Last Updated on October 31, 2025 by Batuhan Temel
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a serious heart condition. It happens when blood flow to the heart suddenly drops. At Liv Hospital, we know how important ACS and chest pain are. Chest pain can be a sign of a serious heart problem.Discover acs medical term meaning, acute coronary syndrome definition, and related chest pain info.
Every second is critical when dealing with ACS. It’s key to know what ACS is, its symptoms, and to get help fast. We aim to save lives and improve heart health with our top-notch care for chest pain and coronary syndromes.

The term ACS, or Acute Coronary Syndrome, is used in medical contexts. It describes conditions where blood flow to the heart is reduced. This includes unstable angina and myocardial infarction. Knowing about ACS is key for both doctors and patients to understand how serious these heart issues are.
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is a range of heart problems caused by reduced blood flow. This can lead to heart damage or even a heart attack. The term ACS includes unstable angina and myocardial infarction (MI). These can happen with or without ST-segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG).
The Medical organization says ACS includes unstable angina and myocardial infarction. This shows why quick medical help is so important.
There are three main types of Acute Coronary Syndrome:
| Type of ACS | Description | ECG Findings |
| Unstable Angina | Reduced blood flow to the heart without evidence of myocardial necrosis | No ST-segment elevation |
| NSTEMI | Myocardial infarction without ST-segment elevation | No ST-segment elevation |
| STEMI | More severe myocardial infarction with ST-segment elevation | ST-segment elevation |
ACS is a serious condition in heart medicine. It’s a medical emergency that needs quick action. Fast diagnosis and treatment are key to reduce heart damage and improve patient results. ACS can lead to serious health problems and even death if not treated right away.
It’s important for doctors and patients to understand ACS. This helps doctors provide the right care. It also helps patients know when to seek medical help quickly.
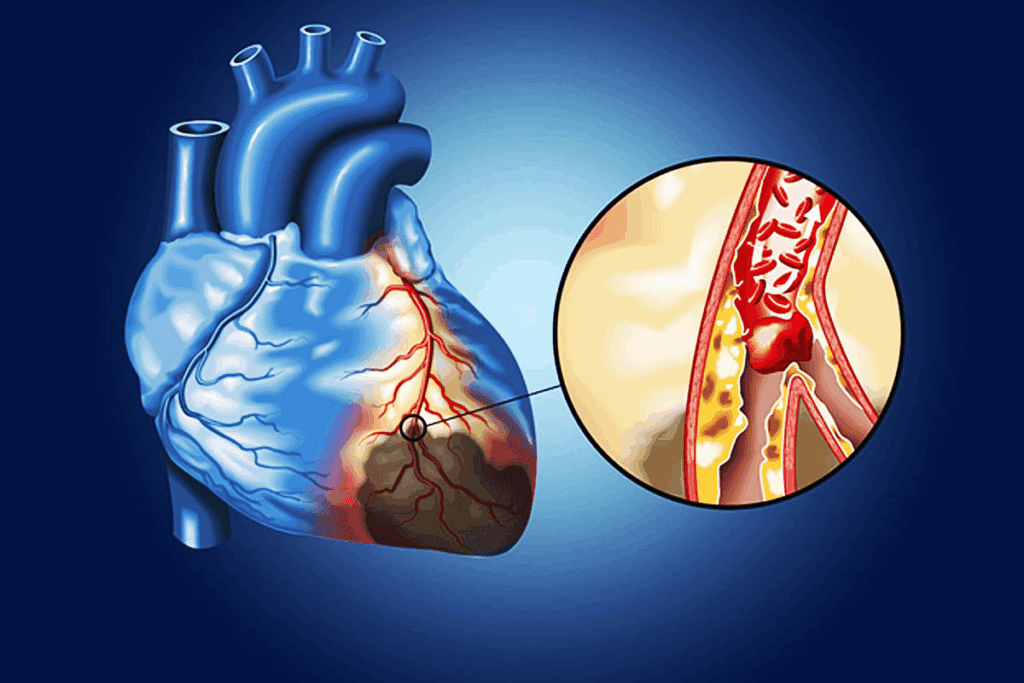
It’s important to understand ACS to see how serious it is. ACS happens when atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary arteries rupture. This leads to a series of events that can cause the heart to not get enough blood.
Atherosclerosis is a long-term inflammation in the arteries. It builds up lipids, macrophages, and smooth muscle cells. This buildup forms plaques that can break easily.
According to the Medical organization, when these plaques rupture, they cause blood clots. This is a key part of ACS. It makes the blood more likely to clot, leading to a blockage.
When a plaque ruptures, it exposes the blood to substances that make clots. This leads to a thrombus forming in the artery. The thrombus can block the artery, cutting off blood to the heart.
The clotting process is ongoing. It involves platelets sticking together and the blood’s clotting system being activated.
When the artery is blocked, the heart doesn’t get enough blood. This is called myocardial ischemia. If it lasts too long, it can cause the heart muscle to die.
“The severity and duration of ischemia determine the extent of myocardial damage.”
Knowing how ACS works helps us see why quick medical help is so important.
It’s important to know about chest pain to diagnose ACS. Chest pain or discomfort is the main reason people go to the doctor for Acute Coronary Syndrome.
The term for chest pain in medical speak is CP. Doctors and nurses use this short form to quickly talk about chest pain symptoms.
Using CP for chest pain makes it easier to write down and understand a patient’s condition. This is very helpful in emergency situations where quick action is needed.
ACS-related chest pain has certain signs that doctors look for. These include:
It’s key to tell ACS chest pain from other kinds. Other chest pain might be from muscle, stomach, or lung problems.
ACS chest pain is different because it happens with effort, has heart disease risk factors, and shows certain ECG changes or heart marker increases.
By looking at these things, doctors can figure out why someone has chest pain and start the right treatment.
ACS can show itself in many ways, not just chest pain. It’s important to know these signs to get help fast.
People with ACS might also feel:
These symptoms can happen with or without chest pain. Doctors need to think of ACS even without the usual chest pain.
Some people might show symptoms that are not typical. These can make diagnosing ACS harder. These include:
Healthcare providers need to know about these unusual symptoms to catch ACS early.
Studies show that ACS symptoms can differ by gender. Women are more likely to have:
Knowing these differences helps both patients and doctors. It ensures ACS is treated quickly, no matter the gender.
By understanding how ACS can show up, we can better diagnose and treat it. This is key to saving lives.
Knowing the risk factors for Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is key to preventing and managing it. ACS is when blood flow to the heart suddenly drops. It’s caused by many factors, some you can change and others you can’t.
Modifiable risk factors are things you can change. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes are examples. By managing these, you can lower your risk of getting ACS.
Non-modifiable risk factors are things you can’t change. These include your age, family history of heart disease, and genetics. Knowing these helps figure out your overall risk.
ACS is a big health problem worldwide. It leads to a lot of deaths every year. Cardiovascular diseases, including ACS, are a major cause of death globally.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on ACS Risk |
| High Blood Pressure | Elevated blood pressure that can damage heart vessels | Increases risk significantly |
| Smoking | Use of tobacco products that damage cardiovascular health | Significantly increases risk |
| Diabetes | Condition characterized by high blood sugar levels | Increases risk due to associated vascular damage |
| Older Age | Advancing age | Non-modifiable risk that increases with age |
Quickly finding out if someone has Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is very important. We will explain how doctors diagnose ACS and why each step is key.
When someone might have ACS, doctors start by asking about their health and doing a physical check. This helps figure out if they are at risk and if ACS is likely.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a big help in diagnosing ACS. It spots signs of heart problems, like changes in the heart’s electrical signals.
Cardiac biomarkers are proteins in the blood that show if the heart is damaged. High levels mean the heart has been hurt, which is a sign of a heart attack.
Tools like echocardiography and coronary angiography give detailed views of the heart. They show how well the heart is working and if there are blockages in the arteries.
| Diagnostic Tool | Description | Significance in ACS Diagnosis |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Records the electrical activity of the heart | Identifies patterns of ischemia or infarction |
| Cardiac Biomarkers | Measures proteins released into the blood due to cardiac damage | Indicates myocardial infarction |
| Echocardiography | Ultrasound imaging of the heart | Assesses cardiac structure and function |
In conclusion, diagnosing ACS needs a mix of talking to the patient, looking at ECGs, checking biomarkers, and using advanced imaging. Each step is important for quick and accurate diagnosis. This helps doctors treat ACS effectively.
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) includes various heart conditions, from unstable angina to myocardial infarction. Each type has its own symptoms and treatment needs. Knowing the differences helps doctors choose the right treatment and predict how well a patient will do.
Unstable angina happens when blood flow to the heart muscle drops, often because of a blocked artery. But, unlike a heart attack, the heart muscle doesn’t get damaged. It’s a serious condition because it can turn into a heart attack if not treated quickly.
NSTEMI is when a coronary artery is only partly blocked, hurting the heart muscle. The ECG doesn’t show ST-segment elevation. Doctors diagnose it by looking at heart enzyme levels and symptoms. Treatment aims to stabilize the patient and may include procedures to open the artery.
STEMI is a serious heart attack where a coronary artery is completely blocked. This causes big damage to the heart muscle. The ECG shows ST-segment elevation, meaning the patient needs quick treatment, usually through opening the artery.
The outlook for ACS patients varies by type. Knowing these differences helps doctors tailor care to each patient. Below is a table that highlights the main differences between unstable angina, NSTEMI, and STEMI.
| ACS Type | ECG Findings | Cardiac Biomarkers | Prognosis |
| Unstable Angina | No ST elevation | Normal | High risk of progression to MI |
| NSTEMI | No ST elevation | Elevated | Variable, depends on extent of damage |
| STEMI | ST elevation | Elevated | High mortality if not promptly treated |
As the table shows, each ACS type has its own traits and outcomes. Quick diagnosis and proper care are key to better results for ACS patients.
ACS needs quick action and following emergency plans. Handling Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) involves many steps. Knowing the acs medical term is key for doctors to give the right care fast.
Pre-hospital care is vital for ACS. Emergency teams quickly check patients, start treatment, and get them to a hospital fast. Important parts of this care are:
Starting treatment early helps a lot. The American Heart Association says early care in emergencies can save lives.
Drugs are a big part of treating ACS. They aim to lessen heart damage, stop clots, and ease symptoms. Common drugs include:
These drugs are very important in the early treatment of ACS. They are often started before the patient gets to the hospital.
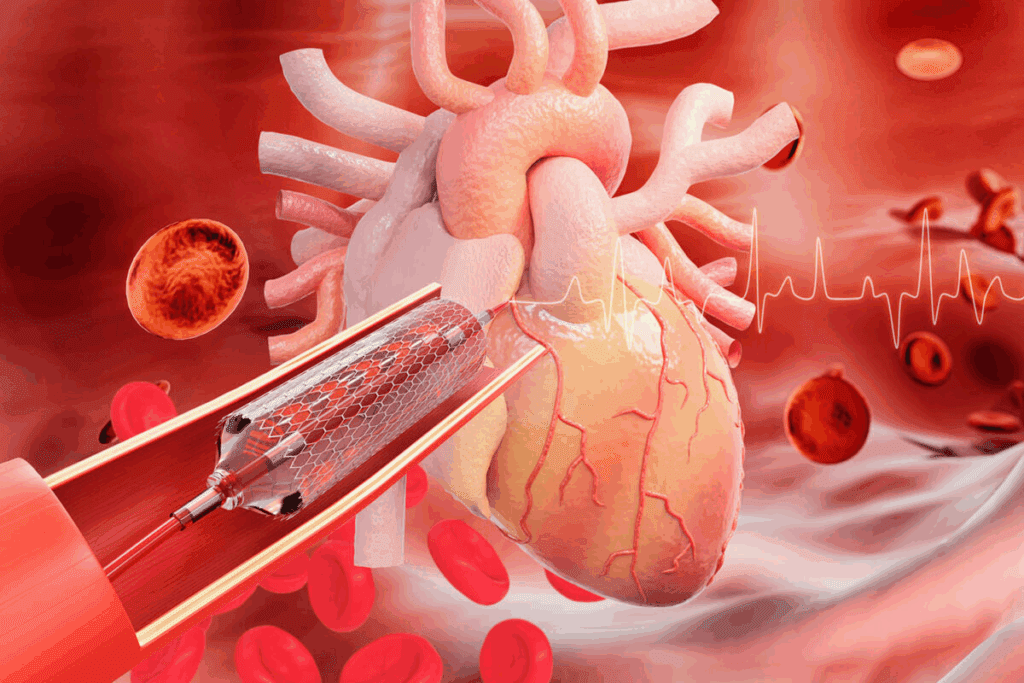
Revascularization helps get blood flowing to the heart again. The main ways to do this are:
Choosing between PCI and CABG depends on many things. These include the type of ACS, how bad the heart disease is, and the patient’s health.
In summary, treating ACS needs a quick and well-coordinated effort. By knowing the acs abbreviation medical and using the right care, doctors can greatly improve patient results.
Managing ACS long-term means using many strategies to help patients. These strategies are key to lowering the chance of more heart problems. They also improve the life quality of those who have had ACS.
Medicine is very important in managing ACS long-term. Doctors usually give patients a mix of drugs. This mix includes antiplatelet agents, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and statins.
Antiplatelet therapy stops blood clots. Beta-blockers make the heart work less. ACE inhibitors lower blood pressure and ease heart strain. Statins control cholesterol levels.
Cardiac rehab is a big part of managing ACS. These programs help patients get better after heart events. They focus on exercise, education, and lifestyle changes.
Being in cardiac rehab can make patients stronger and feel better. It’s led by health experts and meets each patient’s needs.
Changing your lifestyle is key in managing ACS long-term. Patients are advised to eat well, exercise, quit smoking, and manage stress.
Eating a heart-healthy diet means lots of fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean meats. Regular physical activity boosts heart health. Quitting smoking lowers heart risks. Stress management helps with emotional health.
Regular check-ups are vital for ACS patients. They help track progress and adjust treatment plans. This includes visits to doctors, watching heart risk factors, and changing medicines.
Close monitoring helps catch problems early. This way, doctors can act fast to prevent bigger issues. This approach helps patients live healthier, active lives.
Research is changing how we deal with ACS, from finding it to treating it. The medical world is working hard to get better at handling Acute Coronary Syndrome. This has led to big steps forward in the last few years.
Scientists keep finding new signs that help spot ACS early. These signs include:
These new signs make diagnosing ACS faster and more accurate. This means doctors can start the right treatment sooner.
New ways to treat ACS are being developed. Some of these include:
These new methods aim to cut down on heart problems and deaths from ACS.
Personalized medicine is key in treating ACS. It means treatments are made just for each person. This is based on their genes, health history, and other details. Important parts of personalized medicine for ACS are:
This way, care for ACS patients can be more precise and effective.
In summary, ACS research and treatment are getting better. Thanks to new biomarkers, treatments, and personalized care, we can help patients more. This means better health outcomes and less ACS problems.
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) is a serious medical issue that needs quick action. Knowing the acs medical term and its effects is key for doctors and patients. The acs medical meaning includes heart conditions that cause sudden blood flow loss.
Spotting symptoms early and knowing what is acs medical term can help patients a lot. ACS shows as chest pain and other signs, needing fast diagnosis and treatment. Treatment includes medicines, procedures, and changes in lifestyle.
This article shows how important ACS is and the need for full care. Quick action and understanding of ACS can improve patient care. ACS is a medical emergency that needs fast and right treatment to avoid serious harm.
ACS stands for Acute Coronary Syndrome. It’s a serious medical emergency. It happens when the blood flow to the heart is suddenly blocked.
ACS is very important in heart health. It needs quick attention and treatment. This is to prevent serious heart damage or death.
There are a few types of ACS. These include Unstable Angina, Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI), and ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI).
The chest pain medical abbreviation is CP. It’s often linked to ACS.
ACS-related chest pain feels like pressure, tightness, or heaviness. It might spread to the arms, back, or jaw.
Several factors increase the risk of ACS. These include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, and diabetes. Age, family history, and gender also play a role.
Doctors use several methods to diagnose ACS. These include an initial assessment, electrocardiogram (ECG) findings, and cardiac biomarkers. They also use laboratory tests and advanced imaging techniques.
NSTEMI and STEMI are both heart attacks. But, STEMI shows a more severe blockage. This is because of the ECG pattern and the extent of heart muscle damage.
ACS treatment includes pre-hospital care and medicines. It also includes procedures like angioplasty and stenting to open blocked arteries.
After ACS, long-term care is key. It includes medicines, cardiac rehab, lifestyle changes, and follow-up care. These steps help prevent future heart problems.
New research and treatments for ACS are emerging. These include novel biomarkers, new therapies, and personalized medicine in managing ACS.
The outcome for ACS patients varies. It depends on the type and severity of the condition. It also depends on how quickly and effectively treatment is given.
ACS stands for Acute Coronary Syndrome. It’s a serious heart condition.
Coronary syndrome refers to sudden, reduced blood flow to the heart. ACS is a specific term for acute presentations.
ACS is a big health issue worldwide. Its prevalence and death rates vary by region and population.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us