Hgb SS disease, also known as hemoglobin SS or hb ss, is the most common and severe form of sickle cell disease. It happens when a person gets two sickle cell genes, one from each parent. This affects the hemoglobin in red blood cells, causing health problems.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important early detection and expert care are for Hgb SS disease patients. Our team works together to offer advanced, patient-focused care. We help families deal with the challenges of this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the genetic basis of Hgb SS disease is key for diagnosis and care.
- Getting two sickle cell genes leads to the most severe form of sickle cell disease.
- Early detection and expert care can greatly improve patient outcomes.
- Patient-centered protocols are vital for managing Hgb SS disease’s complexities.
- A team approach ensures complete care for patients and their families.
What Is Hgb SS Disease: Definition and Genetic Basis
Hgb SS disease starts with a genetic mutation that changes how hemoglobin works. This change makes sickle hemoglobin, or HbS. It causes red blood cells to bend and break down.
Hgb SS disease, or sickle cell anemia, is the most common type. It happens when someone gets two copies of the mutated HBB gene, one from each parent. This leads to hemoglobin S (HbS) instead of the usual hemoglobin A (HbA).
The Most Common Form of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease affects hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. Hgb SS disease is the most severe, with two HbS genes. About 300,000 babies worldwide are born with sickle cell disease each year, with Hgb SS being the most common.
Inheritance Patterns of Hemoglobin SS
Hgb SS disease follows an autosomal recessive pattern. This means a child needs two defective HBB genes (one from each parent) to have the disease. Carriers, with one normal and one mutated gene, usually don’t show all symptoms but can pass the mutated gene to their kids. Knowing this is key for genetic counseling and planning families.
Hgb SS disease is a big health issue worldwide, affecting millions. It’s common in some areas like Africa, the Middle East, and India. The disease causes pain, infections, and serious health problems.
Key Fact 1: Global Prevalence of Hemoglobin SS Disease
It’s important to know how widespread Hgb SS disease is around the world. This severe form of sickle cell disease is common in some areas. It affects many people globally.
Worldwide Distribution and Statistics
Hgb SS disease is found everywhere, but it’s more common in some places. Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest prevalence. Here, it’s a big health problem.
About 1000 children with SCD are born every day in Africa. This shows how serious the issue is there.
High-Risk Populations in Africa, Middle East, and India
The people most affected by Hgb SS disease live in Africa, the Middle East, and India. In these places, the disease is common and often deadly. This is because many don’t have easy access to healthcare.
Let’s look at the prevalence in these high-risk areas more closely:
| Region | Prevalence of Hgb SS Disease | Annual Births with SCD |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | High | Approximately 300,000 |
| Middle East | Moderate to High | Significant, exact numbers vary |
| India | Moderate | Substantial, with varying prevalence across states |
The global spread of Hgb SS disease shows we need special healthcare plans for high-risk areas. Knowing where and how it affects people helps us improve care and outcomes.
Key Fact 2: How Abnormal Hemoglobin Creates Sickle-Shaped Cells
Abnormal hemoglobin in Hgb SS disease causes red blood cells to become rigid and sickle-shaped. This happens because of a genetic mutation that changes the hemoglobin’s structure. It makes the hemoglobin polymerize under certain conditions.
Normal vs. Sickle Hemoglobin Structure
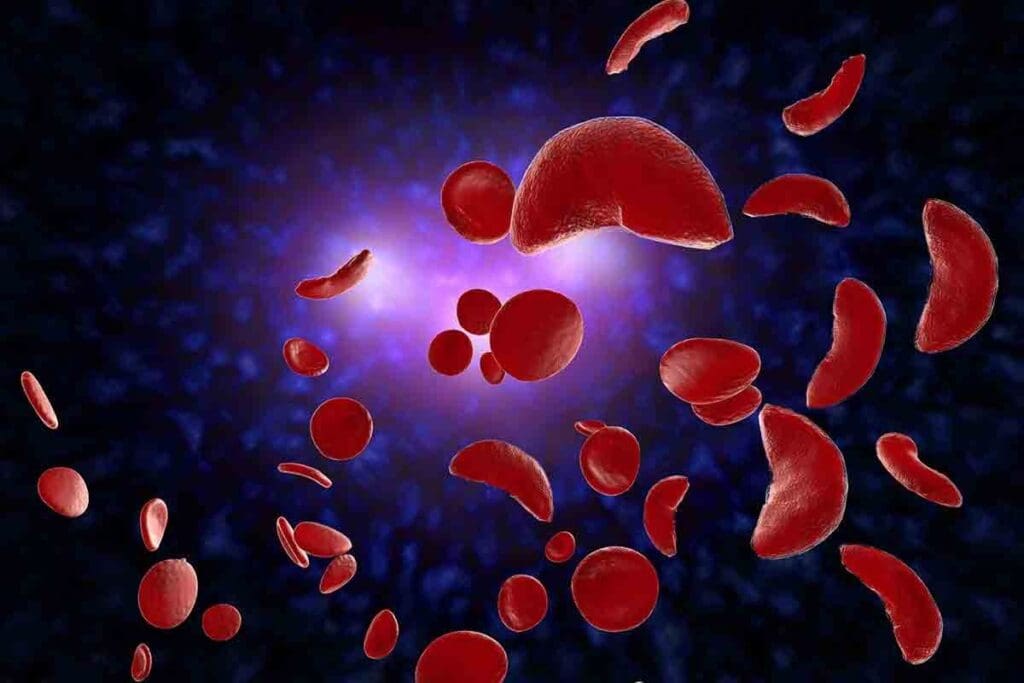
Normal hemoglobin (HbA) and sickle hemoglobin (HbS) are different. HbS has a single amino acid change compared to HbA. This change is due to a mutation that replaces glutamic acid with valine at the sixth position of the beta-globin chain.
This change causes the hemoglobin to form intracellular polymers when it loses oxygen. This results in the characteristic sickle shape.
The Sickling Process and Blood Flow Obstruction
The sickling process involves several steps that lead to blood flow obstruction. When red blood cells with HbS lose oxygen, they become more viscous and prone to polymerization. This makes them rigid and sickle-shaped.
This rigidity causes cellular fatigue, stress, dehydration, and premature hemolysis. The sickling process can be broken down into several stages:
- Deoxygenation of HbS-containing red blood cells
- Polymerization of HbS, leading to cell rigidity
- Sickling of red blood cells, causing cellular damage
- Obstruction of blood flow due to sickled cells
The obstruction of blood flow by sickled red blood cells can lead to various complications. These include vaso-occlusive crises, acute chest syndrome, and other systemic problems.
| Characteristics | Normal Hemoglobin (HbA) | Sickle Hemoglobin (HbS) |
| Structure | Normal beta-globin chain | Mutated beta-globin chain (Glu6Val) |
| Polymerization | No polymerization | Polymerizes upon deoxygenation |
| Red Blood Cell Shape | Flexible, biconcave disk | Rigid, sickle shape |
| Clinical Impact | No disease association | Associated with sickle cell disease |
Understanding the differences between normal and sickle hemoglobin is key to understanding Hgb SS disease. The unique characteristics of HbS lead to the various clinical manifestations of sickle cell disease.
Key Fact 3: Primary Symptoms of Sickle Cell Anemia SS Disease
It’s key for doctors to know the symptoms of sickle cell anemia to give the best care. Sickle cell anemia SS disease, or HBSS, has symptoms that really hurt patients’ lives. The main symptoms are severe pain crises and chronic anemia. These happen because of the sickle-shaped red blood cells.
Acute Pain Crises: Hallmark of HBSS Disease
Acute pain crises, or VOC, are a big deal in HBSS sickle cell disease. They happen when sickled red blood cells block blood vessels. This causes pain and is why many patients with sickle cell anemia SS disease go to the hospital.
The pain is very bad. It’s because of how sickled red blood cells, blood vessel walls, and inflammatory substances work together. This leads to tissue damage, pain, and more.
Chronic Anemia and Fatigue
Chronic anemia is another big symptom of sickle cell anemia SS disease. The sickle-shaped hemoglobin makes red blood cells break down easily. This leads to less hemoglobin and symptoms like tiredness, weakness, and shortness of breath.
How bad the anemia is can vary. But it’s always there. Doctors manage it by checking hemoglobin often, giving nutritional advice, and sometimes blood transfusions.
| Symptom | Description | Impact on Patient |
| Acute Pain Crises | Severe pain due to vaso-occlusion | Hospitalization, significant pain |
| Chronic Anemia | Persistent low hemoglobin | Fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath |
Key Fact 4: Serious Complications of Untreated Hgb SS Disease
Untreated Hgb SS disease can cause severe and life-threatening problems. It affects not just the hemoglobin but also other parts of the body.
Acute Chest Syndrome and Respiratory Complications
Acute chest syndrome is a major cause of illness and death in those with hemoglobin SS disease. It shows up as a new lung issue on X-rays, often with fever, breathing troubles, or chest pain. Problems with blood vessels and high ET-1 levels increase the risk of this syndrome.
Acute chest syndrome can get worse fast, needing quick medical help. It can lead to serious breathing problems and is very dangerous if not treated right.
Stroke Risk and Neurological Damage
People with untreated Hgb SS disease face a higher risk of stroke. This can cause serious brain damage. Sickled red blood cells can damage big blood vessels and increase the chance of blocked brain blood vessels.
Damage from blood flow problems can cause more inflammation, making brain problems worse. It’s important to catch and treat stroke risks early to avoid lasting brain damage.
Organ Damage Patterns
Untreated hemoglobin SS disease often leads to damage in many organs. The spleen, kidneys, liver, and heart are most at risk. This is due to long-term anemia, blocked blood flow, and damage from blood flow problems.
| Organ | Common Complications |
| Spleen | Autosplenectomy, increased risk of infections |
| Kidneys | Chronic kidney disease, renal failure |
| Liver | Cholestasis, liver dysfunction |
| Heart | Cardiomegaly, heart failure |
Knowing about these complications is key to managing Hgb SS disease well. Quick diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve life quality for those with this condition.
Key Fact 5: Diagnostic Testing for Sickle Cell Disease Type SS
Early detection of sickle cell disease type SS is possible through various diagnostic tests. Newborn screening programs are key. Accurate diagnosis is vital for effective management and better quality of life.
Newborn Screening Programs and Early Detection
Newborn screening programs are vital for early detection of sickle cell disease type SS. A simple blood test is performed when the baby is between 24 and 48 hours old. This test checks for abnormal hemoglobin, allowing for early intervention.
We know early detection is key to prevent serious complications. Newborn screening has become common in many countries. It helps healthcare providers start care early.
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis and HPLC Testing
Hemoglobin electrophoresis is a lab technique used to identify different types of hemoglobin. It’s essential for diagnosing sickle cell disease type SS by detecting abnormal hemoglobin S. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is another method that quantifies hemoglobin fractions, providing detailed analysis.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Key Features |
| Hemoglobin Electrophoresis | Identify abnormal hemoglobin | Separates hemoglobin variants based on charge |
| HPLC Testing | Quantify hemoglobin fractions | Provides detailed analysis of hemoglobin variants |
Genetic Testing Methods
Genetic testing is a powerful tool for diagnosing sickle cell disease type SS. It analyzes the HBB gene, which encodes the beta-globin subunit of hemoglobin. This information is invaluable for genetic counseling and family planning.
Genetic testing methods include:
- DNA sequencing to identify specific mutations in the HBB gene
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) to amplify specific DNA sequences for analysis
- Genetic counseling to interpret test results and provide family planning guidance
In conclusion, diagnosing sickle cell disease type SS involves a multi-faceted approach. This includes newborn screening, hemoglobin electrophoresis, HPLC testing, and genetic analysis. These tools help healthcare providers identify the condition early and manage it effectively, improving outcomes for individuals with this condition.
Key Fact 6: Treatment Approaches for HBSS Sickle Cell
Exploring treatments for HBSS sickle cell shows a mix of old and new methods is key. A good plan is needed to ease symptoms, stop problems, and make life better for those with the disease.
Hydroxyurea and Disease-Modifying Therapies
Hydroxyurea is a known treatment that helps by making fewer crises and chest problems. It boosts fetal hemoglobin, which stops red blood cells from sickling. This lowers the chance of serious issues.
Benefits of Hydroxyurea:
- Reduces VOC and ACS episodes
- Decreases the need for blood transfusions
- Improves quality of life
Blood Transfusions and Exchange Procedures
Blood transfusions are vital for managing HBSS sickle cell disease. They help get more oxygen to tissues and lower stroke risk. In urgent cases, exchange transfusions replace bad red blood cells with good ones.
| Treatment | Benefits | Risks |
| Blood Transfusions | Improves oxygen delivery, reduces stroke risk | Iron overload, transfusion reactions |
| Exchange Transfusions | Effective in acute situations, reduces sickled cells | Complex procedure, risk of infection |
Stem Cell Transplantation and Gene Therapy
Stem cell transplant and gene therapy are new, hopeful treatments for sickle cell disease. Transplanting healthy marrow can cure the disease. Gene therapy tries to fix the genetic problem causing the disease.
“Gene therapy has the power to change sickle cell disease treatment by fixing the cause.”
These new therapies bring hope for better lives for those with HBSS sickle cell disease. They offer a chance for a cure, which could greatly improve their lives.
Key Fact 7: Living with Haemoglobin SS Disease
Managing Haemoglobin SS disease is key for a good life. It’s about medical care, lifestyle changes, and support. Together, they help a lot.
Daily Management Strategies
Managing Haemoglobin SS disease daily is complex. It’s important to drink plenty of water, avoid extreme weather, and eat well. Following your medication, like hydroxyurea, is also vital.
Keeping an eye on your health is important too. This means tracking symptoms and blood counts. It helps doctors adjust your treatment.
“Comprehensive care for Sickle Cell Disease includes pain management, infection prevention, and psychosocial support, significantly improving patient outcomes.”
Support Resources and Quality of Life Considerations
Having support resources is essential for those with Haemoglobin SS disease. This includes medical care, mental support, and education. It helps manage the disease well.
New treatments give hope for better lives. Gene therapy and other treatments are being studied. They might cure or change the disease’s course.
Improving life with Haemoglobin SS disease needs a whole approach. It includes medical care, lifestyle changes, and support. Understanding the disease and using available resources helps patients face its challenges.
Conclusion: Advances in Understanding and Managing Hgb SS Disease
Our understanding and management of Hgb SS disease have greatly improved. This has led to better patient outcomes and a higher quality of life. New research and treatments keep bringing hope to those with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD).
New diagnostic tools and treatments like hydroxyurea and gene therapy have made a big difference. These advancements help manage SCD better. They reduce the number of painful crises and other serious problems linked to the disease.
The future for SCD management is bright, with more research on new treatments. As we learn more about Hgb SS disease, we can give better care to patients. This improves their life quality and outcomes. Managing ss$ disease well needs a team effort. We’re dedicated to providing top-notch healthcare and support to patients worldwide.
FAQ
What is Hgb SS disease?
Hgb SS disease, also known as sickle cell anemia, is the most common and severe form of sickle cell disease. It happens when someone gets two sickle cell genes, one from each parent. This leads to abnormal hemoglobin production.
How is Hgb SS disease inherited?
Hgb SS disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. This means a person needs two copies of the mutated gene to have the disease. Carriers have a 50% chance of passing the gene to their children.
What are the primary symptoms of sickle cell anemia SS disease?
The main symptoms include acute pain crises, chronic anemia, and fatigue. These happen because the abnormal hemoglobin makes red blood cells sickle-shaped. This blocks blood flow.
How is Hgb SS disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves newborn screening, hemoglobin electrophoresis, HPLC testing, and genetic testing. Early detection is key for managing the disease and preventing complications.
What are the complications of untreated Hgb SS disease?
Untreated Hgb SS disease can cause serious problems. These include acute chest syndrome, stroke risk, and organ damage. These issues come from the sickling process and tissue damage.
What are the treatment approaches for HBSS sickle cell disease?
Treatments include hydroxyurea, blood transfusions, and newer options like stem cell transplantation and gene therapy. These aim to reduce pain crises, alleviate anemia, and prevent complications.
How can individuals with haemoglobin SS disease manage their condition daily?
Daily management involves staying hydrated, avoiding extreme temperatures, and living a healthy lifestyle. Counseling and patient support groups also help improve quality of life.
What is the global prevalence of Hgb SS disease?
Hgb SS disease is found worldwide, with high prevalence in Africa, the Middle East, and India. Millions are affected, highlighting the need for awareness and care.
Can Hgb SS disease be cured?
There’s no definitive cure yet, but medical advancements offer hope. Treatments like stem cell transplantation and gene therapy may improve management and potentially cure it in the future.
References
- Kato, G. J., Piel, F. B., Reid, C. D., Gaston, M. H., Ohene-Frempong, K., Krishnamurti, L., & Vichinsky, E. (2018). Sickle cell disease. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 4(1), 18010. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29542687/




































