Uterine fibroids are a common condition affecting many women worldwide. We understand the importance of effective treatment options that preserve fertility and minimize recovery time. Laparoscopic myomectomy has emerged as a preferred surgical approach, offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), managing symptomatic uterine leiomyomas involves various treatment options, including surgical procedures like fibroid removal. We specialize in providing world-class care for women undergoing laparoscopic myomectomy surgery, ensuring a patient-centered approach that prioritizes comfort and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Fibroid removal can be achieved through minimally invasive surgery.
- Laparoscopic myomectomy preserves fertility and reduces recovery time.
- Our medical team prioritizes patient comfort and well-being.
- Effective treatment options are available for managing uterine fibroids.
- We provide world-class care for women undergoing fibroid removal surgery.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids and the Laparoscopic Myomectomy Procedure
Understanding the nuances of uterine fibroids and the laparoscopic myomectomy procedure is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are benign tumors that develop in or around the uterus. They are a common condition, affecting a significant percentage of women, particularly during their reproductive years.
Definition and Prevalence of Uterine Fibroids
Research indicates that uterine fibroids affect a substantial proportion of women, with studies suggesting prevalence rates ranging from 20% to 80% depending on the population studied (Stewart et al., 2017). These tumors can vary in size, number, and location, leading to a range of symptoms including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure on adjacent organs.
Comparing Laparoscopic vs. Open Myomectomy Approaches
Laparoscopic myomectomy, a minimally invasive surgical technique, offers several advantages over traditional open myomectomy. The laparoscopic approach involves smaller incisions, resulting in less postoperative pain, reduced risk of complications, and quicker recovery times. A comparison of the two approaches is summarized in the following table:
| Characteristics | Laparoscopic Myomectomy | Open Myomectomy |
|---|---|---|
| Incision Size | Small (less than 1 cm) | Large (often 5-10 cm or more) |
| Postoperative Pain | Less | More |
| Recovery Time | Shorter (often 1-2 weeks) | Longer (often 4-6 weeks) |
| Risk of Complications | Lower | Higher |
Ideal Candidates for Minimally Invasive Fibroid Removal
Not all patients are ideal candidates for laparoscopic myomectomy. Factors such as the size, number, and location of fibroids, as well as the patient’s overall health and previous surgical history, are considered when determining the suitability of this procedure. Patients with fewer, smaller fibroids that are easily accessible laparoscopically tend to have better outcomes. As noted by experts, “the selection of patients for laparoscopic myomectomy is crucial for the success of the procedure”
“Careful patient selection and meticulous surgical technique are key to achieving optimal outcomes in laparoscopic myomectomy.”
Step 1: Comprehensive Preoperative Assessment and Planning
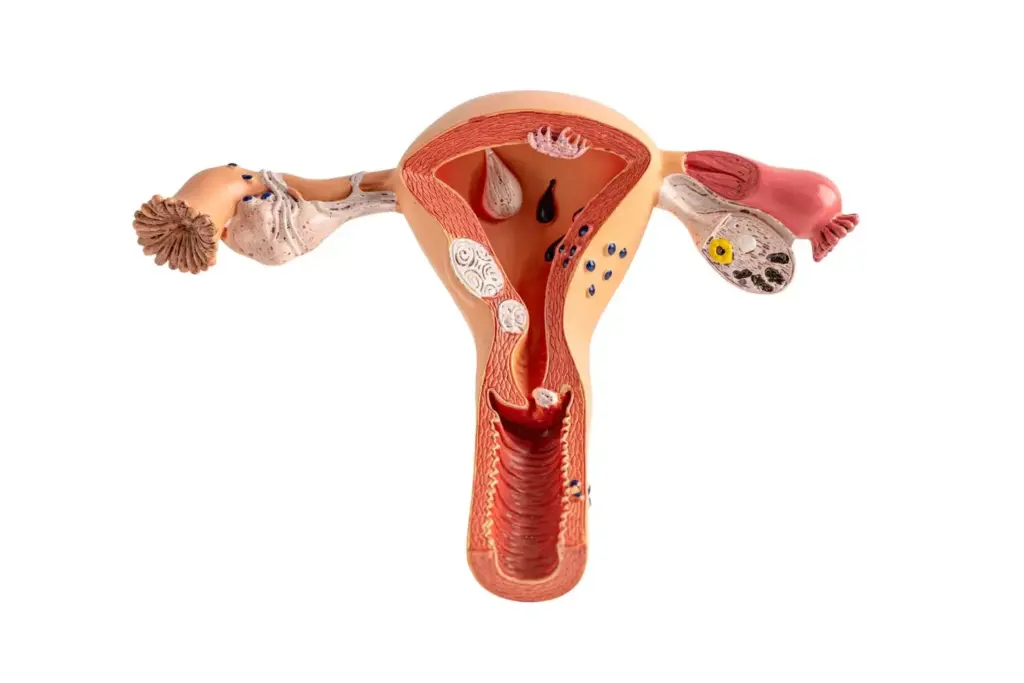
The first step in ensuring a successful laparoscopic myomectomy is a detailed preoperative evaluation. This crucial phase lays the groundwork for a smooth and effective surgical procedure.
Diagnostic Imaging and Fibroid Mapping
Diagnostic imaging plays a vital role in preoperative planning. We utilize advanced imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and MRI, to accurately map the size, number, and location of fibroids. This information is critical in determining the optimal surgical approach.
As noted by experts, “Preoperative imaging helps in identifying the fibroid characteristics, which is essential for planning the surgery”
. This step enables us to anticipate potential challenges and develop strategies to address them.
Patient Selection Criteria and Considerations
Careful patient selection is essential for the success of laparoscopic myomectomy. We consider factors such as the patient’s overall health, the size and number of fibroids, and previous surgical history. Individualized assessment allows us to tailor our approach to each patient’s unique needs.
Preoperative Medical Optimization
Preoperative medical optimization is a critical component of the preoperative assessment. This includes hormonal preparation and anemia management, both of which are crucial for minimizing surgical risks.
Hormonal Preparation Options
Hormonal preparation can help reduce fibroid size and vascularity, making the surgical procedure easier and safer. We consider various hormonal therapies, including GnRH agonists, to optimize the patient’s condition before surgery.
Anemia Management
Anemia management is another important aspect of preoperative care. We implement strategies to correct anemia, such as iron supplementation, to ensure that patients are in the best possible condition for surgery.
By emphasizing comprehensive preoperative assessment and planning, we can significantly improve the outcomes of laparoscopic myomectomy. As highlighted in the literature, a thorough preoperative evaluation is associated with reduced complications and improved patient satisfaction
Step 2: Patient Positioning and Operating Room Setup
Effective laparoscopic myomectomy requires meticulous attention to patient positioning and operating room configuration. Proper setup is crucial for the success of the procedure, as it directly impacts the surgeon’s ability to perform the operation safely and efficiently.
Anesthesia Protocol and Considerations
We administer general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation to ensure patient comfort and safety during the procedure. Monitoring of vital signs is crucial, and we maintain close communication with the anesthesia team throughout the operation.
Strategic Patient Positioning for Optimal Access
Patient positioning is critical for providing optimal access to the pelvic organs. We use the lithotomy position with careful attention to padding pressure points to prevent nerve injury. The patient’s legs are placed in stirrups, allowing for easy access during the procedure.
Ergonomic Port Placement Techniques
Ergonomic port placement is essential for reducing surgeon fatigue and improving the precision of the procedure. We consider the following key aspects:
- Primary and accessory trocar placement
- Equipment and instrument selection
Primary and Accessory Trocar Placement
The placement of primary and accessory trocars is a critical step. We typically use a umbilical port for the laparoscope and additional ports in the lower quadrants for instrumentation.
Equipment and Instrument Selection
Selecting the appropriate equipment and instruments is vital for the success of the procedure. We choose instruments based on the specific needs of the case, considering factors such as fibroid size and location.
By carefully planning and executing patient positioning and operating room setup, we can significantly enhance the safety and efficacy of laparoscopic myomectomy procedures.
Step 3: Systematic Uterine Evaluation and Fibroid Localization
The third step in our laparoscopic myomectomy protocol involves a meticulous assessment of the uterus and fibroid localization. This systematic approach is crucial for identifying the number, size, and location of fibroids, which in turn guides our surgical strategy.
Comprehensive Pelvic Survey Techniques
A comprehensive pelvic survey is the foundation of effective uterine evaluation. We begin by inspecting the pelvic cavity, noting any adhesions, endometriotic lesions, or other abnormalities that could impact the surgery. This survey is conducted using a laparoscope, which provides a clear and magnified view of the pelvic structures.
Key elements of the pelvic survey include:
- Visual inspection of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries
- Assessment of the pelvic peritoneum for any signs of disease
- Identification of any adhesions that may need to be lysed during the procedure
Methods for Identifying Different Fibroid Types
During the uterine evaluation, we employ various techniques to identify and characterize fibroids. These include:
- Visual inspection to identify the number, size, and location of fibroids
- Palpation using laparoscopic instruments to assess fibroid consistency and mobility
- Preoperative imaging studies, such as ultrasound or MRI, to provide detailed information on fibroid characteristics
Different types of fibroids, such as intramural, submucosal, or subserosal, require tailored approaches for removal. Accurate identification of fibroid type is essential for planning the surgical technique.
Intraoperative Decision-Making Process
The information gathered during the uterine evaluation and fibroid localization informs our intraoperative decision-making. We consider factors such as the proximity of fibroids to the endometrial cavity, the presence of any pedunculated fibroids, and the overall uterine architecture.
“The success of laparoscopic myomectomy hinges on meticulous preoperative planning and intraoperative decision-making, which are directly influenced by the thoroughness of the uterine evaluation and fibroid localization.” –
Our intraoperative decisions are guided by the principles of maximizing fibroid removal while preserving uterine integrity and minimizing the risk of complications.
| Decision Factor | Considerations | Surgical Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Fibroid Location | Proximity to endometrial cavity, uterine vessels | Impacts incision placement and repair technique |
| Fibroid Type | Intramural, submucosal, subserosal | Influences removal technique and potential for cavity entry |
| Uterine Architecture | Overall size, shape, and any anomalies | Affects surgical approach and potential need for additional procedures |
Step 4: Advanced Hemostasis Techniques for Laparoscopic Myomectomy
Advanced hemostasis techniques play a vital role in the success of laparoscopic myomectomy procedures. Effective hemostasis is critical to minimize blood loss, reduce the risk of complications, and ensure a clear surgical site. We will discuss various methods to achieve optimal hemostasis during laparoscopic myomectomy.
Vasopressin Injection Methods and Considerations
Vasopressin injection is a widely used technique to reduce bleeding during laparoscopic myomectomy. Vasopressin is a synthetic hormone that causes vasoconstriction, thereby minimizing blood loss. We inject vasopressin directly into the myometrium or the fibroid to achieve the desired effect. However, it’s crucial to carefully consider the dosage and potential contraindications, such as cardiovascular disease, to avoid adverse reactions.
Temporary Uterine Artery Occlusion Approaches
Temporary uterine artery occlusion is another effective method to control bleeding during laparoscopic myomectomy. This technique involves occluding the uterine arteries to reduce blood flow to the fibroid, thereby minimizing blood loss. We can achieve this through various methods, including the use of vascular clips or tourniquets. For more information on this technique, you can visit this educational resource.
Energy Device Selection and Application
The selection of appropriate energy devices is crucial for effective hemostasis during laparoscopic myomectomy. Different energy devices offer unique advantages and are suited for various situations.
Ultrasonic Energy Devices
Ultrasonic energy devices use high-frequency vibrations to coagulate and cut tissue. They are particularly useful for dissecting and coagulating tissue simultaneously, reducing the risk of bleeding. These devices are effective for both superficial and deeper dissections.
Bipolar Electrosurgery Techniques
Bipolar electrosurgery is another effective method for achieving hemostasis. It involves the use of bipolar forceps to coagulate tissue between the electrodes. This technique is precise and can be used to coagulate vessels and tissue effectively, minimizing thermal spread and damage to surrounding structures.
| Hemostasis Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Vasopressin Injection | Reduces bleeding, easy to administer | Potential systemic effects, contraindications |
| Temporary Uterine Artery Occlusion | Effective in reducing blood loss, can be used in conjunction with other methods | Requires precise technique, potential for vascular injury |
| Ultrasonic Energy Devices | Precise dissection and coagulation, minimal thermal spread | Equipment cost, learning curve |
| Bipolar Electrosurgery | Precise coagulation, effective for vessels | Risk of thermal injury if not used correctly |
In conclusion, the choice of hemostasis technique during laparoscopic myomectomy depends on various factors, including the surgeon’s preference, the size and location of the fibroid, and the patient’s overall health. By understanding and effectively utilizing these advanced hemostasis techniques, we can improve surgical outcomes and reduce complications.
Step 5: Precise Hysterotomy and Fibroid Enucleation
In laparoscopic myomectomy, the fifth step involves a critical phase of precise hysterotomy and fibroid enucleation. This stage is crucial for the successful removal of fibroids while preserving uterine integrity.
Strategic Incision Planning and Execution
Strategic incision planning is essential to minimize blood loss and facilitate fibroid removal. We carefully plan the incision site, taking into account the location and size of the fibroid. Preoperative imaging and intraoperative visualization guide our decision-making process to ensure optimal outcomes.
Techniques for Minimizing Endometrial Cavity Entry
Minimizing entry into the endometrial cavity is vital to reduce the risk of complications and promote healing. We employ techniques such as careful fibroid mapping and strategic incision placement to avoid unnecessary disruption of the endometrial layer.
Mechanical and Energy-Based Dissection Methods
Various dissection methods are utilized to enucleate fibroids effectively. These include:
- Blunt Dissection Techniques: Gentle manipulation to separate the fibroid from surrounding tissue.
- Energy-Based Dissection: Utilizing energy devices for precise cutting and coagulation.
Blunt Dissection Techniques
Blunt dissection is a gentle and effective method for separating the fibroid from the uterine tissue. This technique minimizes trauma to the surrounding areas and promotes healing.
Management of Different Fibroid Locations
The location of the fibroid significantly influences the surgical approach. We adapt our techniques to address fibroids in various locations, ensuring comprehensive removal while maintaining uterine function.
By combining precise hysterotomy with effective fibroid enucleation techniques, we achieve successful outcomes in laparoscopic myomectomy. Studies emphasize the importance of these strategies in minimizing complications and promoting patient recovery (Vannuccini et al., 2024).
Step 6: Myometrial Reconstruction and Repair
The sixth step in laparoscopic myomectomy involves meticulous myometrial reconstruction and repair. Effective myometrial reconstruction is crucial for successful outcomes, as it ensures the integrity and strength of the uterine wall after fibroid removal.
Laparoscopic Suturing Techniques and Materials
Laparoscopic suturing is a critical skill for myometrial reconstruction. We use various suturing materials, including absorbable sutures like Vicryl or Monocryl, which are suitable for most cases. The choice of suture material depends on the surgeon’s preference and the specific requirements of the case.
Laparoscopic Suturing Techniques:
- Continuous suturing for larger defects
- Interrupted sutures for precise closure
- Intracorporeal knot-tying for secure closure
Layer-by-Layer Closure Approach
A layer-by-layer closure approach is essential for restoring the uterine anatomy. This involves closing the dead space, approximating the myometrium, and ensuring that the serosa is properly aligned. We typically use multiple layers to achieve a strong repair.
Ensuring Complete Hemostasis During Repair
Complete hemostasis is vital during myometrial reconstruction to prevent postoperative complications. We use a combination of techniques, including electrocautery and hemostatic agents, to achieve a bloodless field.
Barbed Suture Applications
Barbed sutures have gained popularity in laparoscopic myomectomy due to their ability to provide secure closure without the need for knot-tying. These sutures are particularly useful for myometrial reconstruction, as they distribute tension evenly along the suture line.
Extracorporeal Knot-Tying Methods
Extracorporeal knot-tying is another technique used to secure sutures during laparoscopic myomectomy. This method involves tying knots outside the body and then introducing them into the abdominal cavity.
| Suturing Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Suturing | Quick, reduces bleeding | May not be suitable for all defect sizes |
| Interrupted Sutures | Precise, allows for adjustment | Time-consuming, requires more skill |
| Barbed Sutures | Easy to use, distributes tension | May be more expensive |
By employing these techniques and materials, we can achieve a robust and reliable myometrial reconstruction, which is essential for the long-term success of the laparoscopic myomectomy procedure.
Step 7: Specimen Extraction and Morcellation Safety
The seventh step in laparoscopic myomectomy involves careful consideration of specimen extraction and morcellation safety. Safe specimen extraction and morcellation are critical to prevent complications and ensure the success of the procedure.
FDA Guidelines and Current Recommendations
The FDA has issued guidelines on morcellation safety, emphasizing the importance of contained morcellation systems. As of 2014, the FDA recommended using contained morcellation techniques to minimize the risk of spreading cancer cells during the procedure. We adhere to these guidelines to ensure patient safety.
Contained Morcellation Systems and Techniques
Contained morcellation involves using a specialized bag to enclose the specimen before morcellation. This technique reduces the risk of tissue dissemination and potential cancer spread. We utilize advanced contained morcellation systems that are designed to provide a safe and effective extraction process.
Alternative Extraction Methods
In some cases, alternative extraction methods may be considered. These include:
- Mini-Laparotomy Approach: A small incision is made to facilitate the removal of the specimen.
- Vaginal Extraction Options: Specimens can be extracted through the vagina, avoiding additional abdominal incisions.
Mini-Laparotomy Approach
The mini-laparotomy approach involves making a small incision, typically in the lower abdomen, to extract the specimen. This method is considered when the specimen is too large for vaginal extraction or when contained morcellation is not feasible.
Vaginal Extraction Options
Vaginal extraction is a viable alternative for specimen removal. It offers the advantage of avoiding additional abdominal incisions, potentially reducing postoperative pain and improving recovery times.
By carefully selecting the most appropriate extraction method and adhering to FDA guidelines, we ensure that our patients receive safe and effective care during laparoscopic myomectomy procedures.
Step 8: Adhesion Prevention Strategies and Final Inspection
As we conclude the fibroid removal process, our attention turns to preventing adhesions through meticulous surgical techniques and barrier agents. Adhesion prevention is crucial for minimizing postoperative complications and ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Evidence-Based Barrier Agents and Application
We utilize evidence-based barrier agents to reduce the risk of adhesion formation. These agents create a physical barrier between tissues, allowing them to heal without adhering to each other. Research supports the efficacy of barrier agents such as hyaluronic acid-based products in reducing adhesions (Sandberg et al., 2018).
Surgical Technique Modifications to Reduce Adhesions
In addition to barrier agents, we modify our surgical techniques to minimize tissue trauma and reduce the risk of adhesions. This includes gentle tissue handling, meticulous hemostasis, and minimizing the use of electrocautery.
Systematic Final Survey and Port Closure
Before concluding the procedure, we perform a systematic final survey to ensure hemostasis and inspect for any potential complications. Proper port closure is also critical, involving both fascial closure techniques and skin closure methods.
Fascial Closure Techniques
Fascial closure is performed using a non-absorbable suture to ensure the integrity of the abdominal wall.
Skin Closure Methods
Skin closure is achieved with either subcuticular sutures or staples, depending on the surgeon’s preference and the patient’s skin type.
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Barrier Agents | Application of hyaluronic acid-based products | Reduces adhesion formation |
| Gentle Tissue Handling | Minimal manipulation of tissues | Reduces tissue trauma |
| Fascial Closure | Non-absorbable suture use | Ensures abdominal wall integrity |
By combining these strategies, we can significantly reduce the risk of adhesions and improve patient outcomes after laparoscopic myomectomy.
Postoperative Management and Recovery After Laparoscopic Fibroid Removal
Proper postoperative care is essential for minimizing complications and promoting healing after fibroid removal surgery. Effective postoperative management involves a comprehensive approach that includes immediate postoperative care, expected recovery timelines, managing potential complications, and long-term follow-up recommendations.
Immediate Postoperative Care Protocol
Immediate postoperative care begins in the recovery room, where patients are monitored for vital signs and potential complications. We emphasize pain management, using a combination of medications and other techniques to ensure patient comfort. Early mobilization is encouraged to prevent venous thromboembolism and promote recovery.
Expected Recovery Timeline and Milestones
The recovery timeline after laparoscopic myomectomy varies among patients, but most women can expect to resume normal activities within 2-4 weeks. Key milestones include managing postoperative pain, gradual return to normal activities, and follow-up appointments to monitor healing.
Managing Potential Complications
While laparoscopic myomectomy is generally safe, potential complications can arise. We categorize these into early and late complications, each requiring specific interventions.
Early Complications and Interventions
Early complications may include postoperative bleeding, infection, and injury to surrounding organs. Prompt recognition and intervention are crucial, involving imaging studies, antibiotics, and sometimes additional surgery.
Long-Term Follow-Up Recommendations
Long-term follow-up is essential for monitoring for recurrence of fibroids and addressing any long-term consequences of the surgery. We recommend regular check-ups and ultrasounds as part of a comprehensive follow-up plan.
| Recovery Stage | Timeline | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Recovery | 0-48 hours | Rest, pain management, monitoring for complications |
| Early Recovery | 2-7 days | Gradual mobilization, light activities |
| Late Recovery | 2-4 weeks | Return to normal activities, follow-up appointments |
Conclusion: Advancing Outcomes in Laparoscopic Myomectomy
Laparoscopic myomectomy has emerged as a preferred surgical approach for managing uterine fibroids, offering numerous benefits, including faster recovery, reduced blood loss, and improved outcomes. By following the comprehensive steps outlined in this article, surgeons can optimize their technique and enhance patient care. Research continues to support the advancements in laparoscopic myomectomy, with studies demonstrating its safety and efficacy in improving laparoscopic myomectomy outcomes.
As we continue to refine our techniques and incorporate new technologies, we can further improve the care provided to patients undergoing fibroid removal. By emphasizing careful preoperative planning, precise surgical technique, and effective postoperative management, we can achieve optimal results and enhance the overall quality of care. Ultimately, our goal is to provide the best possible outcomes for patients, and laparoscopic myomectomy plays a critical role in advancing outcomes in the treatment of uterine fibroids.
What is laparoscopic myomectomy?
Laparoscopic myomectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove uterine fibroids while preserving the uterus. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to visualize the uterus and remove the fibroids.
What are the benefits of laparoscopic myomectomy compared to open myomectomy?
Laparoscopic myomectomy offers several benefits, including smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times compared to open myomectomy.
Who is a good candidate for laparoscopic myomectomy?
Ideal candidates for laparoscopic myomectomy are women with symptomatic uterine fibroids who wish to preserve their uterus. The decision to undergo laparoscopic myomectomy depends on factors such as the size, number, and location of the fibroids, as well as the patient’s overall health.
What is the role of diagnostic imaging in laparoscopic myomectomy?
Diagnostic imaging, such as ultrasound or MRI, plays a crucial role in preoperative planning for laparoscopic myomectomy. It helps to identify the size, number, and location of the fibroids, which informs the surgical approach and ensures a successful outcome.
How is bleeding controlled during laparoscopic myomectomy?
Advanced hemostasis techniques, such as vasopressin injection, temporary uterine artery occlusion, and energy device application, are used to control bleeding during laparoscopic myomectomy.
What are the risks and complications associated with laparoscopic myomectomy?
As with any surgical procedure, laparoscopic myomectomy carries risks and complications, including bleeding, infection, and adhesions. However, these risks can be minimized with proper preoperative planning, surgical technique, and postoperative care.
How long does it take to recover from laparoscopic myomectomy?
Recovery times vary, but most women can expect to return to normal activities within a few weeks after laparoscopic myomectomy. The exact recovery timeline depends on individual factors, such as the complexity of the procedure and overall health.
Can laparoscopic myomectomy prevent future fibroid growth?
While laparoscopic myomectomy removes existing fibroids, it does not prevent future fibroid growth. However, the procedure can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life for women with uterine fibroids.
What is the difference between laparoscopic myomectomy and robotic myomectomy?
Robotic myomectomy is a type of laparoscopic myomectomy that uses a robotic surgical system to enhance visualization and precision. While both procedures are minimally invasive, robotic myomectomy offers additional benefits, such as improved dexterity and 3D visualization.
Is laparoscopic myomectomy a permanent solution for uterine fibroids?
Laparoscopic myomectomy can provide long-term relief from symptoms, but it is not a guarantee against future fibroid growth. Women who undergo laparoscopic myomectomy should be aware of the potential for future fibroid development and discuss follow-up care with their healthcare provider.
What is morcellation, and how is it used in laparoscopic myomectomy?
Morcellation is a technique used to remove large fibroids or specimens through small incisions during laparoscopic myomectomy. Contained morcellation systems and techniques are used to minimize the risk of tissue dissemination and ensure safe specimen extraction.
References:
• Wang, P. (2025). Advances and Challenges in Minimally Invasive … Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12194428/
• Laparoscopic Myomectomy – PMC. (Year). Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7214085/
• TVASurg. (Year). Laparoscopic Myomectomy – TVASurg – The Toronto Video Atlas of Surgery. Retrieved from https://pie.med.utoronto.ca/TVASurg/project/gyn-lapmyo/
• (2019). Laparoscopic Myomectomy in 10 Steps – PubMed. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30639723/.























