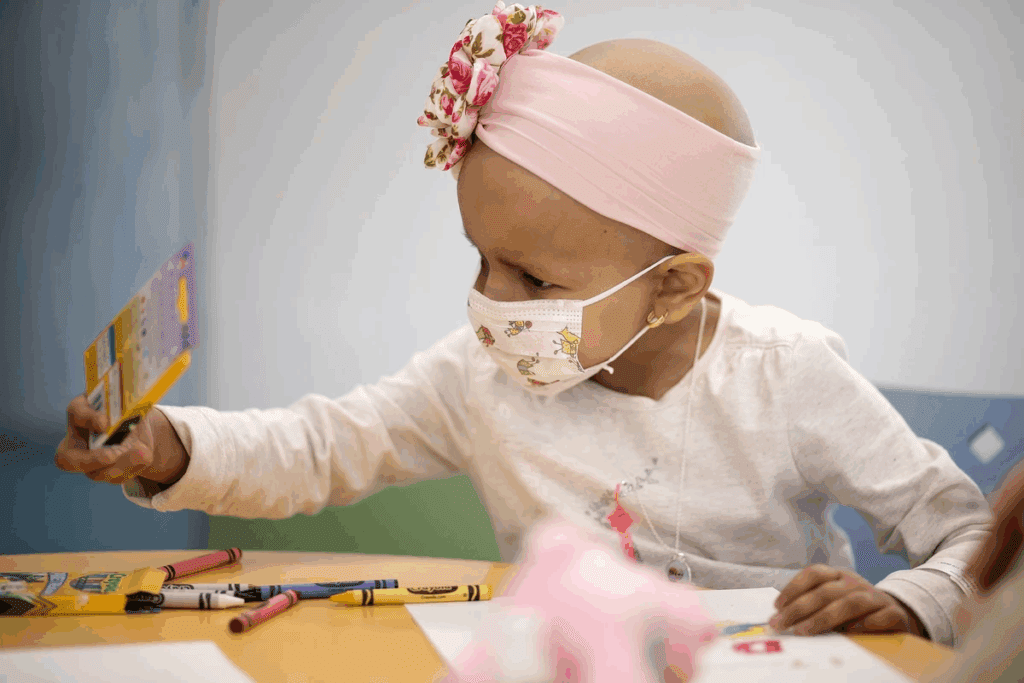
Leukemia is a harsh reality for many families. It is a big part of pediatric cancer cases. Recent statistics show it’s the most common cancer in kids. This makes it a key area for doctors and researchers to focus on.
We know how important it is to understand pediatric cancer types. This helps us give better care and support. Leukemia in children, like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), is a big worry. It’s common and affects kids a lot.
Looking into childhood cancer diagnosis shows us how vital awareness and early detection are. We aim to give full info and support to families dealing with leukemia and other pediatric cancers.
Key Takeaways
- The most common cancer diagnosed in children is leukemia.
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is the most prevalent type of leukemia in children.
- Understanding pediatric cancer types is key for effective care and support.
- Early detection and awareness are vital in fighting childhood cancer.
- Comprehensive support for families affected by leukemia is essential.
Understanding Childhood Cancer
Childhood cancer is a serious illness that needs quick and precise treatment. We will look at the different types of cancer in kids, the latest statistics, and why finding cancer early is key.
Definition and Types of Childhood Cancer
Childhood cancer happens in kids under 20. The most common cancers are leukemia, brain tumors, and lymphomas. Leukemia, like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), is the most common.
Other cancers in kids include neuroblastoma, Wilms tumor, and retinoblastoma. Each cancer type needs its own treatment plan.
Key Statistics on Childhood Cancer Rates
Recent pediatric cancer statistics show that childhood cancer is rare but serious. Here are some important facts:
| Type of Cancer | Percentage of Total Childhood Cancers | Survival Rate |
| Leukemia | 30% | 90% |
| Brain Tumors | 25% | 80% |
| Lymphomas | 10% | 85% |
| Neuroblastoma | 6% | 80% |
Importance of Early Detection
Finding cancer early is vital for better survival rates and less long-term health problems. We stress the need to spot early symptoms and get medical help fast.
Look out for signs like constant tiredness, unexplained weight loss, and unusual bruises or bleeding. Parents and caregivers should watch for these signs and talk to doctors if worried.
By knowing about childhood cancer and its types, we can aim for earlier diagnosis and better treatments. Our goal is to give full care and support to kids and families dealing with this disease.
Most Common Childhood Cancer Types
Types of pediatric cancer
It’s key to know the common childhood cancers for early treatment. Childhood cancer includes many types. Knowing the most common can help improve treatment results.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is the top childhood cancer. It’s a blood cancer that affects the bone marrow. Symptoms include tiredness, pale skin, and often getting sick.
Treatment for ALL usually involves chemotherapy. Sometimes, a bone marrow transplant is needed.
Neuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma starts in nerve tissue in young kids. It often begins in the adrenal glands. Symptoms vary, like a neck or belly lump, or eye issues.
Wilms Tumor
Wilms Tumor, or nephroblastoma, is a kidney cancer in kids. It causes a swelling in the belly. Early treatment with surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation can be very effective.
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rare eye cancer in young children. It starts in the retina. Early signs are a white glow in the pupil or crossed eyes.
Treatment aims to save the eye and vision. It may include chemotherapy, laser therapy, or surgery.
Knowing about these common childhood cancers is vital. Awareness and early detection are key. Understanding each type helps support kids and families.
Symptoms and Warning Signs

Childhood cancer symptoms can vary a lot. They range from common signs like tiredness to specific signs like swelling or pain. It’s key to spot these symptoms early for quick diagnosis and treatment.
General Symptoms of Childhood Cancer
While each cancer type has its own symptoms, there are some common signs. Parents and caregivers should watch out for these. These include:
- Persistent fatigue or weakness that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Unexplained weight loss or loss of appetite.
- Pain or swelling in the abdomen, bones, or joints.
- Fever or infections that recur or won’t go away.
- Bruising or bleeding easily, or petechiae (small red spots on the skin).
These symptoms can mean different things, including childhood cancer. If your child keeps showing these signs, see a doctor right away.
Specific Symptoms for Common Types
Different cancers show different symptoms. Knowing these can help spot the disease early.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), the most common childhood cancer, often shows symptoms like:
- Bone and joint pain.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Enlarged spleen or liver.
Neuroblastoma, another common type, may cause symptoms such as:
- A lump or swelling in the neck, chest, or abdomen.
- Protruding eyes or eyelid swelling.
- Dark circles around the eyes.
Knowing these specific symptoms can help catch the disease early. If your child shows any unusual signs, get medical help fast.
Risk Factors for Childhood Cancer
Risk factors for childhood cancer
It’s important to know the risk factors for childhood cancer to catch it early. While we don’t know all the causes, research has found some key factors. These can increase a child’s chance of getting cancer.
Genetic Factors
Genetic mutations are a big part of childhood cancer. Some genetic conditions, like Down syndrome, raise the risk of certain cancers. We’ll look at how genetics play a role in risk.
- Genetic predispositions: Inherited genetic mutations can greatly raise the risk of childhood cancer.
- Family history: A family history of cancer can help, but it’s not the only factor.
- Genetic syndromes: Some syndromes, like Li-Fraumeni syndrome, are linked to a higher cancer risk.
Environmental Influences
Environmental exposures are also key in understanding childhood cancer risk. Being exposed to ionizing radiation, certain chemicals, and other hazards can up the risk.
- Ionizing radiation: Exposure to ionizing radiation, like from X-rays or nuclear fallout, is a known risk factor.
- Chemical exposures: Being exposed to chemicals like pesticides or heavy metals can raise the risk of childhood cancer.
- Paternal smoking: Some studies show that paternal smoking around conception time may increase childhood cancer risk.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic status also affects childhood cancer risk and outcomes. Things like healthcare access, socioeconomic status, and where you live can change diagnosis and treatment.
- Access to healthcare: Kids from families with less healthcare access might face delays in diagnosis and treatment.
- Socioeconomic status: Lower socioeconomic status is linked to a higher risk of certain childhood cancers and worse outcomes.
- Geographic location: Childhood cancer rates can differ by location, possibly due to environmental factors.
Knowing these risk factors helps us work towards early detection and prevention. This can improve outcomes for kids with cancer.
Diagnosis Process for Childhood Cancer
We use many tests to find childhood cancer accurately. Finding childhood cancer involves several steps. These include first checks, advanced imaging, and biopsies.
Initial Assessments and Tests
When a child shows signs of cancer, we start with the first steps. We look at their medical history and do a physical check. Complete Blood Counts (CBC) and blood chemistry tests are also done.
For example, a CBC can show if there are too many or too few blood cells. This could mean leukemia or other cancers. Blood chemistry tests check for substances from cancer cells or organ problems.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is key in finding childhood cancer. We use different methods to see the tumor and how big it is. Common methods include:
- X-rays: To find bone issues or tumors.
- Ultrasound: To look at internal organs and find tumors.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans: To get detailed images of the body.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): To see soft tissues and organs clearly.
Role of Biopsy
A biopsy is key to confirm cancer. It takes a sample from the tumor. Then, it’s checked under a microscope for cancer cells. There are many types of biopsies.
The biopsy is very important. It not only confirms cancer but also tells us what kind. This helps us plan the right treatment.
| Diagnostic Tool | Description | Use in Childhood Cancer Diagnosis |
| CBC and Blood Chemistry Tests | Tests to analyze blood components and chemistry. | Identify abnormalities suggestive of cancer. |
| Imaging Techniques (X-rays, Ultrasound, CT, MRI) | Various imaging modalities to visualize internal structures. | Locate tumors and assess their extent. |
| Biopsy | Removal and examination of tissue or cells. | Confirm cancer presence and type. |
Treatment Options for Childhood Cancer
There are many ways to treat childhood cancer, each one suited for different types and stages. The right treatment depends on the cancer type, its stage, and the child’s health.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a key treatment for many childhood cancers. It uses drugs to kill or slow cancer cells. Chemotherapy for pediatric cancer is often combined with surgery or radiation.
Some common chemotherapy drugs include:
- Vincristine
- Doxorubicin
- Cyclophosphamide
- Methotrexate
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy for childhood cancer uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It’s carefully planned to target cancer while protecting healthy tissues.
Radiation therapy can be used alone or with other treatments. It’s effective for cancers that are sensitive to radiation, like some brain tumors or lymphomas.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions for pediatric cancer involve removing tumors or cancerous tissues. Surgery can be the main treatment or used with chemotherapy and radiation.
The goal is to remove as much tumor as possible while keeping healthy tissues and organs safe.
Emerging Therapies
New therapies in childhood cancer are showing great promise. These include:
- Immunotherapy, which uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer
- Targeted therapy, which targets specific molecules involved in cancer growth
- Gene therapy, which aims to correct genetic mutations that cause cancer
These emerging therapies offer hope for children with cancer. They could lead to more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Survivor Stories: Hope and Resilience
Childhood cancer survivors show us the power of strong support systems. Their courage and strength inspire us all. They and their families face many challenges during cancer treatment.
Personal Accounts from Childhood Cancer Survivors
Survivors share their stories, talking about the tough times and the help they got. They often mention the emotional support from loved ones and the help of medical teams. These stories show how important a good support system is.
Some survivors talk about how they built emotional strength during treatment. This strength helped them deal with the physical and mental effects of cancer. They also value the support from others who have been through the same thing.
- Survivors often thank their families for emotional support and keeping them hopeful.
- Friends and the community also play big roles in their recovery. They offer practical help and friendship.
- Medical teams are praised for their skill and caring. Their help greatly affects survivors’ treatment results.
Impact of Support Systems and Resources
The role of support systems and resources in helping survivors is huge. Having access to good care, support, and education improves their lives a lot. A strong support system is key in helping them through cancer treatment and after.
Some important resources include:
- Support Groups: They connect survivors with others who have faced similar issues.
- Counseling Services: They offer emotional and psychological help to survivors and their families.
- Educational Programs: They help survivors get back into school and social life.
We share these stories to inspire hope and resilience in those facing cancer. We aim to provide top-notch healthcare and support for international patients. We believe a caring and supportive environment is key to their recovery.
Long-Term Effects of Childhood Cancer Treatment
Surviving childhood cancer is just the start. Many survivors face long-term effects from their treatment. It’s key to understand these effects to give them the best care.
Physical Health Impacts
Childhood cancer treatment can harm physical health long-term. Survivors might deal with:
- Cardiac problems from some chemotherapies or radiation
- Secondary cancers from radiation or chemotherapy
- Endocrine disorders affecting growth and development
- Neurological impairments, like cognitive deficits or hearing loss
Regular follow-up care is vital to manage these effects. Survivors should work with their healthcare providers to create a care plan.
Psychological and Emotional Outcomes
The psychological and emotional impacts of childhood cancer treatment are significant. Survivors may face:
- Anxiety and depression
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Social and emotional challenges, including peer relationship issues
Support from family, friends, and mental health professionals is essential. We encourage survivors to find resources and support groups for emotional recovery.
Educational Challenges
Childhood cancer survivors may also face educational challenges. These can include:
- Cognitive deficits affecting learning and memory
- Missed school time, leading to catching up difficulties
- Special educational needs that require accommodations
We support individualized educational plans for survivors. Collaboration between healthcare providers, educators, and families is vital to address these challenges.
Understanding the long-term effects of childhood cancer treatment helps support survivors. It’s important for healthcare providers, families, and survivors to be aware of these challenges. Working together can help mitigate them.
Resources for Families Affected by Childhood Cancer
When a child gets cancer, the whole family is affected. They need a strong support system. Families facing childhood cancer need many resources to get through it.
National Cancer Organizations
National cancer groups are key in helping families. They offer support, info, and help families speak up. The American Cancer Society and CureSearch for Children’s Cancer are examples. They help with treatment info, money help, and emotional support.
These groups fund research and give out educational materials. They also help families connect and advocate for policies that help kids with cancer.
Online Support Groups
Online groups are a big help for families with childhood cancer. Sites like CureSearch and the Childhood Cancer Support Community are great. They let families share their stories and find support.
These online places have lots of info on treatments and ways to cope. They also offer emotional support to families who can’t get to in-person groups.
“The online support group was a lifeline for us. It connected us with others who understood what we were going through.” – A parent’s testimonial
Financial Aid and Assistance Programs
Childhood cancer treatment can be very expensive. But, there are programs to help with the costs.
- The Pediatric Cancer Research Foundation helps with treatment, travel, and staying costs.
- The Cancer Financial Assistance Coalition has a list of groups that offer financial help to cancer families.
These programs are very important. They help families get the care their kids need without losing everything financially.
With these resources, families can get the support they need. This makes it easier to face the challenges of childhood cancer.
Current Research and Advancements
Childhood cancer research is at a critical point. Studies and clinical trials are leading to better patient care. We’re seeing big changes in how we treat childhood cancer, thanks to new research and tech.
Recent Breakthroughs in Treatment
Recent years have brought remarkable breakthroughs in treating childhood cancer. Targeted therapies are a big step forward. They offer more precise treatment with fewer side effects.
Immunotherapy is another promising area. It uses the immune system to fight cancer. This approach is showing great promise.
Advances in genomic medicine are also exciting. Genetic info helps tailor treatments to each patient. This personalized care is improving survival rates and reducing treatment side effects.
Importance of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are crucial for new treatments in childhood cancer. They test new therapies’ safety and effectiveness. This data helps doctors make better treatment choices.
By joining clinical trials, families get access to new treatments. This is vital for advancing pediatric oncology.
Future Directions in Childhood Cancer Research
Looking ahead, collaboration and innovation will drive progress. We expect more work in gene editing, CAR-T cell therapy, and other new methods.
We’re dedicated to supporting ongoing research. Our goal is to ensure every child with cancer gets the best care. By understanding and treating childhood cancer better, we can help kids all over the world.
Advocacy and Awareness Initiatives
We know how key advocacy and awareness are in the battle against childhood cancer. Non-profit groups are essential in helping families and spreading the word about pediatric cancer.
Supporting Families and Promoting Awareness
Groups focused on childhood cancer offer vital support. They provide emotional help, financial aid, and educational tools. These resources help families deal with the tough times of a cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Campaigns and Events
Campaigns raise awareness about childhood cancer. They teach people about the disease, its signs, and why early detection is key. Joining or starting events can help change lives for kids with cancer.
Getting Involved
There are many ways to help in the fight against childhood cancer. You can volunteer with non-profits or use social media to spread the word. Together, we can build a supportive community for kids with cancer and their families.
FAQ
What is the most common type of cancer diagnosed in children?
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is the most common cancer in kids. It affects the blood and bone marrow.
What are the general symptoms of childhood cancer?
Symptoms include fever, fatigue, weight loss, and pain. The specific symptoms depend on the cancer type.
How is childhood cancer diagnosed?
Doctors use initial assessments, imaging, and biopsy to diagnose. These tools help find the cancer type and stage.
What are the treatment options for childhood cancer?
Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation, surgery, and new therapies. The choice depends on the cancer type and stage.
What are the long-term effects of childhood cancer treatment?
Treatment can affect physical health, mental well-being, and education. Care is needed to manage these effects.
What resources are available for families affected by childhood cancer?
Families can find help from national organizations, online groups, and financial aid. These resources offer support and help.
What is the significance of early detection in childhood cancer?
Early detection is key. It improves treatment success and survival rates. Recognizing symptoms is vital for early diagnosis.
What are some common types of childhood cancer beside ALL?
Other common cancers include neuroblastoma, Wilms tumor, and retinoblastoma. Each has its own characteristics and treatments.
How can families get involved in advocacy and awareness initiatives for childhood cancer?
Families can support non-profits, join campaigns, and share information. This helps raise awareness and support research.
What is the role of clinical trials in childhood cancer research?
Clinical trials are vital. They test new treatments and therapies. This leads to better care and outcomes.
What are the risk factors associated with childhood cancer?
Risk factors include genetics, environment, and socioeconomic status. Knowing these can help in prevention and early detection.
How does childhood cancer treatment impact survivors’ quality of life?
Treatment can affect survivors’ health, mental well-being, and education. Ongoing support and care are essential.
References
- World Health Organization. (2025). Childhood cancer. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer-in-children


































