Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are key in modern medicine. They help doctors find and manage health issues like cancer and brain problems. Over 2 million PET scans are done every year in the United States, showing how important they are.
Patients often ask about the scan duration and when they’ll get their results. Do you get PET scan results straight away? The timing depends on the scan type and the body area, as images usually need to be reviewed by a radiologist before being shared with patients.
Key Takeaways
- PET scans are a vital diagnostic tool for various medical conditions.
- The duration of a PET scan can vary based on the type and area being scanned.
- Understanding the PET scan process can help reduce patient anxiety.
- Results timing can depend on several factors, including the complexity of the scan.
- Healthcare providers will guide patients through the process and timeline.
What Is a PET Scan?
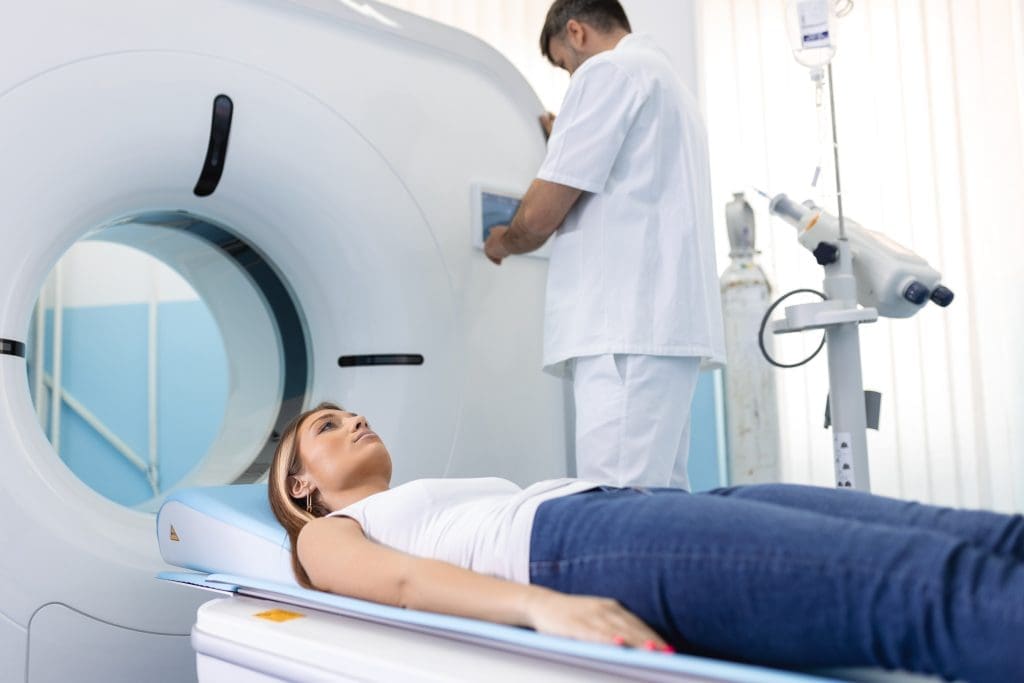
A PET scan, or Positron Emission Tomography, is a detailed imaging test. It helps doctors diagnose and manage health conditions. It shows how active the body’s tissues and organs are.
The term “PET scan” is common in medical diagnostics. Knowing its full meaning helps patients and healthcare professionals. Let’s explore what a PET scan is and what it does.
PET Scan Definition and Meaning
A PET scan uses a radioactive drug to see inside the body. It shows how the body works and helps find diseases like cancer. It also helps with neurological and cardiovascular diseases.
The PET scan’s meaning goes beyond its technical details. It serves as an essential tool in medicine for assessing disease severity and treatment effectiveness. It gives insights into the body’s metabolic activities, guiding patient care.
What Does PET Stand For?
The “PET” in PET scan means Positron Emission Tomography. Let’s break it down:
- Positron: A positron is a small particle from the radioactive tracer.
- Emission: Emission is when energy or particles, like positrons, are released.
- Tomography: Tomography is imaging by sections, using waves.
| Term | Definition |
| Positron | A small particle emitted by the radioactive tracer. |
| Emission | The release of energy or particles. |
| Tomography | Imaging by sections or sectioning. |
Knowing PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography explains the scan’s technology. It’s a complex tool that gives a unique view of the body’s functions and metabolism.
The Science Behind PET Imaging
PET scans use radioactive tracers to see inside the body. They work by using the body’s metabolic processes. This creates detailed images of what’s inside.
How Does a PET Scan Work?
A PET scan detects energy from a radioactive tracer injected into the body. This tracer, often Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), goes to areas that are very active, like cancer cells. The PET scanner then picks up the gamma rays from the tracer.
FDG PET Scan and Radioactive Tracers
The main tracer used in PET scans is Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG). It’s a glucose molecule with a radioactive tag. Cancer cells and other active tissues use more glucose than normal cells.
This makes the FDG tracer show up in these areas on the scan. It helps doctors see where the activity is.
Radioactive tracers in PET scans show how the body’s metabolism works. This info is key for diagnosing and treating many health issues.
| Tracer | Application | Metabolic Process Visualized |
| FDG (Fluorodeoxyglucose) | Cancer detection, neurological disorders | Glucose metabolism |
| Other tracers (e.g., Oxygen-15, Nitrogen-13) | Cardiovascular disease, brain function | Various metabolic processes |
This table shows how different PET tracers work. It shows how PET imaging can help diagnose many health problems.
Medical Conditions Diagnosed with PET Scans
PET scans are key in diagnosing many medical conditions. They show detailed images of the body’s metabolic activity. This makes them very useful in finding and managing diseases.
Cancer Detection and Staging
PET scans are widely used in oncology for finding and staging cancer. They help see how far cancer has spread. This is important for choosing the right treatment.
The most common PET scan for cancer is the FDG PET scan. It uses fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) to spot areas with high glucose uptake. This is common in many cancer cells.
PET scans help check if treatment is working and if cancer comes back. They are very important in managing cancers like lymphoma, melanoma, and colorectal cancer.
Neurological Disorders
PET scans are used to diagnose and assess neurological disorders. They help with conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy. By looking at brain activity, PET scans give insights into disease progression and treatment success.
For Alzheimer’s disease, PET scans show where brain activity is low. This is linked to cognitive decline. This info is key for diagnosing and tracking the disease.
Cardiovascular Disease Assessment
PET scans are used in cardiovascular diseases to check heart viability and blood flow. They find areas of the heart not getting enough blood. This is important for diagnosing coronary artery disease and planning treatments like angioplasty or bypass surgery.
PET scans also check heart tissue viability. This helps doctors choose the best treatment for heart disease. This use of PET scans greatly impacts patient care and outcomes.
Preparing for Your PET Scan
To get the most out of your PET scan, it’s key to follow pre-scan instructions carefully. Proper preparation can greatly improve the quality of the images and the accuracy of the results.
Pre-Scan Instructions
Before your PET scan, you’ll get specific instructions from your healthcare provider. You might need to arrive early to change into a hospital gown and remove any metal objects. It’s vital to follow these instructions for a smooth and successful scanning process.
Be sure to ask questions if you have any uncertainties about the preparation process. Your healthcare team is there to help and ensure you’re comfortable and prepared.
Dietary Restrictions
Dietary restrictions are often needed before a PET scan. You might need to fast for a certain period or follow a specific diet to ensure the tracer is absorbed correctly by your body. Your healthcare provider will give you detailed instructions on what to eat or avoid before the scan.
It’s important to stick to these dietary guidelines to ensure the PET scan produces high-quality images. Proper nutrition before the scan can significantly impact the outcome.
Can You Shower Before a PET Scan?
One common question is whether you can shower before a PET scan. Generally, showering is allowed, but you should avoid using lotions, creams, or deodorants that might interfere with the scan. Your healthcare provider will give you specific guidance on personal hygiene before the scan.
Following these guidelines will help ensure that your PET scan is conducted safely and effectively. If you have any concerns or questions, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider.
How Long Does a PET Scan Take?
Knowing how long a PET scan takes is key for those getting ready for it. The time can change based on a few things. These include the scan type and the body part being checked.
Average PET Scan Duration
The average PET scan duration is usually between 30 minutes and a few hours. Most scans last from 30 to 60 minutes. But, some scans might take longer. This depends on the scan’s complexity and the imaging protocol.
Factors That Affect PET Scan Length
Several factors can influence the length of a PET scan. These include:
- The type of PET scan being performed (e.g., whole-body vs. targeted scan)
- The area of the body being scanned
- The specific imaging protocol used by the radiology department
- The patient’s overall health and ability to remain steady during the scan
Typical PET Scan Time Requirements
Typical PET scan time requirements vary, but most are within a certain range. For example:
| Type of PET Scan | Typical Duration |
| Whole-body PET scan | 60-90 minutes |
| Targeted PET scan (e.g., brain or heart) | 30-60 minutes |
It’s vital for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s pre-scan instructions. This ensures the PET scan is done well and quickly.
The PET Scan Procedure Step by Step
The PET scan procedure has several steps. These include getting ready, the actual scan, and what happens after. Knowing these steps can make you feel less anxious and help the process go smoothly.
Before Entering the PET Scan Machine
Before the scan, you need to follow some steps. You’ll likely have to fast for 4-6 hours. This helps the tracer work right with your body.
Other things you might need to do before the scan include:
- Avoid strenuous exercise or activities that could affect the tracer distribution
- Remove any metal objects, such as jewelry or glasses, that could interfere with the scan
- Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing
During the Imaging Process
When it’s time for the scan, you’ll lie on a table that slides into the PET scanner. The machine uses the signals from the tracer to make detailed images of your body’s inside.
The scanning process usually involves:
- Getting into position on the scanning table
- Staying very quiet while the table moves into the scanner
- The scanner taking images, which can take 30 minutes to an hour
What Happens Immediately After Scanning
Once the scan is done, you can usually go back to your normal activities. Unless your healthcare provider tells you differently.
After the scan, you might need to:
| Activity | Description |
| Drink lots of fluids | To help get rid of the tracer from your body |
| Go back to eating normally | Unless your healthcare provider says not to |
| Have a follow-up appointment | To talk about the results and what to do next |
What to Expect During Your PET Scan Appointment
Knowing what happens during a PET scan can ease your worries. A PET scan appointment includes getting ready, the scan itself, and what happens after.
Total PET Scan Appointment Length
A PET scan appointment usually lasts 2 to 3 hours. This time covers getting ready, changing into a gown, and getting the radioactive tracer.
The actual scan takes 30 to 60 minutes. This depends on the scan type and the body area being checked.
| Procedure | Average Time |
| Registration and Preparation | 30-60 minutes |
| PET Scan | 30-60 minutes |
| Total Appointment Time | 2-3 hours |
The Experience Inside the Scanner
Inside the PET scanner, you’ll lie on a table that moves into the machine. The scanner, shaped like a doughnut, moves around you to capture images.
The inside of the scanner is mostly comfortable. But, some might feel a bit trapped. It’s key to stay very quiet and not move to get good images.
- Talk to the technologist if you’re feeling uneasy or scared.
- Try deep breathing to relax.
- Listen to music or guided meditation if it’s okay with the facility.
After Your PET Scan: What Happens Next?
After your PET scan, you’ll enter a post-scan period that requires some specific considerations. Understanding what happens during this time can help alleviate any concerns you may have.
Immediate Post-Scan Period
After the PET scan, you can generally resume your normal activities unless your doctor advises you to do something else. It’s common to feel a bit tired or weak, so resting for the remainder of the day is recommended. Drinking plenty of water is also advised to help flush out the radioactive tracer used during the scan.
Key Considerations Post-Scan:
- Resume normal activities as advised by your doctor
- Stay hydrated to help eliminate the radioactive tracer
- Rest if you feel tired or weak
How Long Are You Radioactive After a PET Scan?
The radioactive tracer used in PET scans has a relatively short half-life, meaning it loses its radioactivity quickly. Typically, the tracer is almost completely eliminated from your body within a few hours. It’s recommended to follow some precautions to minimize exposure to others, like pregnant women and children.
| Precaution | Duration |
| Drink plenty of water | For 24 hours post-scan |
| Avoid close contact with pregnant women and children | For 6-12 hours post-scan |
| Use good hygiene practices | For 24 hours post-scan |
By following these guidelines, you can minimize any risks associated with the radioactive tracer. If you have any specific concerns or questions, it’s always best to consult with your healthcare provider.
How Long Does It Take to Get PET Scan Results?
PET scan results aren’t immediate. The wait time varies based on several factors. Knowing these can help patients manage their expectations and anxiety while waiting.
Typical Result Timeframes
The time to get PET scan results can vary a lot. Patients usually wait from a few hours to several days.
Typical wait times are usually 24 to 48 hours. But, this can change based on the scan’s complexity and the radiology department’s workload.
| Facility Type | Average Wait Time |
| Hospital Radiology Department | 24-48 hours |
| Private Imaging Center | 12-24 hours |
| Specialized Cancer Center | 2-5 days |
Factors That Affect Result Delivery
Several factors can affect how long it takes to get PET scan results. These include:
- The complexity of the scan
- The workload of the radiology department
- The need for additional imaging or consultations
- The type of PET scan performed (e.g., FDG PET scan)
A radiology expert said, “The interpretation of PET scans requires careful analysis. The time needed can vary based on the case’s complexity.”
“The accuracy of PET scan results is key. While speed is important, it can’t compromise the quality of the interpretation.”
When Expedited Results Are Possible
In some cases, expedited results might be available. This is often for critical or emergency cases. Facilities may offer rapid results for an extra fee or as part of their urgent services.
Understanding what affects PET scan result delivery can help patients navigate their diagnostic journey better. Waiting for results can be tough, but knowing what to expect can help reduce anxiety and improve the experience.
Understanding Your PET Scan Images
It’s key to understand PET scan images well for diagnosing and treating health issues. These scans create detailed pictures that doctors must analyze carefully.
How to Interpret PET Scan Images
PET scan images are complex. They need a deep understanding of the technology and the medical conditions being looked at. Doctors look for areas of increased or decreased activity in these images, which can show different health problems.
The process involves checking how the radioactive tracer is taken up by tissues and organs. Each absorbs the tracer at its own rate. Abnormalities show up as unusual patterns in the uptake.
What Doctors Look For in PET Scans
Doctors check for several important signs when they look at PET scans. These include:
- Metabolic activity: Cancerous tissues have higher metabolic rates, making them show up on PET scans.
- Tissue damage: Damaged tissue can be found by its changed metabolic activity.
- Organ function: PET scans measure how well organs work by looking at tracer uptake.
Understanding these images is a complex task. It requires knowledge of PET scan technology, human anatomy, and pathology.
By accurately reading PET scan images, doctors can make better decisions for patient care. This includes diagnosing, staging diseases, and checking treatment success.
PET Scan Side Effects and Safety Considerations
PET scans are a key tool for doctors to diagnose and monitor health. They use small amounts of radioactive tracers. It’s important to know about their side effects and safety.
Common Side Effects
Most people don’t have big problems with PET scans. But, some might feel a little uncomfortable. You might feel a bit of anxiety or get a headache or feel sick.
- Discomfort or anxiety during the scan
- Mild reactions to the radioactive tracer, such as headache or nausea
- Discomfort from lying on the scanning table
These issues usually go away after the scan is done.
Radiation Exposure Risks
PET scans use small amounts of radiation. This can slightly raise the risk of cancer. But, the scan’s benefits often outweigh this risk.
Doctors use the least amount of radioactive tracer needed. They follow strict rules to keep radiation low. This way, they get the needed images safely.
The radiation from a PET scan is usually safe. The body gets rid of the tracer in a few hours. This means the radiation exposure goes down quickly.
If you’re worried about radiation or side effects, talk to your doctor. They can help you understand the risks and benefits of the PET scan.
Different Types of PET Scans and Their Uses
PET scans come in many types, each with its own use. They are key in medical diagnosis, showing how the body works and what might be wrong. Knowing the differences is important for both patients and doctors.
Whole body PET scans look at the whole body. They help find cancer, see if it has spread, or check how treatments are working. Targeted PET scans focus on specific areas, like the brain or heart. They give detailed info about those areas.
Whole Body vs. Targeted PET Scans
Whole body scans are great for cancer patients. They show how big the cancer is and if treatments are working. They look at the whole body’s activity, helping doctors find problems.
Targeted scans are for specific issues, like brain or heart problems. They give detailed info that whole body scans might miss. This helps doctors understand more about certain areas.
Combined PET-CT and PET-MRI Scans
PET scans can be combined with CT or MRI. Combined PET-CT scans mix metabolic info from PET with CT’s body details. This makes diagnosis more accurate and complete.
PET-MRI scans add PET’s info to MRI’s soft tissue detail. This combo is great for certain areas, like the brain or pelvis, where soft tissue detail is key.
Choosing the right PET scan depends on the patient’s needs and the doctor’s questions. Knowing the differences helps use PET scans well in healthcare.
PET Scans vs. Other Imaging Techniques
Understanding the differences between PET scans and other imaging techniques like CT and MRI scans is key. Each has its own strengths and is best for different medical conditions.
PET vs. CT Scans
PET scans and CT scans are both used for diagnosis but show different things. PET scans look at how cells work, which helps find cancer and see how it spreads. CT scans, on the other hand, show detailed pictures of the body’s structure, helping spot problems.
| Feature | PET Scan | CT Scan |
| Primary Use | Metabolic activity, cancer detection | Anatomical imaging, structural abnormalities |
| Radiation Type | Positron emission | X-rays |
| Contrast Agent | Radioactive tracer (e.g., FDG) | Iodine-based or barium |
PET vs. MRI
MRI scans use magnetic fields to show detailed pictures of the body’s inside. Unlike PET scans, MRI doesn’t use radiation, making it safer for some patients. MRI is great for seeing soft tissues like the brain and organs.
Key differences between PET and MRI scans include:
- PET scans provide functional information about metabolic activity.
- MRI offers high-resolution anatomical images without radiation.
When PET Scans Are Preferred
PET scans are often chosen for several reasons:
- Cancer staging and monitoring: PET scans are very good at seeing how cancer spreads and how well it’s responding to treatment.
- Neurological disorders: PET scans can help diagnose and manage conditions like Alzheimer’s by showing brain changes.
- Cardiovascular disease: PET scans can check how well the heart works and blood flows, helping manage heart disease.
In conclusion, while PET scans, CT scans, and MRI scans are all important, the right choice depends on the medical question. Knowing what each can do is key for the best care.
Technological Advancements in PET Scanning
PET scanning has become more accurate and efficient thanks to new technology. This progress comes from better hardware and software. It makes PET scans more useful and precise.
Modern PET Scan Machines
Today’s PET scan machines are much improved. They have higher resolution, giving clearer images and better results. They also work with CT and MRI, giving a full view of the body.
Key Features of Modern PET Scanners:
- Improved resolution and sensitivity
- Integration with CT and MRI for hybrid imaging
- Advanced software for image reconstruction and analysis
| Feature | Traditional PET | Modern PET |
| Resolution | Lower | Higher |
| Scanning Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Image Detail | Less detailed | More detailed |
Future Developments in PET Technology
The future of PET technology is exciting. Researchers are working on new tracers and smaller scanners. These changes will make PET scans even better.
We can look forward to more accurate and comfortable PET scans. These advancements will make the whole process more efficient.
Conclusion: What to Remember About PET Scan Timing and Results
PET scan timing and results are key in diagnosis. Knowing how long a PET scan takes and when to get results can ease anxiety. It makes the experience smoother.
The time for a PET scan varies. It can be from 30 minutes to several hours. This depends on the scan type and individual factors. Understanding what to expect can help patients prepare better.
PET scan results come in a few days. But, the exact time can change based on the case’s complexity and the healthcare provider’s rules. Knowing about pet scan timing and results helps patients better navigate their diagnostic journey.
FAQ
What happens during a PET scan appointment?
At a PET scan appointment, you’ll get the tracer injection. Then, you’ll lie on a table that moves through the scanner to capture images.
How do I prepare for a PET scan?
To prepare for a PET scan, follow dietary rules and avoid certain medicines. Your healthcare provider or imaging center will give you specific instructions.
Are PET scans safe?
PET scans are mostly safe. They involve some radiation, but the benefits for diagnosis are usually worth it.
What are the benefits of combined PET-CT scans?
PET-CT scans offer detailed views of both how active tissues are and their structure. This gives a clearer picture of many health issues.
Can PET scans diagnose cancer?
Yes, PET scans are used to find, stage, and check how well cancer treatments are working. They spot areas with high activity that might be cancer.
What is an FDG PET scan?
An FDG PET scan uses Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) to find areas with high glucose use. This is often where cancer or other diseases are.
How does a PET scan work?
A PET scan injects a tracer that goes to active areas. Then, a scanner detects the positrons to show where the tracer is.
What is the difference between a PET scan and a CT scan?
PET scans show how active tissues are. CT scans give detailed pictures of the body’s structure. PET-CT scans combine both for a better view.
How long are you radioactive after a PET scan?
The tracer in PET scans stays in your body for a few hours. The radiation levels drop quickly, usually back to normal within 24 hours.
What are the side effects of a PET scan?
Side effects of PET scans are usually mild. You might feel a bit uncomfortable from the injection or have an allergic reaction. Some people might also feel claustrophobic during the scan.
How long does it take to get PET scan results?
You’ll usually get PET scan results in 24-48 hours. But, it can take longer depending on the scan’s details.
Can you shower before a PET scan?
Yes, you can shower before a PET scan. But, avoid using lotions or creams that might mess with the scan.
How long does a PET scan take?
A PET scan usually lasts 30-60 minutes. But, getting ready and scanned can take 2-4 hours.
What does PET stand for in PET scan?
PET stands for Positron Emission Tomography. It’s a way to see how active the body’s tissues are.























