Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer. It mainly affects kids and young adults. This cancer grows fast and can spread to other parts of the body.Learn alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cancer fast facts, symptoms, and treatments for early detection and care.
Knowing the symptoms and treatment options for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is key. This cancer often shows up in the limbs or trunk. It’s a big worry for those who get it.
At Liv Hospital, we offer full and caring care for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma patients. We’ll look at seven important facts about this condition. We’ll cover symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment choices.
Key Takeaways
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is an aggressive subtype of rhabdomyosarcoma.
- It primarily affects children and young adults.
- Symptoms vary depending on the tumor location.
- Early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
- Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Understanding Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Cancer
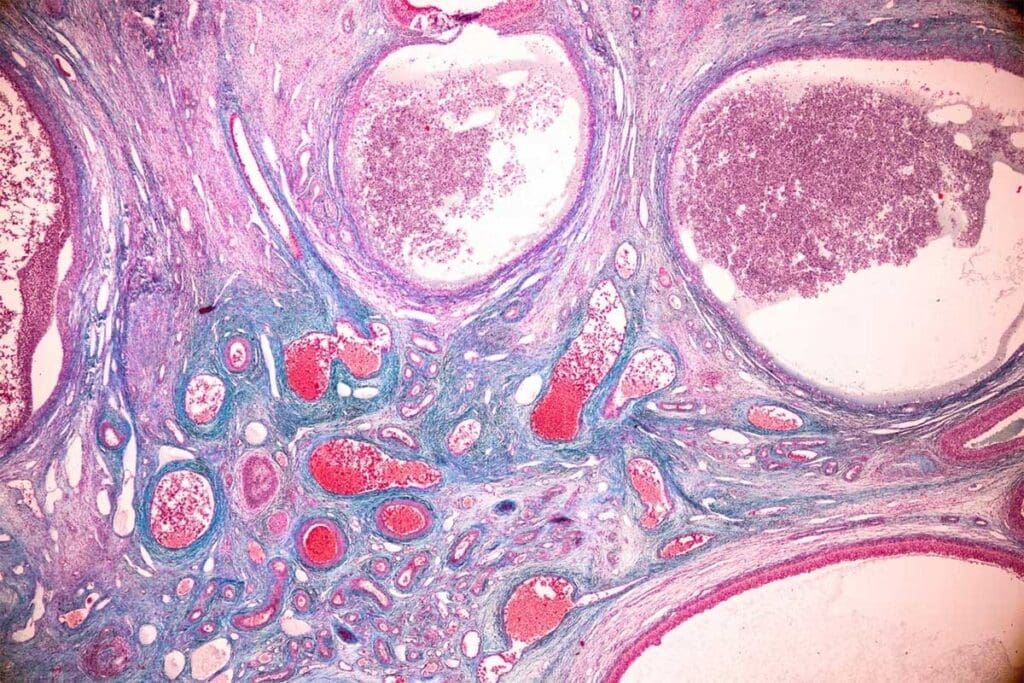
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare cancer found more in older kids and adults. It’s known for being aggressive and hard to treat.
Definition and Classification
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a soft tissue sarcoma that starts in muscle cells. It looks like lung tissue, which is why it’s called alveolar. It’s part of the rhabdomyosarcoma family, with alveolar and embryonal being the main types.
Doctors sort rhabdomyosarcoma by how it looks under a microscope. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma has a special pattern. Knowing this helps doctors figure out how to treat it.
Key Classification Features:
- Histological pattern
- Genetic characteristics
- Age of onset
Prevalence and Demographics
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma makes up about 20-30% of rhabdomyosarcoma cases. It’s more common in teens and young adults. The cancer’s spread varies by age and other factors.
| Age Group | Prevalence |
| 0-9 years | Low |
| 10-19 years | Moderate |
| 20+ years | Higher |
A leading oncologist says, “Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is tough to beat because it grows fast and needs special treatment.” This shows why it’s key to know about this cancer type.
“Diagnosing and treating alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma needs a team effort. They look at the tumor’s appearance and genetics.”
7 Essential Facts About Alveolar RMS Cancer
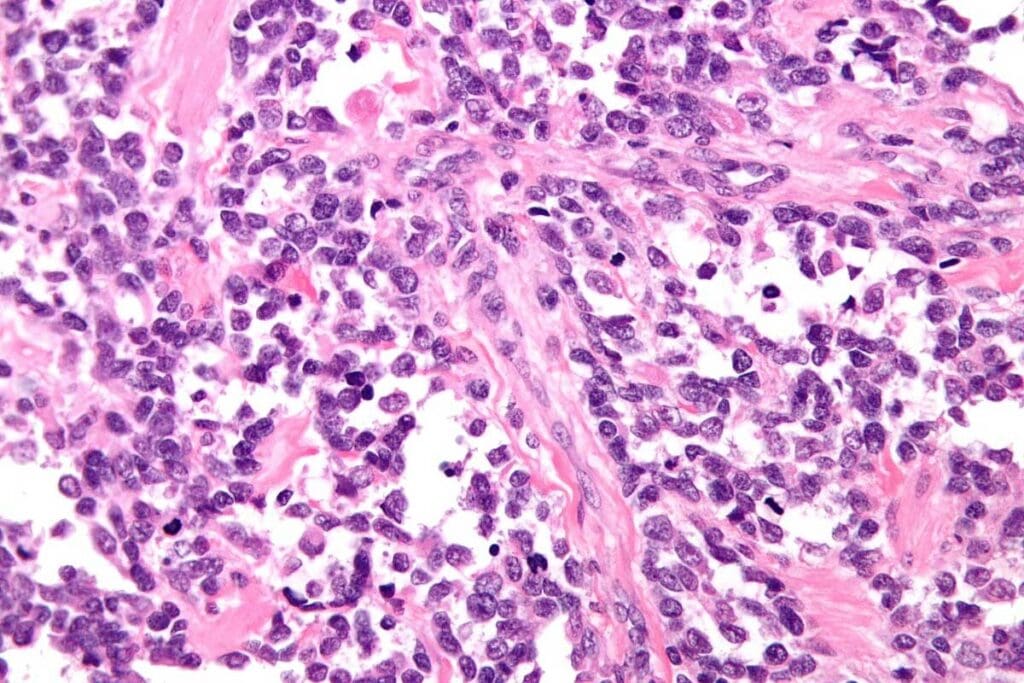
Exploring alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma reveals key facts. It’s a subtype of rhabdomyosarcoma known for its aggressive nature and unique traits.
Fact 1: Aggressive Soft Tissue Sarcoma
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a fast-growing soft tissue sarcoma. It can quickly spread to other parts of the body. This aggressive behavior means it needs quick and effective treatment.
Fact 2: Affects Both Children and Adults
Rhabdomyosarcoma often hits children, but alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma can affect both kids and adults. It shows up differently in each age group, affecting treatment and outlook.
Fact 3: Common Locations in Limbs and Trunk
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma often shows up in limbs and the trunk. These spots are important because they can affect how well a person moves and their quality of life. Knowing where it often appears helps in catching it early and managing it better.
Fact 4: Distinctive Genetic Characteristics
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is known for a specific genetic trait, the PAX/FOXO1 fusion. This genetic change comes from a chromosomal swap. It’s key for diagnosing and figuring out the risk.
These facts highlight the complexity and challenges of dealing with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Understanding these key points helps healthcare teams and patients tackle the disease’s complexities.
The Biology of Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma
To understand alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, we need to know where it comes from and what genes are involved. It’s a type of rhabdomyosarcoma, a cancer that starts in muscle cells. We’ll explore the cells and genes that make up alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.
Cellular Origins and Development
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma starts in muscle precursor cells that don’t grow into muscle properly. These cells are meant to become part of our skeletal muscle but get stuck in an early stage. They start growing out of control because of genetic changes.
The cells look like primitive muscle cells but don’t have the structure of mature muscle. This is because of how they develop.
The growth of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma involves many molecular steps. Scientists have found that certain genetic changes are key to starting and growing this cancer. Knowing these steps is important for finding new treatments.
Genetic Mutations and Risk Factors
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma has specific genetic changes, like the PAX/FOXO1 fusion from chromosomal swaps. This change is a key sign of the disease and is found in most cases. The PAX/FOXO1 fusion protein helps the tumor cells grow fast.
What causes alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma isn’t fully known. But some genetic traits and environmental factors might play a role. More research is needed to understand how these factors work together to cause this cancer.
Recognizing Symptoms of Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma
The symptoms of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma can be hard to spot at first. Knowing what to look for is key. Getting medical help quickly can really help with treatment.
Early Warning Signs
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma often shows signs that are not very specific. You might see swelling or a lump, feel pain or tenderness, or have trouble moving. For example, a tumor in a limb could make it hard to move or do everyday tasks. A Clinic says symptoms vary based on where and how big the tumor is.
Location-Specific Symptoms
The symptoms of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma depend on where the tumor is. For instance:
- Tumors in the limbs may cause swelling, pain, or limited mobility.
- Tumors in the trunk or abdomen can lead to abdominal pain, swelling, or bowel obstruction.
- Tumors in the head and neck region may cause symptoms such as headaches, double vision, or difficulty swallowing.
Knowing these symptoms by location is key to catching it early.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice symptoms like swelling, pain, or trouble moving, see a doctor. Early treatment can greatly improve the chances of beating alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. If you see any unusual signs or symptoms, don’t hesitate to get help.
Diagnostic Procedures for Alveolar RMS Cancer
Getting a correct diagnosis for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is key. It needs a detailed set of medical tests. These tests help find out if the disease is there and how big it is.
Initial Assessment and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed medical history and physical check-up. Doctors look for signs like swelling, pain, or a mass that can be felt. This helps decide if more tests are needed.
Imaging Studies and Tests
Imaging tests are very important for finding alveolar RMS. X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI show the tumor’s size and where it is. They also check if it has spread.
Biopsy and Pathological Analysis
A biopsy is key to confirming alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. A sample of the tumor is taken and looked at under a microscope. Pathologists check for the special features of alveolar RMS, like its genetic makeup.
Molecular and Genetic Testing
Molecular and genetic tests are also crucial. They find specific genetic changes in alveolar RMS, like the PAX3-FOXO1 or PAX7-FOXO1 genes. This helps confirm the diagnosis and plan the treatment.
By using all these tests, doctors can accurately diagnose alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. They can then create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Staging and Classification Systems
It’s key to know about staging and classification systems for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. These systems help doctors figure out the disease’s spread and plan treatments. They are vital for making the right treatment choices.
TNM Staging Framework
The TNM staging framework is a common way to classify tumors. It looks at the tumor size (T), if it has spread to lymph nodes (N), and if it has metastasized (M). For alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, this system is crucial. It helps doctors understand how far the disease has spread and what treatment is best.
Risk Group Stratification
Risk group stratification is another way to classify patients. It looks at factors like age, where the tumor is, and if it has spread. By considering these, doctors can tailor treatments to fit each patient’s risk level.
“Risk stratification allows for a more personalized approach to treatment, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate care based on their individual risk profile.”
Impact of Staging on Treatment Decisions
Staging and classification systems greatly influence treatment choices for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. They help doctors pick the best treatments, like surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. The aim is to give each patient the best care possible, with the least harm.
As a leading oncologist noted,
“The accurate staging of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is critical for developing effective treatment plans and improving patient outcomes.”
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches for Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Cancer
Treatment for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma combines different therapies. This approach aims to get the best results. We will discuss the options, like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. We will also talk about targeted and immunotherapy.
Surgical Management Options
Surgery is key in treating alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. The goal is to remove the tumor completely. The primary goal is to achieve a wide local excision, ensuring that the margins are free of cancer cells. We consider factors such as tumor size, location, and the patient’s overall health when planning surgical interventions.
The surgical approach may vary depending on the tumor’s location. For example, tumors in the limbs may require a different surgical strategy compared to those in the trunk or head and neck region.
Radiation Therapy Protocols
Radiation therapy is often used with surgery and chemotherapy to treat alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and proton therapy are advanced techniques. They allow for precise targeting of the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
The radiation dose and fractionation schedule are carefully planned. This is based on the tumor’s characteristics and the patient’s age and overall health.
Chemotherapy Regimens
Chemotherapy is a cornerstone in treating alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, especially for patients with metastatic disease. Multi-agent chemotherapy regimens are commonly used. These include drugs like vincristine, actinomycin D, and cyclophosphamide.
| Chemotherapy Agents | Common Combinations |
| Vincristine | VAC (Vincristine, Actinomycin D, Cyclophosphamide) |
| Actinomycin D | VA (Vincristine, Actinomycin D) |
| Cyclophosphamide | VAC/VI (Vincristine, Actinomycin D, Cyclophosphamide / Ifosfamide, Vincristine) |
Targeted and Immunotherapy Approaches
Targeted therapies and immunotherapies are promising for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Targeted agents focus on specific molecular abnormalities. Immunotherapies harness the immune system to attack cancer cells.
Examples of targeted therapies include tyrosine kinase inhibitors, which block specific signaling pathways. Immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors, are also being explored in clinical trials.
Comparing Rhabdomyosarcoma Subtypes
It’s important to know the different types of rhabdomyosarcoma for the right treatment. This cancer affects soft tissues and has various subtypes based on how it looks and its genetics.
Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS)
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common in kids. It often shows up in the head, neck, or genitourinary tract. It has a better chance of recovery, especially if caught early.
Anaplastic Rhabdomyosarcoma
Anaplastic rhabdomyosarcoma is rare and grows fast. It has aggressive cells that don’t respond well to usual treatments. This makes it harder to treat.
International Terminology Variations
Doctors around the world use different names for rhabdomyosarcoma subtypes. Knowing these differences helps doctors talk clearly and work together.
Key Differences in Prognosis and Treatment
The outlook and treatment for rhabdomyosarcoma depend on the subtype. Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma usually has a better chance of recovery than alveolar. Anaplastic is the most challenging to treat because it’s so aggressive.
| Subtype | Common Age Group | Typical Locations | Prognosis |
| Embryonal RMS | Children under 10 | Head and neck, genitourinary tract | Favorable |
| Alveolar RMS | Teenagers and young adults | Limbs, trunk | Intermediate to poor |
| Anaplastic RMS | Variable | Variable | Poor |
Prognostic Factors and Survival Rates
The outlook for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma depends on several key factors. These include age and stage at diagnosis. Knowing these factors helps doctors choose the best treatment and predict how well a patient will do.
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Several things can affect how well a patient will do with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Age at diagnosis is very important. Younger patients usually have a better chance of survival than older ones. The stage of cancer at diagnosis also matters a lot. Early stages are more hopeful.
How well a patient responds to treatment is also key. Patients who do well with their first treatment tend to live longer. Genetic characteristics of the tumor, like specific fusion genes, can also change the outlook. For example, the PAX3/7-FOXO1 fusion gene is often found in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma and makes the disease more aggressive.
Survival Statistics by Stage and Age
Survival rates for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma vary a lot. The five-year survival rate for patients with localized disease is about 65%. But, those with metastatic disease at diagnosis have much lower survival rates.
Age also affects survival rates a lot. Kids and teens usually do better than older adults. For example, kids under 10 with localized alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma have a five-year survival rate of about 70%. But, older adults might have survival rates as low as 30%.
Long-term Outlook and Recurrence Risks
The long-term outlook for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma patients depends on several things. These include how well the initial treatment worked and the risk of recurrence. Patients who get complete remission after treatment have a better long-term outlook. But the risk of recurrence is still a big worry, especially in the first few years after diagnosis.
Regular follow-up care is very important. It helps catch recurrence and manage treatment side effects. If a patient does have a recurrence, there might still be options for treatment. But the outlook is usually less good in these cases.
In conclusion, understanding prognostic factors and survival rates is key to managing alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma well. By looking at age, stage, and genetic characteristics, doctors can create treatment plans that help patients the most.
Conclusion
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a tough disease that needs a full treatment plan. We’ve talked about how important it is to know about this condition, its signs, and the treatments out there.
A study on adults with this disease showed they lived about 3.6 years on average. They also had a high success rate with treatment, at 89%. For more info, check out thepublished research.
Knowing about the outlook and treatment choices for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is key. We’ve seen that using radiotherapy and chemotherapy, like VAC and VDI, is crucial in fighting this disease.
More research and new treatments are needed to help patients with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. By keeping up with the latest in rhabdomyosarcoma treatment, we can aim for better results for those dealing with this tough condition.
FAQ
What is alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma?
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare and aggressive soft tissue cancer. It starts in muscles or connective tissues. It’s found in the limbs or trunk and has unique genetic features.
How does alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma differ from embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma?
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is more aggressive than embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. It has specific genetic mutations. Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma is more common in young children and has a different genetic profile.
What are the symptoms of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma?
Symptoms include swelling, pain, or limited mobility. They depend on the tumor’s location. Seeing a doctor for unusual symptoms is important.
How is alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves imaging, biopsy, and molecular testing. These steps confirm the tumor and its genetic traits. Accurate diagnosis is key for treatment planning.
What are the treatment options for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma?
Treatment includes surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and sometimes targeted or immunotherapy. The plan depends on the tumor’s stage, location, and genetics.
What is the prognosis for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma?
Prognosis varies by age, stage, and treatment response. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma generally has a poorer prognosis than embryonal. But, treatment advancements have improved outcomes.
Are there any known risk factors for developing alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma?
The exact causes are not fully known. Genetic mutations and environmental factors might play a role. Ongoing research aims to understand risk factors better.
Can rhabdomyosarcoma be referred to by other names?
Yes, it’s also known as rabdomyosarcoma, rabdomyosarkooma, or rhabdomyoscarcoma. This is due to differences in international terminology.
References
- National Cancer Institute. (2023). Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma treatment (PDQ®)–patient version.
https://www.cancer.gov/types/soft-tissue-sarcoma/hp/rhabdomyosarcoma-treatment-pdq - Parham, D. M., & Barr, F. G. (2013). Classification of rhabdomyosarcoma and its molecular basis. Advances in Anatomic Pathology, 20(6), 387-397.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24142049/



































