Did you know that nearly one in four people worldwide suffer from iron deficiency, a condition that can lead to anemia? Anemia happens when the body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. These cells are needed to carry enough oxygen to the body’s tissues.
We often miss the subtle signs our bodies send us, and anemia is one of them. It’s a condition where the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells. This can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Knowing the symptoms of low iron is key for early detection and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Anemia is a common health issue affecting millions worldwide.
- Iron deficiency is a leading cause of anemia.
- Early detection of anemia symptoms is crucial for effective treatment.
- Proper diagnosis involves understanding the underlying causes of anemia.
- Timely treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with anemia.
What You Need to Know About Anemia
To fight anemia, it’s key to understand what it is and how it shows up. Anemia happens when the body doesn’t have enough healthy red blood cells. These cells are vital for carrying oxygen to our body’s tissues.
Definition and Basic Mechanism
Anemia isn’t a disease itself but a sign of something else going on. It happens when the body lacks red blood cells or when these cells don’t have enough hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is crucial for carrying oxygen around the body.
Common Types of Anemia
There are many types of anemia, each with its own cause. The most common is Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA). This occurs when the body lacks iron, needed to make hemoglobin. Other types include vitamin deficiency anemia, anemia of chronic disease, and anemia from bone marrow issues.
|
Type of Anemia |
Cause |
Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
|
Iron Deficiency Anemia |
Lack of iron |
Low hemoglobin production |
|
Vitamin Deficiency Anemia |
Lack of vitamins like B12 and folate |
Impaired red blood cell production |
|
Anemia of Chronic Disease |
Chronic diseases like cancer, HIV/AIDS |
Inflammation affecting iron availability |
Knowing about these types and their causes is vital for proper diagnosis and treatment. By identifying the specific anemia type, doctors can create targeted treatments.
The 5 Primary Anemia Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

Anemia symptoms can be subtle, but there are key indicators to watch out for. We will explore the primary signs that may signal the presence of anemia. This will help you understand when to seek medical attention.
Extreme Fatigue and Weakness
One of the most common symptoms of anemia is extreme fatigue and weakness. This happens because the body’s tissues don’t get enough oxygen. Oxygen is key for energy production. So, people with anemia might feel tired or weak, even after resting or doing light activities.
Pale Skin and Mucous Membranes
Another indicator of anemia is pale skin and mucous membranes. This pallor comes from fewer red blood cells or less hemoglobin. It makes the skin lose its normal rosy color. Checking the inside of the lower eyelids or the nail beds can show clearer signs of pallor.
Shortness of Breath and Dizziness
Anemia can cause shortness of breath and dizziness. The body tries to make up for the lack of oxygen by breathing more or beating the heart faster. This leads to these symptoms.
Irregular Heartbeat (Palpitations)
Some people with anemia may have an irregular heartbeat or palpitations. This happens because the heart works harder to make up for the lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin. It might lead to an irregular heartbeat or the feeling of skipped beats.
Knowing these primary symptoms can help spot anemia early. If you’re experiencing several of these symptoms at once, it’s important to see a healthcare professional. They can give you a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Additional Anemia Symptoms to Be Aware Of
Anemia has symptoms beyond the usual ones. Knowing these signs is key to getting help early. Anemia can change how the body works, affecting daily life.
Headaches and Difficulty Concentrating
Headaches and trouble focusing are signs of anemia. Not enough oxygen in the brain causes these issues. Headaches can be mild or severe and may make you feel dizzy or lightheaded.
Brittle Nails and Hair Loss
Iron deficiency anemia can make nails and hair weak. Iron helps make hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to cells. This leads to brittle nails and hair loss.
Unusual Cravings (Pica)
Some people with anemia crave non-food items like dirt or clay. Pica is often linked to iron deficiency. Fixing the nutritional issue can stop these cravings.
“Pica is a complex condition that can be linked to various nutritional deficiencies, including iron deficiency anemia.”
– Medical Expert
Restless Legs Syndrome
Restless legs syndrome makes you want to move your legs a lot. Iron deficiency might cause RLS. Treating anemia can ease RLS symptoms, making life better.
Knowing these symptoms helps you get medical help sooner. Early treatment can greatly improve anemia outcomes.
How Iron Deficiency Leads to Anemia
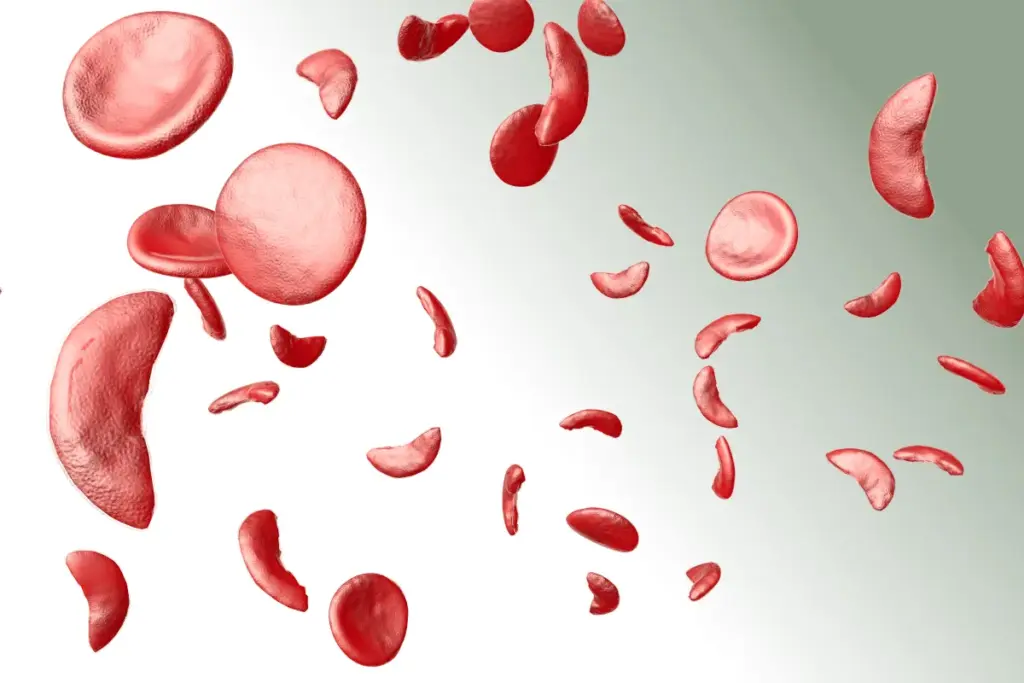
Iron deficiency and anemia are closely linked. Iron is key for making blood. It helps in producing hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
The Essential Role of Iron in Blood Production
Iron is crucial for making heme, a part of hemoglobin. Without enough iron, the body can’t make enough healthy red blood cells. This leads to anemia.
How Iron Levels Affect Oxygen Transport
Oxygen transport is vital for body tissues to work right. Iron deficiency can lower hemoglobin levels. This means less oxygen gets to tissues and organs.
Common Causes of Iron Deficiency
Several things can cause iron deficiency. These include not eating enough iron-rich foods, losing blood too much, and needing more iron. Let’s look at these reasons in more detail.
|
Cause |
Description |
Examples |
|---|---|---|
|
Inadequate Dietary Intake |
Not eating enough iron-rich foods |
Vegetarians, vegans, and those with strict diets |
|
Chronic Blood Loss |
Continuous blood loss depletes iron |
Menstrual bleeding, ulcers, and cancer |
|
Increased Iron Requirements |
More iron needed due to certain conditions |
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fast growth in kids |
Knowing these causes helps prevent and treat iron deficiency anemia. If you think you have iron deficiency or anemia, see a healthcare provider.
Beyond Iron: Other Common Causes of Anemia
Iron deficiency is a known cause of anemia, but other factors also matter. Knowing these can help diagnose and treat anemia better.
Vitamin Deficiencies (B12 and Folate)
Vitamins B12 and folate are key for making red blood cells. Not having enough of these vitamins can cause anemia. Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to pernicious anemia, where the body can’t absorb enough B12. Folate deficiency might happen from a bad diet, pregnancy, or some medicines.
Signs of vitamin deficiency anemia include feeling tired, weak, and having neurological problems. Doctors use blood tests to check B12 and folate levels.
|
Vitamin |
Role in Red Blood Cell Production |
Consequences of Deficiency |
|---|---|---|
|
Vitamin B12 |
Essential for DNA synthesis |
Pernicious anemia, neurological issues |
|
Folate |
Critical for DNA synthesis and repair |
Folate deficiency anemia, fatigue, weakness |
Chronic Diseases and Inflammation
Chronic diseases like kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer can cause anemia. These diseases often cause long-term inflammation. This can stop the body from making enough red blood cells.
“Chronic inflammation can lead to anemia of chronic disease, a condition characterized by impaired iron utilization and reduced red blood cell production.” – Medical Expert
Genetic and Inherited Factors
Genetics can also cause anemia. Inherited disorders like sickle cell anemia and thalassemia affect hemoglobin and red blood cells.
- Sickle cell anemia: A condition where red blood cells are misshapen, leading to anemia and other complications.
- Thalassemia: A genetic disorder affecting hemoglobin production, resulting in anemia.
Knowing the genetic causes helps in diagnosing and managing these conditions.
Diagnosing Anemia: Tests and Procedures
Doctors use a mix of medical history, physical checks, and lab tests to find anemia. Understanding the cause is key for good treatment. Lab tests are very important in this process.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
A CBC is often the first test for anemia. It checks the blood’s parts, like red blood cells, hemoglobin, and hematocrit. These help figure out if you have anemia and what kind.
Ferritin Level Testing
Ferritin tests show iron levels in the body. Low levels mean you might lack iron, a common anemia cause. This test is key for iron deficiency anemia.
Vitamin B12 and Folate Tests
Vitamin B12 and folate tests are vital for megaloblastic anemia. This anemia is from a lack of these vitamins. These tests find nutritional gaps.
Additional Diagnostic Procedures
More tests might include reticulocyte count, bone marrow biopsy, and genetic tests. These depend on what’s thought to cause anemia. They give more details about the condition.
|
Diagnostic Test |
Purpose |
|---|---|
|
Complete Blood Count (CBC) |
Measures red blood cell count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit to diagnose anemia. |
|
Ferritin Level Testing |
Assesses the body’s iron stores to diagnose iron deficiency anemia. |
|
Vitamin B12 and Folate Tests |
Diagnoses megaloblastic anemia caused by vitamin deficiency. |
“Diagnosing anemia typically involves a complete blood count (CBC) and other tests to determine the underlying cause.”
British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines
When to See a Doctor About Anemia Symptoms
It’s important to know when to see a doctor if you have anemia. Symptoms can be mild or severe and affect your daily life. If you feel very tired, have trouble breathing, or get dizzy, you should know when to get help.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
Some symptoms need urgent medical care. These include:
- Chest pain or angina
- Severe shortness of breath
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
If you have these symptoms, get medical help right away. Waiting too long can cause serious problems.
Discussing Symptoms With Your Healthcare Provider
Talking to your doctor about your symptoms is key. Tell them everything about your symptoms, like when they started and how they’ve changed. This helps your doctor figure out what’s wrong and how to treat it.
|
Symptom |
Description |
Action |
|---|---|---|
|
Extreme Fatigue |
Persistent feeling of tiredness |
Discuss duration and impact on daily activities |
|
Pale Skin |
Noticeable paleness |
Mention any changes in skin tone |
|
Shortness of Breath |
Difficulty breathing during normal activities |
Report any instances of shortness of breath |
Knowing the warning signs and talking to your doctor can help you get the right treatment for anemia.
Treatment Options for Different Types of Anemia
Getting the right treatment for anemia starts with finding out why it’s happening. We’ll look at how to treat different types of anemia. This way, we can tackle the root cause effectively.
Iron Supplements: Types and Considerations
For iron deficiency anemia, iron supplements are usually the first step. It’s important to talk to a doctor to find the right supplement and dosage. There are many iron supplements out there, like ferrous sulfate and ferrous gluconate. Each has its own absorption rate and side effects.
Types of Iron Supplements:
|
Type |
Absorption Rate |
Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
|
Ferrous Sulfate |
High |
Gastrointestinal upset, constipation |
|
Ferrous Gluconate |
Moderate |
Less gastrointestinal upset compared to ferrous sulfate |
|
Iron Citrate |
Moderate to High |
Gastrointestinal upset, but generally well-tolerated |
Vitamin Supplements for B12 and Folate Deficiency
For anemia caused by B12 or folate deficiency, supplements are key. It’s important to work with a doctor to keep an eye on vitamin levels. For severe cases, B12 injections might be needed.
Dietary Changes to Improve Blood Health
Changing your diet can help manage anemia. Eating more iron-rich foods like red meat and beans is a good start. Adding vitamin C foods like citrus fruits can also help iron absorption.
Medical Treatments for Severe Cases
For severe anemia, more than just supplements and diet changes might be needed. We talk about options like blood transfusions or ESAs with patients. These can help make more red blood cells or improve oxygen delivery.
Understanding the different treatment options helps people with anemia work with their doctors. Together, they can create a treatment plan that meets the individual’s needs and improves their health.
Iron-Rich Foods to Combat Anemia
Eating foods high in iron is key to fighting anemia. A balanced diet can ease symptoms and boost health. Let’s look at the iron-rich foods that can help.
Animal-Based Iron Sources (Heme Iron)
Animal products are packed with heme iron, which the body absorbs better than non-heme iron. Top sources include:
- Red meat, such as beef and lamb
- Poultry, like chicken and turkey
- Fish and seafood, including shrimp, clams, and oysters
These foods are not just iron-rich. They also offer protein and vitamins. Eating them can keep iron levels healthy.
Plant-Based Iron Sources (Non-Heme Iron)
For those on a plant-based diet, there are many non-heme iron options. Some examples are:
- Legumes, such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale
- Nuts and seeds, including pumpkin seeds and sesame seeds
- Fortified cereals and bread
Non-heme iron isn’t absorbed as well as heme iron. But, eating foods high in vitamin C can help. Vitamin C is found in citrus fruits, bell peppers, and tomatoes.
Foods That Enhance and Inhibit Iron Absorption
Knowing which foods boost or block iron absorption is important. Vitamin C-rich foods, like citrus fruits, help with non-heme iron. But, some foods and drinks can block iron absorption, such as:
- Tea and coffee, due to their polyphenol content
- Calcium-rich foods, which can interfere with non-heme iron absorption
- Foods high in phytates, such as whole grains and legumes, although they can be soaked or fermented to reduce phytate levels
Being aware of these can help make better food choices to fight anemia.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Groups
Some groups are more likely to get anemia because of their health or age. It’s important to know these risks to help prevent and manage anemia. We’ll look at the special challenges for women, children, teens, and older adults with chronic diseases.
Women During Menstruation, Pregnancy, and Postpartum
Women are more at risk for anemia because of menstrual blood loss, pregnancy, and childbirth. Menstrual blood loss can cause iron deficiency if not balanced with iron from food or supplements. During pregnancy, iron needs increase to support the mother and the baby. After childbirth, women may also get anemia from blood loss.
Pregnant women are often advised to take iron supplements. It’s important to check iron levels and overall health during these times to prevent and manage anemia.
Children and Adolescents in Growth Phases
Children and teens are at high risk because of their fast growth and development. Adequate iron intake is crucial for making healthy red blood cells and growth. If they don’t get enough iron, they might get anemia.
Parents and caregivers should watch for signs of anemia in kids, like tiredness, pale skin, and loss of appetite. They should make sure kids eat a balanced diet with plenty of iron.
Older Adults and Chronic Disease Patients
Older adults, especially those with chronic diseases, are more likely to get anemia. Diseases like kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer can cause anemia by affecting iron use.
Managing chronic diseases is key to lowering anemia risk in older adults. It’s important to watch for anemia signs, manage chronic conditions well, and make sure they eat enough.
In summary, knowing and understanding the needs of high-risk groups is vital for preventing and managing anemia. By focusing on the special challenges these groups face, we can offer better health care to improve their outcomes.
Preventing Anemia: Proactive Strategies
To prevent anemia, you need to make changes in your diet, lifestyle, and sometimes take supplements. Knowing and using these strategies can lower your risk of getting anemia.
Dietary Approaches for Optimal Blood Health
Eating a balanced diet is key for healthy blood cells. Iron, vitamin B12, and folate are vital for avoiding anemia.
- Add iron-rich foods like red meat, poultry, fish, beans, and fortified cereals to your meals.
- Include vitamin B12 sources like meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy in your diet.
- Make sure to eat foods high in folate, such as leafy greens, beans, peas, and citrus fruits.
|
Nutrient |
Food Sources |
Role in Preventing Anemia |
|---|---|---|
|
Iron |
Red meat, poultry, fish, beans, fortified cereals |
Essential for hemoglobin production |
|
Vitamin B12 |
Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dairy products |
Crucial for red blood cell formation |
|
Folate |
Leafy greens, beans, peas, citrus fruits |
Necessary for DNA synthesis and red blood cell production |
Lifestyle Modifications and Supplements
Changing your lifestyle can also help prevent anemia. Try to drink less alcohol and manage any chronic diseases. Sometimes, you might need supplements to get enough nutrients.
Talk to a healthcare provider to figure out the best plan for preventing anemia.
Long-term Effects of Untreated Anemia
Anemia can have serious effects if not treated. It affects how the body carries oxygen and impacts many parts of the body. This can greatly affect one’s quality of life.
Impact on Physical Health and Organ Systems
Untreated anemia can harm physical health, especially the heart. Increased strain on the heart can lead to heart failure. The heart works harder because of the lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin.
Other physical health issues include:
- Poor immune function, making individuals more susceptible to infections
- Reduced physical performance and endurance
- Increased risk of falls and fractures due to dizziness and weakness
|
Organ System |
Potential Complications |
|---|---|
|
Cardiovascular |
Heart failure, increased risk of cardiovascular disease |
|
Immune System |
Poor immune function, increased susceptibility to infections |
|
Musculoskeletal |
Reduced physical performance, increased risk of falls and fractures |
Medical experts say untreated anemia can cause many health problems. It affects many organ systems. This shows why early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. This highlights the need for awareness and proactive management of anemia.
Effects on Mental Health, Cognition, and Quality of Life
Anemia also affects mental health, thinking, and quality of life. Chronic fatigue and decreased oxygen delivery to the brain can cause problems with focus, memory, and mood.
“The relationship between anemia and cognitive function is complex, with evidence suggesting that iron deficiency anemia can affect cognitive development in children and cognitive performance in adults.”
The mental and cognitive effects can include:
- Increased risk of depression and anxiety
- Difficulty concentrating and memory issues
- Reduced productivity and overall quality of life
We know untreated anemia can deeply affect a person’s life. It’s important to seek medical help if symptoms last. Understanding these effects helps us see why early diagnosis and treatment are key.
Conclusion
Anemia is a common condition that affects millions worldwide. It is caused by various factors like iron deficiency, vitamin deficiencies, and chronic diseases. We have looked at the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for anemia in this article.
Iron deficiency is a major cause of anemia. Knowing about iron deficiency is key to preventing and treating it. By making dietary changes and using iron supplements if needed, people can manage iron deficiency anemia well.
Effective treatment for anemia includes medical treatments, dietary changes, and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding the causes of anemia and taking proactive steps can help reduce its risk. This can also improve overall health.
We stress that anemia is a treatable condition. It needs proper diagnosis and treatment, as the British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines suggest. By managing anemia comprehensively, individuals can achieve better health outcomes.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of anemia?
Symptoms of anemia include extreme fatigue and weakness. You might also notice pale skin and shortness of breath. Dizziness and irregular heartbeat are common too.Other signs include headaches, trouble concentrating, and brittle nails. Hair loss and unusual cravings are also symptoms.
What is iron deficiency anemia?
Iron deficiency anemia happens when your body lacks enough iron. This is needed to make hemoglobin. Hemoglobin carries oxygen to your body’s cells.
How is anemia diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to diagnose anemia. They look at your medical history and do a physical exam. They also run tests like a complete blood count (CBC).Other tests include checking ferritin levels and testing for vitamin B12 and folate.
What are the treatment options for anemia?
Treatment for anemia depends on the cause. It might include iron or vitamin supplements. Changing your diet can also help.In some cases, you might need blood transfusions or special medicines.
How can I prevent anemia?
To prevent anemia, eat a balanced diet. Make sure it has iron, vitamin B12, and folate. Avoid too much alcohol.Also, manage any chronic diseases you have.
What are the long-term effects of untreated anemia?
Untreated anemia can cause serious problems. It can lead to heart disease and mental health issues. It can also affect your brain and lower your quality of life.
Who is at risk of developing anemia?
Some groups are more likely to get anemia. Women during menstruation, pregnancy, and after giving birth are at risk. So are children and teens going through growth spurts.Older adults with chronic diseases are also at risk.
What foods are rich in iron?
Foods high in iron include red meat, poultry, and fish. Beans, lentils, and fortified cereals are good too. Eating foods high in vitamin C can help your body absorb iron better.
Can anemia be caused by factors other than iron deficiency?
Yes, anemia can be caused by other things. Vitamin deficiencies, chronic diseases, and genetic factors can all play a role. Bone marrow disorders can also cause anemia.
How can I manage anemia through dietary changes?
To manage anemia through diet, eat foods rich in iron, vitamin B12, and folate. Avoid foods that can block iron absorption.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from