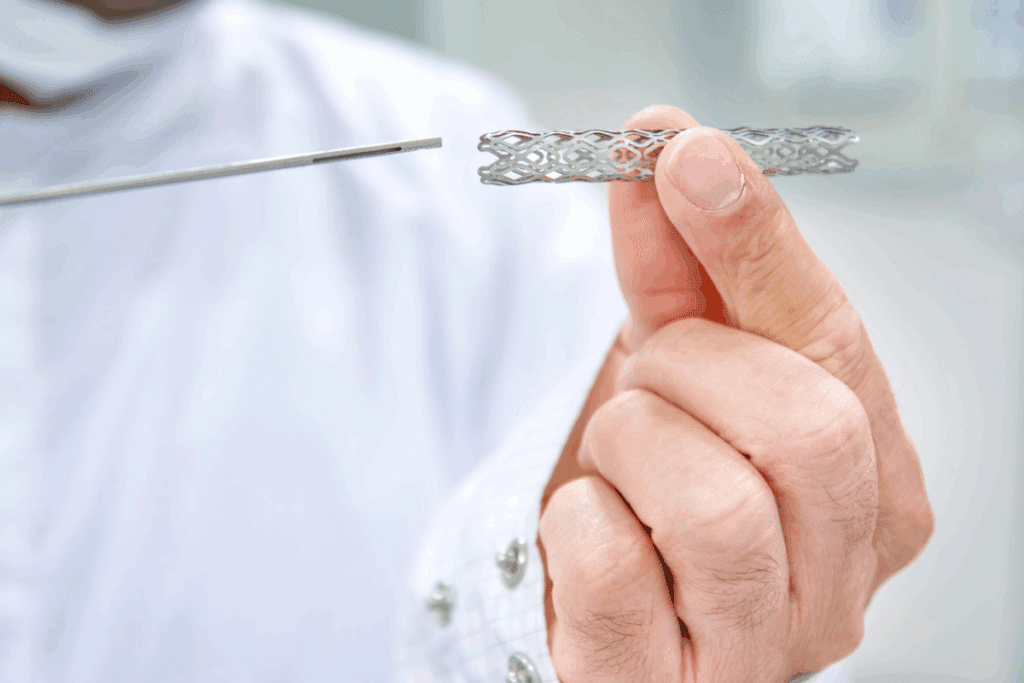
At Liv Hospital, we are committed to providing world-class healthcare guidance for managing heart health, including the use of heart stents. A heart stent is a small mesh tube placed in an artery to keep it open after procedures like angioplasty.
Many patients ask, “can stents be replaced?” In most cases, heart stents are designed to last for many years without needing replacement. However, in certain situations—such as blockage, collapse, or narrowing of the artery—a new stent may be required.
In this article, we’ll explore the facts about stent longevity, when stents can be replaced, and how ongoing care plays a vital role in maintaining heart health. At Liv Hospital, our experts are dedicated to ensuring you receive the safest and most effective treatment for lasting results.
Key Takeaways
- Heart stents are used to keep arteries open after angioplasty.
- Most stents are designed to be permanent fixtures.
- Potential complications include blockage or collapse.
- Understanding heart stent longevity is key for ongoing care.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to providing top-notch healthcare guidance.
Understanding Heart Stents and Their Purpose
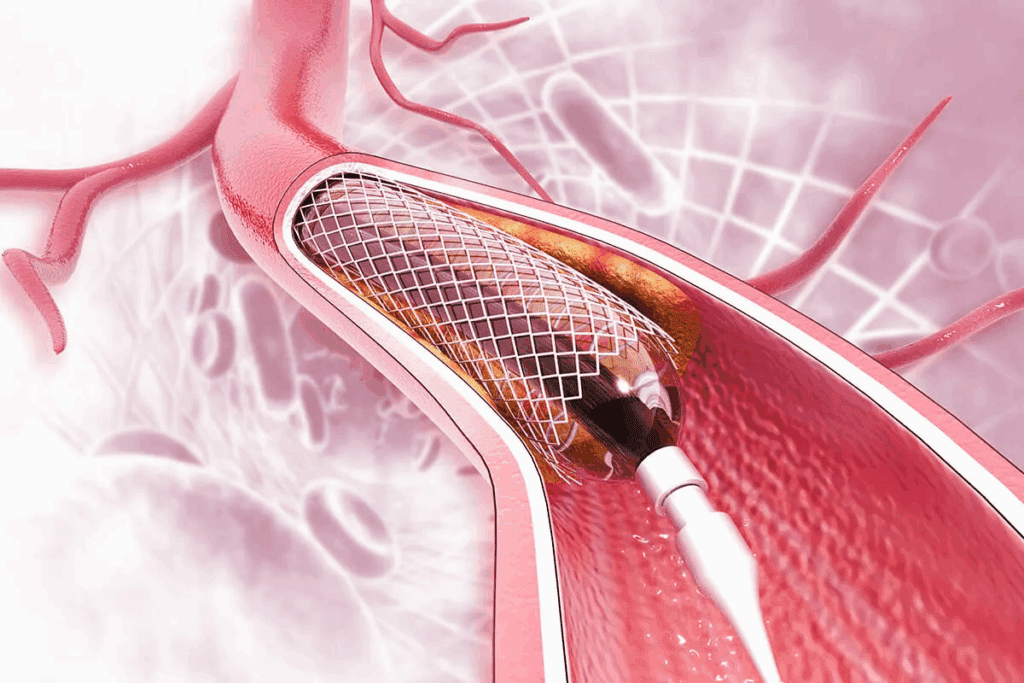
Heart stents are key in fighting coronary artery disease. They act as a scaffold to keep arteries open. These small, mesh-like devices are used after angioplasty to ensure arteries stay open.
What Are Heart Stents?
Heart stents are tiny, expandable tubes put into narrowed or blocked arteries. They help keep the artery open, boosting blood flow to the heart. Stents are a vital tool in cardiology, a less invasive option compared to bypass grafting.
How Stents Function in Coronary Arteries
After a stent is placed in a coronary artery, it expands to keep it open. This is done through a balloon angioplasty, where the balloon inflates to deploy the stent. The stent then stays in place permanently, preventing the artery from narrowing again.
Types of Heart Stents Available
There are mainly two types of heart stents: bare-metal stents and drug-eluting stents. Bare-metal stents are made of metal mesh and physically hold the artery open. Drug-eluting stents release medication to prevent the artery from re-narrowing.
| Stent Type | Description | Key Benefits |
| Bare-Metal Stents | Made of metal mesh, these stents physically keep the artery open. | Simple design, less risk of late complications |
| Drug-Eluting Stents | Release medication to prevent artery re-narrowing. | Reduced risk of restenosis, improved long-term outcomes |
The Lifespan of Heart Stents
Heart stents are meant to be permanent, but their life span can change. This depends on the patient and the stent itself. We’ll look into how long stents last and what patients can expect.
Are Stents Permanent Fixtures?
Most heart stents are made to last forever for coronary artery disease. But, “permanent” might not mean what you think. It really depends on the stent type and the patient’s health.
Bare-metal stents and drug-eluting stents are the main types. Drug-eluting stents release medicine to stop arteries from narrowing. They’re more common because they work well to prevent restenosis.
How Long Do Stents Last in Arteries?
Stent life span varies. Drug-eluting stents usually work better and last longer than bare-metal stents.
Research shows drug-eluting stents can last many years. For some, they might last a lifetime. But, results can differ based on patient health, lifestyle, and medication use.
Factors Affecting Stent Durability
Several things can affect how long a stent lasts, including:
- Stent type: Drug-eluting stents tend to have better long-term outcomes than bare-metal stents.
- Patient health: Conditions like diabetes can affect stent longevity.
- Lifestyle choices: Smoking and lack of exercise can negatively impact stent durability.
- Medication adherence: Taking prescribed medications as directed is key for stent longevity.
| Factor | Impact on Stent Durability |
| Stent Type | Drug-eluting stents generally last longer |
| Patient Health | Conditions like diabetes can reduce stent lifespan |
| Lifestyle Choices | Smoking and inactivity can negatively affect stent durability |
| Medication Adherence | Adhering to prescribed medications improves stent longevity |
Understanding these factors and living a healthy lifestyle can help stents last longer. Regular check-ups with doctors are also important. They help keep an eye on the stent’s health and catch any problems early.
Can Stents Become Blocked? Understanding Restenosis
Heart stents can sometimes become blocked, a problem called restenosis. This happens when the artery that was opened by the stent narrows again. This can lead to less blood flow to the heart.
Restenosis is a big worry because it can cause symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath. Knowing about restenosis, its causes, and symptoms is key to managing and possibly avoiding it.
The Process of In-Stent Restenosis
In-stent restenosis occurs when the artery grows new tissue around the stent. This can narrow the artery again. Many things can affect this process, like the stent type and the person’s health.
Risk Factors for Stent Blockage
Several factors can raise the risk of restenosis. These include:
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are more likely to get restenosis.
- Chronic kidney disease: Kidney disease can make healing harder and increase risks.
- Metal allergy: Some might be allergic to stent metals, causing inflammation.
Symptoms of a Blocked Stent
The signs of a blocked stent can differ but often include:
- Chest pain: This is a common symptom, similar to the pain before the stent was put in.
- Abnormalities on stress tests: Even without symptoms, a blocked stent can show up on stress tests or other tests.
It’s important to know these symptoms and risk factors for early detection and treatment of restenosis. If you notice any symptoms or have concerns about your stent, talk to your doctor right away.
Stent Collapse: Causes and Consequences
It’s key to understand stent collapse causes and effects for better patient care. Stent collapse, though rare, can greatly affect those with coronary artery disease.
Mechanical Failures in Heart Stents
Mechanical failures lead to stent collapse. These failures stem from several reasons, including:
- Inadequate stent sizing or placement
- External compression forces on the stent
- Material fatigue over time
Mechanical integrity is vital for a stent’s long-term success. When a stent collapses, it can block blood flow in the artery.
Signs of Stent Collapse
The signs of stent collapse resemble symptoms before the stent was placed. These include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
It’s vital for patients to notice these signs and get medical help right away.
Immediate Risks of Stent Failure
The risks of stent failure are serious and can be deadly. These risks include:
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Myocardial infarction (heart attack)
- Need for emergency revascularization procedures
Prompt medical intervention is essential to handle stent collapse and lessen its effects. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are important to watch stent function and heart health.
Do Heart Stents Need Replacing?
Heart stents are meant to stay in place forever. But sometimes, they can fail or get blocked. We look into when this might happen and how often stents need to be replaced.
Common Scenarios Requiring Stent Intervention
Stents can fail or get blocked due to in-stent restenosis. This is when plaque or scar tissue builds up inside the stent.Medical News Today says new stent technologies have made this risk much lower. This includes drug-eluting stents and drug-coated balloons.
Frequency of Stent Replacement
Whether a stent needs to be replaced depends on many things. This includes the patient’s health and how well the stent is working. Usually, stents only need to be replaced if they fail or get blocked.
Decision-Making Process for Replacement
We decide if a stent needs to be replaced based on the patient’s health and the stent’s performance. We often check in with patients every 3–6 months in the first year. This helps us see how well the stent is working and catch any problems early.
FAQ
Does a stent have to be replaced?
Not always, but sometimes a stent needs to be replaced. This happens if there’s a blockage or other issues. We talk about when it’s necessary.
How long do stents last in arteries?
Stent lifespan depends on the type and patient health. They can last many years. But, they’re not always permanent.
Can stents be removed and replaced?
Sometimes, a stent can be taken out and put back in. But, this is a complex process. We decide on a case-by-case basis.
Are stents permanent fixtures?
Stents are made to last long, but they’re not always permanent. Things like restenosis or mechanical failure can shorten their life.
What are the symptoms of a blocked stent?
Signs of a blocked stent include chest pain, shortness of breath, and feeling tired. If you notice these, get medical help right away.
How often should a heart stent be checked?
How often to check a stent varies. It depends on the patient and the stent type. We give personalized advice on follow-up care.
Can cardiac stents be removed?
Taking out a cardiac stent is a complex task. It’s usually only done in certain situations. We weigh the risks and benefits for each case.
What is the lifespan of a stent?
Stent lifespan can be quite long. With proper care, many can last 10-15 years or more.
Can a heart stent be removed and replaced with a new one?
In some cases, a heart stent can be removed and replaced. But, this needs careful planning and evaluation by a doctor.
How long are heart stents good for?
Heart stents are made to be durable. But, their effectiveness can change over time. Regular check-ups and care are key to keeping them working well.
References
- Modi, K. (2023). Stent Thrombosis. StatPearls. National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441908/




































