At Liv Hospital, we use the EVAR stent procedure to fix abdominal aortic aneurysms. This method is less invasive. It involves putting a stent graft through the femoral arteries to the aneurysm. This is done with the help of imaging technology to strengthen the weak vessel wall.
The EVAR stent procedure is a big step forward in treating abdominal aortic aneurysms. It’s safer than traditional open surgery. Choosing EVAR means patients can heal faster and face less risk. It’s perfect for those at high risk.
Key Takeaways
- EVAR stent procedure is a minimally invasive solution for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair.
- The procedure involves threading a stent graft through the femoral arteries to the aneurysm site.
- EVAR offers quicker recovery times and reduced risk compared to traditional open surgery.
- It is an ideal option for high-risk patients.
- Liv Hospital provides international standards and patient-centered care for EVAR procedures.
Understanding Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
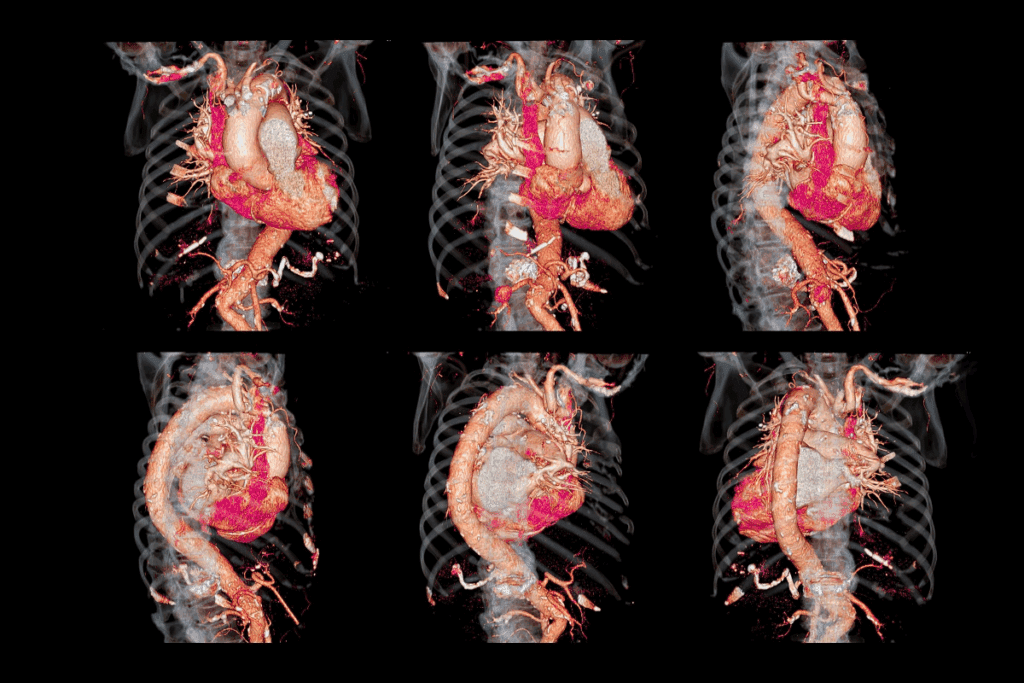
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a serious condition where the aorta, the main blood vessel, gets too big. The aorta carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. If the aorta’s wall weakens, it can bulge out, creating an aneurysm.
Definition and Pathophysiology
An aortic aneurysm is when the aorta gets at least 1.5 times bigger than normal. It happens because of a mix of genetic, environmental, and biomechanical factors. The aortic wall weakens due to inflammation and damage to elastin and collagen.
Most people with AAA don’t show symptoms until it’s too late. But, knowing how it works helps doctors find better treatments. EVAR (Endovascular Aneurysm Repair) is a new, less invasive way to fix AAA.
Risk Factors and Prevalence
AAA can be caused by many things, like being older, male, smoking, high blood pressure, and family history. Men over 65 are more likely to get it. Smoking makes the problem worse by damaging the aortic wall.
Worldwide, about 5% of men between 65 and 74 have AAA. Knowing who’s at risk helps doctors screen and prevent it.
Natural History and Rupture Risk
AAA can grow slowly or stay the same size for years. But, bigger aneurysms are more likely to burst. Aneurysms over 5.5 cm are at high risk.
The risk also depends on how fast it grows. Rupture of an AAA is a catastrophic event with a high death rate. EVAR is often used for big AAAs or those at high risk of bursting.
Evolution of AAA Treatment Approaches
The way we treat AAA has changed a lot. Now, we use less invasive methods. This has greatly improved how we care for patients with Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.
Traditional Open Surgical Repair
For a long time, open surgery was the main way to fix AAA. Surgeons made a big cut in the belly to reach the aorta. They then put in a new graft to replace the bad part.
This method works well but comes with big risks. It’s tough on older people or those with other health problems.
Key aspects of open surgical repair include:
- Major abdominal surgery with a lengthy recovery period
- Higher risk of complications, specially in high-risk patients
- Effective for treating AAA, with durable long-term results
Development of Endovascular Techniques
EVAR changed AAA treatment a lot. It’s a less invasive way to fix the aorta. A stent graft is put in to block the bad part from getting worse.
The advantages of EVAR include:
- Reduced risk of perioperative complications
- Shorter hospital stays and recovery times
- Less invasive, resulting in smaller incisions and reduced trauma to the patient
Current Treatment Guidelines
Today, EVAR is often the first choice for treating AAA. The decision between EVAR and open surgery depends on many things. These include the patient’s health, the size and shape of the aneurysm, and what the patient wants.
Key considerations for current treatment guidelines include:
- Anatomical suitability for EVAR
- Patient’s overall health and risk profile
- Surgeon’s expertise and institutional experience with EVAR
As EVAR gets better, so do the results for patients with AAA.
EVAR Stent Technology and Components
EVAR stent technology has evolved, giving doctors new stent grafts for treating abdominal aortic aneurysms. These stent grafts are fabric tubes with metal wire stents. They reinforce the weak spot in the aorta, making aneurysm repair durable and effective.
Bifurcated Stent Grafts
Bifurcated stent grafts are the most used in EVAR procedures. They fit the aorta’s bifurcation into the iliac arteries, providing a secure repair. The main body of the graft is in the aorta, and the limbs go into the iliac arteries, covering the aneurysm fully.
Aorto-Uni-Iliac Stent Grafts
Aorto-uni-iliac (AUI) stent grafts are for patients with complex anatomy or need a custom approach. They have a single iliac limb and often use a femoral-femoral bypass for the other limb. This method offers a flexible solution for tough cases.
Fenestrated and Branched Stent Grafts
Fenestrated and branched stent grafts are for complex aortic aneurysms with major branch vessels. Fenestrated grafts have holes for the branch vessels, and branched grafts have extra limbs. These grafts make treating previously inoperable aneurysms possible.
Recent Technological Advancements
Recent years have brought big improvements in EVAR stent technology. There are now lower profile devices, better delivery systems, and improved imaging. These changes have led to higher success rates, fewer complications, and better patient outcomes. Ongoing research will keep improving EVAR stent technology.
Patient Selection Criteria for EVAR Procedure
The success of the EVAR procedure depends on choosing the right patients. We carefully check each patient to see if they’re a good fit for this treatment for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA).
Anatomical Considerations
When picking patients for EVAR, we look at their body’s shape. We check the size of the aneurysm and if the stent graft can fit well. Adequate neck length and diameter are critical for achieving a secure seal and preventing endoleaks.
Risk Stratification
We also look at how risky the procedure is for each patient. We check their health, including heart disease, diabetes, and kidney function. Patients with high surgical risk may benefit from EVAR as it is less invasive compared to open repair. But we make sure the patient can handle the procedure.
Contraindications
Some things can make EVAR not suitable. Significant aortic neck angulation, large neck diameter, or inadequate access vessel size can make it risky. We also think about how long the patient will live and if they’ll need more treatments later.
Preoperative Assessment
Before the procedure, we do a detailed check-up. This includes CT scans to measure the aneurysm and plan the stent graft. We also do blood tests and heart checks to get the patient ready.
By following these steps, we make sure EVAR is safe and effective for our patients with AAA.
Pre-Procedure Planning and Imaging
The success of EVAR procedures depends a lot on good planning and imaging before the procedure. Effective planning makes sure the stent graft fits right and is in the right place. This lowers the chance of problems during and after the procedure.
CT Angiography Requirements
CT angiography is key in planning for EVAR. It gives clear pictures of the aorta and its branches. Contrast-enhanced spiral CT scans help measure the aneurysm and spot any issues with placing the stent graft.
Stent Graft Selection and Sizing
Choosing the right stent graft is very important for EVAR success. The graft must fit the patient’s body perfectly. Accurate sizing is key to avoid leaks and make sure the graft lasts long.
Procedure Simulation and Measurements
Special software lets doctors simulate the EVAR procedure. This helps predict and plan for any issues. Detailed measurements help place the stent graft just right, making the procedure safer.
Team Preparation and Communication
Good communication among the medical team is essential for EVAR success. Pre-procedure planning meetings are held to go over the patient’s details, the plan, and possible problems. This makes sure everyone knows their part, leading to a smooth procedure.
Step-by-Step EVAR Procedure Technique
Understanding the EVAR procedure is key. It involves a series of steps to place a stent graft. Each step is planned carefully to ensure success.
Operating Room Setup
The operating room setup is vital for EVAR success. We make sure all needed equipment is ready. The room is set up for a smooth procedure.
Anesthesia Considerations
Anesthesia is very important in EVAR. We use local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia. This keeps the patient comfortable and stable.
Arterial Access Methods
Accessing the arteries is a key step. We choose between a percutaneous or open surgical approach. The choice depends on the patient’s anatomy and the stent graft’s needs.
Guidewire and Catheter Navigation
Guidewire and catheter navigation are critical. We use fluoroscopy to guide them to the aneurysm. This ensures the stent graft is placed correctly.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
| 1. Operating Room Setup | Configuring the OR for the procedure | Equipment availability, room configuration |
| 2. Anesthesia Considerations | Managing anesthesia for patient comfort | Type of anesthesia, patient condition |
| 3. Arterial Access Methods | Accessing femoral arteries for stent graft delivery | Access method, patient anatomy |
| 4. Guidewire and Catheter Navigation | Navigating to the aneurysm site | Fluoroscopic guidance, precise placement |
By following these steps and considering the key factors, we can ensure a successful EVAR procedure with optimal outcomes for the patient.
Intraoperative Imaging and Assessment
Intraoperative imaging is key to the success of EVAR. It gives us a live view of the aneurysm and the blood vessels around it. We use top-notch imaging to place the stent graft just right, avoiding problems.
Fluoroscopic Guidance Techniques
Fluoroscopy is vital for EVAR imaging. It lets us see the stent graft as we put it in. We use it to navigate the blood vessels and adjust as needed. Fluoroscopic imaging with IV contrast helps us see the blood vessels and place the stent accurately.
Contrast Angiography Protocols
Contrast angiography is also key for EVAR. We follow special protocols to see the aneurysm and blood vessels. This makes sure the stent graft is in the right spot. It also helps us spot any leaks or issues early.
Endoleak Detection and Classification
Finding endoleaks is a big part of EVAR imaging. We use fluoroscopy and contrast angiography to spot and classify them. Knowing about endoleaks lets us fix them right away, making the procedure safer.
Completion Angiography and Verification
At the end of EVAR, we do a final angiography. This checks if the aneurysm is closed off and there are no leaks. It confirms the stent graft is in place and there are no immediate problems. This step is vital for the procedure’s success and for future checks.
Managing Complications During EVAR
Managing complications during EVAR is key to keeping patients safe and outcomes successful. Even though EVAR is minimally invasive, problems can happen. It’s vital for vascular surgeons to be ready to handle them.
Endoleaks: Types and Management
Endoleaks are a common issue with EVAR. They happen when blood keeps flowing outside the stent graft but inside the aneurysm sac. We divide endoleaks into five types: Type I, Type II, Type III, Type IV, and Type V. Effective management means watching closely and sometimes fixing the problem to avoid rupture.
Access Site Complications
Problems at the access site, like bleeding or injury, can happen during EVAR. Careful planning and precise technique can lower these risks. If issues arise, quick action is key to avoid more harm.
Stent Graft Maldeployment
Stent graft maldeployment is a serious issue. It can mean the aneurysm isn’t fully covered or important branches are blocked. Accurate deployment needs careful planning and imaging during surgery. If it goes wrong, we might need to do more to fix it or keep the patient safe.
Conversion to Open Repair: Indications and Technique
Sometimes, we need to switch to open repair because of serious problems. This could be due to stent graft maldeployment, big endoleaks, or aneurysm rupture. Being prepared for this is important. It lets us safely move to open repair when it’s needed.
By knowing how to handle these issues, we can make EVAR better for our patients. This way, we can give them the best care possible.
Advantages and Limitations of EVAR vs. Open Repair
EVAR and open repair are two ways to treat abdominal aortic aneurysm. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks. Knowing these differences helps in making the best choice for patient care.
Perioperative Outcomes Comparison
EVAR is linked to lower risks during surgery compared to open repair. This is because EVAR is less invasive. It causes less damage to tissues and lowers the chance of complications.
| Outcome | EVAR | Open Repair |
| Mortality Rate | 1-2% | 3-5% |
| Major Complications | 5-10% | 15-20% |
| Length of Stay | 2-3 days | 7-10 days |
Recovery Time and Hospital Stay
EVAR has a shorter recovery time and hospital stay compared to open repair. EVAR patients often have less pain and can get back to normal activities faster.
Recovery Time Comparison: EVAR patients recover in 1-2 weeks. Open repair patients may take 6-12 weeks to fully recover.
Long-term Durability Considerations
EVAR has many short-term benefits but raises concerns about long-term durability. The need for ongoing monitoring and possible future surgeries are important to consider.
Long-term studies show EVAR and open repair have similar survival rates. But EVAR might need more frequent check-ups.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Deciding if EVAR is cost-effective compared to open repair is complex. Costs include procedure fees, hospital stay, and follow-up needs. EVAR might have higher upfront costs but could be more cost-effective due to shorter hospital stays and less intensive care.
In conclusion, choosing between EVAR and open repair for AAA treatment requires careful consideration. Factors like perioperative outcomes, recovery time, long-term durability, and cost-effectiveness are key. Healthcare providers can make informed decisions based on these factors to meet individual patient needs.
Conclusion: Future Directions and Outcomes of EVAR for AAA
The future of EVAR for AAA is bright, thanks to new tech and techniques. EVAR is becoming more common around the world. This is because of better stents and more skilled surgeons.
Studies show EVAR is safer and faster than old methods. We expect even better results as new tech comes along.
New stent grafts and better imaging are on the horizon. These will make EVAR even safer and more precise. We’re looking forward to better patient care as these advancements happen.
EVAR has changed how we treat aortic aneurysms, making it less invasive. We’re dedicated to making it even better. Our goal is to keep improving care for patients through innovation and expertise.
FAQ
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) and how is it treated?
An abdominal aortic aneurysm is a bulge in the aorta. It can be treated with open surgery or EVAR. EVAR is a less invasive method using a stent graft to support the aorta.
What is the EVAR procedure?
EVAR is a minimally invasive method. It involves placing a stent graft through the femoral arteries to the aneurysm. This is done under imaging guidance.
What are the benefits of EVAR compared to traditional open surgical repair?
EVAR has many benefits. It leads to quicker recovery, fewer complications, and better outcomes. It’s great for patients at high risk.
What are the different types of stent grafts used in EVAR?
EVAR uses various stent grafts. These include bifurcated, aorto-uni-iliac, and fenestrated and branched grafts. Each type fits different aortic shapes.
How is patient selection critical for the success of the EVAR procedure?
Choosing the right patient for EVAR is key. It involves checking the patient’s anatomy, risk level, and any contraindications.
What is the importance of pre-procedure planning and imaging for EVAR?
Planning and imaging are vital for EVAR. They help pick the right stent graft size and ensure a smooth procedure.
What are the possible complications during EVAR?
EVAR can face complications like endoleaks and access site issues. Stent graft maldeployment and the need for open repair are also risks.
How are endoleaks detected and managed during EVAR?
Endoleaks are spotted with imaging like contrast angiography. Their management depends on their type and severity.
What are the advantages and limitations of EVAR compared to open repair?
EVAR has quick recovery and shorter hospital stays. But, it might have durability and cost concerns.
What is the future of EVAR for AAA treatment?
EVAR’s future looks bright. Advances in technology and techniques will likely improve outcomes and expand treatment options.
What is the role of CT angiography in EVAR planning?
CT angiography is essential for EVAR planning. It gives detailed images of the aorta and its branches, aiding in stent graft selection.
How is the EVAR procedure performed?
The EVAR procedure involves guiding a stent graft through the femoral arteries to the aneurysm. It’s done under imaging guidance to support the aorta.
References
- Wanhainen, A., Verzini, F., Van Herzeele, I., Allaire, E., Bown, M., Cohnert, T., Dick, F., van Herwaarden, J., Karkos, C., Koelemay, M., Kolbel, T., Loftus, I., Mani, K., Melissano, G., Powell, J., Szeberin, Z., Esvs Guidelines Committee, Bjorck, M., & Debus, S. (2019). Editor’s Choice – European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS) 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Abdominal Aorto-iliac Artery Aneurysms. European Journal of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, *57*(1), 8-93. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7025346/



































