Heart stents are tiny mesh tubes that help keep arteries open. They are made from strong materials like stainless steel or cobalt chromium alloy. These materials make them last for a long time.
Most heart stents are meant to stay in the body forever. They help keep arteries open for years. The lifespan of heart stents depends on the material and the patient’s health.
Key Takeaways
- Heart stents are designed to be permanent and last for many years.
- Modern stents are made from durable materials like stainless steel or cobalt chromium alloy.
- The primary purpose of heart stents is to keep previously blocked arteries open.
- Lifespan can be influenced by material and individual patient health.
- Heart stents provide a long-term solution for artery blockage.
Understanding Heart Stents: Purpose and Function
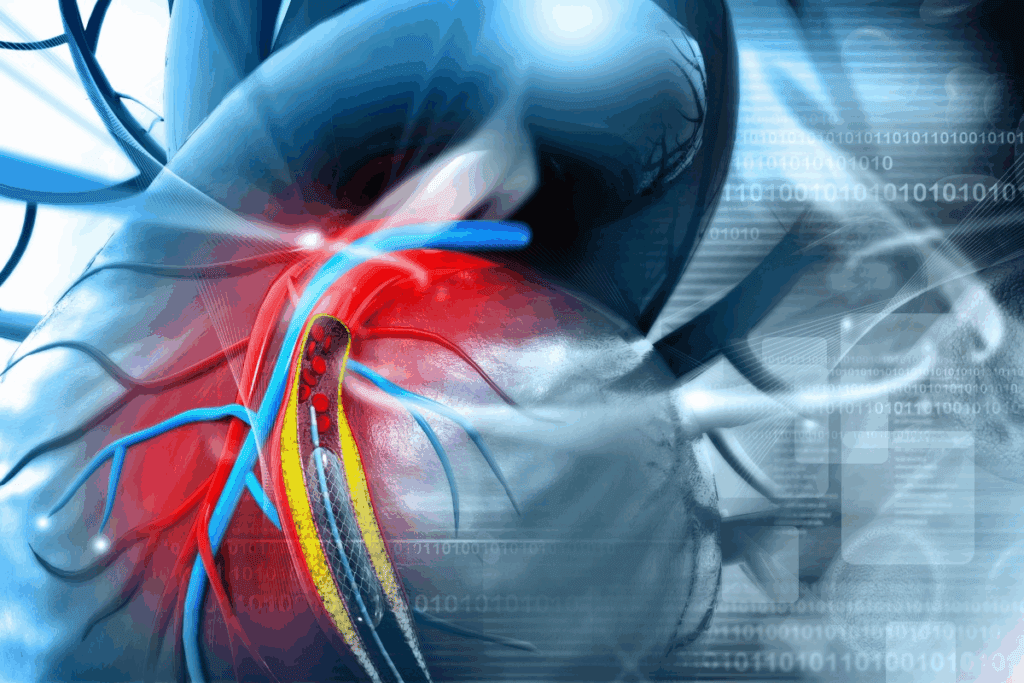
Cardiac stents are small, mesh-like tubes that help keep blood flowing through the coronary arteries. They are used to treat coronary artery disease. This disease narrows or blocks arteries due to plaque buildup.
What Are Cardiac Stents and Why Are They Used?
Cardiac stents are made of metal or polymer. They are designed to keep the artery open, improving blood flow to the heart. They help patients with coronary artery disease by relieving symptoms like chest pain and preventing heart attacks.
The main job of a cardiac stent is to act as a scaffold inside the coronary artery. This prevents it from becoming blocked or narrowed again. By doing so, stents restore normal blood flow to the heart muscle.
How Stents Work to Improve Blood Flow
Stents are placed at the site of the blockage in the coronary artery. Once in place, they expand to keep the artery open. This allows for better blood flow, helping to relieve symptoms like angina.
Key benefits of stents include:
- Improved blood flow to the heart muscle
- Relief from angina symptoms
- Reduced risk of heart attack
The stent stays in the artery permanently, providing ongoing support to keep it open.
The Stent Placement Procedure
The stent placement procedure is a minimally invasive treatment for coronary artery disease. It uses a catheter to deliver the stent to the blocked artery.
Here’s an overview of the procedure:
| Step | Description |
| 1 | A catheter is inserted into the blocked artery. |
| 2 | The stent is delivered to the site of the blockage. |
| 3 | The stent is expanded to keep the artery open. |
After the procedure, patients are monitored for a short time before being discharged. Most can return to their normal activities within a few days.
Understanding how stents work and the procedure for placing them helps patients appreciate their role in managing coronary artery disease.
Types of Heart Stents and Their Durability
There are many heart stents available, each with its own benefits. The right stent depends on the patient’s health, the blockage’s size, and the doctor’s advice.
Bare-Metal Stents: Structure and Lifespan
Bare-metal stents are the first type of coronary stent. They are a metal mesh that keeps the artery open after an angioplasty. These stents are known for their durability and have been used for decades. But, they can cause scar tissue, leading to restenosis.
The life of bare-metal stents varies. They are seen as a long-term fix. Patients with these stents need to take two medicines to prevent clots for at least a month after the procedure.
Drug-Eluting Stents: Enhanced Longevity Benefits
Drug-eluting stents are an upgrade from bare-metal stents. They have a coating that slowly releases medicine into the artery wall. This reduces scar tissue and lowers restenosis risk. This technology has made drug-eluting stents a popular choice among cardiologists.
Drug-eluting stents last longer and have less risk of early restenosis than bare-metal stents. They’re great for complex cases or those at high risk of restenosis. The coating keeps the artery open over time.
Bioresorbable Stents: Temporary by Design
Bioresorbable stents are a newer type of coronary stent. They dissolve in the body over time, supporting the artery during healing and then disappearing. This design aims to reduce long-term complications associated with permanent stents.
Bioresorbable stents are meant to be temporary. They might lower the risk of long-term problems like late stent thrombosis. They’re an interesting option for some patients, but more research is needed.
How Long Do Stents Last in Your Heart?
Knowing how long heart stents last is important for those who have had them placed. Heart stents keep arteries open, improving blood flow to the heart. It’s a big concern for both patients and doctors.
Permanent Nature of Most Heart Stents
Most heart stents are meant to stay in the artery forever. Bare-metal stents and drug-eluting stents are the most common. Each type has its own benefits and characteristics.
Stents are made to last a long time, but their success can depend on several factors. The fact that stents are permanent means patients should watch out for restenosis, or the artery narrowing again. But, thanks to new stent technology, this risk has gone down a lot.
Average Lifespan Expectations (10+ Years)
Research shows that heart stents can last over 10 years. Many patients keep getting good blood flow in the treated artery for years. In fact, studies say stents can keep the coronary artery stable for 10-15 years or more.
- Drug-eluting stents have a lower chance of restenosis than bare-metal stents.
- How a patient lives and takes their medicine affects stent longevity.
- It’s important to keep up with doctor visits to check on the stent.
Long-term Clinical Studies on Stent Durability
Many studies have looked into how long heart stents last. These studies give us important information on stent performance over time. They also tell us what makes stents last longer.
One key thing studies have found is that stent success can be affected by patient health and lifestyle. This means that by making healthy choices and following doctor’s advice, patients can help their stents last longer.
Factors Affecting Heart Stent Longevity
Many things affect how long a heart stent lasts. The stent’s durability comes from a mix of patient, stent, and procedure factors.
Patient-Related Factors
Things about the patient greatly influence stent longevity. Age and overall health are key. Older or sicker patients might not do as well as younger, healthier ones.
A study in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology showed that diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol can lead to stent problems. Following medication and lifestyle advice is important for keeping the stent in good shape.
“The presence of comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension can significantly impact the long-term success of stent placement.”
Medical Expert, Cardiologist
Stent-Related Factors
The kind of stent used is very important. Drug-eluting stents, for example, have fewer restenosis issues than bare-metal stents. The stent’s material, design, and coating all affect how long it lasts.
| Stent Type | Restenosis Rate | Average Lifespan |
| Bare-Metal Stents | 20-30% | 5-10 years |
| Drug-Eluting Stents | 5-10% | 10+ years |
Procedural Factors
How the stent is placed and the vessel’s condition are key. Proper placement and vessel preparation are critical for the stent’s success and longevity.
A study in the Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine found that using advanced imaging during stent placement can lead to better results. This ensures the stent is deployed correctly.
Understanding these factors helps doctors manage patient expectations and find ways to extend stent life.
Restenosis: When Stents Narrow Again
Restenosis is a big worry for both patients and doctors. It happens when the artery gets narrower again after a stent is put in. This can be due to new tissue growth, inflammation, or lifestyle choices.
Early Restenosis (1-6 Months After Placement)
Early restenosis usually happens in the first six months after a stent is placed. The body’s reaction to the stent can cause new tissue to grow, narrowing the artery. Drug-eluting stents are better at preventing this early restenosis than bare-metal stents.
| Stent Type | Early Restenosis Rate |
| Bare-Metal Stents | 15-20% |
| Drug-Eluting Stents | 5-10% |
Late Lumen Loss (Beyond 4 Years)
Late lumen loss is when the stented artery gets narrower over time, often years after the procedure. It’s linked to atherosclerosis getting worse. Keeping an eye on risk factors and managing them is key to preventing this.
Signs and Symptoms of Stent Failure
It’s important to know the signs of stent failure. Look out for recurring angina, shortness of breath, or symptoms like before the stent was put in. If these symptoms come back, get medical help right away.
Understanding restenosis helps patients and doctors take steps to manage and prevent it. A healthy lifestyle and following medication can help keep the stent working well for longer.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Heart Stent
To keep your heart stent working well, you need a good care plan. This plan includes taking your medicine, making lifestyle changes, and seeing your doctor regularly.
Medication Adherence (Antiplatelet Therapy)
Following your doctor’s advice on antiplatelet therapy is key. These medicines, like aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitors, stop blood clots on the stent. It’s important to take them as your doctor says to work right.
Don’t skip or change your doses without talking to your doctor. Doing so can lead to serious problems. Your doctor will tell you how long to take these medicines, based on your situation and the stent type.
Lifestyle Modifications for Optimal Stent Function
Living a heart-healthy lifestyle helps your stent last longer. This means:
- Eating a balanced diet with lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean meats
- Doing regular exercise, like walking, to keep your heart strong
- Quitting smoking if you smoke, as it harms your stent
- Managing stress with activities like meditation or yoga
These changes help your stent work better and keep your heart healthy.
Regular Medical Follow-ups and Monitoring
Seeing your doctor often is important for checking your stent. These visits help:
- Check your heart health and fix any problems
- Change your medicines if needed to keep your stent working
- Do tests to see if your stent is open and working right
By being proactive and talking to your doctor, you can make sure your heart stent works well for a long time.
Managing Chronic Conditions to Improve Stent Outcomes
Managing chronic conditions is key to better heart stent outcomes. Patients with heart stents must manage their conditions well. This ensures their stents last longer.
Diabetes Management and Its Effect on Stent Longevity
Diabetes can shorten the life of heart stents. High blood sugar causes increased inflammation and accelerated plaque buildup. This can narrow the stent again.
Effective diabetes management is vital. This includes diet, exercise, and medication. It helps keep the stent open.
It’s important to monitor blood sugar and follow treatment plans. Controlling diabetes reduces stent failure risk. It also improves heart health.
Controlling Cholesterol Levels to Prevent Plaque Buildup
High cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup, affecting stent longevity. Managing cholesterol through dietary changes, exercise, and medication can prevent atherosclerosis.
Doctors may prescribe statins to lower cholesterol. Regular lipid profile checks are necessary to see if these treatments work.
Hypertension Management and Its Impact on Stents
Hypertension can stress the heart and arteries, impacting stent longevity. Managing hypertension through lifestyle modifications and antihypertensive medications can reduce this stress.
It’s important to regularly check blood pressure and follow treatment plans. Controlling blood pressure lowers cardiovascular event risk. It also improves stent outcomes.
In conclusion, managing chronic conditions like diabetes, high cholesterol, and hypertension is essential for better stent outcomes. Effective control of these conditions can extend stent life and improve heart health.
When Might a Stent Need Replacement or Additional Treatment?
Stents are usually permanent, but sometimes they need more help. How long a stent lasts depends on many things. These include the patient’s health, the type of stent, and how it was put in.
Clinical Indicators of Stent Failure
Stent failure can show up in different ways. Restenosis, or the arteries getting narrow again, is a big worry. Signs that a stent might not be working right include:
- Recurring chest pain or angina
- Abnormal stress test results
- Detection of restenosis through imaging tests
These symptoms mean the stent might not be doing its job. It’s time to check it out more closely.
Diagnostic Procedures to Evaluate Stent Function
To see how well a stent is working, doctors use several tests. Angiography is one way to look at the stent and the artery. Other tools include:
- Stress tests to check the heart’s function when it’s working hard
- Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) for detailed images of the stent and artery
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) for very detailed images of the stent and the inside of the artery
Treatment Options for Failed or Narrowed Stents
If a stent fails or gets narrow, there are ways to fix it. The right treatment depends on how bad the problem is and the patient’s health.
| Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
| Additional Stenting | Putting another stent inside the old one | Works well for restenosis, is a small procedure |
| Angioplasty | Using a balloon to open up the narrow spot | Fast, can be done with stenting |
| Medication Therapy | Changing medicines to stop more plaque from forming | Doesn’t need surgery, can be used for a long time |
Knowing about these options helps both patients and doctors make the best choices for stent care.
Conclusion: Living Confidently with Heart Stents
Living with heart stents means knowing how to keep them working well. Managing health conditions, taking medicine as directed, and choosing a healthy lifestyle are key. These steps help your heart stents work better and keep your heart healthy.
How long your heart stents last depends on sticking to your treatment plan and seeing your doctor regularly. Eating right and exercising often also helps. These habits lower the chance of stent problems and keep your heart strong for a long time.
Heart stents are a good way to fight coronary artery disease when used right. Knowing the value of healthy living and following your doctor’s advice helps. This way, you can live well with heart stents, enjoying better heart health and a happier life.
FAQ
How long do heart stents typically last?
Heart stents are made to last a long time. They can last 10 years or more. This depends on the patient’s health and lifestyle.
What is the average lifespan of a stent in the heart?
The lifespan of a heart stent varies. But, most stents can last for 10 years or more. This is with the right care and management.
Do drug-eluting stents last longer than bare-metal stents?
Yes, drug-eluting stents release medication. This helps prevent the artery from narrowing again. So, they can last longer than bare-metal stents.
What factors affect the longevity of a heart stent?
Several factors affect a heart stent’s longevity. These include the patient’s age and health, the stent’s material and design, and how it was placed.
Can lifestyle changes help extend the lifespan of a heart stent?
Yes, making healthy lifestyle choices can help. Eating well, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking can improve stent function. This might extend its lifespan.
How often should I have medical follow-ups after getting a stent?
It’s important to have regular medical check-ups after getting a stent. How often depends on your health needs. Your doctor will decide.
What are the signs and symptoms of stent failure?
Signs of stent failure include chest pain and shortness of breath. These symptoms are similar to those before the stent was placed. If you experience them, seek medical help right away.
Can managing chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension improve stent outcomes?
Yes, managing conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure can help. It can improve stent longevity and overall heart health.
When might a stent need replacement or additional treatment?
A stent might need replacement if it fails or narrows again. This is determined by tests like angiography.
What are the treatment options for a failed or narrowed stent?
Treatment options include more stenting, angioplasty, or other procedures. The choice depends on the case and how severe the failure is.
How long can a stent last in an artery?
A stent can last many years in an artery. Often, it’s 10 years or more, with proper care.
What is the lifespan of stents?
Stents are made to last a long time. Most are designed to be permanent and last for many years.
Are bioresorbable stents a more temporary solution?
Yes, bioresorbable stents dissolve over time. They provide temporary support to the artery as it heals.
References
- Udriște, A. S., et al. (2021). Cardiovascular stents: A review of past, current, and emerging devices. Materials Sciences and Applications, 12(5), 245-262. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8151529/


































