Last Updated on November 20, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir

Getting a cancer diagnosis can feel overwhelming. It’s important to know about the treatment options. At Liv Hospital, patients get care tailored to their needs, using the latest medical knowledge. Find out whether is radiation therapy chemo and how both treatments differ in cancer care.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are two common treatments for cancer. They are often used together with other therapies. Both aim to kill cancer cells, but they do it in different ways.
It’s key to understand the difference between radiation therapy and chemotherapy. The right choice depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
It’s important for patients and doctors to know about cancer treatments. There are many options, depending on the cancer type and stage.
Choosing a treatment depends on the patient’s health, the cancer’s details, and the treatment’s side effects.
Cancer treatments are key in modern medicine. They give patients hope and better chances of recovery. Thanks to new technology and research, treatments are getting better and more precise.
Key advancements include:
Every patient gets a treatment plan made just for them.
Tailored treatments are vital in cancer care. They help doctors target the cancer’s specific traits. This approach can make treatments more effective and improve patient results.
A comparison of different cancer treatment options is provided in the table below:
| Treatment Type | Description | Key Benefits |
| Radiation Therapy | Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells | Localized treatment, minimal damage to surrounding tissue |
| Chemotherapy | Uses drugs to kill cancer cells | Systemic treatment, effective against widespread cancer |
| Targeted Therapy | Targets specific cancer cell characteristics | Reduced side effects, improved efficacy |
Knowing about the different cancer treatments helps patients make informed choices about their care.
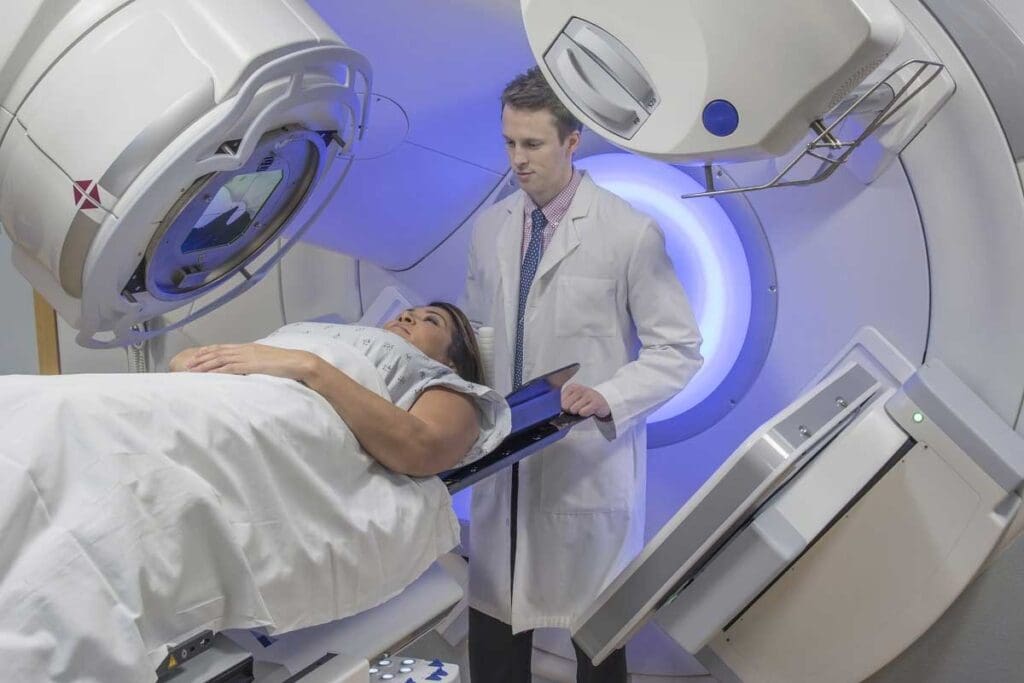
Radiation therapy is a key part of cancer treatment. It uses ionizing radiation to kill cancer cells or slow them down. This method damages the DNA of cancer cells, stopping them from growing and dividing.
Radiation therapy sends high-energy particles or waves to the tumor. This energy harms the DNA of cancer cells, stopping them from growing. The aim is to hit the tumor just right, without harming healthy tissues nearby.
The science behind it is simple. Ionizing radiation has enough power to knock electrons out of atoms. This creates ions that damage DNA in cells, causing them to die or stop growing.
There are many types of radiation therapy, each with its own use. The main ones are:
Each type is chosen based on the patient’s needs and the tumor’s characteristics. The right choice depends on the cancer type, stage, and the patient’s health.
Chemotherapy is a treatment that targets cancer cells all over the body. It’s different from treatments that only focus on one area. This way, chemotherapy fights cancer in a more complete way.
Chemotherapy uses strong drugs to find and kill fast-growing cells, like cancer cells. These drugs can be taken by mouth or given through an IV. This lets them reach cancer cells in different places in the body.
Chemotherapy works best on cancer cells that have spread or might spread. It helps slow down the disease and sometimes even stop it.
Chemotherapy treatments often mix different drugs. These include anthracyclines, taxanes, and platinum-based drugs. The choice of drugs and how they’re used depends on the cancer type, its stage, and the patient’s health.
Doctors carefully plan chemotherapy to make it work well and have fewer side effects. Each treatment plan is unique, showing how cancer care is tailored for each person.
Chemotherapy’s ability to reach all over the body is both its biggest plus and a possible drawback. Because it goes everywhere, it can harm not just cancer cells but also healthy cells that grow fast. This includes cells in the bone marrow, hair follicles, and digestive tract lining.
It’s important to understand how chemotherapy affects the whole body. This helps doctors manage side effects and support patients during treatment. By knowing both the good and the bad of chemotherapy, healthcare teams can give better care to the whole person.
It’s important to know the difference between radiation therapy and chemotherapy for cancer treatment. Both are used to fight cancer, but they work differently and have unique features.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves to kill cancer cells. This includes X-rays, gamma rays, or proton beams. On the other hand, chemotherapy uses drugs to stop cancer cells from growing.
Radiation therapy targets a specific area of the body. Chemotherapy, by contrast, affects the whole body. This difference is key because it affects how each treatment is used and its side effects.
Radiation therapy is mainly used for tumors in one place, while chemotherapy treats cancers that have spread or are at risk of spreading.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy have different ways of treating cancer. Radiation therapy focuses on a specific tumor or area. This method allows for higher doses of radiation to be given directly to the tumor, reducing harm to healthy tissues nearby.
Many people think radiation therapy and chemotherapy are the same or that one is a form of the other. But they are different treatments with unique ways of working and uses. Some believe radiation therapy is only for localized tumors, while chemotherapy is for widespread disease. But the choice between them depends on many factors, like the cancer type and stage, the patient’s health, and the treatment goals.
Knowing the differences between radiation therapy and chemotherapy helps patients make better choices about their treatment. This way, they can be more informed about their care.
It’s important for patients to know how radiation therapy and chemotherapy are given. Both are key in fighting cancer but in different ways.
Radiation therapy comes in various forms, based on the cancer’s type and location. The most common is external beam radiation therapy (EBRT). This method uses a machine outside the body to send beams to the tumor.
Internal radiation therapy, or brachytherapy, places radioactive material inside or near the tumor. This method is used for certain types of cancer.
Chemotherapy is usually given through an IV, letting the drugs reach all parts of the body. This can be via a peripheral IV line or a central venous catheter. The choice depends on the patient’s needs and the treatment plan.
Another way is oral chemotherapy, where patients take pills or liquids. This is easier for some patients to manage.
The schedule and length of treatment differ for each patient. Radiation therapy is often given daily, Monday through Friday, for weeks. Chemotherapy cycles include treatment days followed by rest days to help the body recover.
| Treatment Type | Typical Administration Frequency | Average Treatment Duration |
| Radiation Therapy | Daily, Monday-Friday | Several weeks |
| Chemotherapy | Cyclic, varying intervals | Several months |
It’s important for patients to know about the side effects of cancer treatments. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are effective but can affect the body in many ways.
Radiation therapy can cause different side effects based on the treated area. Common issues include fatigue, skin changes, and hair loss in the treated area. Patients might also feel nausea and vomiting if the treatment area is near the stomach.
Chemotherapy can cause a variety of side effects because it affects the whole body. Common side effects are hair loss, nausea and vomiting, and fatigue. It can also increase the risk of infection and bruising or bleeding because it impacts blood cells.
Both treatments can have lasting effects on the body. Radiation therapy can lead to scarring, secondary cancers, and organ damage. Chemotherapy’s long-term effects include infertility, heart problems, and nerve damage.
| Side Effect | Radiation Therapy | Chemotherapy |
| Fatigue | Common | Common |
| Hair Loss | Localized to treatment area | Often widespread |
| Nausea and Vomiting | Possible, with abdominal treatment | Common |
| Skin Changes | Common in treatment area | Rare |
It’s key to manage side effects to keep quality of life during treatment. Patients can work with their healthcare team to find ways to manage side effects. This includes medications for nausea, skin care routines, and rest and nutrition plans. By managing side effects, patients can better handle their treatment and improve their outcome.
Choosing between radiation therapy and chemotherapy for cancer treatment depends on many factors. Doctors look at several things to decide what’s best for each patient.
The type and stage of cancer are key in picking a treatment. For example, early-stage cancers might get radiation therapy to hit the tumor directly. But, advanced cancers might need chemotherapy to fight off spread in the body.
Table: Treatment Approaches for Different Cancer Types
| Cancer Type | Common Treatment | Rationale |
| Breast Cancer (Early Stage) | Radiation Therapy | Targets the tumor site post-surgery |
| Lung Cancer (Advanced Stage) | Chemotherapy | Addresses possible metastasis |
| Prostate Cancer (Localized) | Radiation Therapy | Precisely targets the prostate gland |
Other factors like health, age, and personal wishes also matter. For example, older patients or those with health issues might get treatments with fewer side effects.
“The choice of cancer treatment is not one-size-fits-all; it’s a tailored approach that considers the unique aspects of each patient’s case.” –
For breast cancer, the choice between radiation and chemotherapy depends on the cancer’s stage and type. Early-stage breast cancer might get lumpectomy and then radiation. But, more advanced cases might need chemotherapy.
Each cancer type has its own treatment plan. For example, leukemia usually gets chemotherapy because it’s systemic. But, localized cancers like some skin cancers might get radiation therapy.
Understanding these factors helps patients see why they’re getting a certain treatment. It also helps them make informed decisions about their care.
Cancer treatment has evolved to include combined approaches. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are used together to enhance outcomes. This strategy can be tailored to each patient’s needs, making the fight against cancer more effective.
Concurrent therapy involves giving radiation therapy and chemotherapy at the same time. This method is very effective for some cancers. It creates a synergistic effect that boosts the treatment’s overall outcome.
Benefits of Concurrent Therapy:
Sequential therapy uses radiation therapy and chemotherapy one after the other. This method helps reduce side effects. It makes the treatment more tolerable for patients.
Advantages of Sequential Therapy:
Combined treatments attack cancer cells in multiple ways. They combine the localized effects of radiation therapy with the systemic effects of chemotherapy. This makes it easier to target cancer more effectively.
| Treatment Approach | Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
| Concurrent Therapy | Enhanced tumor response, improved survival rates | Increased risk of side effects |
| Sequential Therapy | Reduced side effects, adjustable treatment plans | Potential for longer overall treatment duration |
Many case studies show the success of combined treatments in different cancers. For example, in locally advanced breast cancer, combining radiation therapy with chemotherapy has improved local control and survival rates.
Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of combined treatments helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions. This ensures the most effective treatment strategies are used.
It’s key to know the differences between radiation therapy and chemotherapy for cancer treatment. We’ve looked at how they work, their uses, and side effects. This shows their important roles in fighting cancer today.
There are many ways to treat cancer, depending on the type and stage, and the patient’s situation. Knowing the main differences helps patients choose the best treatment. They can then work well with their doctors.
Choosing the right cancer treatment means looking at the treatment’s focus, side effects, and if it can be used with other treatments. We’ve seen that both radiation and chemotherapy can be used alone or together for the best results.
Being well-informed about cancer treatment options lets patients be more involved in their care. They can make choices that fit their needs and wishes. This leads to more effective and tailored cancer treatment.
No, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are not the same. They are both used to fight cancer but in different ways.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to fight cancer all over the body. Radiation therapy uses rays to kill cancer cells in one area.
No, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are not the same. Radiotherapy kills cancer cells with rays, while chemotherapy uses drugs.
For breast cancer, radiation targets the breast area. Chemotherapy fights cancer cells all over the body. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage and type.
No, chemotherapy does not use radiation. It uses drugs to fight cancer, unlike radiation therapy.
Yes, they can be used together. This is called combined modality therapy. It can make treatment more effective.
Both can cause side effects like fatigue and hair loss. The side effects and how bad they are vary by treatment and patient.
Doctors look at the cancer type, stage, and patient health. They choose based on what’s best for each patient.
Chemotherapy fights cancer all over the body. Radiotherapy targets cancer in one area.
No, radiation therapy is not chemotherapy. They are different treatments for cancer.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!