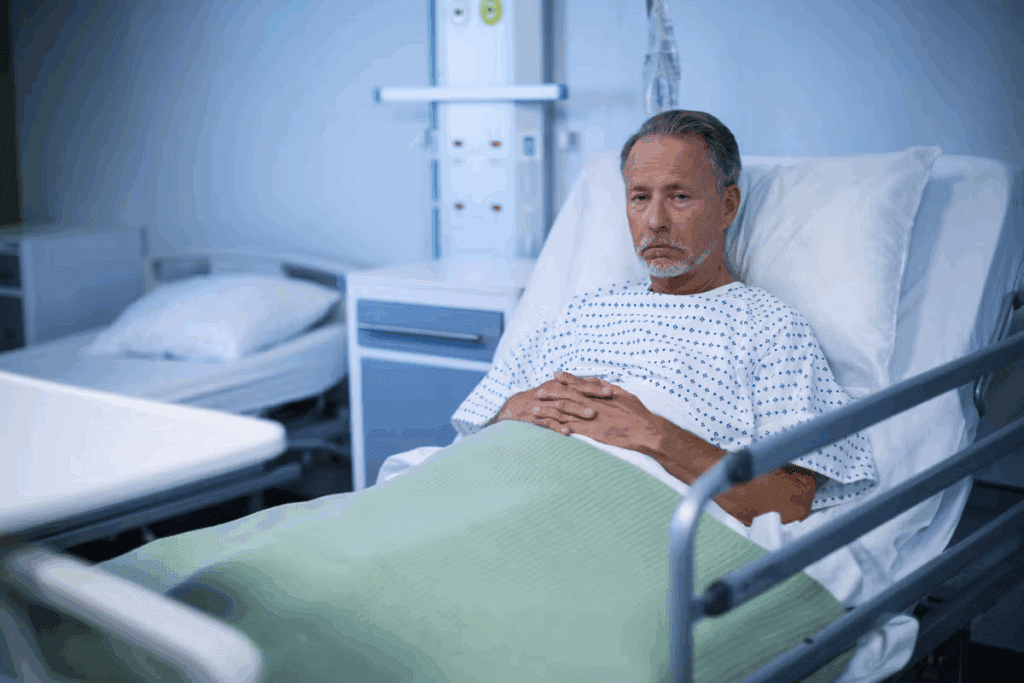
A dyscrasia is when a body system or function is not normal. It often deals with blood and its parts.
To define dyscrasia in health, it covers many conditions. These can be mild or very serious, affecting the blood, bone marrow, or lymph tissue. Knowing what dyscrasia means is key for finding and treating it.
The term has changed over time. Now, it mainly talks about specific blood issues.
Key Takeaways
- A dyscrasia is a broad term describing abnormal conditions or diseases.
- It often involves changes in blood cells, platelets, or plasma components.
- Understanding dyscrasia is essential for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
- The condition can range from mild to life-threatening.
- Liv Hospital provides patient-centered care for managing complex blood disorders.
The Medical Significance of Blood Dyscrasia

It’s important to understand blood dyscrasias to catch them early and treat them well. These conditions affect blood, bone marrow, lymph tissue, or blood vessels. They are complex to diagnose and manage.
Current Understanding in Clinical Practice
Doctors diagnose blood dyscrasias by looking at patient history, doing physical exams, and running lab tests. Early detection is key to avoid serious problems and help patients get better. Thanks to new tech and treatments, doctors now know more about these diseases.
Blood dyscrasias are grouped into several types. These include problems with red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma cells. Each type needs a special treatment plan.
Impact on Patient Health and Healthcare Systems
Blood dyscrasias can really hurt patients and cost a lot for healthcare. They can cause infections, bleeding, and damage to organs. This affects how well patients live and how long they survive.
Managing these conditions well is vital. Doctors use medicines and blood transfusions to help. Personalized medicine is also used to make treatments fit each patient better. This helps patients get better and saves money for healthcare.
Etymology and Historical Evolution of the Term “Dyscrasia”

The word “dyscrasia” comes from Greek. “Dys” means bad and “krasis” means mixture. This background helps us understand the term’s history in medicine.
Greek Origins: From “Dys” (Bad) and “Krasis” (Mixture)
In ancient Greek medicine, “dyscrasia” meant a bad or unhealthy mixture. This was about the balance of bodily fluids or humors. The Greeks thought health came from balancing four substances: blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile.
The imbalance or “dyscrasia” of these humors was thought to cause various diseases.
The Four Humors Theory in Ancient Medicine
The four humors theory was key in ancient Greek medicine. It shaped medical practice for centuries. Practitioners believed a balance among these humors was vital for health.
The theory was used to explain various physiological and pathological phenomena. Though discredited, its impact on medical terms, like “dyscrasia,” is huge.
Transition to Modern Medical Terminology
As medical knowledge grew, “dyscrasia” changed. It moved from the four humors theory to blood disorders. Today, “dyscrasia” means a disorder or abnormality, mainly in blood cells or hematological conditions.
This change shows how medical terms evolve. It shows how ancient ideas have been updated to match our modern understanding of health and disease.
Blood Dyscrasia: Definition and Modern Medical Usage
In today’s medicine, blood dyscrasia refers to blood disorders. This includes problems with blood cells and plasma cells. It covers a wide range of conditions.
Contemporary Clinical Definition
The modern definition of blood dyscrasia is about blood cell issues. It includes anemia, which is a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin. It also includes problems with white blood cells, like too many or too few.
Key aspects of blood dyscrasias include:
- Abnormalities in blood cell counts or function
- Disorders affecting the bone marrow, where blood cells are produced
- Conditions that impact the lifespan or survival of blood cells
How Medical Professionals Use the Term Today
Doctors use “blood dyscrasia” to talk about many blood disorders. It’s a term for conditions that need more study or special treatment. It’s not a single diagnosis but a wide category of blood issues.
Relationship to Other Hematological Concepts
Blood dyscrasias are linked to other blood and immune system problems. Knowing these connections helps doctors diagnose and treat blood dyscrasias better. For example, lymphoma and multiple myeloma are part of blood dyscrasias because they affect blood cells or plasma cells.
Diagnosing and treating blood dyscrasias involve many tests. These include complete blood counts, bone marrow biopsies, and genetic tests. Treatment options vary, from supportive care to bone marrow transplants, depending on the condition.
Major Categories of Blood Dyscrasias
Blood dyscrasias affect how blood cells work. This includes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These disorders are grouped into main types based on which blood component is affected.
Red Blood Cell Disorders: Anemias and Polycythemias
Red blood cell disorders involve problems with red blood cells. Anemia means not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. Hemoglobin carries oxygen. Polycythemia is when there are too many red blood cells, making blood thicker and clotting risk higher. For more on blood dyscrasias.
White Blood Cell Abnormalities: Leukopenia and Leukocytosis
White blood cell issues can weaken the body’s fight against infections. Leukopenia is when there are too few white blood cells, making infections more likely. Leukocytosis is when there are too many, often due to infection or inflammation.
Platelet Disorders: Thrombocytopenia and Thrombocytosis
Platelet disorders affect clotting. Thrombocytopenia means too few platelets, leading to easy bruising and bleeding. Thrombocytosis means too many, raising clotting risk.
Plasma Cell Dyscrasias: Multiple Myeloma and Related Conditions
Plasma cell dyscrasias involve too many plasma cells. Multiple myeloma is a cancer that affects these cells, causing anemia and bone pain. Waldenström macroglobulinemia and MGUS are related conditions.
Etiology and Risk Factors of Blood Dyscrasias
Blood dyscrasias have many causes, including genetics, environment, and medicine. Knowing these causes helps doctors diagnose and treat these conditions.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
Genetics play a big role in some blood dyscrasias. For example, sickle cell anemia and thalassemia come from specific genetic changes.
Some cases of leukemia and lymphoma also show a family link. This suggests a genetic factor.
Environmental Triggers and Exposures
Being exposed to certain things can raise the risk of blood dyscrasias. These include:
- Ionizing radiation
- Chemical exposures (e.g., benzene, pesticides)
- Viral infections (e.g., HTLV-1, EBV)
Medication-Induced Blood Abnormalities
Some medicines can cause blood dyscrasias as a side effect. Examples are:
| Medication Class | Examples | Associated Blood Dyscrasia |
| Anticonvulsants | Carbamazepine, Phenytoin | Aplastic anemia, Agranulocytosis |
| Antibiotics | Chloramphenicol, Sulfonamides | Aplastic anemia, Thrombocytopenia |
Secondary Dyscrasias from Underlying Diseases
Some blood dyscrasias come from other diseases. For example:
- Cancer: Some cancers can cause secondary blood dyscrasias.
- Chronic diseases: Diseases like chronic kidney disease can lead to anemia.
- Autoimmune disorders: Diseases like lupus can cause various cytopenias.
Knowing all these causes is key to managing and treating blood dyscrasias well.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Blood Dyscrasias
Blood dyscrasias show many symptoms, making diagnosis hard. Doctors must be careful and thorough in their checks.
Common Signs and Symptoms
People with blood dyscrasias might feel tired, have trouble breathing, or bleed easily. These signs can point to different problems. So, doctors need to do a detailed test to find the cause.
- Fatigue and weakness due to anemia or other cytopenias
- Bleeding manifestations such as petechiae, ecchymoses, or mucosal bleeding
- Infections resulting from leukopenia or immune dysfunction
Diagnostic Approach and Laboratory Evaluation
Diagnosing blood dyscrasias starts with a detailed medical history and physical check. Then, laboratory evaluations are done. First, a complete blood count (CBC) with differential is taken. It shows if there are any problems with blood cells.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) with differential
- Blood smear examination to assess cell morphology
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy for detailed cellular analysis
Advanced Testing Methods and Biomarkers
Along with basic tests, advanced diagnostic techniques and biomarkers are key. These include flow cytometry, cytogenetic analysis, and molecular diagnostics.
- Flow cytometry for immunophenotyping
- Cytogenetic studies to identify chromosomal abnormalities
- Molecular tests to detect specific genetic mutations
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
Because blood dyscrasias can look like many other conditions, differential diagnosis is very important. Doctors must think about other diseases that could look similar. This includes infections, autoimmune disorders, and other blood cancers.
Getting the right diagnosis is key to treating the right way. A detailed check-up helps doctors give the best treatment for each patient.
Treatment Strategies and Management Approaches
Managing blood dyscrasias requires a personalized plan. This plan uses various treatments to help patients. The disorders are complex, so a mix of treatments is often needed.
Pharmacological Interventions
Medicines are key in treating blood dyscrasias. They include:
- Chemotherapy for some cancers like leukemia and lymphoma
- Immunosuppressive therapy for aplastic anemia and immune issues
- Growth factors to boost blood cell production
These drugs are often used with other treatments for the best results.
Blood Component Therapy and Transfusions
Blood component therapy is vital for managing blood dyscrasias. It involves:
- Red blood cell transfusions for anemia
- Platelet transfusions to stop bleeding
- Plasma transfusions for clotting factors or proteins
Cellular Therapies: Stem Cell and Bone Marrow Transplantation
Cellular therapies like stem cell and bone marrow transplants offer hope. They involve:
- Allogeneic transplantation with donor cells
- Autologous transplantation with the patient’s cells
These cutting-edge treatments have changed how we treat blood disorders.
Novel and Emerging Treatment Modalities
Hematology is always evolving, with new treatments on the horizon. These include:
- Gene therapy to fix genetic issues in blood disorders
- Targeted therapies to tackle specific molecular problems
- Immunotherapies, like CAR-T cell therapy, to boost the immune system
These new methods are opening up more treatment options and better outcomes for patients.
Complications, Prevention, and Long-term Monitoring
It’s important to know about the complications of blood dyscrasias for good patient care. Blood dyscrasias are disorders that affect blood function. They can lead to serious problems.
Potential Complications and Their Management
Blood dyscrasias can cause infections, bleeding issues, and damage to organs. Infections are a big worry, mainly for those with low white blood cells or on immunosuppressive drugs.
Managing these issues needs a few steps:
- Quick treatment of infections with antibiotics or antifungals
- Transfusions to handle bleeding or anemia
- Watching for signs of organ failure
Preventive Measures and Risk Reduction
Stopping complications is key in managing blood dyscrasias. This can be done by:
- Vaccinations to stop infections
- Staying away from harmful substances or triggers
- Regular checks on blood counts and organ health
Follow-up Protocols and Monitoring Guidelines
Regular check-ups are vital for blood dyscrasias patients. This includes:
| Monitoring Parameter | Frequency | Purpose |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Weekly to Monthly | Check blood cell counts |
| Liver and Kidney Function Tests | Every 3-6 Months | Check organ health |
| Bone Marrow Biopsy | As needed | Look at bone marrow health |
Quality of Life Considerations for Patients
Good care for blood dyscrasias means thinking about the patient’s life quality. This means dealing with symptoms, managing treatment side effects, and supporting their mental health.
With a full care plan, doctors can help patients live better lives.
Conclusion: Advancing Our Understanding of Blood Dyscrasias
Medical research and technology have made big strides in understanding blood dyscrasias. These disorders affect the blood, including red and white cells, and platelets.
It’s vital to keep learning about these conditions. Research and education help improve treatment and patient care. By studying these disorders, we can better manage them.
New treatments are on the horizon. This includes targeted therapies and gene editing. As we learn more, we’ll see better care for those with blood dyscrasias.
FAQ
What is blood dyscrasia?
Blood dyscrasia is a disorder in the blood. It affects the blood cells, like red and white blood cells, and platelets.
What is the medical significance of blood dyscrasia?
Blood dyscrasias can cause serious health issues. They can lead to anemia, infections, and bleeding problems.
What are the major categories of blood dyscrasias?
Blood dyscrasias are divided into several types. These include disorders of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma cells.
What are the causes and risk factors of blood dyscrasias?
Blood dyscrasias can be caused by genetics, environment, or medication. They can also be triggered by other diseases.
How are blood dyscrasias diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose blood dyscrasias. These include clinical exams, lab tests, and advanced tests like biomarkers and genetic analysis.
What are the treatment options for blood dyscrasias?
Treatments for blood dyscrasias vary. They include medicines, blood transfusions, cellular therapies, and new treatments.
References
- Blood dyscrasia – an overview. (n.d.). ScienceDirect Topics. Retrieved October 17, 2025, from https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/blood-dyscrasia