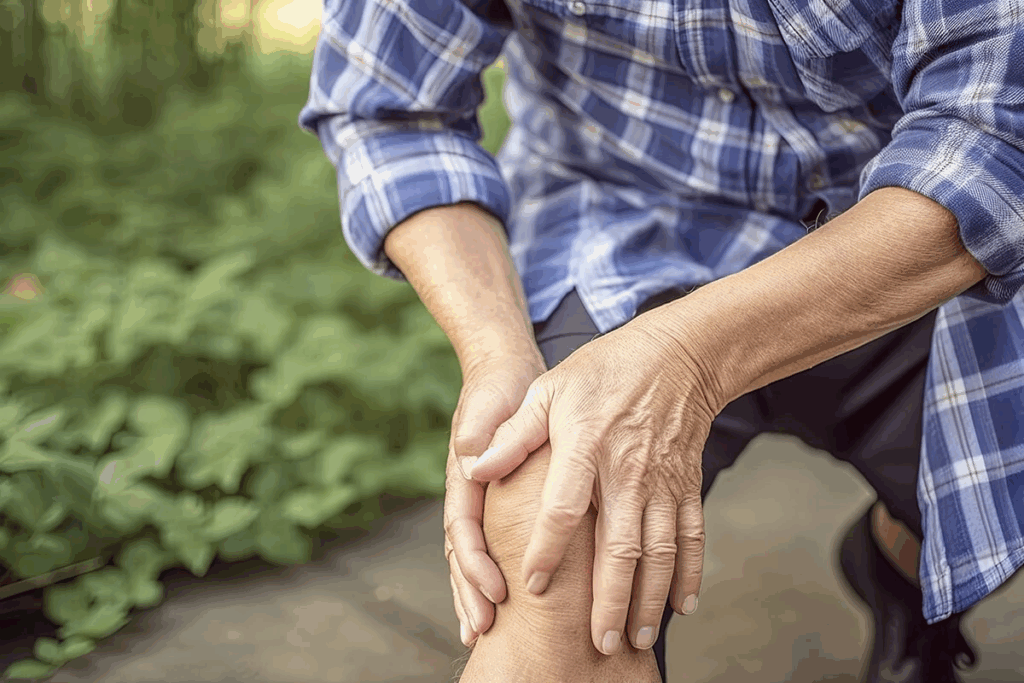
Did you know bursitis can hit anyone, no matter their age or how active they are? Knee bursitis is a common issue that requires prompt attention and appropriate care.ppens when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed.
We’ll dive into what causes knee bursa inflammation, its symptoms, and how to treat it. We aim to give you a full picture of knee bursitis and its impact on people.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes of knee bursitis
- Recognizing the symptoms of bursitis
- Exploring treatment options for knee bursitis
- The importance of seeking medical attention
- Preventive measures to avoid bursitis
What is a Knee Bursa and How Does it Function

A knee bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that helps reduce friction between bones, tendons, and ligaments in the knee. These bursae are key for smooth movement and preventing knee irritation. Let’s dive into what knee bursae are, why they’re important, and their role in keeping the knee healthy.
Definition and Purpose of Bursae
Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion the spaces between bones, tendons, and ligaments. They reduce friction and allow for smooth movement. The main job of bursae is to minimize wear and tear on the knee joint, making daily activities easier. By doing so, they help prevent inflammation and pain in the knee.
Anatomy of Knee Bursae
The knee has several bursae, with the most important being the prepatellar, infrapatellar, and pes anserine bursae. These bursae are placed to reduce friction between different structures in the knee. For example, the prepatellar bursa is between the skin and the kneecap, and the infrapatellar bursa is between the patellar tendon and the shinbone.
Understanding the anatomy of these bursae is key for diagnosing and treating knee bursitis. The knee bursae work together to make movement smooth and reduce friction in the knee joint. Knowing how they function helps us see why keeping them healthy is so important.
Types of Knee Bursitis
It’s important to know about the different types of knee bursitis. Each type affects a different area around the knee. We’ll look at prepatellar, infrapatellar, suprapatellar, and pes anserine bursitis. This will give you a full picture of these conditions.
Prepatellar Bursitis (Housemaid’s Knee)
Prepatellar bursitis, also called “housemaid’s knee,” happens when the prepatellar bursa gets inflamed. It’s often seen in people who kneel a lot or get a direct hit to the knee. You might notice swelling, redness, and tenderness at the knee’s front.
Infrapatellar Bursitis (Clergyman’s Knee)
Infrapatellar bursitis, or “clergyman’s knee,” is when the infrapatellar bursa gets inflamed. It usually comes from kneeling a lot or getting hits to the knee. You’ll feel pain and swelling below the kneecap.
Suprapatellar Bursitis
Suprapatellar bursitis happens when the suprapatellar bursa gets inflamed. It’s often from bending the knee a lot or getting a direct hit. You might feel pain and swelling above the kneecap, which can make moving the knee hard.
Pes Anserine Bursitis
Pes anserine bursitis is when the pes anserine bursa gets inflamed. It’s common in athletes, like runners. You’ll feel pain on the inner side of the knee, worse when climbing stairs or bending the knee.
Here’s a table that shows the main things about each type of knee bursitis:
| Type of Bursitis | Common Name | Location of Pain/Swelling | Common Causes |
| Prepatellar Bursitis | Housemaid’s Knee | Front of the knee | Repetitive kneeling, direct trauma |
| Infrapatellar Bursitis | Clergyman’s Knee | Below the kneecap | Repetitive stress, direct blows |
| Suprapatellar Bursitis | – | Above the kneecap | Repetitive knee flexion, direct trauma |
| Pes Anserine Bursitis | – | Lower inner aspect of the knee | Overuse, running, knee flexion activities |
Each type of knee bursitis has its own signs and needs its own treatment. Knowing these differences is key to managing and preventing future problems.
Knee bursitis is a common issue that requires prompt attention and appropriate care.
Knee bursitis can happen for a few main reasons. These include repetitive pressure, bacterial infections, and inflammatory conditions. Knowing these causes helps in preventing and managing the condition.
Repetitive Pressure or Trauma
Repetitive pressure or trauma to the knee often leads to bursitis. Activities like kneeling, crawling, or direct blows to the knee can irritate the bursae. This leads to inflammation.
People who work on their knees, like plumbers or roofers, are at higher risk. Repetitive strain can make the bursae inflamed, causing pain and swelling.
Bacterial Infections (Septic Bursitis)
Bacterial infections can cause septic bursitis, where the bursa gets infected. This happens when bacteria get into the bursa through a cut or scrape. Septic bursitis needs quick medical attention because it can lead to serious problems if not treated.
Symptoms include increased redness, warmth, and swelling around the affected bursa.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout can raise the risk of knee bursitis. These conditions can make the bursae inflamed, causing pain and discomfort. It’s important to manage the underlying condition to prevent bursitis.
Age-Related Factors
Age is a big factor in knee bursitis. As we get older, the bursae can become more prone to inflammation. Older adults may lose the cushioning effect of the bursae, making them more likely to get bursitis.
Age-related conditions like osteoarthritis can also increase the risk.
Recognizing Knee Bursitis Symptoms
Knowing the signs of knee bursitis is key to catching it early. This helps in getting the right treatment. We’ll look at the common symptoms of knee bursitis. This will help you know when to see a doctor.
Pain and Tenderness
Pain and tenderness are main signs of knee bursitis. The pain can be mild or very bad. It gets worse when you move your knee or put pressure on it.
Swelling and Warmth
Swelling and warmth are also signs of knee bursitis. The inflamed bursa makes the knee swell, turn red, and feel warm. Sometimes, the swelling is so bad it limits how you can move your knee.
Limited Range of Motion
Knee bursitis can also make it hard to move your knee. As the condition gets worse, the pain and swelling make it hard to bend or straighten your knee. This can make simple tasks hard to do.
Differences Between Acute and Chronic Symptoms
It’s important to know if your symptoms are acute or chronic. Acute symptoms come on fast, often after an injury or infection. Chronic symptoms last a long time and can come from repeated strain or ongoing inflammation. Knowing this helps doctors decide how to treat you.
- Acute symptoms: Sudden onset, often due to injury or infection, severe pain and swelling.
- Chronic symptoms: Persistent pain, recurring swelling, and limited mobility over time.
Spotting these symptoms early can make treatment more effective. If you notice any of these signs, seeing a doctor is important. They can give you the right diagnosis and treatment.
Knee Bursa Inflammation: Risk Factors and Prevention
Knee bursitis can happen for many reasons. These include work, sports, and personal health. Knowing these reasons helps in preventing and managing the condition.
Occupational Risks
Some jobs put you at risk for knee bursitis. For example, construction workers, plumbers, and housecleaners often kneel a lot. This can lead to “housemaid’s knee.”
- Jobs involving frequent kneeling or crawling
- Professions with direct pressure on the knee
- Workplaces with inadequate knee protection
Employers can help by making workspaces better and providing protective gear.
Sports and Athletic Activities
People who play sports like running, jumping, or contact sports face a higher risk. Soccer players, football players, and gymnasts are at risk because of their sports.
- High-impact sports
- Activities with frequent knee bending or direct trauma
- Inadequate warm-up or cool-down routines
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender also matter. Older people might be more at risk because of weaker muscles and other health issues. Some studies show women might be more likely to get certain types of knee bursitis.
- Age-related decline in physical condition
- Gender differences in muscle strength and anatomy
- Hormonal influences
Pre-existing Medical Conditions
People with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or diabetes are at higher risk. These conditions can make the body more likely to get bursitis.
“Managing underlying health conditions is key to avoiding knee bursitis.”
— Medical Expert
By knowing and dealing with these risk factors, we can prevent knee bursitis and keep our knees healthy.
Diagnosing Bursitis of the Knee
To diagnose knee bursitis, we use many tools and techniques. We’ll go over each step to make sure we get it right.
Physical Examination
The first thing we do is a physical check-up. A doctor will look for swelling, redness, and warmth in the knee. They also check how well the knee moves and if it’s sore.
This check helps find where and how bad the bursitis is. It helps decide what tests and treatments are needed.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests help confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes of pain. We often use:
- X-rays: To check for bone fractures or other bone problems.
- Ultrasound: To see the bursa and check for inflammation or fluid.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): To get detailed pictures of soft tissues like the bursa, tendons, and ligaments.
Fluid Analysis
Sometimes, we take fluid from the bursa for analysis. This is done with a needle. We look for signs of infection or inflammation in the fluid.
This test helps us tell if the bursitis is caused by infection or not. It helps us choose the right treatment.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is key. It’s about ruling out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms. These include:
- Arthritis: Inflammation of the joint.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons.
- Ligament sprains: Injuries to the ligaments.
- Fractures: Breaks in the bones around the knee.
By looking at the results of the physical exam, imaging tests, and fluid analysis, doctors can make an accurate diagnosis. Then, they can create a good treatment plan.
Conservative Treatment Options for Knee Bursitis
The first step in treating knee bursitis is to use conservative methods. These methods aim to lessen pain and swelling. They help ease symptoms, aid in recovery, and prevent more irritation.
Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the knee is key in the early stages of treatment. Avoid activities that make the condition worse, like kneeling or bending a lot. Changing daily activities to ease knee stress helps a lot in healing.
Ice and Heat Therapy
Using ice packs on the affected area can lessen swelling and pain. Ice therapy is best in the early stages. When the swelling goes down, heat therapy can help by improving blood flow and relaxing muscles.
Compression and Elevation
Compression bandages or sleeves can help by reducing swelling. They limit fluid in the bursa. Elevating the knee also helps by reducing swelling and promoting drainage.
Over-the-Counter Pain Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, like NSAIDs, can help with pain and swelling. It’s important to follow the dosage and talk to a doctor if needed.
Medical experts say, “Conservative management strategies are often enough to fix knee bursitis symptoms and get function back.” Using these treatments can help manage knee bursitis and lower the risk of complications.
“Conservative management strategies are often sufficient to resolve knee bursitis symptoms and restore normal function.” – Medical Professional
Medical Interventions for Severe Knee Bursitis
When knee bursitis gets severe, medical treatments can help. These treatments aim to relieve pain and restore function. For those who don’t get better with simple treatments, there are several medical options.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are a common treatment for severe knee bursitis. They put anti-inflammatory medicine right into the bursa. This reduces swelling and pain. The procedure is done in a doctor’s office and works quickly.
Benefits: Quick relief from inflammation and pain, and it’s a minimally invasive method.
Risks: It might cause infection, temporary pain increase, and weaken tissues with repeated use.
Aspiration Procedures
Aspiration removes extra fluid from the inflamed bursa with a needle. It helps reduce swelling and pressure on the knee. It’s often done under ultrasound to ensure it’s done right.
Benefits: It immediately reduces swelling, can help diagnose by analyzing the fluid, and is minimally invasive.
Risks: It might cause infection, fluid can come back, and it can be uncomfortable during.
Antibiotics for Infected Bursae
Antibiotics are key when knee bursitis is caused by a bacterial infection. The antibiotic choice depends on the bacteria found through tests.
| Antibiotic Type | Common Use | Administration |
| Penicillin derivatives | Effective against a wide range of bacteria | Oral or IV |
| Cephalosporins | Used for more severe infections | IV |
| Fluoroquinolones | Effective against various bacterial infections | Oral or IV |
Surgical Options
In rare cases, surgery might be needed if other treatments fail. This involves removing the bursa. It can be done through open surgery or arthroscopy.
Benefits: It can offer long-term relief and lower the chance of it coming back.
Risks: Surgery carries risks like infection, scarring, and possible complications.
Medical treatments for severe knee bursitis offer different options. Understanding these can help patients make informed choices about their care.
Effective Knee Bursa Exercises and Physical Therapy
Physical therapy and exercises are key in treating knee bursitis. A good physical therapy plan can ease symptoms, boost knee function, and stop future problems.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the knee muscles is vital. It lessens bursa stress and improves joint stability. Here are some exercises we suggest:
- Quadriceps Sets: Straighten the knee by tightening the quadriceps muscle.
- Straight Leg Raises: Lift the leg while keeping it straight.
- Hamstring Curls: Curl the heel towards the buttocks.
Do these exercises gently and without pain.
Flexibility and Range of Motion Exercises
Keeping the knee flexible and mobile is important. Try these exercises:
- Knee Bends: Gently bend the knee.
- Straight Leg Swings: Swing the leg forward and backward.
- Heel Slides: Slide the heel towards the buttocks.
Balance and Proprioception Training
Balance and proprioception exercises are key for knee stability. They help prevent injuries. Try these:
- Single-Leg Stance: Stand on one leg.
- Balance Boards: Use a balance board or wobble board.
- Heel-To-Toe Walking: Walk along a straight line.
These exercises boost neuromuscular control.
Gradual Return to Activities
Returning to activities and sports slowly is important to avoid injury. We recommend:
- Progressive Loading: Gradually increase activity intensity.
- Activity Modification: Modify activities to reduce knee stress.
Listen to your body and don’t rush recovery.
| Exercise Type | Examples | Benefits |
| Strengthening | Quadriceps Sets, Straight Leg Raises | Reduces stress on bursa, improves joint stability |
| Flexibility and Range of Motion | Knee Bends, Straight Leg Swings | Maintains or improves knee mobility |
| Balance and Proprioception | Single-Leg Stance, Balance Boards | Improves knee stability, prevents injuries |
Adding these exercises and physical therapy to your plan can help manage knee bursitis. It also lowers the chance of it coming back.
“Physical therapy plays a key role in managing knee bursitis. It helps patients recover and get back to their normal activities.”
Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy
Home Remedies and Alternative Therapies
Home remedies and alternative therapies can help with knee bursitis. They can ease symptoms, aid in healing, and boost overall health.
Natural Anti-inflammatory Approaches
There are natural ways to fight knee bursitis. Omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil are known for their anti-inflammatory powers. Turmeric and ginger also have anti-inflammatory effects.
A study found that omega-3 fatty acids are great for fighting inflammation. This makes them a good addition to knee bursitis treatment.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments can target knee bursitis pain. Arnica gel or cream is popular for its pain and inflammation relief. Capsaicin cream from chili peppers can also help by blocking pain signals.
Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques can help with knee bursitis stress and pain. Meditation and deep breathing exercises can calm the mind. Yoga and tai chi improve flexibility and balance.
- Meditation can help reduce stress and anxiety.
- Deep breathing exercises promote relaxation.
- Yoga improves flexibility and balance.
- Tai chi enhances overall well-being.
Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies can boost recovery with conventional treatments. Acupuncture uses needles to stimulate healing and reduce pain. Massage therapy can also ease pain and improve movement.
A study showed that acupuncture can greatly reduce knee pain. It also improves function.
Preventing Knee Bursitis Recurrence
To prevent knee bursitis from coming back, you need to use protective gear, follow proper techniques, exercise regularly, and keep a healthy weight. These steps can greatly lower your chance of getting knee bursitis again.
Protective Gear and Padding
Protective gear and padding are key in stopping knee bursitis from coming back. Knee pads or sleeves offer extra support and cushioning. This helps reduce the impact on the knee bursae. It’s a good idea to wear protective gear when kneeling or putting direct pressure on your knees.
- Knee pads for kneeling activities
- Knee sleeves for additional support
- Padding for sports equipment
Proper Technique and Ergonomics
Using the right technique and ergonomics in daily activities and sports can help a lot. Make sure your workspace and equipment support good posture and don’t stress your knees too much.
Tips for Proper Technique:
- Align your knees with your toes during exercises
- Avoid overreaching or twisting
- Use ergonomic equipment and furniture
Regular Exercise and Conditioning
Regular exercise and conditioning strengthen the muscles around your knee. This provides better support and lowers the risk of bursitis. A balanced routine that includes strengthening, flexibility, and cardio exercises is best.
| Exercise Type | Examples | Benefits |
| Strengthening | Leg press, squats | Muscle support around the knee |
| Flexibility | Leg swings, knee bends | Improved range of motion |
| Cardiovascular | Cycling, swimming | Enhanced overall fitness |
Maintaining Healthy Weight
Keeping a healthy weight is very important to reduce knee joint pressure. Extra weight can make the bursae work harder, raising the risk of bursitis. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help you stay at a healthy weight.
By following these tips every day, you can lower your risk of getting knee bursitis again. This helps keep your knees healthy for a long time.
Complications of Untreated Knee Bursitis
Untreated knee bursitis can cause chronic pain and long-term damage to joints. It can severely affect a person’s quality of life and mobility. This is because knee bursitis, if not managed, can lead to several serious complications.
Chronic Pain and Disability
Untreated knee bursitis often leads to chronic pain. The bursa’s inflammation and irritation cause ongoing discomfort. This makes simple tasks hard to do. In severe cases, it can even lead to disability, limiting a person’s ability to do daily activities or engage in physical activities.
Bursa Rupture
Knee bursitis is a common issue that requires prompt attention and appropriate care.
Spread of Infection
If knee bursitis is caused by a bacterial infection, not treating it can spread the infection. This can lead to severe health issues, including life-threatening systemic infections. It’s very important to get medical help if you think you have an infection.
Long-term Joint Damage
Untreated knee bursitis can also damage the joint over time. Chronic inflammation can harm the tissues around the joint, like tendons and ligaments. This can lead to conditions like osteoarthritis, making knee health even harder to manage.
| Complication | Description | Potential Outcome |
| Chronic Pain and Disability | Ongoing inflammation leading to persistent discomfort | Disability, limited mobility |
| Bursa Rupture | Release of inflammatory fluid into surrounding tissues | Increased pain, swelling |
| Spread of Infection | Bacterial infection spreading to other body parts | Systemic infections, life-threatening conditions |
| Long-term Joint Damage | Chronic inflammation affecting surrounding tissues | Degenerative changes, osteoarthritis |
In conclusion, untreated knee bursitis can have severe and lasting effects. It’s vital to see a doctor if symptoms don’t get better or get worse. This way, you can avoid these complications and take care of your knee health.
When to See a Doctor for Knee Bursa Problems
Knowing when to see a doctor for knee bursitis is key. Some cases can be treated at home, but others need a doctor’s help. It’s important to know when to seek medical advice.
Severe or Worsening Symptoms
Severe pain, swelling, or redness that gets worse needs a doctor’s attention. Severe symptoms might mean a serious issue that needs quick action. For example, sudden pain or swelling could be a sign of infection or a serious injury.
Signs of Infection
Seeing signs of infection like more redness, warmth, or pus means you need to see a doctor. Untreated infections can cause serious problems. Watch the area closely and get medical help if you see these signs.
“In cases of septic bursitis, prompt medical intervention is critical to stop the infection from spreading and to avoid long-term damage.”
Failure of Home Treatments
If home treatments don’t work in a few weeks, it’s time to see a doctor. Persistent symptoms might mean you need stronger treatments like injections or physical therapy.
| Treatment Option | Description | Benefit |
| Corticosteroid Injections | Injecting steroids into the bursa | Reduces inflammation and pain |
| Physical Therapy | Guided exercises and stretches | Improves flexibility and strength |
Recurrent Episodes
Having knee bursitis keep coming back means there’s an underlying problem. A doctor can find out why and suggest ways to prevent it or treat it better.
Being aware of these signs and acting quickly can help manage knee bursitis. This reduces the chance of complications and helps you recover faster.
Conclusion
Knee bursitis is a common issue that requires prompt attention and appropriate care. We’ve covered its causes, symptoms, treatments, and how to prevent it. Knowing about the knee bursa’s anatomy and the types of bursitis is key to treating it well.
Knee bursitis can come from many sources like repeated pressure or bacterial infections. It’s also linked to age and some inflammatory conditions. Spotting symptoms like pain, swelling, and stiffness is vital for getting help.
Treatments vary from simple rest and ice to more serious steps like injections. Understanding knee bursitis helps people prevent it and manage its symptoms. This detailed look at knee bursitis shows why quick action and proper care are so important.
FAQ
What is knee bursitis?
Knee bursitis is when the bursae, small sacs filled with fluid, get inflamed. This leads to pain and swelling in the knee.
What are the symptoms of knee bursitis?
Symptoms include pain, tenderness, swelling, warmth, and limited movement in the knee.
What causes knee bursitis?
It can be caused by repetitive pressure, trauma, bacterial infections, inflammatory conditions, and age-related changes.
Knee bursitis is a common issue that requires prompt attention and appropriate care.
Doctors use physical exams, imaging tests, and fluid analysis to diagnose knee bursitis.
What are the treatment options for knee bursitis?
Treatments include rest, ice and heat, compression, and elevation. Medical options include corticosteroid injections and antibiotics.
Can knee bursitis be prevented?
Yes, by using protective gear, maintaining proper technique, exercising regularly, and keeping a healthy weight.
What are the complications of untreated knee bursitis?
Untreated knee bursitis can cause chronic pain, bursa rupture, infection spread, and joint damage.
When should I see a doctor for knee bursitis?
See a doctor for severe symptoms, signs of infection, treatment failure, or recurring episodes.
What is the role of physical therapy in managing knee bursitis?
Physical therapy strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and promotes joint movement in knee bursitis management.
Are there any home remedies for knee bursitis?
Yes, home remedies include natural anti-inflammatory approaches, topical treatments, and mind-body techniques.
Can knee bursitis recur?
Yes, it can recur without preventive measures like protective gear and proper technique.
How can I reduce the risk of knee bursitis recurrence?
Reduce risk by using protective gear, maintaining proper technique, exercising regularly, and keeping a healthy weight.
References
- American Academy of Family Physicians. (2017). Common superficial bursitis. AFP. Retrieved from https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2017/0215/p224.html



































