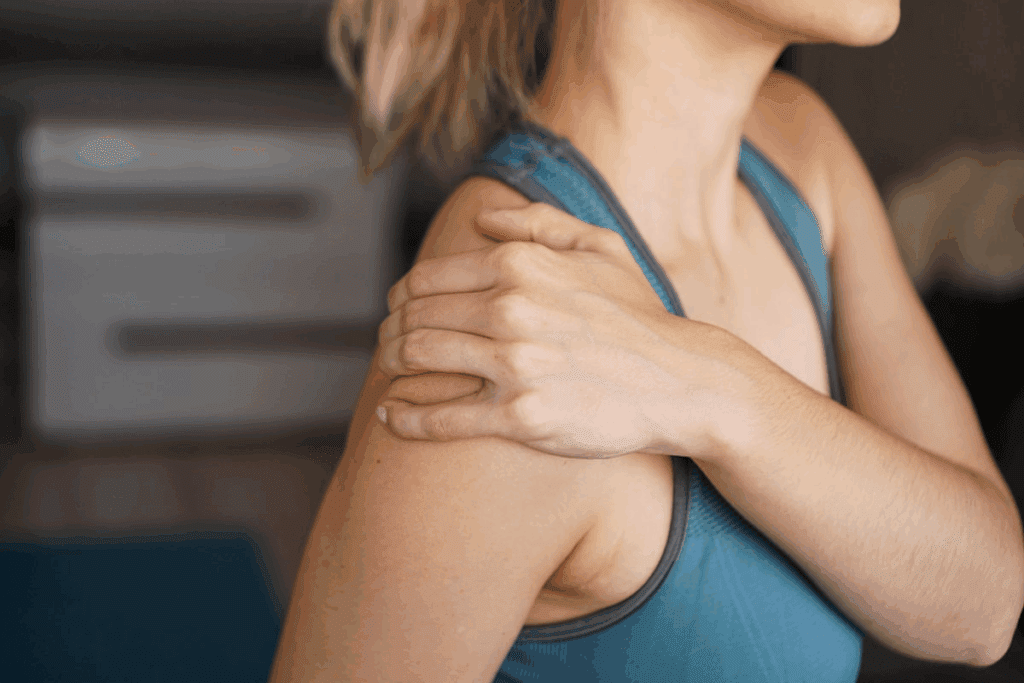
Shoulder injuries are a significant global concern, and understanding the causes of shoulder bursitis is essential for effective treatment.
We’ll look at why the shoulder joint gets inflamed and develops bursitis. Bursitis in the shoulder can happen from repetitive motion, direct hits, or problems like rotator cuff injury and bursitis, or shoulder tendonitis and bursitis.
Knowing the causes of shoulder bursitis is vital for stopping and treating bursitis. We’ll get into the details of how these issues affect the shoulder.
Key Takeaways
- Shoulder bursitis can result from repetitive motion or direct trauma.
- Understanding the causes is key to effective treatment.
- Conditions like rotator cuff injury can lead to bursitis.
- Shoulder tendonitis and bursitis often go hand in hand.
- Prevention and treatment rely on knowing these factors.
Understanding Shoulder Bursitis
It’s important to know about shoulder bursitis to manage and treat it well. Shoulder bursitis happens when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles.
What Is a Bursa and Its Function
A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that helps reduce friction and cushion joints. In the shoulder, bursae let tendons and muscles move smoothly over bones. They are key to healthy joint function and preventing wear and tear.
“The bursa acts as a cushion, absorbing shock and reducing friction between moving parts in the shoulder joint.”
Definition of Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis happens when the bursae in the shoulder get inflamed. This leads to pain, swelling, and less mobility. It can be caused by many things, like repetitive motion or infection. Knowing what causes shoulder bursitis helps in diagnosing and treating it.
“Bursitis is a significant cause of shoulder pain, affecting individuals from various backgrounds and activity levels.”
Types of Shoulder Bursae Affected
The shoulder has several bursae, but the subacromial and subdeltoid bursae are most often affected. The subacromial bursa is between the acromion and rotator cuff tendons. The subdeltoid bursa is between the deltoid muscle and rotator cuff tendons. Inflammation here can cause pain and discomfort, mainly when moving.
Orthopedic physical therapy can help with pain and improve movement for those with shoulder bursitis. Knowing which bursae are affected and the causes helps healthcare professionals create effective treatment plans.
Anatomy of the Shoulder Joint
The shoulder joint is very flexible, which makes it useful but also injury-prone. Knowing how the shoulder works is key to understanding bursitis.
Key Structures in the Shoulder
The shoulder joint, or glenohumeral joint, is a ball-and-socket joint. It has the humerus, scapula, and clavicle. The key structures include bones, tendons, ligaments, and muscles. They all work together to help us move.
Location of Shoulder Bursae
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. They reduce friction between bones, tendons, and ligaments. In the shoulder, bursae are found where these structures rub against each other. The location of the shoulder bursae is important because these areas can get inflamed.
How the Shoulder Mechanism Works
The shoulder mechanism is complex. It involves bones, muscles, and tendons. The rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons, keeps the shoulder stable. This allows for many movements, like lifting the arm and rotating it.
Understanding the shoulder’s anatomy is important. It helps us see how bursitis happens. Knowing about the shoulder’s structures and how it works helps us take care of it better.
Causes of Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis can come from many sources. These include repetitive motion, direct trauma, infection, and systemic inflammatory conditions. Knowing these causes helps in preventing and treating the condition.
Repetitive Motion and Overuse
Repetitive motion injuries often lead to shoulder bursitis. This is true for people who do activities that involve moving their arms overhead a lot. Athletes, like tennis players and baseball pitchers, are at higher risk because of the strain on their shoulders. Workers who lift or reach overhead are also at risk.
A study on professional tennis players showed that repetitive motion plays a big role in shoulder bursitis. It stresses the need for good training and injury prevention.
Direct Trauma to the Shoulder
Direct trauma to the shoulder, like a fall or a blow, can also cause bursitis. This happens when the bursa gets inflamed. Such injuries can happen in contact sports or accidents.
For example, a football player hit in the shoulder during a game might get bursitis. This is because of the trauma from the impact.
Infection (Septic Bursitis)
Septic bursitis happens when the bursa gets infected. This usually comes from a bacterial infection. It can occur through a cut or wound in the skin that lets bacteria into the bursa.
People with weakened immune systems are more likely to get septic bursitis. This shows why keeping wounds clean and practicing good hygiene is so important.
Systemic Inflammatory Conditions
Systemic inflammatory conditions, like rheumatoid arthritis, can also lead to shoulder bursitis. These conditions cause widespread inflammation. This can affect the bursae in the shoulder.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis might get shoulder bursitis as part of their condition. They need a full treatment plan.
Repetitive Motion and Overuse Injuries
Shoulder bursitis often comes from doing the same thing over and over. This can happen at work, in sports, or just doing daily tasks. We’ll look at how these actions can cause shoulder bursitis, focusing on overhead activities, work tasks, and sports.
Overhead Activities and Their Impact
Doing things overhead can lead to shoulder bursitis. This is because lifting arms high puts strain on the bursae. Here are some examples:
- Throwing sports, such as baseball or softball
- Swimming, mainly strokes that go overhead
- Construction work that requires overhead labor
- Reaching for high shelves or doing tasks that lift arms high
These actions can cause the bursae to get inflamed and irritated, leading to bursitis. Using the right technique and taking breaks can help lower this risk.
Work-Related Repetitive Movements
Jobs that make you do the same thing over and over can also cause shoulder bursitis. Jobs with lots of overhead, reaching, lifting, or hard work can lead to injuries. Here are some examples:
| Occupation | Common Tasks | Risk Factors |
| Construction Worker | Overhead labor, lifting heavy materials | Repetitive strain, direct trauma |
| Warehouse Worker | Lifting, carrying, and placing items | Overuse, repetitive motion |
| Assembly Line Worker | Repetitive tasks, often involving overhead movements | Repetitive strain, overuse |
Improving work ergonomics and taking regular breaks can help prevent shoulder bursitis at work.
Sports That Commonly Cause Shoulder Bursitis
Some sports are more likely to cause shoulder bursitis because of the repetitive and high-impact nature of the activities. Here are some sports that often lead to shoulder bursitis:
- Swimming, due to the repetitive overhead motion
- Tennis and other racquet sports, which involve rapid arm movements
- Baseball and softball, mainly pitching and throwing
- Gymnastics, which involves various overhead and high-impact movements
Athletes in these sports should know the risks and take steps to prevent them. This includes proper training, using the right equipment, and getting enough rest.
Rotator Cuff Injuries and Their Relationship to Bursitis
Rotator cuff injuries can change how the shoulder moves, making bursitis more likely. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons around the shoulder. It helps keep the shoulder stable and moves smoothly.
When the rotator cuff gets hurt, it can cause the bursa to become inflamed. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints and reduce friction. This inflammation can cause bursitis, leading to pain, swelling, and limited shoulder mobility.
How Rotator Cuff Tears Affect the Bursa
A rotator cuff tear can really affect the bursa, causing bursitis. When a tendon tears, it can cause the bursa to become inflamed due to increased friction. This can cause shoulder pain and stiffness, making daily tasks hard.
Also, a rotator cuff tear can change how the shoulder moves. This puts more stress on the bursa and surrounding tissues. This stress can make bursitis worse if not treated.
Tendonitis and Its Connection to Bursitis
Tendonitis, or inflammation of the tendons, is closely linked to bursitis. When tendons get inflamed, they can rub against the bursa, causing Tendonitis often happens from repetitive motion or overuse, common in activities that involve arm movements.
The link between tendonitis and bursitis shows why treating both is key. By reducing tendon inflammation, we can also help with bursitis symptoms.
Impingement Syndrome and Bursitis
Impingement syndrome happens when rotator cuff tendons get irritated or inflamed as they pass through the shoulder. This can cause bursitis, as inflamed tendons rub against the bursa, causing friction.
Impingement syndrome is linked to repetitive overhead activities. It’s important to address the root causes to prevent both impingement syndrome and bursitis. By changing activities and doing exercises to strengthen the shoulder, we can lower the risk of these conditions.
Shoulder Trauma and Acute Bursitis
Shoulder trauma often leads to acute bursitis. A big impact on the shoulder can cause bursitis. This results in pain and discomfort. We’ll look at how trauma, like direct impacts and falls, can cause this inflammation.
Direct Impact Injuries
Direct hits to the shoulder can hurt the bursae. This happens in sports, accidents, or other incidents. The impact can make the bursae swell, causing pain and stiffness.
Falls and Shoulder Dislocation
Falling on the shoulder can dislocate it and cause bursitis. When the shoulder joint moves out of place, the bursae get irritated. This injury can be very painful and may lead to lasting problems if not treated properly.
Post-Traumatic Inflammation
After a shoulder injury, inflammation can happen. This is the body’s way of reacting to the damage. It can lead to acute bursitis. It’s important to manage this inflammation to avoid long-term damage and help the healing process.
Knowing how shoulder trauma and bursitis are linked is key to proper treatment. By understanding the causes and symptoms, we can offer the right care to those affected.
Age-Related Factors Contributing to Shoulder Bursitis
As we get older, our shoulders change in ways that can lead to bursitis. The wear and tear on our joints can cause inflammation and irritation of the bursae. This results in pain and discomfort.
Natural Degeneration of Shoulder Tissues
With age, the tissues in our shoulder, like tendons and bursae, naturally degenerate. This can reduce the bursae’s cushioning effect, making them more prone to irritation and inflammation. Age-related degeneration is a key factor in shoulder bursitis, as it weakens the protective mechanisms around the joint.
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy showed that age-related changes in the shoulder increase bursitis and other pathologies. This emphasizes the need to keep our shoulders healthy as we age.
Calcium Deposits and Aging
Calcium deposits in the tendons and bursae are another age-related factor in shoulder bursitis. These deposits can irritate and inflame, leading to bursitis. The risk of these deposits grows with age, making older adults more likely to develop this condition.
| Age Group | Prevalence of Calcium Deposits | Risk of Shoulder Bursitis |
| 40-59 years | Moderate | Increased |
| 60 years and above | High | Significantly Increased |
Decreased Shoulder Mobility in Older Adults
Older adults often see a drop in shoulder mobility due to joint stiffness and reduced muscle flexibility. This reduced mobility can lead to altered movement patterns. These patterns put extra stress on the bursae, raising the risk of bursitis.
“Maintaining flexibility and range of motion is key to preventing shoulder bursitis, mainly in older adults.”
Regular exercises that boost shoulder mobility and strength can help counteract some age-related factors in shoulder bursitis. It’s wise to talk to a healthcare professional to create a tailored exercise plan.
Posture and Body Mechanics
Knowing how to keep good posture and body mechanics is key to avoiding shoulder bursitis. Our daily actions and movements greatly affect our shoulder health. It’s important to understand how these habits can either help or harm our shoulders.
Poor Posture Effects on Shoulder Health
Poor posture can increase the risk of getting shoulder bursitis. Slouching or hunching puts extra stress on the bursae, causing inflammation and pain. Maintaining a correct posture helps spread the weight and stress evenly across the shoulder joint.
Long-term poor posture can cause chronic strain on the shoulder muscles and bursae. This strain can lead to bursitis, marked by pain, swelling, and limited shoulder mobility.
Improper Lifting Techniques
Bad lifting techniques are another common cause of shoulder bursitis. Lifting heavy objects the wrong way can strain the shoulder joint and bursae, causing inflammation and injury. It’s vital to use proper lifting techniques, bending at the knees and lifting with the legs, not the back or shoulders.
Using the right body mechanics when lifting can greatly lower the risk of shoulder bursitis. This means avoiding twisting motions and keeping the load close to the body.
Muscle Imbalances Around the Shoulder
Muscle imbalances around the shoulder can also lead to bursitis. When some muscles are too strong and others too weak, it can cause abnormal movement and stress on the bursae. Doing exercises that strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve flexibility can help keep the shoulder balanced.
Fixing muscle imbalances through physical therapy or specific exercises can prevent shoulder bursitis. By making sure the muscles around the shoulder are strong and balanced, people can lower their risk of getting this condition.
Medical Conditions Associated with Shoulder Bursitis
Many medical conditions can raise the risk of getting shoulder bursitis. These conditions often harm the joints and the tissues around them. This leads to inflammation and irritation of the bursae.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inflammatory Conditions
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder. It causes inflammation in the joints, including the shoulder. This inflammation can reach the bursae, causing bursitis.
Other inflammatory conditions, like psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, can also lead to shoulder bursitis.
Gout and Crystal Deposition
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by urate crystals in the joints. While it often hits the big toe, it can also affect the shoulder. This leads to bursitis.
The crystals in the bursae cause sudden and severe inflammation.
Autoimmune Disorders Affecting the Shoulder
Autoimmune disorders make the body attack its own tissues. They can harm the shoulder and cause bursitis. Conditions like lupus and scleroderma can damage the shoulder joint and bursae.
Bone Spurs and Structural Abnormalities
Bone spurs can irritate the bursae and tendons around the shoulder. This leads to bursitis. Structural issues, like osteophytes or irregular bones, can also cause bursitis. They do this by causing mechanical irritation.
Recognizing Shoulder Bursitis Symptoms
Knowing the signs of shoulder bursitis is key to getting the right treatment. We’ll look at the common symptoms and when you should see a doctor.
Pain Patterns and Characteristics
Pain is a main symptom of shoulder bursitis. It can feel sharp or dull and is usually near the bursa. Moving the shoulder can make the pain worse, which is common if you do the same motion a lot.
The pain might spread down your arm or hurt when you lie on your shoulder. The type of pain can change based on why you have bursitis. For example, if it’s from an infection, the pain is often more intense and comes with signs like redness and warmth.
Range of Motion Limitations
Shoulder bursitis can make it hard to move your arm or shoulder. Trying to lift your arm or rotate your shoulder might feel tough. This is because your body is trying to avoid pain, but it can also make your shoulder stiffer if not treated.
Visual and Physical Signs
You might see swelling, redness, and warmth if you have shoulder bursitis. Sometimes, the swelling is big enough to see. You might also feel sore when someone touches the area or notice you’re weaker because of the pain or stiffness.
| Symptom | Description |
| Pain | Sharp or dull pain around the affected bursa, exacerbated by movement |
| Reduced Range of Motion | Difficulty in lifting the arm or rotating the shoulder due to pain and inflammation |
| Visual Signs | Swelling, redness, and warmth around the affected area |
Diagnosis of Shoulder Bursitis
Healthcare providers look at many factors to figure out if you have shoulder bursitis.
Physical Examination Techniques
A detailed physical check is key in diagnosing shoulder bursitis. We check how well your shoulder moves and if it hurts. Palpation helps find tenderness or swelling.
We also check your shoulder muscles’ strength and look for signs of inflammation or infection.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies like X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans might be needed. They help see the bursae and the area around them.
An ultrasound is great for spotting fluid in the bursa. An MRI gives detailed views of soft tissues, helping to rule out other issues.
Differential Diagnosis from Other Shoulder Conditions
Distinguishing shoulder bursitis from other shoulder problems is important. This includes rotator cuff injuries or tendinitis.
We look at your history, symptoms, and what we find during the exam. Sometimes, more tests are needed to make sure it’s not something else causing your pain.
Treatment Approaches for Shoulder Bursitis
Dealing with shoulder bursitis needs a detailed treatment plan. Every patient is different, so we tailor our approach. This helps manage symptoms and aid in recovery.
Conservative Management Strategies
First, we try conservative methods to ease shoulder bursitis symptoms. This includes rest, ice, and avoiding activities that make it worse. Resting the shoulder is key to preventing more irritation and helping it heal.
Changing how you do things to avoid making it worse is also key. This might mean doing tasks differently or taking breaks to rest your shoulder.
Medications and Injections
If these steps don’t work, we might use medications or injections. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) help with pain and swelling. Sometimes, corticosteroid injections are used for stronger anti-inflammatory effects right where it hurts.
Physical Therapy Interventions
Physical therapy is essential for treating shoulder bursitis. It helps improve shoulder movement and strength. A physical therapist creates a plan to boost flexibility and strengthen muscles around the shoulder. This helps support the joint and prevent future problems.
- Range of motion exercises to maintain flexibility
- Strengthening exercises for the rotator cuff and other shoulder muscles
- Posture correction and body mechanics education
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
If other treatments don’t work, or if the bursitis is severe, surgery might be needed. This could include removing the inflamed bursa or other procedures to fix underlying issues.
Choosing surgery is a big decision. It’s important to talk about the pros and cons with a healthcare expert.
Prevention Strategies for Shoulder Bursitis
To prevent shoulder bursitis, we need to use several methods. This includes using the right techniques, making ergonomic changes, and exercising regularly. By doing these things, we can lower our chances of getting shoulder bursitis.
Proper Technique for Overhead Activities
It’s important to use the right technique when doing overhead activities. This means keeping the right posture, not overreaching, and moving smoothly. For those who do overhead tasks often, like athletes or workers, training on technique is very helpful.
Workplace Ergonomics
Improving workplace ergonomics is another key step. This means setting up workspaces to lessen shoulder strain, using ergonomic tools, and taking breaks to stretch. Employers can help a lot by checking ergonomics and making changes as needed.
Strengthening and Flexibility Exercises
Doing strengthening and flexibility exercises is key to a healthy shoulder. Exercises that strengthen the rotator cuff and nearby muscles help keep the shoulder stable. Stretching regularly also boosts flexibility and lessens muscle tightness.
Rest and Recovery Practices
It’s important to have rest and recovery practices to let the shoulder heal. This means getting enough rest, not pushing too hard, and using ice or heat to ease pain. By focusing on rest and recovery, we can avoid shoulder bursitis.
By adding these prevention steps into our daily lives, we can lower our risk of shoulder bursitis. This helps keep our shoulders healthy and working well.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into shoulder bursitis, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatments, and how to prevent it. Knowing the causes of shoulder bursitis is key to managing and preventing it.
Recognizing risks like repetitive motion, direct trauma, and systemic inflammation helps. Taking steps to avoid these can lower your chance of getting shoulder bursitis. Using proper techniques, improving ergonomics at work, and doing strengthening exercises can help a lot.
For those with shoulder bursitis, there are many treatment options. These range from non-surgical methods like medications and physical therapy to surgery for severe cases. Learning how to relieve shoulder bursitis pain is vital for a better life.
Understanding shoulder bursitis helps in managing it better. It’s important to focus on both treating and preventing it. This way, we can improve our care and work towards recovery.
FAQ
What is shoulder bursitis, and how does it occur?
Shoulder bursitis occurs when the bursae in the shoulder joint become inflamed. This can happen from doing the same motion over and over, getting hit directly, getting an infection, or having a condition that makes the body’s immune system attack itself.
What are the common symptoms of shoulder bursitis?
You might feel pain, have trouble moving your shoulder, see swelling, and feel tenderness in the area.
How is shoulder bursitis diagnosed?
Doctors will check you physically, use X-rays or MRI scans, and sometimes take fluid from the bursa to look for infection or other problems.
What are the treatment options for shoulder bursitis?
Treatment can include resting and icing the area, taking medicine like NSAIDs, doing physical therapy, and sometimes getting injections or surgery.
Can shoulder bursitis be prevented?
Yes, you can prevent it by doing activities correctly, keeping good posture, using ergonomic tools at work, and doing exercises to keep your muscles strong and flexible.
How do repetitive overhead movements contribute to shoulder bursitis?
Doing the same overhead movements over and over can irritate and inflame the bursae. This is common in sports players and people with jobs that require these movements.
What is the role of the rotator cuff in shoulder bursitis?
Injuries to the rotator cuff, like tears or tendonitis, can make the shoulder joint work differently. This extra stress can cause bursitis.
Can poor posture lead to shoulder bursitis?
Yes, bad posture can cause muscle imbalances and change how the shoulder moves. This can increase the risk of getting bursitis.
Are there any medical conditions that increase the risk of shoulder bursitis?
Yes, conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and autoimmune diseases can raise your risk. This is because they cause inflammation in the body.
How does aging affect the risk of developing shoulder bursitis?
As you get older, your tissues naturally wear down, calcium deposits can form, and you might move less. All these things can make you more likely to get bursitis.
What exercises can help prevent or manage shoulder bursitis?
Doing exercises that strengthen and stretch the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles can help prevent and manage bursitis.
References
- Bedi, A., & Rodeo, S. A. (2016). What is the role of biologics in rotator cuff injuries? Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 25(12), e387-e392. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5119682/



































