As a leading healthcare provider, we know how worried parents are about their kids’ health. Childhood cancer leukemia is a scary reality for many families. It’s a blood cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, common in kids.Learn leukemia in babies signs, causes, and symptoms for early detection and care guidance.
Spotting early signs of leukemia can help kids get the right treatment fast. At Liv Hospital, we offer top-notch healthcare and support for families from around the world. Here, we’ll share important signs, causes, and symptoms of leukemia that parents need to know.
Key Takeaways
- Leukemia is the most common type of cancer in children.
- Early detection is key for effective treatment.
- Knowing the signs and symptoms helps in quick diagnosis.
- We offer full support for families dealing with leukemia.
- New advances in pediatric care are helping kids with leukemia.
Understanding Childhood Cancer: The Prevalence of Leukemia in Babies
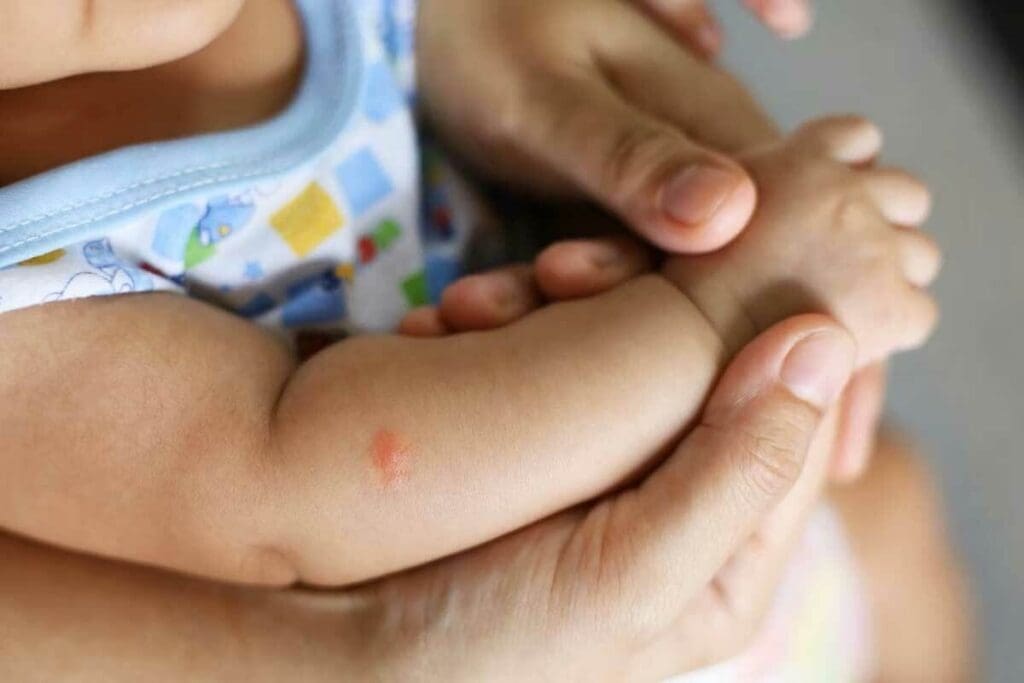

It’s key to know how common leukemia is in kids to catch it early. Leukemia is a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It’s the most common cancer in children.
The Most Common Cancer in Children
Leukemia is a big worry for parents and doctors. It’s a cancer that can happen at any age. But it’s most often found in kids between 2 and 10 years old.
Key statistics on childhood leukemia include:
- About 4.8 per 100,000 kids get leukemia each year.
- It’s the top cause of cancer deaths in kids under 20.
- There are two main types: Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).
Incidence Rates and Statistics
Leukemia in kids is a big issue that needs attention. It’s a major health problem worldwide.
Some critical statistics to consider are:
- Leukemia is most common in kids aged 2 to 5.
- More boys get leukemia than girls.
- Thanks to better treatments, more kids survive leukemia.
Knowing these facts helps us support families and doctors. We can work together to find and treat leukemia early.
Types of Leukemia That Affect Infants
When a baby is diagnosed with leukemia, doctors need to know the type. This can be either Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) or Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Knowing the type helps doctors choose the best treatment.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
ALL is the most common leukemia in kids, making up about 75 percent of cases in infants. It starts in lymphoid cells and grows fast. It’s a blood cancer that affects the bone marrow, where white blood cells are made.
ALL is caused by too many immature lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. This makes it hard for the body to make normal blood cells. As a result, the immune system gets weaker.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
AML is less common than ALL but is more aggressive. It affects the myeloid cells in the bone marrow, which make different types of blood cells. In AML, the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloid cells that block normal blood cell production.
AML can cause symptoms like tiredness, infections, and easy bruising or bleeding. Because of its aggressive nature, AML needs quick and intense treatment.
It’s important to know the difference between ALL and AML for the right treatment. While ALL is more common, AML’s fast growth means it needs fast and specific treatment.
Genetic and Environmental Causes of Pediatric Leukemia
The causes of pediatric leukemia are complex. They involve genetics and the environment. Leukemia in children can start early and is different from adult forms. It often has unique genetic types.
Leukemia is a cancer that starts in the bone marrow. This is where blood cells are made. In leukemia, the bone marrow makes bad white blood cells. These cells grow fast but don’t work right.
It’s important to know what causes pediatric leukemia. This helps doctors find it early and treat it.
Inherited Genetic Factors and Mutations
Some genetic conditions raise the risk of leukemia. For example, kids with Down syndrome are more likely to get acute leukemia. Other genetic syndromes, like Li-Fraumeni and ataxia-telangiectasia, also increase the risk.
- Down syndrome: associated with a 20- to 30-fold increased risk of acute leukemia
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome: characterized by a genetic mutation that increases the risk of several types of cancer, including leukemia
- Ataxia-telangiectasia: a rare genetic disorder that affects the nervous system and increases the risk of cancer
Environmental Exposures and Prenatal Influences
Some environmental factors can raise the risk of leukemia. These include:
- Exposure to ionizing radiation, such as from prenatal X-rays or nuclear fallout
- Pesticide exposure: some studies have suggested a link between pesticide exposure and an increased risk of childhood leukemia
- Maternal infection during pregnancy: some research has suggested that maternal infection during pregnancy may increase the risk of leukemia in the child
While these factors may raise the risk, they don’t mean a child will definitely get leukemia. More research is needed to understand how genetics and environment work together in pediatric leukemia.
Physical Warning Sign #1: Unusual Bruising and Bleeding
One of the first signs of leukemia in infants is unusual bruising and bleeding. This is scary for parents. It happens because leukemia affects the production of platelets, which help blood clot.
When platelet counts are low, even small injuries can cause big bruises or bleeding.
Identifying Abnormal Bruising Patterns
Parents should know that babies can bruise easily, thanks to their growing activity. But, bruising without an apparent cause or in odd places like the face, back, or chest is a red flag. It could mean childhood leukemia.
It’s key to watch the size, color, and how often bruises appear.
Prolonged Bleeding from Minor Injuries
Another warning sign is when a baby’s cuts or injuries won’t stop bleeding after a few minutes of pressure. This could mean a problem with blood clotting due to leukemia. It’s a sign that needs to be checked out right away.
In short, while some bruising is normal in kids, unusual patterns or bleeding that lasts too long should make parents call their pediatrician. Catching childhood cancer leukemia early can really help with treatment.
Physical Warning Sign #2: Persistent Fever and Recurring Infections
A big sign of childhood leukemia is a persistent fever and recurring infections. This shows the immune system is weak. Leukemia makes it hard for the body to fight off infections, leading to frequent illnesses.
Unexplained Fevers That Don’t Resolve
Children with leukemia often have fevers that don’t go away. These fevers can happen without a clear reason. They are a sign of a weakened immune system, making it hard to fight off infections.
Key characteristics of fevers associated with leukemia include:
- Persistence: Fevers that last for an extended period or recur frequently.
- Unexplained origin: Fevers without an obvious infection or cause.
- Resistance to treatment: Fevers that do not respond to typical fever-reducing medications.
Increased Susceptibility to Common Illnesses
Leukemia affects the production of healthy white blood cells. These cells are key in fighting infections. So, children with leukemia get sick more easily and often have severe or long-lasting illnesses.
Signs of increased susceptibility include:
- Frequent colds and flu that are more severe than usual.
- Prolonged recovery times from common infections.
- Recurring infections such as pneumonia or other serious infections.
Spotting these signs early is key to diagnosing and treating leukemia. If your child keeps getting fevers or infections, see a doctor. They can find out why and help your child.
Physical Warning Sign #3: Pallor, Fatigue, and Weakness in Leukemia in Babies
Leukemia in babies can show signs like pallor, fatigue, and weakness. These symptoms are linked to anemia. Leukemia affects the body’s ability to make normal blood cells, including red blood cells.
Understanding Anemia in Pediatric Leukemia
Anemia means not enough red blood cells to carry oxygen. In leukemia, the bone marrow makes too many white blood cells. This leaves less room for healthy red blood cells.
This leads to less oxygen for the body’s tissues. The skin may look paler, a sign of anemia. It’s important for parents to watch their baby’s skin and energy levels.
When to Be Concerned About Your Baby’s Energy Levels
Fatigue and weakness are big signs of leukemia in babies. Not enough oxygen from red blood cells can make a baby tired. Look for signs like less activity or less interest in play.
If your baby is always tired or weak, see a doctor. Catching leukemia early is key to better treatment and outcomes.
Key signs to watch for include:
- Pale skin or pallor
- Unusual fatigue or weakness
- Less responsiveness or activity
Knowing these signs and acting fast can help treat leukemia in babies. It’s a big role for parents to play.
Physical Warning Sign #4: Bone and Joint Pain
Leukemia in babies can show as bone and joint pain. This is a sign that needs quick medical help. The pain happens when leukemia cells build up in the bone marrow, causing swelling and discomfort.
Infants might get upset or show pain when moved or touched. This is because of the pain in their bones and joints.
Bone and joint pain is a big worry. It can be an early sign of leukemia. We will look at how leukemia affects bones and how to tell if it’s leukemia pain or just growing pains in babies.
How Leukemia Affects the Skeletal System
Leukemia cells can get into the bone marrow. This can lead to different problems with the bones. The cells can make the marrow space bigger, causing bone pain.
In some cases, this can weaken or even break bones. This makes it hard for the baby to move or carry their weight.
Key effects on the skeletal system include:
- Bone pain due to marrow expansion
- Joint pain from leukemia cell infiltration
- Increased risk of fractures
Distinguishing Leukemia Pain from Growing Pains
Growing pains are common in kids and usually happen in the legs. But leukemia pain is often worse and lasts longer. We need to look at how long the pain lasts and what else is happening with the baby.
Signs that may indicate leukemia pain include:
- Persistent pain not relieved by simple measures like massage or rest
- Pain accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, bruising, or fatigue
- Pain that interferes with the infant’s normal activities or sleep
Knowing the difference is key for catching leukemia early. If you think your baby might have leukemia, see a doctor right away.
Physical Warning Sign #5: Swollen Lymph Nodes and Abdominal Distension
We’re looking at the fifth warning sign of leukemia in babies: swollen lymph nodes and a big belly. Leukemia can make lymph nodes, spleen, and liver swell. This can cause a swollen belly to show up.
Identifying Abnormal Swelling in Babies
Swollen lymph nodes in babies might mean something serious, like leukemia. Usually, you can’t feel lymph nodes, but when they swell, you can. It’s important to tell if swelling is from a common cold or something more serious.
Watch for any swelling that doesn’t go away or comes with fever or tiredness. Seeing a pediatrician regularly can spot problems early.
When Enlarged Organs Cause Visible Symptoms
Leukemia can make organs like the spleen and liver get bigger. This makes the belly look bigger. This is called hepatosplenomegaly and is a sign of leukemia in kids.
Keep an eye on your baby’s belly for swelling or discomfort. If it looks big or your baby is uncomfortable, see a doctor. Catching it early is key to treating it well.
Diagnosis and Treatment: The Path Forward After Suspecting Leukemia
Diagnosing leukemia in babies is a detailed process. Pediatricians start with a medical history and physical exam. They look for signs like unusual bruising, fever, or swollen lymph nodes.
Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing leukemia requires several tests. The first step is a Complete Blood Count (CBC). This test checks blood cell levels. If the results are off, more tests follow.
A Bone Marrow Biopsy is key for a diagnosis. It takes a bone marrow sample for a microscope check. This finds cancer cells.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Measures levels of different blood cells to identify abnormalities. |
| Bone Marrow Biopsy | Examines bone marrow for cancerous cells. |
| Lumbar Puncture | Checks for leukemia cells in the cerebrospinal fluid. |
Modern Treatment Approaches and Survival Rates
Treatment for pediatric leukemia has gotten better. Survival rates have risen. The treatment plan depends on the leukemia type, the child’s age, and other factors.
Chemotherapy is the main treatment. It uses drugs to kill leukemia cells. Sometimes, Targeted Therapy is used, focusing on leukemia cell traits.
Today, over 85 percent of children with leukemia survive five years or more. This success comes from better treatments and care.
Knowing about leukemia diagnosis and treatment helps parents. It’s a tough journey, but understanding it can offer comfort and guidance.
Conclusion: Early Detection and the Improving Outlook for Childhood Leukemia
Early detection of leukemia in children is key for better treatment and survival. Knowing the signs like unusual bruising, persistent fever, and bone pain helps. This leads to quicker diagnosis and better treatment results.
Thanks to new medical treatments, the outlook for kids with leukemia is much better. Most kids can survive and live healthy lives after being diagnosed. Early diagnosis, tailored treatment, and family support are important for this.
Getting a leukemia diagnosis can be tough for families. But, with the right info and care, they can get through it. Recognizing the signs early and getting medical help fast can greatly help young patients.
The progress in treating childhood leukemia is amazing. We keep working to improve care and support for kids with leukemia and their families.
FAQ
What are the most common signs of leukemia in babies?
Signs include unusual bruising and bleeding, and persistent fever. Babies may also have recurring infections, look pale, and feel tired. They might experience bone and joint pain, and have swollen lymph nodes and a big belly.
What is the prevalence of leukemia in children?
Leukemia is the most common cancer in kids. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is the most common type.
What are the types of leukemia that affect infants?
Infants can get Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). ALL is more common.
What causes pediatric leukemia?
Leukemia in kids is caused by genetics and the environment. This includes inherited genes and things that happen before birth.
How is leukemia in babies diagnosed?
Doctors use blood tests and a bone marrow biopsy to find leukemia cells.
What is the treatment for leukemia in children?
Treatment depends on the type and how severe it is. It often includes chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and sometimes bone marrow transplantation.
What is the survival rate for childhood leukemia?
Survival rates for childhood leukemia have gotten much better. Many kids with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) are cured.
How can parents identify abnormal bruising patterns in their baby?
Watch for unusual or unexplained bruises. Also, be concerned if your baby has fever or is very tired.
Can leukemia in babies be prevented?
There’s no sure way to prevent leukemia. But knowing the risks and signs can help catch it early.
What is the role of genetic factors in pediatric leukemia?
Genetics play a big role in pediatric leukemia. Some genetic mutations increase the risk.
How does leukemia affect the immune system in children?
Leukemia weakens the immune system. This makes kids more likely to get sick and catch infections.
What is the difference between leukemia pain and growing pains?
Leukemia pain is constant and can be very bad. Growing pains are usually mild and come and go.
References
- Gözdaşoğlu, S. (2022). Infant leukemia. Blood, 140(15), 161-172. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36395313/




































