and how well they work. Looking into the parts of artificial hip replacements shows that the materials used are key to success.
Primary Material Categories
Artificial hips are made from metals, polymers, and ceramics. Metals like titanium and cobalt-chromium are strong, don’t rust, and are safe for the body. Polymers, like ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), are used for the liner. They make the hip move smoothly. Ceramics are also used, known for their toughness and safety.
Material Selection Criteria
Choosing materials for artificial hips is important. They must be biocompatible, safe for the body. They also need to last a long time, resist corrosion, and work well with bone and tissue.
Balancing Durability and Biocompatibility
Finding the right balance between strength and safety is a big challenge. Metals like titanium are strong but might release ions. Ceramics are tough but can break. Polymers like UHMWPE are safe and work well but may not last as long. The right choice depends on the patient’s needs, like age and activity level.
Understanding the materials in artificial hips shows how complex hip replacement technology is. Advances in material science are making hip replacement surgery better for patients.
Titanium Alloys in Artificial Hip Replacements
Titanium alloys are key in making artificial hips strong and safe. They help make hip prosthetics that greatly improve patients’ lives.
Composition and Properties of Medical-Grade Titanium
Medical-grade titanium alloys have titanium, aluminum, and vanadium. These mix to create a material that’s strong, light, and doesn’t corrode easily. The exact mix can change, but they’re great for supporting heavy loads like hips.
What makes titanium alloys good for hips includes:
- High tensile strength and durability
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Low modulus of elasticity, which helps reduce stress shielding
- High biocompatibility, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions
Benefits of Titanium’s Biocompatibility
Titanium alloys are very compatible with the body. This means they’re less likely to cause allergic reactions or be rejected. This is key for the success of hip replacement surgeries, helping the implant bond with the bone.
Also, titanium doesn’t corrode, keeping the implant stable and strong over time.
Applications in Femoral Stems and Acetabular Cups
Titanium alloys are used in two main parts of hip replacements: femoral stems and acetabular cups.
Femoral stems made from titanium alloys give a strong base for the artificial hip. They’re designed to handle loads well, helping to keep the bone healthy around the implant.
Acetabular cups, often made of titanium, hold the artificial hip socket firmly in place. Titanium ensures these cups work well with the femoral head, whether it’s ceramic, metal, or another material.
Together, these titanium alloy parts make a hip replacement system that’s both strong and functional. This offers patients a chance for a more active and pain-free life.
Cobalt-Chromium Alloys: The Workhorse of Hip Implants
Cobalt-chromium alloys are key in orthopedic implants. They are strong and safe for the body, perfect for hip replacements. Their durability and resistance to wear make them great for hip prosthetics.
Composition and Mechanical Properties
Cobalt-chromium alloys mainly have cobalt, chromium, and molybdenum. This mix makes them strong, resistant to corrosion, and able to handle the body’s harsh conditions.
Key Mechanical Properties:
- High tensile strength
- Excellent fatigue resistance
- Superior hardness
Wear Resistance Characteristics
Cobalt-chromium alloys are known for their wear resistance. In hip implants, they wear down very little over time. This reduces the chance of implant failure and the need for more surgeries.
| Material | Wear Rate | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloy | Low | High |
| Titanium Alloy | Moderate | High |
| Stainless Steel | Moderate | Moderate |
Common Applications in Femoral Heads
Cobalt-chromium alloys are often used in femoral heads. Their durability and compatibility with different surfaces make them a top choice. This helps hip implants last longer and work better.
Using cobalt-chromium alloys helps us offer patients reliable hip replacements. This improves their quality of life.
Polymers Used in Artificial Hip Replacements
Polymers have made artificial hip replacements better. They last longer and work better. We’ll look at the different polymers, their qualities, and how they help in hip surgery.
Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE)
UHMWPE is key in hip replacements. It’s tough and safe for the body. It’s often used in the acetabular cup, making it smooth for the femoral head to move.
UHMWPE has gotten better, thanks to cross-linking. This makes it even more durable. Hip implants now last longer because of it.
Cross-Linked Polyethylene Advancements
Cross-linked polyethylene is a big step forward. It’s made by linking polyethylene molecules together. This makes it even better at resisting wear.
Research shows it lowers the chance of osteolysis and implant loosening. For example, a case report on polyethylene liner wear shows how important the right material is.
Polymer Liner Functions and Benefits
The polymer liner is essential in hip replacements. It acts as a shock absorber. This reduces friction and wear, making the implant last longer.
Using polymer liners has many benefits. It lowers the chance of implant failure. It also means less metal ion release, which is good for those with metal-on-metal implants. Overall, it makes hip replacements work better.
| Material | Wear Resistance | Biocompatibility |
|---|---|---|
| UHMWPE | High | Excellent |
| Cross-linked Polyethylene | Very High | Excellent |
Ceramic Materials in Modern Hip Prostheses
Ceramic materials have changed hip prosthetics a lot. Now, we see more advanced ceramics in hip surgeries. This is because they last long and don’t wear out easily.
Alumina and Zirconia Ceramics
Alumina (aluminum oxide) and zirconia (zirconium dioxide) are top picks for hip prosthetics. Alumina ceramics are hard and safe for the body. Zirconia ceramics are even tougher and less likely to break.
Choosing between alumina and zirconia depends on the patient’s needs and the surgeon’s choice.
Ceramic Composite Developments
New ceramic composites are being made. They mix different materials to make hip prostheses better. These composites aim to make prostheses last longer and work better.
Advantages in Reducing Wear Particles
Ceramic materials help reduce wear particles in hip prosthetics. For example, ceramic-on-ceramic bearings make less debris. This can lower the chance of implant failure and better results for patients.
| Ceramic Material | Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina | Hardness, Biocompatibility | Femoral Heads, Acetabular Liners |
| Zirconia | Toughness, Fracture Resistance | Femoral Heads, Ceramic Composites |
Bearing Surface Combinations in Artificial Hips
Choosing the right bearing surface in artificial hips is key to their success. We’ll look at the different options, their benefits, and what to consider for each.
Metal-on-Plastic Bearings: The Traditional Choice
Metal-on-plastic has long been a top choice for hip replacements. It pairs a metal ball with a plastic socket. Its long history, ease of making, and lower cost are big pluses. But, worries about plastic wear have led to new options.
Ceramic-on-Plastic Options: Reducing Wear
Ceramic-on-plastic is a newer option. It uses a ceramic ball with a plastic socket. This combo can reduce wear, making the implant last longer. It’s great for younger, more active people.
Ceramic-on-Ceramic Systems: Maximum Durability
Ceramic-on-ceramic is a cutting-edge choice. It has a ceramic ball and socket. Its top benefit is its durability and safety. But, there are worries about ceramic breakage and noise. We’re watching how these implants do over time.
Metal-on-Metal Considerations and Concerns
Metal-on-metal was once popular for its strength. But, metal ions can harm the body. So, it’s now used less, mainly for special cases. We must think carefully about each patient’s needs.
In summary, picking the right bearing surface for artificial hips is complex. It depends on many factors, like the patient’s age and activity level. By understanding each option, we can give patients the best care for hip surgery.
Material Testing and Quality Standards for Hip Implants
To make sure hip implants are safe and work well, they go through tough testing and meet high quality standards. These implants are checked closely to make sure they last a long time and work right.
FDA and International Regulatory Requirements
The FDA has strict rules for approving hip implants. Some implants need a special approval called pre-market approval (PMA). Groups like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) also have rules for makers to follow. For example, ISO 5832 lists what materials can be used in implants.
When we look at hip implants, we must think about these rules. Important things include:
- Biocompatibility: Making sure materials don’t harm the body.
- Mechanical Performance: Checking if implants can last and work well.
- Labeling and Documentation: Giving clear info to doctors and patients.
Mechanical Testing Protocols
Testing how implants hold up is key. Some tests include:
- Wear Testing: Seeing how implants wear down over time.
- Fatigue Testing: Checking if implants can handle stress and strain.
- Strength Testing: Finding out how much weight an implant can take before breaking.
Biocompatibility Evaluation Methods
It’s vital that hip implants are safe for the body. Makers use different ways to check this, like:
- Cytotoxicity Tests: Seeing if materials are harmful to cells.
- Sensitization Tests: Checking for allergic reactions.
- Implantation Tests: Studying how the body reacts to implants.
By using these tests together, makers can make sure implants are safe and work well.
Patient Considerations in Material Selection
When we talk about hip replacement surgery, it’s key to know how materials affect patients. Choosing the right materials for hip implants is not a simple task. It depends on many factors specific to each patient.
Age and Activity Level Factors
A patient’s age and how active they are play big roles in picking the right materials. Younger, more active people might need materials that can handle more stress, like advanced ceramics or special polyethylene. Older patients might want materials that help them recover faster and offer more stability.
Doctors look at these factors to suggest the best material for each patient. They aim to find a balance between durability and smooth movement without pain.
Metal Sensitivity and Allergies
Some patients might be allergic to metals used in implants, like nickel or cobalt. For these patients, doctors might choose materials that are less likely to cause a reaction. Titanium alloys, for example, are often used because they are safe for people with metal allergies.
It’s very important for patients to tell their doctors about any metal allergies. This ensures the chosen materials are safe and right for them.
Discussing Material Options With Your Surgeon
Talking about material options with your surgeon is a big part of the hip replacement process. Patients should learn about the different materials, their benefits, and how they might affect them. This way, patients can make choices that fit their lifestyle and health needs.
By considering personal factors and talking openly with their doctors, patients can make smart choices about their hip replacement materials. This leads to better results and more happiness.
Innovations and Future Trends in Artificial Hip Materials
The future of artificial hip replacements looks bright. New materials and technologies are changing the game. These advancements promise better results and a better life for patients.
3D-Printed Custom Implants
3D-printed custom implants are a game-changer. They’re made to fit each patient perfectly. This means:
- Improved fit and comfort: Custom implants fit better, reducing discomfort and complications.
- Enhanced durability: 3D printing can make implants last longer by optimizing their design.
- Faster recovery: A better fit means less damage during surgery, leading to quicker healing.
Surface Modification Technologies
Surface modification technologies are also making waves. They aim to improve how implants interact with the body. Techniques include:
- Porous coating: Encourages bone growth, making the implant more stable.
- Nanostructuring: Boosts biocompatibility and wear resistance of implant surfaces.
- Bioactive coatings: Promote bone growth and reduce the risk of implant loosening.
| Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Porous Coating | Enhances bone ingrowth, improves stability |
| Nanostructuring | Improves biocompatibility, wear resistance |
| Bioactive Coatings | Promotes bone growth, reduces loosening |
Bioactive and Smart Materials
Bioactive and smart materials are a big step forward. They interact with the body in new ways. This could mean:
- Enhanced osseointegration: Bioactive materials help implants bond better with bone.
- Real-time monitoring: Smart materials can send feedback on implant and tissue health.
- Adaptive properties: Some smart materials can change their properties in response to the body’s needs.
In conclusion, the future of artificial hip replacements is promising. With ongoing innovation, we can expect better performance, longer-lasting implants, and improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The choice of materials for artificial hips is key to their success. It affects how long they last and how well patients do. Over time, we’ve made big strides in making these materials better.
Different materials like titanium, cobalt-chromium, polymers, and ceramics are used in hip prostheses. Each has its own strengths and benefits. The right material depends on the patient’s age, how active they are, and if they’re sensitive to metals.
New advancements are on the horizon for hip replacement materials. We’re talking about 3D-printed implants, new surface technologies, and materials that interact with the body. These changes will likely lead to better results for patients.
In short, finding the right balance between durability and how well the body accepts these materials is vital. As we keep improving, we’ll see even better care for those getting hip replacements.
What are artificial hips made of?
Artificial hips use advanced materials. These include metals like titanium and cobalt-chromium alloys. They also use polymers, such as ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), and ceramics like alumina and zirconia.
What is the most common material used in hip replacements?
Common materials include titanium alloys for the stem and cup. Cobalt-chromium alloys are used for the femoral head. The liner is made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE).
Are artificial hip materials safe?
Yes, hip replacement materials are safe. They go through strict testing. The FDA sets high standards for these tests, including mechanical and biocompatibility evaluations.
How long do artificial hips last?
Hip replacement longevity varies. It depends on the materials, patient age, activity level, and surgery. Modern hip replacements can last 15-20 years or more.
Can I be allergic to artificial hip materials?
Yes, some may be allergic to certain metals. This includes nickel or chromium. Talking to your surgeon about material options can help find the best fit for you.
What are the benefits of using ceramic materials in hip replacements?
Ceramic materials have many benefits. They reduce wear particles and improve durability. They also lower the risk of metal sensitivity. Ceramic-on-ceramic bearings are very effective in reducing wear.
How are artificial hip materials tested for quality?
Materials are tested through various protocols. This includes mechanical testing for durability and wear resistance. They also check for biocompatibility to ensure they don’t cause adverse reactions.
Can I request specific materials for my hip replacement?
Yes, discussing your preferences with your surgeon is important. They can choose the best materials based on your age, activity level, and other factors.
What are the latest advancements in artificial hip materials?
New advancements include 3D-printed custom implants. There are also surface modification technologies and bioactive materials. These aim to improve implant fixation and reduce wear.
How do bearing surface combinations affect hip replacement outcomes?
The choice of bearing surface combination is key. Options like metal-on-plastic, ceramic-on-ceramic, or ceramic-on-plastic impact longevity and performance. Each has its own advantages and considerations.
References
PubMed Central (NCBI): Academic Article on Hip Replacement Implant Materials