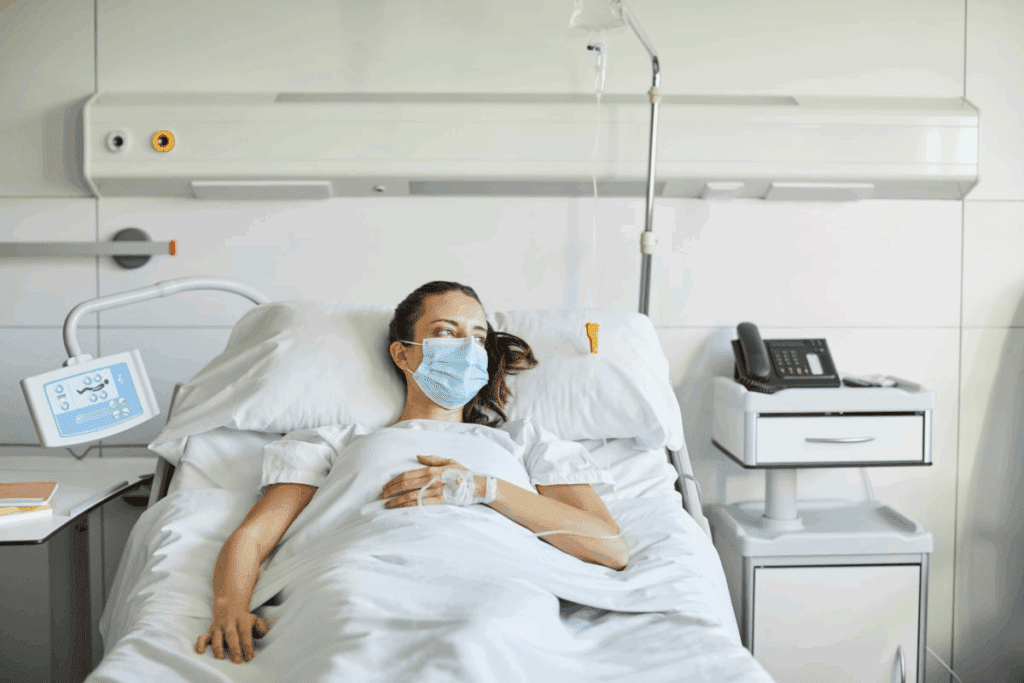
Stereotactic biopsy calcifications are often performed when breast imaging shows small calcium deposits that may need further evaluation. Dealing with breast calcifications can be scary, but choosing the right biopsy is key for peace of mind and a correct diagnosis.
At Liv Hospital, we use trusted expertise, cutting-edge technology, and a patient-first approach. We make sure every step of your journey is handled with care and precision.
Getting a breast biopsy can be overwhelming. Our aim is to help you understand the stereotactic biopsy for breast calcifications — a minimally invasive method that uses mammography to locate and collect tissue samples from suspicious areas in the breast.
Knowing more about stereotactic biopsy calcifications helps patients feel informed and confident throughout the process, ensuring better understanding and comfort during diagnosis.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the process of stereotactic biopsy for breast calcifications.
- The importance of choosing the right biopsy method for accurate diagnosis.
- Liv Hospital’s approach to patient care and advanced technology.
- The role of mammography imaging in stereotactic biopsy.
- Guidance and support throughout the biopsy process.
Understanding Breast Calcifications
Breast calcifications are common on mammograms. Knowing what they are helps decide if a biopsy is needed. These calcifications are small crystals that form when cells divide or die. Most are not cancerous.
What Are Breast Calcifications?
Breast calcifications are tiny calcium deposits in the breast tissue. They show up on mammograms. They can mean different things, from benign changes to serious issues like cancer.
Types of Breast Calcifications
There are two main types of breast calcifications: macrocalcifications and microcalcifications.
- Macrocalcifications are larger and usually not harmful. They often come with aging and are not a worry.
- Microcalcifications are smaller and might mean cancer or a precancerous condition. If they’re clustered or in a certain pattern, they need more checking.
When Calcifications Require Further Investigation
Not every calcification needs a biopsy. But, some signs might mean you need to check further:
- Clustered or tightly grouped calcifications
- Calcifications that are new or have changed in appearance
- Calcifications with other suspicious findings on the mammogram
About 10% of nonpalpable breast lesions get biopsied for calcifications. Half are ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), and a quarter are invasive cancer. Knowing this helps figure out if a breast calcification biopsy is needed.
If a biopsy for breast calcifications is suggested, a stereotactic biopsy is usually chosen. It’s accurate in finding the calcified area. The results of a breast calcification biopsy are key for deciding on treatment.
What Is a Stereotactic Biopsy for Calcifications?

A stereotactic biopsy for calcifications is a precise way to check out suspicious breast calcifications. It uses mammography to guide a needle to the exact spot in the breast where calcifications are found. This allows for a tissue sample to be taken for further study.
Definition and Purpose
A stereotactic biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure. It uses a special mammography machine to find the exact location of calcifications in the breast. The main goal is to figure out if these calcifications are benign or malignant. This is key for making a diagnosis and planning treatment.
We use advanced imaging technology to accurately target the calcified area. This reduces the chance of sampling error and boosts diagnostic accuracy.
When Stereotactic Biopsy Is Recommended
A stereotactic biopsy is usually suggested when mammography or other imaging tests show suspicious calcifications. This is true when calcifications are new, changing, or have a higher risk of being cancerous.
Our medical team looks at several factors. These include the patient’s medical history, imaging results, and overall health. They decide if a stereotactic biopsy is the best next step.
Advantages Over Other Imaging Methods
Stereotactic biopsy has several benefits over other imaging-guided biopsy methods, mainly for diagnosing calcifications. Higher accuracy is achieved because of the precise location of calcifications using mammography. Also, this procedure is generally less invasive than surgical biopsies. This means less discomfort and scarring for the patient.
- Precise targeting of calcifications
- Minimally invasive with less discomfort
- Reduced risk of complications
- Quick recovery time
Choosing a stereotactic biopsy for calcifications offers a reliable diagnostic method. It provides vital information for patient care.
Types of Breast Biopsies Compared
There are several types of biopsies for breast abnormalities, each with its own method and benefits. Knowing about these can help patients make better choices for their care.
Fine Needle Aspiration
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) uses a thin needle to take a cell sample from the breast. It’s less invasive and quicker, often without anesthesia. But, it might not always get enough cells for a clear diagnosis, like for calcifications.
Core Needle Biopsy
Core needle biopsy (CNB) uses a bigger needle to get a tissue sample. It gives more tissue for tests, making it better for diagnosing many breast issues, including calcifications. CNB is chosen for its good balance of invasiveness and accuracy.
Surgical Biopsy
Surgical biopsy, or excisional biopsy, removes part or all of the suspicious area. It’s very accurate but more invasive, needing stitches and a longer recovery. It’s used when other methods don’t work or when cancer is likely.
Why Stereotactic Biopsy Is Preferred for Calcifications
Stereotactic biopsy is great for calcifications because it’s accurate and not too invasive. It uses mammography to find and sample calcified areas. Unlike FNA, it gets enough tissue, and unlike surgical biopsy, it’s less invasive.
The following table compares the different types of breast biopsies:
| Biopsy Type | Invasiveness | Diagnostic Accuracy for Calcifications | Recovery Time |
| Fine Needle Aspiration | Low | Low to Moderate | Minimal |
| Core Needle Biopsy | Moderate | High | Short |
| Surgical Biopsy | High | Very High | Longer |
| Stereotactic Biopsy | Moderate | High | Short |
Comparing these biopsies shows that a stereotactic biopsy is best for calcifications. It’s a top choice for many patients and doctors.
Preparing for Your Stereotactic Biopsy
Getting ready for a stereotactic biopsy is important. We’ll help you understand what to do. There are key steps to take for a smooth procedure.
Medical Considerations and Contraindications
Talk to your doctor about your health before the biopsy. Some conditions or medicines might change things.
Important Medical Considerations:
- Any allergies or sensitivities to medications or materials used in the biopsy process
- Current medications, including blood thinners like aspirin or NSAIDs
- Previous surgeries or biopsies in the breast area
- Any pacemakers or other implanted medical devices
What to Tell Your Doctor
Tell your doctor about your health and any medicines you’re taking. This includes supplements and vitamins. Also, mention any allergies or medical conditions.
Medication Guidelines
Stop taking aspirin and NSAIDs seven days before the biopsy. This helps avoid bleeding. Your doctor may also tell you to stop other medicines that could affect the procedure.
| Medication | Action Required | Timing |
| Aspirin and NSAIDs | Stop taking | 7 days before biopsy |
| Blood Thinners | Consult your doctor | As advised by your doctor |
What to Wear and Bring
Wear comfy clothes that let you easily access your breasts. Bring a friend or family member for support. Also, bring any medical records or imaging results.
By following these tips and talking to your doctor, you’ll be ready for a successful biopsy.
The Stereotactic Biopsy Procedure: Step-by-Step
A stereotactic biopsy is a precise way to diagnose breast calcifications. Knowing what to expect can make a big difference. We’ll walk you through each step, so you’re ready for the procedure.
Positioning and Comfort Measures
The first step is getting you comfortable on a special table. You’ll lie on your stomach with your breast in a hole. This lets us get the best images. Our team will make sure you’re comfy, as you might stay like this for 30 to 60 minutes.
Breast Compression and Imaging
Next, your breast will be pressed between two plates, like a mammogram. This is key for clear images and finding the right spots. You might feel some discomfort, but it’s needed for the procedure.
Local Anesthesia Administration
To reduce discomfort, we’ll numb the area with local anesthesia. This is done with a small needle, and you might feel a pinch. But don’t worry, the numbness will kick in fast, so you won’t feel pain.
Needle Insertion and Sample Collection
With your breast compressed and numb, we’ll use a special needle to take tissue samples. The needle is guided by mammography, so we get the right samples. We might take a few samples to make sure we’re accurate.
| Procedure Step | Description |
| Positioning | Lying on stomach with breast through a dedicated opening |
| Breast Compression | Compressing breast between two plates for clear imaging |
| Local Anesthesia | Numbing the area around the biopsy site |
| Needle Insertion | Inserting a biopsy needle to collect tissue samples |
Knowing about the stereotactic biopsy can help ease your worries. Our team is here to make the process as smooth and comfortable as possible for you.
Equipment Used in Stereotactic Biopsy of Calcifications
The stereotactic biopsy for breast calcifications uses top-notch equipment. This tech is key for getting accurate samples for tests.
Stereotactic Mammography Machine
The mammography machine is at the heart of the system. It takes clear images of the breast. This helps pinpoint calcifications and guides the needle.
Biopsy Needles and Devices
Special needles are used to take tissue samples. They’re made to get enough tissue for tests without causing too much pain. The needle’s type and size depend on the calcification and the patient’s body.
Tissue Markers
After the biopsy, a marker might be left at the site. These markers are small and show up on scans. They help doctors keep an eye on the area later.
Specimen Handling Equipment
Special tools are used to handle the tissue samples. They make sure the samples stay good for tests. This includes containers and fixatives that keep the tissue in top shape.
These advanced tools make stereotactic breast biopsy for calcifications more accurate and safe. Knowing about each piece helps patients trust the process more.
Post-Procedure Care and Recovery
After a stereotactic biopsy for breast calcifications, taking care of yourself is key. We know the recovery is as important as the procedure. We’re here to help you through it.
Immediate Aftercare at the Facility
Right after the biopsy, you’ll go to a recovery area. Our medical team will watch over you and give you tips for the biopsy site.
- Apply pressure to the biopsy site to minimize bruising
- Keep the area clean and dry
- Monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or increased pain
Managing Discomfort and Pain
It’s normal to feel some discomfort or pain after the biopsy. We suggest taking over-the-counter pain relievers as directed. Sometimes, we might prescribe stronger medication.
Tips for managing pain:
- Take pain medication as directed, usually before the pain becomes severe
- Apply ice packs to the affected area to reduce swelling
- Rest and avoid strenuous activities
Activity Restrictions
It’s important to follow activity restrictions after your biopsy. Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous exercises for at least 24 hours. You can usually get back to normal activities in a day or two. Just listen to your body and adjust as needed.
Normal vs. Abnormal Symptoms
Knowing the difference between normal and abnormal symptoms is key. Common symptoms include mild pain, bruising, and swelling. But, if you have severe pain, heavy bleeding, or signs of infection, call us right away.
If you notice any of the following, seek medical attention:
- Increasing redness or swelling around the biopsy site
- Pus or discharge from the biopsy site
- Fever or chills
- Severe pain not relieved by medication
By following these guidelines and knowing what to expect, you can avoid complications. If you have any questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
Understanding Your Breast Calcification Biopsy Results
Your breast calcification biopsy results will tell you if the changes are benign or malignant. This will help decide what treatment you need next. Waiting for these results can be nerve-wracking. We’ll explain what your biopsy results might mean, including the time it takes to get them.
We’ll also talk about what benign, atypical, or malignant findings mean for your health. And what steps you should take next.
Timeframe for Results
How long it takes to get your biopsy results depends on the lab and the test’s complexity. Usually, it’s a few days to a week. We’ll call you as soon as we have the results to talk about them and what to do next.
Benign Findings
If your biopsy shows benign changes, it means the calcifications are not cancerous. Benign breast calcifications are common and usually don’t need treatment. But your doctor might want to keep an eye on them to make sure they don’t change.
Atypical or High-Risk Findings
Atypical or high-risk lesions are abnormal cell changes that are not cancer but could become cancerous. If you get this diagnosis, your doctor will talk about what it means and what to do next. They might suggest more tests or treatment.
Malignant Findings
If the biopsy shows malignancy, it means cancer cells were found. Malignant breast calcifications are linked to certain types of breast cancer, like DCIS. If you get this diagnosis, your healthcare team will create a treatment plan just for you.
Understanding your biopsy results is key to managing your health. We’re here to support you, from explaining your results to helping with any treatment you need.
Risks, Complications, and Limitations
It’s important for patients to know about the risks of stereotactic biopsy for breast calcifications. This procedure is generally safe but can have risks and limitations like any medical treatment.
Common Side Effects
Most people have little to no side effects from this biopsy. Common issues include:
- Bruising or hematoma at the biopsy site
- Discomfort or pain during or after the procedure
- Mild swelling
These side effects are usually short-lived and go away in a few days.
Rare Complications
While rare, there are some complications to be aware of:
- Infection at the biopsy site
- Allergic reactions to the local anesthetic
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lung), though very rare
Following the post-procedure care instructions can help avoid these complications.
Accuracy and False Negatives
Stereotactic biopsy is very accurate for diagnosing breast calcifications. But, no test is perfect, and false-negative results can happen. A false-negative result means the biopsy shows no cancer, but there is actually cancer.
To lower this risk, we use the latest imaging and make sure the biopsy sample is enough. If there’s any doubt, we might suggest more tests.
When Additional Testing May Be Needed
In some cases, more tests might be needed after a stereotactic biopsy. This could be because of:
- Inconclusive or discordant biopsy results
- Atypical or high-risk findings
- New or changing symptoms
We will talk about the need for more tests or follow-ups based on your results and situation.
| Potential Risks | Frequency | Management |
| Bruising/Discomfort | Common | Over-the-counter pain relievers |
| Infection | Rare | Antibiotics |
| False-Negative Results | Small chance | Additional testing or follow-up |
Conclusion
We’ve looked into how important stereotactic biopsy is for diagnosing breast calcifications. This method is key in managing breast health. It helps doctors find the right treatment for patients with suspicious calcifications seen on mammograms.
The stereotactic biopsy is a precise way to check calcifications that can’t be seen clearly by other methods. It helps doctors figure out if these calcifications are harmless or if they might be cancer.
This guide has shown how a breast biopsy is essential for catching and managing breast health problems early. The results from a stereotactic biopsy help doctors plan the best treatment. This leads to better care for patients.
Knowing about stereotactic biopsy helps both patients and doctors make better choices for breast health. This method is a big part of diagnosing and treating breast issues.
FAQ
What type of biopsy is typically done for breast calcifications?
A stereotactic biopsy is often used for breast calcifications. It uses mammography to target the calcified area accurately.
How is a stereotactic breast biopsy for calcifications performed?
The breast is compressed during the biopsy. Mammography images guide the needle to the calcification. Then, a tissue sample is taken for examination.
What are the different types of breast biopsies?
There are several types of breast biopsies. These include fine needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, surgical biopsy, and stereotactic biopsy. Each has its own use and benefits.
Why is stereotactic biopsy preferred for diagnosing calcifications?
Stereotactic biopsy is preferred because it targets the calcification precisely. This is done under mammographic guidance, making the sample collection more accurate.
What should I expect during a stereotactic biopsy procedure?
Your breast will be compressed, and local anesthesia will be given to reduce discomfort. The needle is guided to the calcification using mammography images. A tissue sample is then taken.
How long does it take to receive the results of a breast calcification biopsy?
You can expect to get your biopsy results in a few days to a week after the procedure.
What are the possible outcomes of a breast calcification biopsy?
The results can be benign, atypical, or malignant. Your healthcare provider will discuss the results with you and suggest next steps.
Are there any risks or complications associated with stereotactic biopsy?
Common side effects include bruising, swelling, and discomfort. Rare complications include infection or significant bleeding. The accuracy of the biopsy is high, but sometimes more testing is needed.
How can I prepare for a stereotactic biopsy?
Discuss your medical history and medications with your doctor. Avoid medications that may increase bleeding risk. Wear comfortable clothing and bring a support person.
What is the post-procedure care for a stereotactic biopsy?
You may feel some discomfort, which can be managed with pain relievers. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for activity restrictions and watch for any abnormal symptoms.
References
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2022, March 24). Angioplasty and stent placement for the heart. National Institutes of Health.https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/angioplasty


































