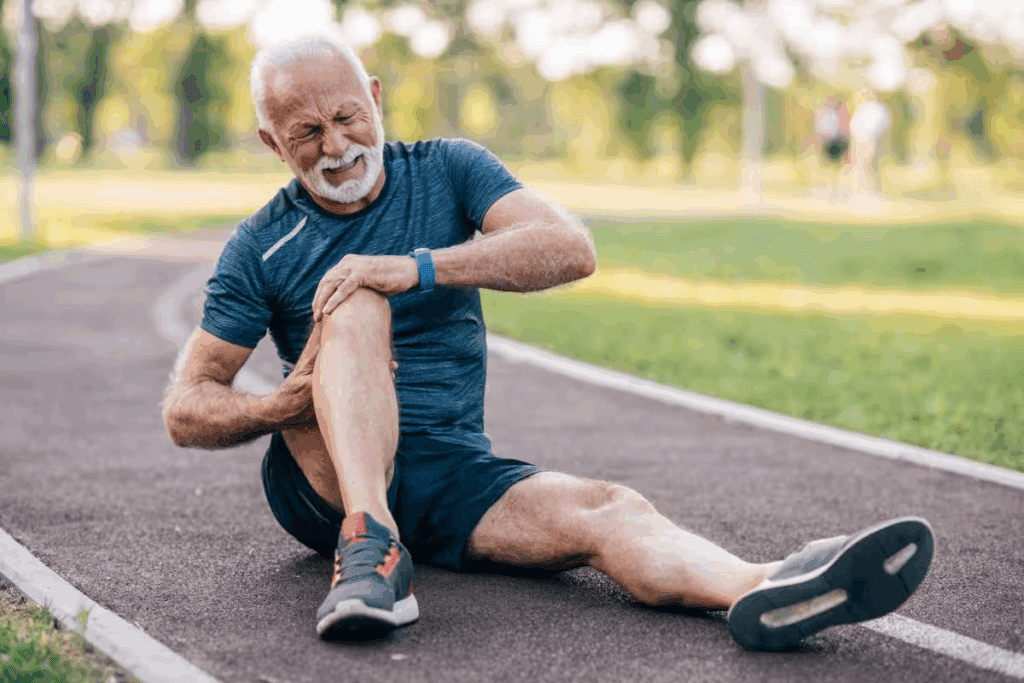
Bursitis affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant discomfort and mobility issues. It’s a condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae, fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints and reduce friction between bones, tendons, and skin.
When bursitis strikes, everyday activities become challenging. But incorporating walking into your routine can be beneficial. Walking is a low-impact exercise that can help improve joint mobility and reduce bursitis pain.
Understanding the effects of walking on bursitis enables individuals to make informed choices regarding their management strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Walking can help alleviate bursitis symptoms.
- Regular walking can improve joint mobility.
- Low-impact exercises like walking are beneficial for bursitis pain relief.
- Understanding the benefits of walking can help individuals manage their condition.
- Incorporating walking into your routine can reduce bursitis discomfort.
Understanding Bursitis: Causes and Symptoms
Bursitis is a common problem that happens when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction. The American College Health Association says students with bursitis may feel pain and have trouble moving. Knowing what causes and symptoms of bursitis is key to managing it well.
What is a Bursa and How Does it Function?
A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that cushions joints and reduces friction between bones, tendons, and skin. It helps joints move smoothly. But, if a bursa gets inflamed, it can cause pain and discomfort.
Common Types of Bursitis
There are many types of bursitis, each affecting different parts of the body. Some common ones include:
- Prepatellar bursitis, also known as housemaid’s knee, which affects the knee.
- Trochanteric bursitis, which affects the hip.
- Olecranon bursitis, which affects the elbow.
These types of bursitis usually happen from repetitive motion or direct blows to the area.
Recognizing Bursitis Symptoms
The symptoms of bursitis can vary based on where and how bad the inflammation is. Common signs include:
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area.
- Swelling or redness around the joint.
- Limited mobility or stiffness.
- Warmth or a burning sensation in the affected area.
Spotting these symptoms early is important for getting the right treatment and avoiding more problems.
The Science Behind Walking and Bursitis

Walking is a low-impact exercise that helps with bursitis. It reduces inflammation and improves joint mobility. This section explores the science behind walking’s benefits for bursitis sufferers.
How Movement Affects Inflamed Bursae
Movement is key to keeping joints healthy. When a bursa gets inflamed, moving it can help reduce swelling. Walking, a gentle exercise, boosts blood flow to the area, aiding in healing.
Mechanisms through which walking benefits inflamed bursae include:
- Enhanced circulation, which helps in reducing inflammation
- Promotion of synovial fluid circulation, aiding in joint lubrication
- Gentle stress on the joint, which can help in preventing further inflammation
Walking’s Impact on Joint Lubrication
Joint lubrication is vital for smooth movement and less friction between bones. Walking stimulates the production of synovial fluid, keeping joints lubricated.
“Exercise is a critical component of maintaining healthy joints. Low-impact activities like walking can significantly contribute to joint health by promoting lubrication and reducing stiffness.”
| Benefits of Walking | Impact on Joint Lubrication |
| Increased Synovial Fluid Production | Enhanced joint lubrication |
| Improved Circulation | Reduced joint stiffness |
| Gentle Joint Stress | Maintenance of healthy joint space |
Research on Low-Impact Exercise and Inflammation
Many studies have looked into low-impact exercise and inflammation. They show that walking can lower systemic inflammation and improve symptoms in those with inflammatory joint conditions.
A study found that regular walkers had lower inflammatory markers than non-exercisers.
Benefits of Walking for Bursitis Management
Walking offers many benefits for managing bursitis. It improves blood flow, strengthens muscles, helps with weight control, and boosts joint mobility. These advantages help ease bursitis symptoms and improve joint health.
Improved Circulation and Healing
Walking boosts blood circulation, which is key for healing inflamed bursae. It brings oxygen and nutrients to damaged areas, aiding recovery. Increased blood flow also helps in reducing inflammation, a major factor in bursitis.
Muscle Strengthening Around Affected Joints
Walking strengthens muscles around joints with bursitis. This support reduces strain on the bursae. Stronger muscles also help in stabilizing the joints, lowering the risk of further irritation.
Weight Management and Reduced Joint Pressure
Walking helps manage weight, which is vital for reducing joint pressure. Excess weight can worsen bursitis symptoms by increasing joint stress. By walking, individuals can keep their weight in check and reduce this stress.
Enhanced Joint Mobility and Function
Walking keeps joints lubricated and flexible, improving mobility. This mobility helps maintain functional ability, making daily activities easier. Enhanced joint function also reduces stiffness, a common issue for bursitis sufferers.
| Benefits | Description | Impact on Bursitis |
| Improved Circulation | Enhanced blood flow promotes healing | Reduces inflammation and promotes recovery |
| Muscle Strengthening | Strengthens muscles around affected joints | Provides additional support and stability to joints |
| Weight Management | Aids in maintaining a healthy weight | Reduces pressure on joints, alleviating symptoms |
| Enhanced Joint Mobility | Improves joint lubrication and flexibility | Maintains functional ability and reduces stiffness |
Potential Risks: When Walking May Worsen Bursitis
Walking is usually good for bursitis, but sometimes it can make it worse. People with bursitis should know these risks to manage their condition well.
Signs Walking is Aggravating Your Condition
One key sign is more pain when or after walking. If your symptoms get worse, it’s time to change your walking plan.
- Increased pain or discomfort
- Swelling or redness around the affected area
- Reduced mobility or stiffness
Watching for these signs and adjusting your walks is important. Ignoring them can make things worse.
Acute vs. Chronic Bursitis Considerations
Knowing if you have acute or chronic bursitis helps set the right walking plan. Acute bursitis comes on suddenly and is very painful. Chronic bursitis is ongoing and less severe.
Acute Bursitis: Be careful with walking. Start with very gentle, short walks.
Chronic Bursitis: Regular, gentle walks help keep joints moving and reduce stiffness. But don’t overdo it.
Understanding Your Pain Threshold
Finding the right balance is key when walking with bursitis. You want to exercise enough to keep joints healthy but not too much to hurt yourself.
Overtraining Pitfalls to Avoid
Starting a new walking routine can lead to overtraining, which is bad for bursitis. Increase the walk’s intensity and length slowly to avoid making things worse.
- Start with short walks and gradually increase the distance.
- Monitor your body’s response and adjust your routine as needed.
- Make sure to include rest days for your joints to heal.
Knowing these risks and how to avoid them helps people with bursitis walk safely and manage their condition.
Walking and Hip Bursitis: Special Considerations
Walking can be tricky when you have hip bursitis. It’s important to know how to walk without making it worse. Hip bursitis, like trochanteric bursitis, can change how you walk and move.
Trochanteric Bursitis and Gait Mechanics
Trochanteric bursitis is when the bursa near the femur’s greater trochanter gets inflamed. This can mess up your walking, making it abnormal and stressful for the affected area. It’s key to understand how it affects your walk to find ways to lessen its impact.
Gait analysis can spot any walking issues that might be causing pain. By tweaking your walk, you can ease the pressure on the inflamed bursa.
Recommended Walking Modifications
To help with hip bursitis while walking, try these changes:
- Shorten your stride to lessen hip joint stress
- Avoid long strides to prevent making it worse
- Take regular breaks to rest and stretch
- Use trekking poles for extra support, if needed
Supporting Exercises for Hip Stability
Strengthening the hip muscles can offer more support and stability. This can help ease some of the pain from hip bursitis. Try these exercises:
| Exercise | Target Muscle | Benefit |
| Clamshell Exercise | Gluteus Medius | Improves hip stability |
| Side-Leg Raises | Gluteus Medius, Tensor Fasciae Latae | Strengthens hip abductors |
| Glute Bridges | Gluteus Maximus | Enhances hip extension strength |
Adding these exercises to your routine can boost hip stability. This might help reduce hip bursitis symptoms.
Walking with Knee Bursitis: What You Need to Know
Walking with knee bursitis needs careful planning to manage pain and avoid more irritation. Knee bursitis makes walking painful because of the swelling around the knee joint.
Prepatellar and Pes Anserine Bursitis Concerns
Knee bursitis includes several types, like prepatellar and pes anserine bursitis. Prepatellar bursitis is at the front of the knee, causing pain and swelling. Pes anserine bursitis is on the lower inner knee, causing pain when walking or climbing stairs.
Prepatellar Bursitis: This condition is linked to kneeling often. To manage it, avoid direct pressure on the knee and use knee pads when kneeling.
Pes Anserine Bursitis: It’s common in athletes and those who run or cycle a lot. Treatment includes doing less of these activities and doing exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee.
Adjusting Stride Length and Cadence
Changing your walking stride can help with knee bursitis. A shorter stride puts less stress on the knee. Walking faster can also spread out the impact better.
- Shorten your stride to reduce knee joint stress.
- Increase your cadence to improve walking efficiency.
- Avoid overstriding, which can exacerbate knee pain.
Supportive Measures for Knee Protection
Changing how you walk is just one part of protecting your knee. Using knee sleeves or braces can also help by adding support and stability.
| Supportive Measure | Description | Benefit |
| Knee Sleeves | Provides compression and warmth | Reduces pain and inflammation |
| Knee Braces | Offers additional stability | Supports the knee joint |
| Orthotics | Corrects foot alignment | Reduces stress on the knee |
The Walking and Bursitis Connection: Finding the Right Balance
Walking can help with bursitis, but finding the right balance is key. It’s important to know when to walk and when to rest. This balance helps avoid making the condition worse.
Determining Your Optimal Activity Level
Knowing your optimal activity level is vital for managing bursitis. It means understanding your limits and slowly increasing your walks. This way, you challenge yourself without hurting your joints too much.
- Start with short walks and monitor your body’s response.
- Gradually increase your walking distance and intensity.
- Pay attention to any signs of increased pain or discomfort.
Progressive Loading Principles
Progressive loading means slowly increasing demands on your body to build strength. When walking with bursitis, it’s important to do this carefully.
Key considerations for progressive loading include:
- Gradually increasing your walking distance.
- Adjusting your walking intensity.
- Incorporating varied terrain to challenge different muscle groups.
Listening to Your Body’s Signals
Listening to your body is key when walking with bursitis. It’s important to know the difference between normal discomfort and pain that means you’re doing too much.
Pay attention to:
- Increased pain during or after walking.
- Swelling or redness around the affected joint.
- Changes in your gait or walking pattern.
By paying attention to these signs and adjusting your walks, you can keep your joints healthy.
Creating a Safe Walking Program for Bursitis Relief
Creating a safe walking program is key for those with bursitis. It helps ease symptoms and boosts joint health. A good program can make a big difference.
Starting Slow: The First Two Weeks
Start slow when you begin a walking program for bursitis. Begin with short walks of 10-15 minutes, 2-3 times a week. This lets your joints get used to the exercise.
Watch how your body reacts to walking in the first two weeks. Notice any pain or stiffness changes. If it hurts more, cut back on walking time or frequency.
Progressive Distance and Intensity Guidelines
After two weeks, you can walk further and faster. Try to walk 5-10 minutes more each week. This helps strengthen muscles without stressing joints too much.
Make your walks more interesting by changing the pace. Try brisk walking for a bit, then slow down. This improves your heart health and joint movement.
| Week | Walking Duration (minutes) | Frequency (days per week) |
| 1-2 | 10-15 | 2-3 |
| 3-4 | 15-20 | 3-4 |
| 5-6 | 20-25 | 4-5 |
Incorporating Rest Days Strategically
Rest days are important in a walking program for bursitis. They help your joints heal and prevent injuries. Try to have at least one or two rest days a week, more in the beginning.
On rest days, do something easy like stretching or swimming. These activities keep you flexible and promote blood flow without straining your joints too much.
Proper Walking Techniques to Minimize Bursitis Pain
Walking right is key for those with bursitis. It helps cut down on pain and keeps you moving. Focus on good posture, how you step, and breathing to ease bursitis symptoms.
Posture and Alignment Fundamentals
Walking with the right posture is vital for those with bursitis. It means keeping your head up, shoulders down, and body straight. Good posture spreads out your weight, easing pressure on sore spots. To do this, remember to:
- Keep your ears in line with your shoulders
- Use your core to support your back
- Avoid slouching or leaning forward
Stride Mechanics for Reduced Joint Stress
Your walking style, or gait, affects bursitis pain. Optimizing stride mechanics means taking strides that are just right, not too long or too short. This reduces stress on your joints. To do this, aim for:
- Mid-length strides that feel natural
- Avoid overstriding to prevent jarring impacts
- Smooth, fluid movements
Breathing and Relaxation While Walking
Breathing and relaxing can also help with bursitis pain. Deep, steady breathing relaxes muscles and makes walking better. Try to:
- Use deep diaphragmatic breathing to calm down
- Relax your shoulders and arms while walking
- Stay loose, avoiding tension in sore areas
By using these walking tips every day, people with bursitis can lessen pain and move better.
Walking Surfaces and Environments for Bursitis Management
Different terrains and walking environments can either help or hurt bursitis symptoms. The surface you walk on is key to managing bursitis well.
Impact of Different Terrains on Joints
The terrain you walk on affects your joints’ stress and impact. Hard surfaces like concrete can make bursitis worse. But softer surfaces, like grass or a treadmill, are gentler on your joints.
Terrain Types and Their Effects:
- Hard Surfaces (Concrete, Asphalt): Can increase the impact on joints, potentially worsening bursitis symptoms.
- Soft Surfaces (Grass, Dirt Trails): May reduce the impact on joints, making walking more comfortable.
- Inclined or Uneven Surfaces: Can alter gait mechanics, potentially putting additional stress on bursae.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Walking Considerations
Indoor and outdoor walking have their own benefits and drawbacks for bursitis. Treadmills offer controlled conditions and softer surfaces, which is good. Outdoor walking, with its varied terrains, can strengthen the muscles around the affected joints.
Key Considerations:
- Weather Control: Indoor walking is not affected by weather, which is a big plus.
- Surface Variety: Outdoor walking offers a range of surfaces and terrains, which can help in strengthening the muscles.
- Scenic Variety: Outdoor environments can provide mental health benefits due to scenic variety.
Weather Factors and Joint Health
Weather conditions can also impact bursitis management. Some people find that certain weather conditions make their symptoms worse.
Weather-Related Considerations:
- Cold Weather: May increase stiffness and pain in some individuals.
- High Humidity: Can potentially increase inflammation.
- Barometric Pressure Changes: Some people report increased pain with changes in barometric pressure.
Understanding how different walking surfaces and environments affect your bursitis is key to managing it well. By choosing the right terrain and being mindful of weather, you can reduce discomfort and enjoy the benefits of walking for bursitis relief.
Choosing the Right Footwear for Bursitis
For those with bursitis, the right shoes can really help. Shoes that support and cushion can ease pain and help you move better.
Key Features in Supportive Walking Shoes
When picking walking shoes for bursitis, look for these important features:
- Adequate Arch Support: Good arch support lessens strain on the joints.
- Cushioning: Cushioning in the midsole and forefoot absorbs shock, easing bursae pain.
- Comfortable Fit: A comfy fit with room for toes prevents more irritation.
- Stability: Shoes that are stable prevent too much movement, which can make bursitis worse.
Insoles and Orthotics Considerations
Using insoles or orthotics can also boost comfort and support. Custom orthotics, in particular, can be made to fit your foot’s unique needs.
It’s key to talk to a healthcare expert to find the best insole or orthotic for you.
When to Replace Your Walking Shoes
It’s important to replace your walking shoes regularly. They should be swapped out every 300 to 500 miles or when you notice wear.
- Check your shoes often for wear.
- Notice if they feel less comfortable or supportive.
- Keep a log of how far you walk to know when to replace them.
Choosing the right shoes and keeping them in good shape can greatly improve your walking. It can also reduce discomfort for those with bursitis.
Pre-Walking Warm-Up Exercises for Bursitis Sufferers
Gentle warm-up exercises can help those with bursitis get ready for walking. They prepare the joints and muscles, reducing the chance of making bursitis worse. These exercises also improve how well you can walk.
Gentle Joint Mobilization Techniques
Mobilizing joints gently is a good way to get them ready for walking. It involves small movements that boost blood flow and cut down on stiffness in the affected areas.
- Ankle circles: Rotate your ankles in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions to loosen the ankle joint.
- Knee bends: Slightly bend your knees to mobilize the knee joint and prepare the surrounding muscles.
- Hip rotations: Gently rotate your hips to improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
Dynamic Stretching Sequence
Dynamic stretching moves your joints through a range of motion while keeping your muscles active. It boosts flexibility and lowers the risk of injury.
- Leg swings: Stand with your feet hip-width apart and swing one leg forward and backward, then switch to the other leg.
- Hip flexor stretches: Stand with your feet together, take a large step forward with one foot, and lower your body slightly to stretch the front of your hip.
- Calf raises: Stand on the edge of a step or curb with your heels hanging off, raise up onto your tiptoes, and then lower back down.
| Exercise | Repetitions | Benefits |
| Ankle Circles | 5-10 repetitions | Improves ankle mobility and reduces stiffness |
| Leg Swings | 10-15 repetitions per leg | Enhances hip flexibility and prepares legs for walking |
| Calf Raises | 15-20 repetitions | Strengthens calf muscles and improves ankle mobility |
Activation Exercises for Supporting Muscles
Activation exercises engage the muscles that support the joints affected by bursitis. Strengthening these muscles can make the joints more stable and reduce discomfort when walking.
- Glute bridges: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground, lift your hips towards the ceiling to engage your glutes.
- Core exercises: Engage your core muscles by drawing your belly button towards your spine, holding for a few seconds, and releasing.
Adding these warm-up exercises to your routine can help prepare your joints and muscles for walking. This might lower the risk of bursitis flare-ups.
Post-Walking Recovery Strategies
After walking, it’s key to use good recovery methods to ease bursitis symptoms. These strategies help cut down inflammation, ease pain, and boost joint health.
Effective Cooling Down Methods
Cooling down after walking is vital. It helps slow down your heart rate and breathing. This can lessen muscle soreness and boost flexibility.
- Static stretches for major muscle groups, such as hamstrings, quadriceps, and calf muscles.
- Short walks at a leisurely pace to gradually decrease intensity.
- Breathing exercises to help relax and reduce stress.
Ice and Heat Application Guidelines
Ice and heat can both help with bursitis symptoms. Ice is used to cut down inflammation, while heat relaxes muscles and boosts blood flow.
“The application of ice or heat should be done carefully, as both can cause skin irritation if not used properly.”
Here are some guidelines for use:
- Use ice for 15-20 minutes, right after activity.
- Apply heat for 15-20 minutes, before activity or at night.
- Always wrap ice or heat in a towel to protect the skin.
Gentle Stretching for Recovery
Gentle stretching after walking can improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension. Focus on stretches for the areas around the affected bursae.
For trochanteric bursitis, stretches for the hip and gluteal area are very helpful.
- Standing hamstring stretch.
- Lying hip flexor stretch.
- Calf stretch against a wall.
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Your Walking Routine
Starting a walking routine for bursitis is exciting. But, tracking your progress is key to getting the best results. It helps you see what works and what doesn’t, so you can improve your walking plan.
Monitoring Pain Levels and Joint Response
It’s important to watch your pain and how your joints react. Use a pain scale to rate your pain before, during, and after walking. This helps you spot patterns and what might be causing pain.
- Note any changes in pain intensity or duration
- Record the time of day when pain is most pronounced
- Observe any correlations between walking and pain levels
By keeping an eye on these things, you can tweak your walking routine to better handle your bursitis.
Using Activity Journals and Apps
Activity journals or apps can really help you track your progress and manage bursitis. They let you log details about your walks, like how far you go, how long you walk, and how hard you walk.
Some popular options include:
- Fitbit
- MyFitnessPal
- Strava
- Google Fit
When picking an app, think about how easy it is to use, if you can export your data, and if it tracks important stuff like steps and heart rate.
When and How to Modify Your Program
Changing your walking program based on your progress is vital for getting better. Look for trends in your data that show it’s time to make changes.
If you see:
- Increasing pain or discomfort
- Plateaus in progress
- Changes in your overall health or fitness level
It’s time to tweak your routine. This could mean walking more often, harder, or longer. But, always do it slowly to avoid hurting your joints.
By keeping track of your progress and making smart changes to your walking routine, you can manage your bursitis better. And, you’ll get the most out of walking.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
It’s important to know when you need to see a doctor for bursitis. While walking can help, there are times when you need a doctor’s help.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Knowing the signs that mean you need a doctor is key. Look out for:
- Severe pain that makes it hard to do daily tasks
- Swelling or redness around the joint
- Warmth or tenderness when you touch it
- Reduced mobility or stiffness in the joint
- Fever with bursitis symptoms
Diagnostic Procedures for Bursitis
When you see a doctor, they will check you physically. They might also do tests to find out if you have bursitis. These tests include:
- X-rays to check for fractures
- Ultrasound to see the bursa and tissues around it
- MRI for detailed soft tissue images
Getting a correct diagnosis is important for the right treatment.
Treatment Options Beyond Self-Management
Depending on your bursitis, you might need more than just self-care. Treatment options can be:
- Physical therapy to move the joint better and strengthen muscles
- Medications like NSAIDs to lessen inflammation and pain
- Corticosteroid injections to fight inflammation
- Aspirating the bursa to take out extra fluid
- Surgery if other treatments don’t work
A doctor will decide the best treatment for you.
Knowing when to get medical help and what treatments are available helps you manage bursitis better. This improves your life quality.
Conclusion: Integrating Walking into Your Bursitis Management Plan
Walking can be a key part of managing bursitis. Knowing what causes and symptoms of bursitis are helps a lot. Adding walking to your treatment plan can ease pain and boost joint health.
Creating a walking plan that fits you, wearing the right shoes, and using good walking techniques are important. It’s also key to rest and recover well. Always watch how you’re doing and change your plan if needed. If you’re unsure, talk to a doctor.
Walking helps with better blood flow, stronger muscles, and more joint movement. This approach can help manage bursitis symptoms better. It can also make life feel better overall.
FAQ
What is bursitis and how does it affect the body?
Bursitis is when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction. It leads to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the affected joint.
Can walking help alleviate bursitis symptoms?
Yes, walking can help manage bursitis symptoms. It improves circulation, strengthens muscles, and increases joint mobility. These benefits can reduce inflammation and ease pain.
How can I modify my walking technique to minimize bursitis pain?
To reduce bursitis pain while walking, keep a proper posture. Use a heel-to-toe stride and avoid overstriding. Adjust your stride length and cadence to lessen stress on the joint.
What type of footwear is best for walking with bursitis?
Wear supportive shoes with good arch support and cushioning for walking with bursitis. Consider insoles or orthotics for extra support and stability.
How can I warm up before walking with bursitis?
Start with gentle joint mobilization before walking with bursitis. Then, do dynamic stretching to loosen muscles and improve flexibility. Activation exercises can prepare the muscles for walking.
What are some post-walking recovery strategies for bursitis?
Cool down with gentle stretching after walking with bursitis. Apply ice or heat to the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. Gentle stretching can also improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
How can I track my progress and adjust my walking routine for bursitis management?
Monitor your pain levels, joint response, and mobility to track progress. Use activity journals or apps to track your progress. Modify your program as needed to avoid worsening the condition.
When should I consult a healthcare professional for bursitis?
Seek a healthcare professional if you have severe pain, swelling, or limited mobility. If symptoms worsen over time, get professional help. They can guide you on the best treatment, including physical therapy, medication, or other interventions.
Can walking help prevent bursitis?
Walking can’t guarantee prevention, but regular exercise helps. It keeps joints mobile, strengthens muscles, and reduces bursitis risk.
How can I balance walking with rest to manage bursitis effectively?
Balance walking with rest by listening to your body. Avoid overtraining and include rest days. This helps prevent worsening the condition and allows for recovery.
Are there any specific considerations for walking with hip or knee bursitis?
Yes, modify your gait mechanics when walking with hip or knee bursitis. Use supportive measures like orthotics. Incorporate exercises to strengthen muscles and improve joint stability.
Reference
- Gomez, L. P. (2024). Greater trochanteric pain syndrome. StatPearls. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557433/



































