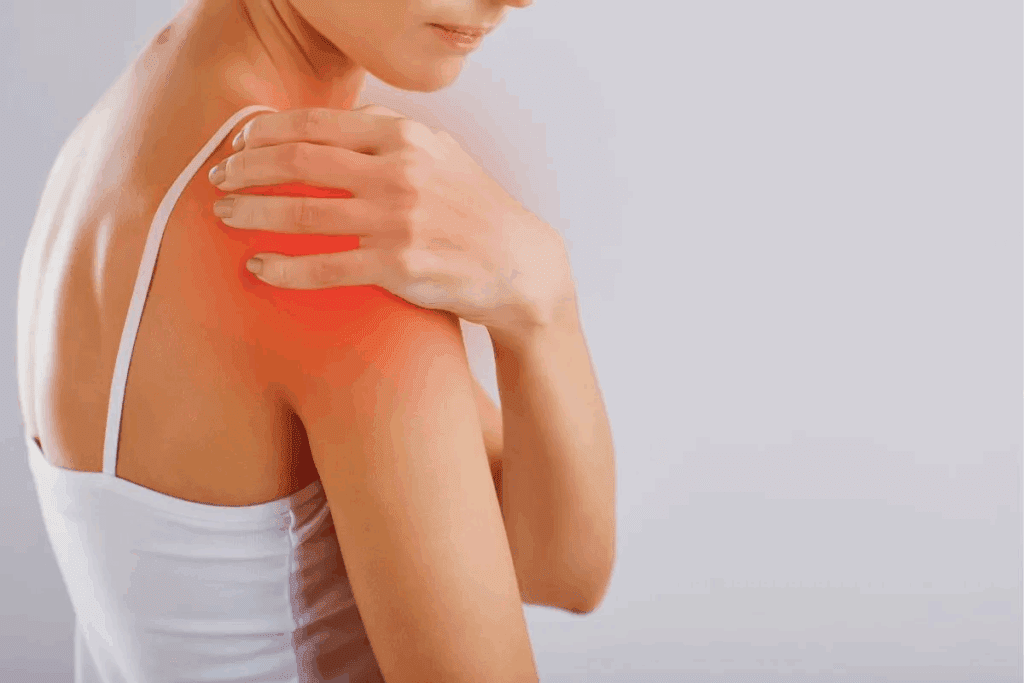
Nearly 1.5 million people in the United States are diagnosed with trochanteric bursitis every year. They face different levels of hip pain intensity. This condition can make daily activities hard, causing pain that’s mild to severe.
It’s important to understand trochanteric bursitis pain to manage it well. Trochanteric bursitis pain often occurs on the outer part of the hip and can worsen with movement or pressure. We’ll look at what causes it, its symptoms, and how to treat it. This will help us understand the chronic hip pain it brings.
Key Takeaways
- Trochanteric bursitis affects a significant number of people, causing varying levels of hip pain.
- The condition can impact daily activities, causing discomfort that ranges from mild to debilitating.
- Understanding the characteristics of trochanteric bursitis pain is key for effective management.
- Treatment options are available to ease chronic hip pain from this condition.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve life quality for those affected.
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
The trochanteric bursa is a fluid-filled sac that helps the hip joint move smoothly. To grasp trochanteric bursitis, we must explore its anatomy and role.
What is a Bursa and Its Function
A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that lessens friction between bones, tendons, and muscles. The trochanteric bursa is near the greater trochanter of the femur. It cushions the area and makes hip movement smooth. When it gets inflamed, it can cause a lot of pain and discomfort.
Location and Anatomy of the Trochanteric Bursa
The trochanteric bursa is between the greater trochanter of the femur and soft tissues like tendons and muscles. Knowing where it is helps in diagnosing and treating trochanteric bursitis.
| Structure | Description | Function |
| Trochanteric Bursa | Fluid-filled sac | Reduces friction between the greater trochanter and surrounding soft tissues |
| Greater Trochanter | Bony prominence on the femur | Attachment site for muscles and tendons |
| Femur | Long bone of the thigh | Supports body weight and facilitates movement |
In summary, the trochanteric bursa is key to hip anatomy. Its inflammation can cause trochanteric bursitis. Knowing its function and location is vital for diagnosing and treating it effectively.
Causes and Risk Factors of Trochanteric Bursitis
Knowing what causes trochanteric bursitis helps in preventing and treating it. This condition is when the trochanteric bursa, a fluid-filled sac, gets inflamed. It’s located around the hip joint.
Several factors can lead to trochanteric bursitis. We’ll look at common causes of inflammation and who’s most at risk.
Common Causes of Inflammation
Many things can cause the trochanteric bursa to get inflamed. These include:
- Repetitive Motion Injury: Activities like cycling or running can irritate the bursa, causing inflammation.
- Direct Trauma: A fall or direct hit to the hip can inflame the bursa.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can increase the risk of trochanteric bursitis.
- Poor Posture or Gait: Abnormal gait or posture can stress the hip, leading to bursitis.
Who is Most at Risk
Some people are more likely to get trochanteric bursitis. This is due to their activities, medical history, or other factors. These include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Athletes | Individuals who participate in sports involving running or repetitive hip movements. |
| History of Hip Injury | People who have previously experienced hip injuries are more susceptible. |
| Inflammatory Conditions | Patients with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis are at a higher risk. |
| Poor Posture or Gait | Individuals with abnormal gait or posture are more likely to develop trochanteric bursitis. |
By understanding these causes and risk factors, individuals can take preventive measures. This can help reduce their chance of getting trochanteric bursitis.
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
Understanding trochanteric bursitis pain means knowing its sensations and where it hurts. This pain can feel different for everyone. So, it’s key to know how to manage it well.
Typical Pain Sensations and Descriptions
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations. Some people feel a sharp pain on the outside of their hip. This pain gets worse when they walk or climb stairs.
Others might feel a aching or persistent discomfort even when they’re not moving.
Pain Distribution Patterns
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations. the outside of the hip. But it can also go down to the thigh or even the buttock.
Knowing where the pain goes is important for diagnosing trochanteric bursitis. It helps doctors tell it apart from other hip problems.
At times, the pain is worse during certain activities or at night. This is because lying on the affected side can make it worse. Doctors can use this info to make treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Pain Intensity Scale for Trochanteric Bursitis
Understanding the pain intensity scale for trochanteric bursitis is key. It helps figure out how bad the condition is and what treatment to use. Trochanteric bursitis pain can really affect someone’s life, so knowing how intense it is is important for a good treatment plan.
Mild Pain Symptoms
Mild pain feels like a dull ache or slight discomfort on the outer hip. People with mild trochanteric bursitis pain can usually handle it. “
Moderate Pain Symptoms
Moderate pain is more uncomfortable and can mess with daily life. Those with moderate trochanteric bursitis pain might feel sharp pains or aching. A patient said, “The pain was constant and made it hard to sleep on my side or walk long distances.”
Severe Pain Symptoms
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
By dividing trochanteric bursitis pain into mild, moderate, and severe, doctors can understand its impact better. They can then create treatment plans that fit each person’s needs.
Factors That Influence Trochanteric Bursitis Pain
Understanding what affects trochanteric bursitis pain is key to managing it. Many things can impact this pain, so knowing them helps in finding relief.
Physical Activity Impact
Physical activity greatly affects trochanteric bursitis pain. Running or cycling, which involve repetitive hip movements, can make the pain worse. High-impact exercises put more stress on the bursa, leading to more pain.
But, some activities can help. Gentle exercises like stretching and strengthening the hip muscles can improve mobility and reduce pain. Finding the right balance between rest and activity is important.
| Activity Type | Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations. |
| High-impact exercises (e.g., running) | Increases pain |
| Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises | Reduces pain |
Body Position Effects
Body position greatly affects trochanteric bursitis pain. Lying on the affected side can put pressure on the bursa, making the pain worse. Standing or sitting for long periods also adds to the discomfort.
Keeping a proper posture and using supports like pillows can help. Adjusting daily habits to avoid direct pressure on the hip can also manage pain.
“Proper posture and positioning can significantly reduce the strain on the trochanteric bursa, helping to alleviate pain.”
Medical Expert
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Environmental and lifestyle factors also play a role in trochanteric bursitis pain. For example, weather changes can affect joint pain, with some people feeling more pain in cold or damp weather.
- Weather changes
- Poor footwear or walking surfaces
- Obesity or weight gain
Adjusting lifestyle factors, like maintaining a healthy weight and wearing proper footwear, can help manage pain.
Common Triggers That Worsen Trochanteric Bursitis Pain
Some activities and positions can make trochanteric bursitis pain worse. Knowing what these triggers are is key to managing the condition. It helps in reducing the discomfort.
Movement-Related Triggers
Movement-related triggers can make trochanteric bursitis pain worse. Here are some examples:
- Climbing stairs puts extra stress on the hip joint and bursae.
- Running or jogging on hard surfaces increases hip impact.
- Prolonged walking or standing can irritate the bursa.
- Repetitive hip movements, like those in cycling or rowing, can also cause pain.
Avoiding or changing these activities can help. For example, using a stairlift or taking breaks during long walks can ease hip strain.
Pressure-Related Triggers
Pressure-related triggers involve direct pressure on the affected bursa. Typical examples include:
- Lying on the affected side can compress the trochanteric bursa.
- Sitting or standing for long periods can irritate the bursa.
- Tight clothing or belts that press against the hip area.
To avoid these triggers, patients can try using a pillow between the knees when lying on their side. They should also wear loose, comfortable clothing that doesn’t press on the hip.
By identifying and managing these triggers, people with trochanteric bursitis can lessen their pain. It’s about making smart choices and adjusting daily activities and habits.
Comparing Trochanteric Bursitis Pain to Other Hip Conditions
It’s important to know the differences between trochanteric bursitis pain and other hip issues. This helps doctors give the right treatment. When people have hip pain, it can be hard to tell what’s causing it because the symptoms can be similar.
Osteoarthritis vs. Bursitis Pain
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
The main difference is where and how the pain feels. Osteoarthritis pain can go down to the knee. But trochanteric bursitis pain stays around the greater trochanter.
Tendinitis vs. Bursitis Pain
Tendinitis, like the gluteal tendons, can feel similar to trochanteric bursitis. Tendinitis pain gets worse with activity and specific movements. Trochanteric bursitis pain is constant and gets worse with pressure on the bursa.
The big difference is how pain reacts to movement. Tendinitis pain gets worse with movement. Bursitis pain gets worse with movement and direct pressure.
Sciatica vs. Bursitis Pain
Sciatica, which irritates the sciatic nerve, can be mistaken for trochanteric bursitis. Both can cause pain down the leg. But sciatica pain goes below the knee and can cause numbness or tingling.
Trochanteric bursitis pain doesn’t go below the knee. It doesn’t usually cause numbness or tingling. Doctors can tell these apart by looking closely at the patient and their history.
How Medical Professionals Assess Trochanteric Bursitis Pain
Healthcare experts use many methods to check trochanteric bursitis pain. It’s key to get this right to make a good treatment plan. They look at physical exams, patient history, and sometimes, imaging tests.
Physical Examination Techniques
A physical check-up is very important for trochanteric bursitis pain. Doctors do tests to see how well the hip moves, its strength, and what hurts. They might do:
- Palpation: Pressing on the sore spot to see if it hurts.
- Range of motion testing: Moving the hip to find out what hurts.
- Strength testing: Checking how strong the hip muscles are.
Table 1: Physical Examination Techniques for Trochanteric Bursitis
| Technique | Description | Purpose |
| Palpation | Applying pressure to the affected area | Assess tenderness and pain |
| Range of Motion Testing | Moving the hip through various motions | Identify painful positions and assess flexibility |
| Strength Testing | Evaluating the strength of the hip muscles | Assess muscle strength and identify weaknesses |
Pain Assessment Tools and Scales
Tools and scales help measure how much pain a patient feels. They help doctors understand how bad the pain is and how it affects daily life. Some common tools are:
- Numeric Rating Scale (NRS): Patients rate their pain from 0 to 10 or 0 to 100.
- Visual Analog Scale (VAS): Patients mark their pain level on a continuous scale.
- McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ): Assesses the quality and intensity of pain.
Diagnostic Imaging for Pain Evaluation
Imaging tests can help confirm the diagnosis and check for other causes of hip pain. Common tests include:
- X-rays: To check bone structure and find any bone problems.
- Ultrasound: To see soft tissue, like the trochanteric bursa.
- MRI: To get detailed pictures of soft tissues and find inflammation or other issues.
Table 2: Diagnostic Imaging for Trochanteric Bursitis
| Imaging Modality | Description | Use in Trochanteric Bursitis |
| X-rays | Evaluate bone structure | Detect bony abnormalities |
| Ultrasound | Visualize soft tissue structures | Assess trochanteric bursa inflammation |
| MRI | Provide detailed images of soft tissues | Detect inflammation and other abnormalities |
When to Seek Medical Attention for Trochanteric Bursitis Pain
Knowing when to seek medical help for trochanteric bursitis pain is key. Mild cases might get better with simple care. But, some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Care
Some signs show your trochanteric bursitis pain needs more than just home care. Look out for:
- Severe pain that stops you from doing daily things or keeps you awake at night.
- Sudden onset of pain, often after a fall or hit to the hip.
- Swelling or redness around the hip that gets worse or comes with a fever.
- Instability or feeling like your hip might collapse.
- Numbness or tingling in your leg or hip.
If you notice any of these, get medical help fast. Quick action can stop problems and help you heal better.
Differentiating Normal from Concerning Pain
It’s important to know the difference between normal and concerning pain. Normal pain usually:
- Gets better with over-the-counter pain meds.
- Improves with rest and simple treatments.
- Doesn’t stop you from doing everyday tasks.
But, concerning pain often:
- Is very bad and doesn’t get better with rest or meds.
- Comes with other scary symptoms like those mentioned before.
- Really hurts your ability to do daily tasks.
Knowing these differences helps you take care of your health better. If you’re not sure about your symptoms, always talk to a doctor.
The Psychological Impact of Chronic Trochanteric Bursitis Pain
Trochanteric bursitis pain can really affect a person’s mind and feelings. It’s hard to live with pain that doesn’t go away. It can change many parts of a person’s life.
Sleep Disruption and Fatigue
Pain from trochanteric bursitis can make it hard to sleep. It’s hard to find a comfy spot or stay asleep. This can make you feel tired and make pain feel worse.
Some common effects of sleep disruption include:
- Increased sensitivity to pain
- Reduced pain tolerance
- Impaired cognitive function
- Mood disturbances
Mood and Emotional Effects
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
Key emotional challenges include:
- Frustration due to reduced mobility
- Anxiety about future pain episodes
- Feelings of isolation or depression
Impact on Daily Activities and Quality of Life
Pain from trochanteric bursitis can really change your daily life. Even simple things like walking or going up stairs can be hard. This can make you feel less independent and more reliant on others.
Some strategies to mitigate this impact include:
- Engaging in physical therapy to improve mobility
- Using pain management techniques, such as medication or alternative therapies
- Adapting daily routines to minimize pain triggers
Understanding the psychological effects of chronic trochanteric bursitis pain helps us meet the needs of those affected. This can improve their quality of life.
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
Managing pain from trochanteric bursitis is key. It’s not just about easing pain. It’s about living better and moving freely again.
Non-Prescription Pain Relief Options
For many, the first step is using non-prescription pain relief. Over-the-counter (OTC) medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help. Also, cold or heat packs on the area can offer quick relief.
Making lifestyle changes helps too. Avoiding activities that make it worse and doing gentle stretching exercises keeps the hip moving.
Prescription Medications for Severe Pain
If OTC meds don’t work, prescription medications might be needed. These can include stronger anti-inflammatory drugs or muscle relaxants. Always follow your doctor’s advice to avoid side effects.
Corticosteroid injections might be suggested to cut down inflammation in the bursa. They’re usually considered after other treatments have been tried.
Alternative Pain Management Approaches
There are also alternative pain management approaches to try. Physical therapy is often suggested to strengthen the muscles around the hip. This improves stability and lessens pain.
Other options include acupuncture and massage therapy. Some find acupuncture helpful for chronic pain. Massage can also ease muscle tension around the hip.
| Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
| OTC Medications | Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen | Reduces inflammation and pain |
| Prescription Medications | Stronger pain relievers or muscle relaxants | Effective for severe pain management |
| Corticosteroid Injections | Direct injection of corticosteroids into the bursa | Reduces inflammation directly |
Looking at these strategies, a comprehensive approach works best. Mixing medical treatments with lifestyle changes and alternative therapies helps a lot. People with trochanteric bursitis can find a lot of relief this way.
Physical Therapy for Trochanteric Bursitis Pain Relief
Physical therapy is key in managing trochanteric bursitis pain. It offers various methods to ease discomfort and boost hip function. Let’s dive into how physical therapy can help with trochanteric bursitis pain.
Effective Stretching Exercises
Stretching is a core part of physical therapy for trochanteric bursitis. It helps loosen hip muscles and boosts flexibility. Here are some effective stretches:
- IT Band Stretch: Stand with your affected side near a wall. Cross the opposite leg over the affected one and lean towards the wall.
- Piriformis Stretch: Sit on the floor with the affected leg crossed over the other. Pull the knee towards the opposite shoulder.
- Gluteal Stretch: Lie on your back, cross the affected leg over the other. Pull the knee towards the opposite shoulder.
Strengthening Exercises for Hip Stability
Strengthening hip muscles is vital for stability and pain relief. Key exercises include:
- Glute Bridges: Lie on your back with knees bent, lift your hips towards the ceiling.
- Clamshell Exercise: Lie on your side with knees bent, lift the top knee away from the bottom knee.
- Side-Leg Raises: Lie on your side, lift the top leg towards the ceiling.
Manual Therapy Techniques
Manual therapy is a critical part of physical therapy for trochanteric bursitis. It includes massage, joint mobilization, and soft tissue mobilization. These techniques help reduce pain and enhance hip function. Our therapists use them to:
- Reduce muscle tension
- Improve joint mobility
- Promote healing
By adding these physical therapy techniques to your treatment, you can see a big improvement in trochanteric bursitis pain relief and hip function.
Medical Interventions for Severe Trochanteric Bursitis Pain
When other treatments don’t work, medical interventions are key for severe trochanteric bursitis pain. These steps aim to help when other methods fail.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are a common treatment for trochanteric bursitis. They contain a corticosteroid like triamcinolone or methylprednisolone. This is injected directly into the bursa.
These injections offer:
- Quick reduction in inflammation
- Significant pain relief
- A minimally invasive procedure
But, there are risks and side effects to consider:
- Temporary pain at the injection site
- Infection risk
- Potential for tendon weakening or rupture with repeated injections
Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is a new treatment. It involves injecting platelet-rich plasma from the patient’s blood into the affected area. PRP has growth factors that help heal and repair tissues.
| Therapy | Benefits | Risks |
| PRP Therapy | Promotes healing, minimally invasive | Infection risk, variable efficacy |
| Corticosteroid Injections | Rapid pain relief, reduces inflammation | Tendon weakening, infection risk |
Surgical Options for Persistent Pain
If other treatments and injections don’t help, surgery might be needed. Surgical options include bursectomy (removing the bursa) or fixing any tendon issues.
Surgical considerations:
- Reserved for severe, persistent cases
- May involve addressing underlying conditions
- Requires post-operative rehabilitation
Talking to a healthcare professional is key. They can help decide the best treatment for severe trochanteric bursitis pain.
Conclusion
Trochanteric bursitis pain can really affect how you live your day-to-day life. It makes simple tasks hard. Knowing what causes it and how to manage it can help you find better ways to feel better.
Hip pain management is key to easing Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations. tips on how to handle the pain. It covers everything from simple remedies to more serious treatments.
It’s important to see a doctor if the pain doesn’t go away. Using a mix of treatments can help you feel less pain. This way, you can live a better life.
Managing trochanteric bursitis means making big changes in your life. It’s about changing how you live, doing physical therapy, and getting medical help. By understanding and tackling the problem, you can start to feel better and live healthier.
FAQ
What is trochanteric bursitis and how does it cause pain?
Trochanteric bursitis is when the trochanteric bursa gets inflamed. This bursa is a fluid-filled sac that helps reduce friction between the femur’s greater trochanter and soft tissues. The inflammation causes pain and discomfort in the hip area.
What are the common causes of trochanteric bursitis?
It’s often caused by repetitive motion, direct trauma, or inflammatory conditions. People with a history of hip injury, those who do repetitive activities, and those with inflammatory conditions are more likely to get it.
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations.
The pain can be sharp, aching, or burning. It can also spread to the thigh or buttock. Knowing how the pain feels helps doctors diagnose and treat it.
What is the pain intensity scale for trochanteric bursitis?
Pain is rated as mild, moderate, or severe. Mild pain is easy to manage and doesn’t affect daily life much. Moderate pain can make daily activities hard, and severe pain can make it hard to move or sleep.
How can physical activity impact trochanteric bursitis pain?
Physical activity can either make the pain worse or better. Activities that move the hip a lot or put pressure on it can hurt more. Gentle exercises and stretches can help manage the pain.
What are common triggers that worsen trochanteric bursitis pain?
Climbing stairs, lying on the affected side, or activities that put direct pressure on the hip can make the pain worse. Avoiding these can help manage the pain.
How does trochanteric bursitis pain compare to other hip conditions?
Trochanteric bursitis pain is often characterized by sharp, aching, or burning sensations. other hip conditions like osteoarthritis, tendinitis, or sciatica. Knowing the differences is key for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How do medical professionals assess trochanteric bursitis pain?
Doctors use physical exams, pain assessment tools, and imaging tests to evaluate the pain. This helps them decide on the best treatment.
When should I seek medical attention for trochanteric bursitis pain?
You should see a doctor if the pain is severe, starts suddenly, or if you have other symptoms like fever or swelling.
What are the psychological effects of chronic trochanteric bursitis pain?
Chronic pain can disrupt sleep, affect mood, and impact daily life. Understanding these effects is important for full care.
What are the management strategies for trochanteric bursitis pain?
Management includes over-the-counter pain relief, prescription meds for severe pain, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
How can physical therapy help in managing trochanteric bursitis pain?
Physical therapy uses stretching, strengthening, and manual therapy to reduce pain and improve function. It helps stabilize the hip.
What medical interventions are available for severe trochanteric bursitis pain?
For severe pain, doctors may suggest corticosteroid injections, platelet-rich plasma therapy, or surgery. Each option has its benefits and risks.
Reference
- Edelson, G. (2015). Greater Trochanteric Pain Syndrome (Greater Trochanteric Bursitis). In StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557433/



































