A heart blockage operation, also known as coronary angioplasty, is a procedure to fix blocked arteries. These blockages can happen when plaque builds up. This can lead to less blood flow and serious health problems.
During the procedure, a stent is put in the artery. This keeps it open and improves blood flow. Liv Hospital is known for its top-notch, patient-focused heart care. It’s a go-to place for heart procedures like angioplasty and stent insertion.
Key Takeaways
- Coronary angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure to restore blood flow.
- A stent is used to keep the artery open after the procedure.
- Liv Hospital offers patient-centered cardiac care for advanced heart procedures.
- The procedure is used to treat narrowed or blocked arteries.
- Stent placement helps improve blood flow and reduce symptoms.
Understanding Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Blockages
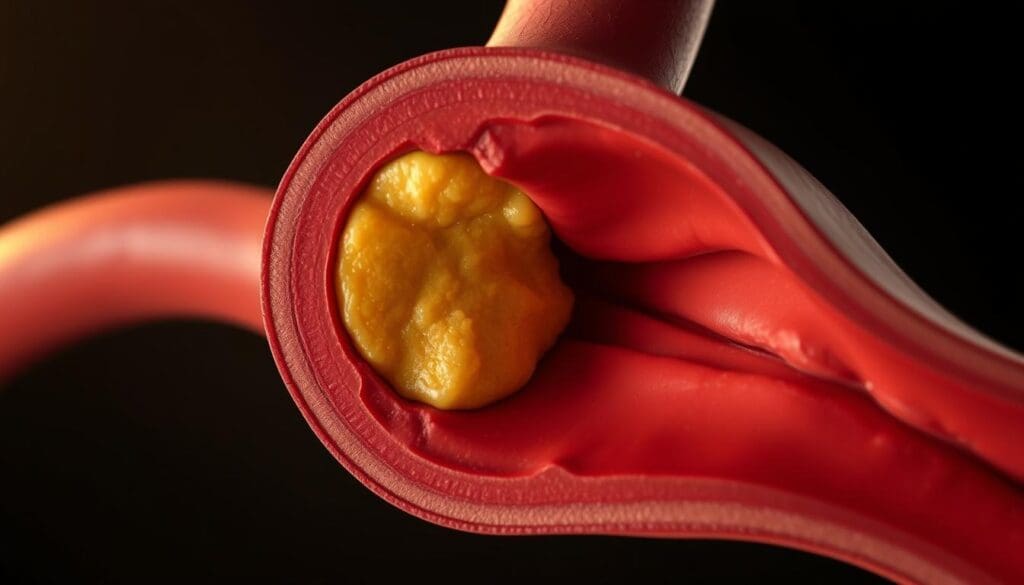
It’s important to know about coronary artery disease and heart blockages. This knowledge helps us see why stent placement is needed. Coronary artery disease happens when the main blood vessels to the heart get damaged or diseased. This damage is caused by plaque buildup.
Plaque Buildup in Arteries
Plaque buildup, or atherosclerosis, is when fatty deposits, like cholesterol, gather inside artery walls. This can narrow or block the coronary arteries. It limits blood flow to the heart muscle.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Blockage
Symptoms of coronary artery blockage can be different. They often include chest pain or discomfort, known as angina. You might also feel short of breath or tired. A complete blockage can cause a heart attack. It’s key to notice these symptoms early for quick medical help.
Diagnosing Heart Blockages
To diagnose heart blockages, doctors use several tests. These include electrocardiograms (ECGs), stress tests, and coronary angiography. Coronary angiography uses dye and X-rays to see the coronary arteries. It helps find any blockages.
| Diagnostic Test | Description | Key Findings |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Measures the electrical activity of the heart | Identifies patterns that may indicate ischemia or previous heart damage |
| Stress Test | Evaluates heart function under physical stress | Reveals signs of ischemia or blockages when the heart is under strain |
| Coronary Angiography | Uses dye and X-rays to visualize coronary arteries | Directly shows the location and severity of blockages |
Knowing about these tests is key to finding the right treatment for coronary artery disease and heart blockages.
What Is a Heart Blockage Operation?
When coronary arteries get blocked, doctors use different methods to fix them. A heart blockage operation is a term for these methods. They aim to clear blockages in the coronary arteries.
Types of Interventions for Blocked Arteries
There are two main types of treatments for blocked arteries. Minimally invasive procedures are often chosen because they are safer and have quicker recovery times. These include coronary angioplasty and stenting.
“The use of stents in coronary angioplasty has changed how we treat coronary artery disease,” says a top cardiologist. This shows how important stent placement is in treating heart blockages.
Coronary Angioplasty Explained
Coronary angioplasty, or PTCA, is a way to open blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. It’s a surgical repair of a blood vessel. A catheter with a balloon tip is used to reach the blockage.
The balloon is then inflated to move the plaque and stretch the artery.
When Surgery Is Necessary vs. Minimally Invasive Options
The choice between surgery and less invasive options depends on several things. These include how bad the blockage is, the patient’s health, and other medical conditions. Minimally invasive procedures are usually better for less complex blockages.
In summary, knowing about the different treatments for heart blockages is key to making good health choices. While coronary angioplasty is a common and effective method, choosing between surgery and less invasive options should be discussed with a doctor.
The Evolution of Stent Technology
Stent technology has seen big changes over the years. It has changed how we treat heart problems. It all started with balloon angioplasty, a big step forward but with some limits.
From Balloon Angioplasty to Modern Stents
Balloon angioplasty was a new way to fix heart issues without surgery. But, it had a big problem: the artery could close up again. To fix this, stents were created.
A stent is a tiny, metal mesh that keeps the artery open. Modern stents are now more advanced. They are flexible and can release medicine to stop the artery from closing again.
Types of Cardiac Stents
There are many kinds of cardiac stents, each with special features:
- Bare-metal stents: The first kind, but they can sometimes cause the artery to narrow again.
- Drug-eluting stents: These have medicine on them to stop the artery from narrowing.
- Bioresorbable stents: Made to dissolve over time, they might reduce long-term problems.
The growth of stent technology has greatly helped in treating heart disease. It has given patients better and safer treatments. With ongoing research, we can look forward to even more improvements.
How Stent Placement Works: The Procedure Step by Step
Learning about stent placement is key for those going through it. It’s a detailed process, from start to finish. It includes getting ready, inserting a catheter, and making sure the stent is in the right place.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before starting, patients get medicine to relax. The spot where the catheter goes is cleaned and numbed. This makes the procedure less painful.
Catheter Insertion and Navigation
A small cut is made, and a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel. It’s guided through the body using X-rays to reach the blocked artery. Getting it to the right spot is very important.
Balloon Inflation and Stent Deployment
With the catheter in place, a balloon is inflated to open the artery. This pushes the plaque against the walls, improving blood flow. Then, the stent is put in, expanding to keep the artery open. It supports the artery walls and prevents future blockages.
Confirming Successful Placement
After the stent is in, more X-rays are taken to check its position and blood flow. This step confirms the procedure’s success and the patient’s safety.
The whole stent placement procedure usually takes an hour to an hour and a half. It can take longer if the case is more complex. Knowing these steps helps patients understand the care and precision in this important procedure.
What to Expect During a Heart Blockage Operation
When you’re getting ready for a heart blockage operation, knowing what to expect is key. This knowledge can make you feel less anxious and help the process go smoother.
Anesthesia and Comfort Measures
You’ll get medicine to relax during the operation. You’ll be awake but feel sleepy and comfortable. Local anesthesia will make the area where the catheter goes numb, so you won’t feel pain.
Duration of the Procedure
The time it takes for a heart blockage operation varies. It usually lasts from 30 minutes to a few hours. The complexity of the blockage and how many stents are needed can affect the time.
The Patient Experience in the Catheterization Lab
In the catheterization lab, you’ll lie on a table. The medical team will watch your vital signs closely. They’ll put a catheter through an artery in your leg or arm, leading to your heart. You’ll be awake and can talk to the staff if you need to.
| Aspect | Description |
| Anesthesia | Local anesthesia to numb the catheter insertion area |
| Procedure Duration | Typically 30 minutes to a few hours |
| Patient Experience | Awake, relaxed, and monitored closely by medical staff |
Knowing these details about a heart blockage operation can make patients feel more ready and less worried about it.
Alternatives to Stent Placement for Heart Blockages
Stent placement is a common treatment for heart blockages. But, there are other ways to manage coronary artery disease. These alternatives can help control symptoms and slow disease progression.
Medication Therapy
Medication therapy is a good option for some patients. It uses drugs to manage symptoms and slow disease. These drugs can lower blood pressure, cholesterol, and prevent blood clots.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
CABG is a surgical procedure that creates a new path for blood to the heart. It’s recommended for complex or multiple blockages. CABG can offer a long-lasting solution, improving blood flow and reducing symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications as Treatment
Lifestyle changes are key in managing heart blockages. They can be used alone or with other treatments. Changes include a healthy diet, more exercise, quitting smoking, and stress management. These can greatly improve heart health.
In conclusion, while stent placement is common, other options like medication, CABG, and lifestyle changes are also available. The right treatment depends on the patient’s condition and needs.
Benefits and Effectiveness of Stent Placement
Stent placement has changed how we treat heart disease. It’s not just effective; it also makes life better for those who get it.
Immediate Relief of Symptoms
Stent placement quickly eases symptoms of heart blockages. People often feel less chest pain and shortness of breath. This lets them do more of what they love every day.
Long-term Outcomes and Success Rates
Research shows stent placement works well over time. It keeps arteries open and lowers the chance of needing more surgeries. The long-term outcomes are mostly good, thanks to the right stent and care.
- High success rates in maintaining artery patency
- Reduced need for repeat procedures
- Improved long-term health outcomes with proper care
Quality of Life Improvements
Stent placement greatly improves life quality. People can start doing physical activities they used to avoid. This makes life better and more enjoyable.
In short, stent placement brings many benefits. It relieves symptoms right away and improves health over time. Knowing these benefits helps patients choose the best treatment for them.
Potential Risks and Complications
Stent placement is a common treatment for coronary artery disease. But, it’s important to know the risks involved. Complications can happen during, right after, or even long after the procedure.
During the Procedure
Several risks can happen during stent placement. These include allergic reactions to the dye used, damage to blood vessels, and bleeding or clotting at the catheter site. In rare cases, the stent might not expand right or dislodge from its place.
Short-term Complications
Short-term issues can include infection at the catheter site, bleeding needing a transfusion, and blood clots on the stent. These clots can cause a heart attack if not treated quickly.
For more details on the procedure and its risks, check out this resource. It offers a detailed look at angioplasty and stent placement.
Long-term Considerations
Long-term risks include restenosis, where the artery narrows again, and stent thrombosis, a blood clot inside the stent. Making lifestyle changes and taking medication can help reduce these risks.
| Complication | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
| Allergic Reactions | Reactions to contrast dye | Pre-medication, alternative dyes |
| Bleeding/Clotting | Bleeding or clotting at catheter site | Close monitoring, medication |
| Restenosis | Narrowing of treated artery | Lifestyle changes, medication |
Recovery and Life After Stent Placement
Recovering after stent placement involves several steps. These include staying in the hospital, taking medication, and making lifestyle changes. Knowing about these steps can help patients recover better.
Hospital Stay and Immediate Recovery
Most patients leave the hospital within 2 days after the stent is placed. You might be able to walk around 6 to 8 hours after the procedure. This time can vary based on your health and the procedure details.
A medical expert says, “The first few days are very important. Patients should follow their doctor’s advice closely for a smooth recovery.” Resting and avoiding hard activities are important during this time.
| Activity | Recommended Timing | Notes |
| Walking | Within 6-8 hours | Start with short walks and gradually increase distance |
| Driving | 24 hours post-procedure | Avoid driving if you’re feeling weak or uncomfortable |
| Strenuous Activities | Avoid for 1 week | This includes heavy lifting, bending, or exercise |
Medication Regimen
After the stent is placed, you’ll take medicine to prevent clots and manage symptoms. It’s very important to take this medicine as directed to avoid problems.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle changes is key to recovery and long-term health. This includes eating right, exercising, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
“A heart-healthy lifestyle can greatly improve outcomes after stent placement,” a cardiologist notes. “This means eating well, staying active, and not smoking.”
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
Regular check-ups with your doctor are vital. They help check how well the stent is working and your heart health. These visits can catch any problems early.
By understanding the recovery process and following care instructions, patients can improve their outcomes and quality of life after stent placement.
Conclusion
It’s important for patients with coronary artery disease to know about heart blockage operations and stent placement. These procedures, like angioplasty and stenting, help get blood flowing to the heart again.
Stent placement is a big step forward in treating blocked arteries. It’s less invasive than old surgeries. Places like Liv Hospital use new stent designs to help patients get better.
Stent placement can quickly ease symptoms and has good long-term results. But, it’s key to know the possible risks and complications of heart stint surgery.
Learning about heart blockage operations and stent placement helps patients make better choices. This knowledge can lead to better health outcomes.
FAQ
What is a heart stent operation?
A heart stent operation is a way to open blocked arteries. It uses a small, mesh-like device called a stent. This keeps the artery open, improving blood flow to the heart.
What is the purpose of stent placement in the heart?
Stent placement treats coronary artery disease. It restores blood flow, relieves chest pain, and lowers heart attack risk.
How is a stent placed in the heart?
To place a stent, a catheter is inserted through an artery. It’s guided to the blocked artery. A balloon inflates the artery, and the stent expands to keep it open.
What are the different types of stents used in heart procedures?
There are several cardiac stents, like bare-metal, drug-eluting, and bioresorbable stents. Each type is chosen based on the patient’s condition.
What is angioplasty, and how does it relate to stent placement?
Angioplasty widens narrowed or blocked arteries. It often uses a balloon and may include stent placement. This is a common treatment for coronary artery disease.
Are there alternatives to stent placement for treating heart blockages?
Yes, alternatives include medication, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, and lifestyle changes. These include diet, exercise, and quitting smoking.
What are the possible risks and complications of stent placement?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and reaction to the stent. Restenosis (re-narrowing) and stent thrombosis are long-term risks.
How long does it take to recover from a stent placement procedure?
The hospital stay is usually short, often just overnight. Recovery takes a few days to a week. Patients follow a medication regimen and make lifestyle changes.
Can stent placement improve quality of life?
Yes, successful stent placement can greatly improve life. It relieves symptoms, improves exercise tolerance, and lowers heart attack risk.
What follow-up care is required after stent placement?
Follow-up care includes monitoring for complications and following a medication regimen. Lifestyle changes and regular appointments with a healthcare provider are also important.
References:
- Zhang, N., et al. (2021). Efficacy and safety of coronary stent intervention for coronary heart disease: A comparative study with drug therapy. Annals of Medicine, 53(1), 545-553. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8507088/





