For those with knee osteoarthritis in just one part, unicompartmental knee replacement (UKR) is a good choice. It’s less invasive than a full knee replacement. This option is perfect for younger, active people who want to keep their knee moving naturally.
Partial knee operation only fixes the damaged area. This means healthy parts stay intact, leading to faster recovery. At Liv Hospital, we aim to give top-notch care to our patients from around the world.
Key Takeaways
- UKR is a less invasive procedure compared to total knee replacement.
- It is suitable for younger, active patients with localized osteoarthritis.
- Faster recovery is one of the significant benefits of this operation.
- Preservation of healthy tissue is a key advantage.
- Liv Hospital provides extensive support for international patients.
What is a Partial Knee Operation?
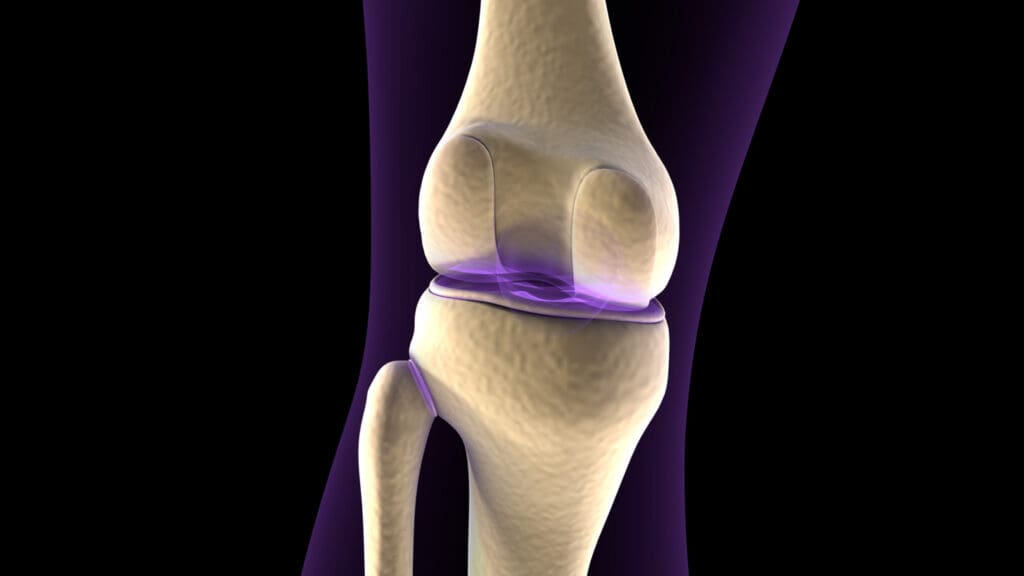
Understanding partial knee operations is key for those thinking about knee replacement surgery. We’ll dive into the details of this procedure, its benefits, and how it stacks up against other options.
Defining Unicompartmental Knee Replacement (UKR)
Unicompartmental knee replacement, or partial knee replacement, is a surgery for knee osteoarthritis in one part of the knee. It’s different from total knee replacement, which replaces the whole knee. UKR only resurfaces the damaged part.
Key aspects of UKR include:
- Minimally invasive approach
- Preservation of healthy bone and ligaments
- Faster recovery times compared to total knee replacement
How Partial Knee Operations Differ from Total Knee Replacements
The main difference between partial and total knee replacements is how much of the knee is replaced. Total knee replacement replaces the whole knee. Partial knee replacement only fixes the damaged part.
| Characteristics | Partial Knee Replacement | Total Knee Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Extent of Replacement | Only the damaged compartment | Entire knee joint |
| Preservation of Healthy Tissue | Yes, preserves healthy bone and ligaments | No, removes more bone and ligaments |
| Recovery Time | Generally faster | Generally longer |
The Evolution of Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty has seen big changes over the years. It started in the 1970s and has improved a lot. This includes better designs and surgical techniques.
“The evolution of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty has been marked by a shift towards more conservative and patient-specific treatments, providing a more tailored approach to knee replacement surgery.” –
Today’s UKR uses advanced implants, better materials, and improved surgery methods. This makes it a good choice for more people.
Fact 1: Partial Knee Operation Targets Localized Osteoarthritis
Partial knee operations are a precise way to treat localized osteoarthritis. They offer a more focused approach than traditional knee replacements. This method targets the specific area of the knee with osteoarthritis, while keeping the healthy parts intact.
Understanding Compartmental Knee Damage
The knee has three main areas: the medial, lateral, and patellofemoral. Compartmental knee damage happens when osteoarthritis hits one or more of these spots. Knowing which area is damaged helps surgeons decide if a partial knee operation is right.
The Medial Compartment: Most Common Treatment Area
The medial compartment is often treated with partial knee operations. It carries a lot of body weight and is prone to wear. Focusing on this area helps surgeons ease pain for those with medial compartment osteoarthritis.
Diagnosing Suitable Candidates for UKA Knee Arthroplasty
Finding the right candidates for UKA knee arthroplasty involves detailed checks. We use imaging and physical exams to see how bad the osteoarthritis is. We also check the health of the surrounding tissue and the patient’s overall health.
Partial knee operations target localized osteoarthritis with great precision. They offer a hopeful solution for those wanting to improve knee function and lessen pain. As we keep improving, these targeted treatments show more promise.
Fact 2: Modern Advances Have Expanded Patient Eligibility
Medical technology has made partial knee replacement surgery available to more people. Now, younger, active patients can get this surgery. Before, it was mainly for older, less active folks.
More people are getting partial knee operations today. This is thanks to better implants, surgery methods, and knowing who’s a good candidate.
Age Considerations for Partial Knee Implants
Before, only older patients got partial knee replacements. But now, younger ones are being considered too. It’s not just about age, but also health, activity level, and knee damage.
Younger patients (under 60) are being looked at for this surgery. This is because research shows it can help them avoid more serious knee surgery later on.
Activity Level and Lifestyle Factors
How active you are and your lifestyle matter for getting a partial knee replacement. Active people or those with high physical demands might choose this surgery. It lets them move more naturally and recover faster than total knee replacement.
Active individuals can keep their lifestyle with partial knee replacement. It keeps healthy parts of the knee, allowing for natural movement and better results for those who stay active.
Contraindications for Uni Arthroplasty Knee Procedures
Even with more people getting surgery, there are some who shouldn’t have it. This includes severe osteoarthritis in many parts of the knee, big ligament damage, and certain inflammatory arthritides.
Those who are severely overweight or have very active lifestyles might also be considered. Our doctors look at each case to decide the best treatment.
Fact 3: The Partial Knee Operation Procedure Preserves Healthy Tissue
Partial knee operations only fix the damaged part of the knee. This keeps the healthy tissue and ligaments safe. This method is key to the success of unicompartmental knee replacement (UKR) procedures.
Surgical Techniques in Unicompartmental Knee Replacement
The way surgeons do UKR is very important. They use small incisions to get to the damaged area. This minimally invasive approach causes less damage and helps the knee heal faster.
During surgery, the damaged parts are carefully removed. The surgeon makes sure to keep the healthy parts safe. Then, a partial knee implant is put in place to match the knee’s natural shape.
Types of Partial Knee Implants
There are many types of partial knee implants. They are made from materials like metal, plastic, or ceramic. The right one depends on the patient’s age, how active they are, and how damaged their knee is.
- Metal-backed implants
- All-polyethylene implants
- Mobile-bearing implants
Each implant has its own benefits. The surgeon will choose the best one for each patient.
Preservation of Natural Ligaments and Bone
Partial knee replacement is great because it keeps the knee’s natural parts intact. This means patients can move their knee more naturally after they recover. Keeping the ligaments, like the ACL, helps patients feel more natural and have better balance.
Keeping the bone healthy is also important. It makes future surgeries easier if needed. This is very helpful for younger patients who might need more surgeries later.
Fact 4: Recovery After PKR Knee Surgery is Typically Faster
Patients who have PKR knee surgery often get back to normal faster than those with total knee replacement. This is a big plus for those who choose partial knee surgery. We’ll look at the recovery process, from hospital stay to getting back to normal activities.
Hospital Stay and Immediate Post-Operative Period
The hospital stay for PKR knee surgery is usually shorter. Most patients go home within a day or two after surgery.
The first days after surgery are key for a smooth recovery. Patients get pain meds and start moving early to avoid problems.
First Few Weeks of Recovery
In the first weeks, patients might feel some pain and swelling. This can be managed with meds and rest. Starting with gentle exercises helps improve knee movement and strength.
Studies show that 90 percent of patients get back to normal in 3-6 weeks after partial knee surgery.
The 3-6 Week Milestone: Returning to Normal Activities
By 3-6 weeks, most patients have made a big recovery. They can start doing light sports and exercises again. This shows how fast PKR knee surgery recovery can be.
Complete Recovery Timeline
While a lot of recovery happens in 3-6 weeks, it can take longer to fully recover. It might take months for the knee to fully heal and for patients to do all they did before surgery.
Fact 5: Benefits of Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Over Total Replacement
Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA) is becoming more popular. It offers many benefits over traditional total knee replacement (TKR) surgery. This makes UKA a top choice for those with localized knee osteoarthritis.
Less Tissue Disruption and Blood Loss
UKA has a big advantage: it causes less tissue damage during surgery. Unlike TKR, which needs a big cut and harms more tissue, UKA uses a smaller cut. This means less blood loss and fewer blood transfusions needed.
Studies show UKA patients face less trauma to the knee. This leads to a smoother recovery.
Reduced Postoperative Pain
UKA patients often feel less pain after surgery than TKR patients. This is because UKA is less invasive and keeps more healthy tissue. So, patients can move more easily and quickly, helping them recover faster.
More Natural Knee Motion and Function
UKA keeps the healthy parts of the knee. This means patients can move more naturally and function better after surgery. This is a big plus for those who want to stay active or play sports.
Lower Complication Rates
UKA has lower complication rates than TKR. Its less invasive nature lowers risks like infection, blood clots, and nerve damage. Also, keeping more bone and tissue healthy reduces long-term risks, making UKA safer.
| Benefits | Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty (UKA) | Total Knee Replacement (TKR) |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue Disruption | Less invasive, smaller incision | More extensive incision, greater tissue disruption |
| Postoperative Pain | Generally less pain | Typically more pain |
| Knee Motion and Function | More natural motion, preserves healthy compartments | Less natural motion, replaces entire knee joint |
| Complication Rates | Lower risk of complications | Higher risk of complications |
The table shows UKA’s clear advantages over TKR. Knowing these benefits helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment for knee osteoarthritis.
“The preservation of healthy tissue and the less invasive nature of UKA contribute to its growing popularity among both surgeons and patients.” – An Orthopedic Surgeon
Fact 6: Medial UKR Risks and Complications
Medial UKR has many benefits, but it’s important to know the risks. Like any surgery, it can have short and long-term complications.
Short-term Complications
Short-term issues can include infections, blood clots, and anesthesia problems. Infection is a big worry, as it can make recovery longer and might need more surgeries. Studies say the risk of infection in UKR is similar to total knee replacement.
Blood clots are another risk, but they can be prevented with medicine and moving around early. Rarely, anesthesia can cause problems, so it’s good to talk to the anesthesiologist about this.
Long-term Considerations
Long-term, medial UKR might face issues like implant wear and loosening. Osteoarthritis could spread to other parts, and you might need another surgery. Implant wear is normal, so regular check-ups are important.
Osteoarthritis spreading is a worry, but choosing the right patients can help. An orthopedic surgeon says, “Choosing the right patients is key for UKR success.”
In summary, while medial UKR is a good option for many, knowing the risks is vital. Understanding these can help patients make better choices about their treatment.
Fact 7: Partial Knee Implants Have a Finite Lifespan
Partial knee operations come with a key fact: the implants have a limited life span. It’s important for patients to know this before deciding on surgery.
Expected Longevity
Partial knee implants usually last 10 to 15 years. But, this time can change based on several things. These include the implant type, how active the patient is, and their overall health.
Factors Affecting Implant Durability
Many things can affect how long a partial knee implant lasts. These include:
- Patient’s age and activity level
- Type of implant material used
- Surgical technique and precision
- Post-operative care and rehabilitation
Knowing these factors can help patients make better choices about partial knee replacement.
Conversion to Total Knee Replacement
If a partial knee implant fails or wears out, conversion to total knee replacement might be needed. This surgery is more complex than a first-time total knee replacement. But, it’s a good option for fixing knee problems.
Technological Advances Improving Longevity
New technology is making partial knee implants last longer. Better materials and surgical methods are being developed. These advancements aim to reduce the need for more surgeries.
As technology keeps improving, we’ll see even better partial knee implants in the future.
Rehabilitation After Unilateral Knee Replacement
After a unilateral knee replacement, a good rehab plan is key for a full recovery. We know that rehab is vital for patients to get their strength and mobility back. It also helps with knee function.
Early Mobilization Protocols
Early movement is very important after a knee replacement. We start with gentle exercises to help with movement and reduce stiffness. This starts a few days after surgery.
Patients do simple knee and ankle movements. These actions help prevent blood clots and aid in healing.
Progressive Strengthening Program
As patients get better, we introduce a progressive strengthening program. This program includes more challenging exercises to strengthen the knee muscles. It helps with stability and function.
We work with physical therapists to create a strengthening plan. This plan might include squats, lunges, and leg press. The goal is to build strength without harming the new knee.
Return to Sports and Active Lifestyle
One big plus of knee replacement is getting back to sports and an active life. We help our patients slowly get back to their favorite activities. This way, they can enjoy their hobbies without hurting their knee.
Low-impact activities like cycling, swimming, and golf are good choices. But high-impact sports need more caution and advice from doctors.
Long-term Maintenance Exercises
To keep the new knee joint healthy, long-term maintenance exercises are essential. We teach patients exercises to do at home. These help keep the knee mobile and strong.
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are also important. They help monitor the knee’s health and address any issues quickly.
Types of Partial Knee Operations
Partial knee replacement isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It comes in various forms to tackle different knee areas. We’ll look at the different partial knee operations, each tailored for specific knee damage.
Medial Unicondylar Knee Arthroplasty
Medial unicondylar knee arthroplasty is a common partial knee replacement. It replaces the damaged inner knee part with artificial parts. This is great for those with arthritis mainly in the inner knee.
Lateral Compartment Replacement
Lateral compartment replacement is less common but works well for outer knee arthritis. It resurfaces the outer knee with prosthetics to improve function and ease pain.
Patellofemoral Joint Replacement
Patellofemoral joint replacement targets the kneecap and femur area. It’s best for those with arthritis mainly in this spot. Resurfacing these areas can greatly improve knee function and reduce pain.
Bicompartmental Knee Replacement
Bicompartmental knee replacement covers two knee areas. It can include the inner and kneecap areas or the outer and kneecap areas. It’s for those with arthritis in two spots, a more conservative option than total knee replacement.
As we’ve seen, partial knee operations vary by the knee areas affected. Choosing the right partial knee replacement is key for the best results. Understanding the options helps patients and doctors make the best choice.
“The key to successful partial knee replacement lies in selecting the appropriate procedure based on the patient’s specific knee anatomy and the extent of their arthritis.”
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision About Partial Knee Surgery
Partial knee surgery is a good option for some patients with osteoarthritis. It helps by preserving healthy tissue and allowing for faster recovery. This makes the knee move more naturally than with total knee replacements.
But, it’s important to know the risks and how long the implants last. This information helps patients decide if partial knee surgery is right for them.
Patients should think about their own situation and talk to their doctor. They should consider their age, how active they are, and their lifestyle. This way, they can choose the best treatment for their needs and get the best results.
What is a partial knee operation?
A partial knee operation, also known as unicompartmental knee replacement (UKR), is a surgery. It replaces only the damaged part of the knee, not the whole joint.
How does partial knee operation differ from total knee replacement?
Total knee replacement changes the whole knee. But, partial knee operation only fixes the damaged part. This keeps healthy tissue and ligaments intact.
What are the benefits of partial knee operation?
Benefits include a quicker recovery and less pain after surgery. It also helps the knee move more naturally.
Who is a suitable candidate for UKA knee arthroplasty?
People with localized osteoarthritis and knee pain are good candidates. They should have tried other treatments first.
What are the age considerations for partial knee implants?
People over 60 are usually good candidates. But, younger patients might be considered too.
How long does it take to recover from PKR knee surgery?
Recovery time is a few weeks to months. Most people can get back to normal in 3-6 weeks.
What are the possible risks and complications of medial UKR?
Risks include infection, blood clots, and implant problems. There’s also a chance of needing a total knee replacement later.
How long do partial knee implants last?
They usually last 10-15 years. But, this can change based on how active you are and the quality of the implant.
What is the rehabilitation process after unilateral knee replacement?
It starts with early movement and strengthening. Long-term exercises help keep the implant working well.
What are the different types of partial knee operations?
There are several types. These include medial unicondylar, lateral, patellofemoral, and bicompartmental knee replacements.
Can I return to sports and active lifestyle after partial knee surgery?
Yes, many can get back to sports. It depends on the implant and your health.
REFERANCE
- https://henryford.com/Blog/2023/09/Should-I-Get-A-Partial-Or-Full-Knee-Replacement henryford.com

































