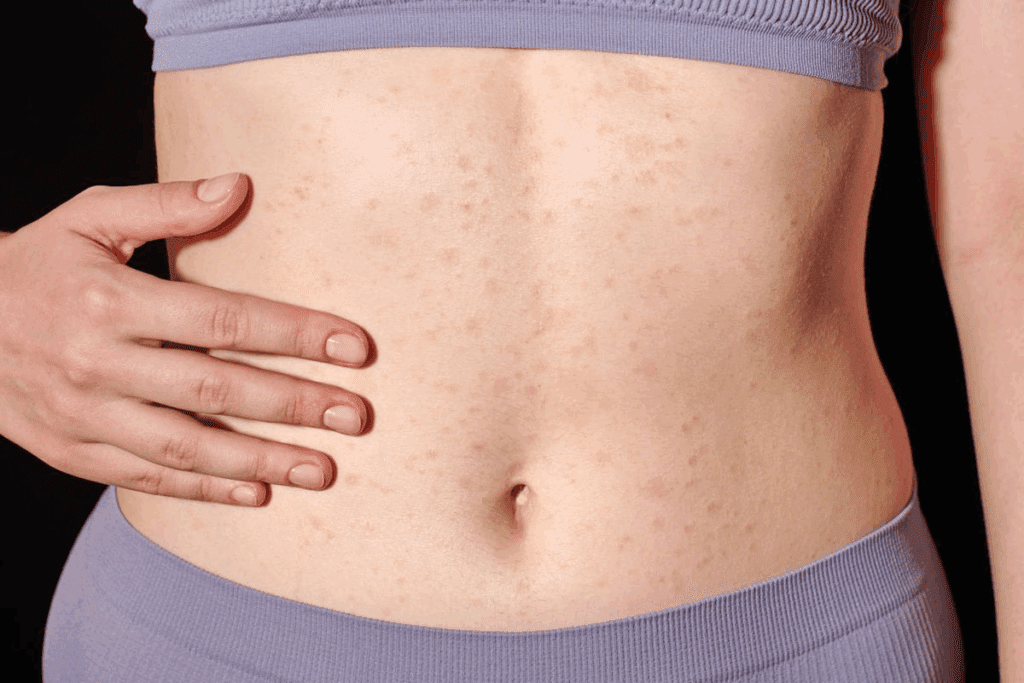
At Liv Hospital, we know how worrying it is to see tiny red spots on your skin. These spots, called petechiae, are flat and happen when blood leaks from capillaries under the skin. Many patients also wonder, does petechiae itch — understanding this can help identify the cause and guide proper care.
Petechiae themselves are not typically itchy. But, if you notice them with easy bruising and itching, it might mean there’s something more serious going on. We’re here to give you the right diagnosis and care.
It’s important to understand how petechiae, itching, and bruising are connected. Our team works hard to find out why these symptoms happen. This way, we can treat them properly and quickly.
Key Takeaways
- Petechiae are tiny red spots caused by blood leaking from capillaries.
- They are not typically itchy but can be associated with underlying conditions that cause itching and bruising.
- Easy bruising and itchy skin can be related to the underlying causes of petechiae.
- Accurate diagnosis is key for effective treatment.
- Liv Hospital is committed to providing complete care for patients with these symptoms.
Understanding Petechiae: Tiny Spots with Significant Health Implications

Petechiae are tiny red or purple spots on the skin. They can signal health issues. Blood leaking from capillaries causes these spots. Knowing about petechiae helps find the cause and get the right medical care.
What Are Petechiae and How Do They Form?
Petechiae are small spots from broken capillaries. They are red or purple and don’t change color when pressed. Many things can cause them, like infections, blood disorders, and injuries.
Common Locations and Characteristic Appearance
Petechiae often show up on legs, arms, and the torso. They can be alone or in groups, sometimes forming big patches. They are flat and don’t change color when pressed, which is a key sign.
Differentiating Petechiae from Other Skin Conditions
It’s important to tell petechiae apart from other rashes. Unlike some rashes, petechiae aren’t itchy or painful. They’re different from bruises because of their size and look. Conditions like vasculitis, thrombocytopenia, and infections can cause them, so correct identification is key.
Does Petechiae Itch? The Relationship Between Petechiae and Pruritus

Petechiae are usually not itchy. But, some causes can make them itch. We’ll look into this complex relationship and explain when petechiae might itch.
The Typically Non-Itchy Nature of Petechiae
Petechiae are small spots on the skin from minor bleeding. They are not itchy because they come from blood vessel damage, not skin irritation. But, sometimes, petechiae can itch if there’s an underlying condition.
When and Why Petechiae Might Cause Itching
In some cases, petechiae can itch. This usually happens because of an underlying cause or condition. For example, infections, inflammatory disorders, or allergic reactions can cause both petechiae and itching. Finding the root cause is key to managing symptoms.
Conditions that might cause both petechiae and itching include:
- Allergic reactions to medications or substances
- Infections such as meningitis or sepsis
- Autoimmune disorders like vasculitis
- Blood disorders or platelet abnormalities
How to Distinguish Petechiae from Itchy Rashes
It’s important to tell petechiae from itchy rashes for the right diagnosis and treatment. Petechiae are flat and don’t change color when pressed. Here’s a table to help you tell them apart:
| Characteristics | Petechiae | Itchy Rashes |
| Appearance | Small, pinpoint, flat spots | Variable; can be raised, red, and widespread |
| Color | Purple or red; do not blanch when pressed | Red, pink, or skin-colored; may blanch |
| Itching | Typically not itchy | Often accompanied by itching |
| Causes | Blood vessel damage, bleeding disorders | Allergic reactions, infections, dermatitis |
Knowing the differences between petechiae and itchy rashes helps identify the cause. It also guides you to the right medical care.
The Connection Between Petechiae and Bruising: Understanding the Overlap
Petechiae and bruising look similar but are different in how they happen. Both show bleeding under the skin. But, their reasons and effects can be quite different.
Physiological Differences Between Petechiae and Bruises
Petechiae are small spots from tiny blood vessel breaks. They don’t feel hard and don’t change color when pressed. Bruises, on the other hand, are bigger and happen from more damage or broken blood vessels.
A study onpurpura vs petechiae shows their main difference. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat better.
Why These Conditions Frequently Occur Together
Petechiae and bruising often happen together. This is because of problems with blood vessels or blood clotting. For example, low platelet count can cause both.
Easy bruising and itchy skin can also mean other health issues. This includes liver problems, vitamin shortages, and some autoimmune diseases. Itching with these symptoms might point to a bigger problem.
The Clinical Significance of Easy Bruising with Petechiae
When you bruise easily and have petechiae, it might mean a serious health problem. Leukemia and other blood cancers can cause these symptoms. So, seeing a doctor is key if you notice both.
In short, knowing about petechiae and bruising is key. It helps find the cause and treat the symptoms right. Doctors can then give the right care for these skin signs.
Medical Causes of Itchy Skin with Petechiae and Bruising
Itchy skin, petechiae, and bruising can be signs of many health issues. These symptoms together might mean a serious problem.
Blood Disorders and Platelet Abnormalities
Blood disorders, like those affecting platelets, can cause these symptoms. Thrombocytopenia, with low platelet count, makes it hard to form blood clots.
Leukemia, a blood cancer, can also cause these symptoms. Itchy skin might happen because of waste products from abnormal white blood cells.
Autoimmune Conditions That Affect Blood Vessels
Autoimmune diseases attack the body’s own tissues. Vasculitis, which inflames blood vessels, can lead to petechiae and bruising. Itchy skin might also occur due to inflammation and damage to blood vessels.
“Autoimmune disorders can manifest in various ways, including skin symptoms like itching, petechiae, and bruising, making diagnosis challenging but critical.”
Infections and Inflammatory Responses
Certain infections can cause inflammation, leading to itchy skin, petechiae, and bruising. For example, septicemia, or blood infection, can affect blood clotting and skin health.
Infections like meningitis can also cause petechiae and sometimes itchy skin and bruising. This is due to a severe inflammatory response.
Medication Side Effects and Drug Reactions
Some medications can cause itchy skin, petechiae, and bruising as side effects. Anticoagulant medications can increase bruising risk and affect platelet function. Drug reactions can also cause itchy skin due to allergies or sensitivity.
It’s important for patients to tell their healthcare provider about any medications they’re taking. This helps check if the symptoms are drug-related.
Specific Conditions That Cause the Triad of Itchy Skin, Bruising, and Petechiae
Many medical conditions can lead to itchy skin, bruising, and petechiae. These symptoms often point to serious health issues. It’s important to get medical help right away.
Leukemia and Other Hematologic Malignancies
Leukemia, a blood cancer, can cause itchy skin, bruising, and petechiae. It affects blood cells, leading to clotting problems. Early diagnosis is key for effective treatment.
Thrombocytopenia and Related Platelet Disorders
Thrombocytopenia, or low platelet count, can cause bruising and petechiae. Itchy skin may also appear due to related conditions or treatments. We’ll look at how platelet disorders cause these symptoms and treatment options.
Vasculitis and Vascular Inflammation Syndromes
Vasculitis is inflammation of blood vessels, leading to itchy skin, bruising, and petechiae. It can be caused by infections, autoimmune disorders, or other factors. Understanding the cause is vital for managing vasculitis.
Allergic Reactions, Dermatitis, and Skin Sensitivities
Allergic reactions and dermatitis can cause itchy skin, sometimes with bruising and petechiae. We’ll explore how these reactions and sensitivities lead to symptoms. We’ll also discuss how to tell them apart from other conditions.
If you have itchy skin, bruising, and petechiae, see a doctor. These symptoms can signal serious health issues.
Unexplained Itching and Bruising on Legs: Causes and Concerns
Seeing unexplained bruising and itching on your legs is a sign to check further. These signs can point to health problems like vascular issues, skin diseases, or systemic diseases.
Vascular Issues Specific to Lower Extremities
Vascular problems are a big worry for unexplained itching and bruising on legs. Chronic venous insufficiency can cause blood to pool, leading to itching and bruising. Varicose veins also cause these symptoms because of bad blood flow.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious issue that can cause pain, swelling, and bruising in the legs. While itching isn’t a main symptom of DVT, swelling and skin changes can make the skin itchy.
Dermatological Conditions Affecting the Legs
Dermatological issues are a common reason for itchy skin and bruising on legs. Eczema or dermatitis can make the skin itchy and inflamed, leading to easy bruising from scratching. Psoriasis causes itchy, scaly patches on the legs, which can bruise if scratched or irritated.
Also, stasis dermatitis happens due to poor circulation, causing itchy, swollen, and bruised skin on the legs.
When Leg Symptoms Signal Systemic Disease
In some cases, unexplained itching and bruising on legs can signal a systemic disease. For example, liver disease can cause itching from bile salts in the skin. Diabetes can lead to poor circulation and neuropathy, causing itchy skin and increasing bruising risk.
Also, certain autoimmune disorders can cause vasculitis, leading to inflammation of blood vessels. This can show as itchy skin and bruising on the legs.
Seeing a healthcare professional is key if you have persistent or severe itching and bruising on your legs. These symptoms can mean an underlying condition that needs medical care.
Diagnostic Approach: How Doctors Evaluate Petechiae, Bruising, and Itching
Doctors use a detailed method to find the cause of petechiae, bruising, and itching. They look at many possible reasons, from simple to serious diseases.
The Importance of Medical History and Physical Examination
Getting a full medical history is key when dealing with these symptoms. We ask about when symptoms started, any recent sicknesses, and medicines taken. A detailed physical check is also important. It helps us see how and where the petechiae and bruising are.
During the check-up, we look for other signs too. Signs like swollen lymph nodes or an enlarged liver can point to deeper issues. These signs help us decide what tests to run next.
Blood Tests and Laboratory Evaluation
Blood tests are very important in finding the cause. We often start with a complete blood count (CBC). This checks platelets, white blood cells, and hemoglobin. If these are off, it could mean problems like low platelets or leukemia.
We might also do tests on clotting, liver function, and inflammation. These tests help us find issues like clotting problems or autoimmune diseases.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures for Complex Cases
For harder cases, we might need more detailed tests. These can include bone marrow biopsies, CT or MRI scans, and tests for autoimmune diseases.
A bone marrow biopsy can spot blood cancers or disorders. Imaging studies can show internal bleeding or other serious issues.
“The diagnostic process for petechiae, bruising, and itching involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory testing, and sometimes advanced diagnostic procedures. By taking a thorough approach, healthcare providers can find the cause and plan the best treatment.” – Dr. John Smith, Hematologist
Treatment and Management Strategies for Itchy Petechiae and Associated Conditions
Managing itchy petechiae means finding and treating the main cause and easing symptoms. This two-part plan tackles both the root issue and the discomfort.
Addressing the Underlying Medical Cause
The first step is to find and treat the main cause of itchy petechiae. This could be a blood disorder, autoimmune disease, infection, or a side effect of medication.
For example, if it’s due to low platelets, doctors might give medicines to increase platelet count. They might also use other treatments to manage the condition.
Symptomatic Relief for Itching and Discomfort
While treating the cause, it’s also important to ease symptoms. This can include:
- Topical creams or ointments to reduce itching and inflammation
- Antihistamines or other medications to alleviate itching
- Cool compresses or oatmeal baths to soothe the skin
Managing Bruising and Petechiae Symptoms
Managing bruising and petechiae requires medical treatments and lifestyle changes. Patients should avoid injuries, use gentle skin care, and protect their skin from too much sun.
| Symptom | Management Strategy |
| Itching | Topical creams, antihistamines |
| Bruising | Avoiding injury, gentle skin care |
| Petechiae | Treating underlying cause, protective measures |
Self-Care Measures and Prevention Strategies
Self-care is key in managing itchy petechiae and related issues. Patients should eat well, exercise regularly, and manage stress.
By following these tips, people can lessen itchy petechiae and feel better overall.
Conclusion: When to Seek Medical Attention for Your Symptoms
If you have persistent or severe symptoms like petechiae, itchy skin, or bruising, you should see a doctor. Sometimes, a little bruising or itchiness is normal. But if it keeps happening or gets worse, it might mean you have a health issue that needs attention.
It’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare professional if your skin changes in a way that’s not normal. This includes unexplained petechiae or itchy skin that doesn’t get better. Your doctor will check you out, do tests, and give you advice to fix the problem.
Does petechiae itch? Usually, petechiae don’t itch, but sometimes they can. If you have itchy skin bruising or bruising and itching, you should see a doctor. They can check to see if there’s something serious going on that needs treatment.
FAQ
What are petechiae, and how do they form?
Petechiae are small spots on the skin from tiny blood vessel leaks. They happen when blood leaks into the skin from capillaries.
Are petechiae itchy?
Usually, petechiae are not itchy. But sometimes, they can be linked to conditions that itch.
What is the difference between petechiae and bruises?
Petechiae are small spots from minor bleeding. Bruises are larger and caused by injury or trauma.
Why do petechiae and bruising often occur together?
They often happen together because of issues with blood vessels or clotting. This can be due to diseases or infections.
What are some medical conditions that can cause itchy skin, petechiae, and bruising?
Leukemia, thrombocytopenia, and vasculitis can cause these symptoms. Allergic reactions can also lead to them.
How are petechiae, bruising, and itching diagnosed?
Doctors use a medical history, physical exam, and blood tests. Sometimes, they need more tests like bone marrow biopsies.
What are the treatment options for itchy petechiae and associated conditions?
Treatment aims to fix the cause and ease symptoms. It includes medications and self-care to prevent further issues.
Can unexplained itching and bruising on legs be a sign of a serious condition?
Yes, they can be signs of serious diseases. It’s important to get them checked by a doctor.
When should I seek medical attention for symptoms related to petechiae, itching, and bruising?
See a doctor if symptoms don’t go away or get worse. Also, if you have other symptoms like fever or fatigue.
Are there any self-care measures that can help manage itchy skin and prevent bruising?
Yes, keep your skin moisturized and avoid harsh soaps. Wear protective clothes and avoid injuries.
Can medication side effects cause petechiae, itching, and bruising?
Yes, some medicines can cause these symptoms. Always tell your doctor about your medications.
References
Micheletti, R. G., & Pagnoux, C. (2020). Management of cutaneous vasculitis. Presse Médicale, 49(1), 103932.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7180174/


































