At Liv Hospital, we use minimally invasive therapies to treat cerebral aneurysms and vascular disorders. Aneurysm embolization is a procedure where a catheter is guided into a cerebral aneurysm. Then, coils or other agents are deployed to block blood flow, preventing rupture.
By blocking the flow of blood into the aneurysm, we prevent it from bleeding. This reduces the risk of rupture. This innovative treatment is key for patients with cerebral aneurysms. It offers a less invasive option compared to traditional surgery.
Key Takeaways
- Aneurysm embolization is a minimally invasive procedure to treat cerebral aneurysms.
- The procedure involves guiding a catheter into the aneurysm and deploying coils or other agents.
- Embolization blocks blood flow into the aneurysm, preventing rupture.
- This treatment is a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery.
- Liv Hospital delivers advanced embolization techniques with precision and safety.
Understanding Cerebral Aneurysms and Their Risks
It’s important to know about cerebral aneurysms to understand the risks they pose. A cerebral aneurysm is a weak spot in a brain artery that can bulge or rupture. This can lead to serious problems.
Definition of a Cerebral Aneurysm
A cerebral aneurysm, or brain aneurysm, is a bulge in a brain blood vessel. It happens when the vessel wall weakens. If it ruptures, it can cause bleeding in the brain.
Risk Factors for Aneurysm Rupture
Several factors can make an aneurysm more likely to rupture. These include:
- High Blood Pressure: High blood pressure can stress the aneurysm wall, making rupture more likely.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and raises blood pressure, increasing rupture risk.
- Family History: If your family has a history of cerebral aneurysms, you’re at higher risk.
- Size and Location: Larger aneurysms and those in certain brain areas are more prone to rupture.
Signs and Symptoms of Brain Aneurysms
Brain aneurysms often don’t show symptoms until they rupture. But, some people may notice:
- Severe Headaches: Often described as the worst headache of their life.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These can happen due to increased pressure in the brain.
- Neurological Deficits: Symptoms can include vision changes, trouble speaking, or weakness on one side of the body.
Spotting these signs early is key for getting medical help quickly. We’ll look at treatment options for cerebral aneurysms next.
Aneurysm Embolization: Definition and Purpose
Aneurysm embolization blocks blood flow into an aneurysm to stop it from bursting. This method is a safer choice than open surgery for treating brain aneurysms.
The Science Behind Embolization
Embolization stops blood flow into the aneurysm sac. This prevents it from growing or bursting. It uses materials like coils or liquid agents under guidance.
This method is based on understanding aneurysm growth and blood flow. By stopping blood flow, we lower pressure on the aneurysm wall, preventing it from bursting.
History and Development of the Procedure
Embolization has come a long way. Detachable coils in the 1990s were a big step forward. New materials and devices have made the procedure safer and more effective.
These improvements mean more people can benefit from embolization. Ongoing research keeps making the procedure better.
When Embolization Is Recommended
Doctors recommend embolization for high-risk aneurysms and those that have already ruptured. The choice depends on the aneurysm’s size, location, and the patient’s health.
- Unruptured Aneurysms: Embolization is suggested for unruptured aneurysms at high risk of rupture.
- Ruptured Aneurysms: For ruptured aneurysms, embolization is often an emergency to stop bleeding.
Understanding embolization helps us see its importance in treating cerebral aneurysms. It improves patient outcomes significantly.
Differentiating Between Aneurysms and Embolisms
It’s important to know the difference between aneurysms and embolisms. Both are vascular conditions but they are not the same. Knowing the difference helps in choosing the right treatment.
Defining an Aneurysm
An aneurysm is a bulge in an artery’s wall. This happens when the artery wall gets damaged. It can balloon outward.
Aneurysms can be dangerous because they can burst. This can cause severe bleeding. Causes include genetics, high blood pressure, and atherosclerosis. Symptoms include pain and pressure in the affected area.
Understanding an Embolism
An embolism happens when a blood clot or particle blocks a vessel. This can damage tissue or organs. Symptoms depend on where it happens and can include sudden pain or numbness.
Embolisms can come from different sources like blood clots, fat globules, or air bubbles. The symptoms vary based on the location.
Key Differences and Relationships
The main difference is in how they affect blood vessels. Aneurysms are about a weak vessel wall that can burst. Embolisms are about a blockage by a clot or particle.
- Causes: Aneurysms are often due to vessel wall damage or disease. Embolisms are caused by a clot or particle moving.
- Symptoms: Symptoms depend on the location and type. They usually include pain, pressure, or dysfunction.
- Treatment: Treatment varies. Aneurysms might need embolization to prevent rupture. Embolisms require immediate removal of the blockage.
It’s key for patients to understand their diagnosis and treatment. Healthcare providers must accurately diagnose to give the right care.
Types of Brain Embolization Procedures
There are several brain embolization methods, each with its own benefits. We’ll look at these techniques and how they meet different patient needs and vascular conditions.
Coil Embolization for Aneurysms
Coil embolization is a common method for treating cerebral aneurysms. It uses coils to block blood flow in the aneurysm, preventing rupture. This is done through a catheter that guides through blood vessels to the aneurysm.
Key Benefits: This method is less invasive than open surgery. It reduces recovery time and lowers the risk of complications.
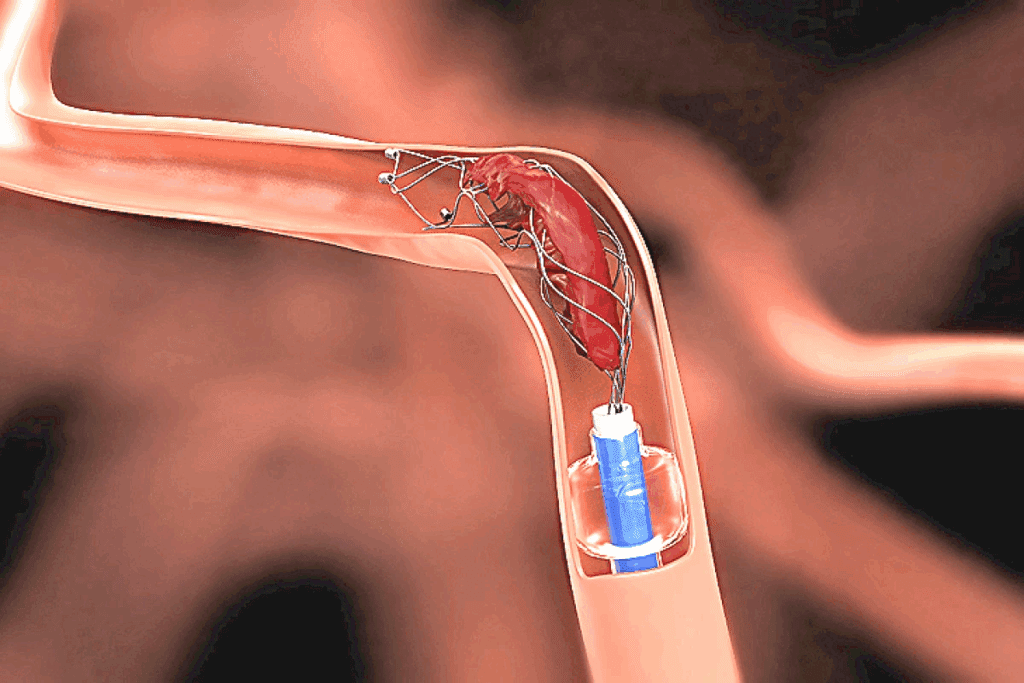
Stent-Assisted Coiling
Stent-assisted coiling is for complex or wide-necked aneurysms. A stent is placed across the aneurysm’s neck to hold the coils in place. This ensures the coils don’t move into the parent artery, improving stability and outcomes.
“Stent-assisted coiling has revolutionized the treatment of complex aneurysms, making it safer and more effective.” Flow Diversion Devices
Flow diversion devices treat aneurysms by redirecting blood flow. They promote clotting in the aneurysm, aiding in healing. They’re great for large or complex aneurysms that are hard to treat with traditional coiling.
| Procedure | Description | Benefits |
| Coil Embolization | Deploying coils into the aneurysm to block blood flow | Minimally invasive, reduces recovery time |
| Stent-Assisted Coiling | Using a stent to support coils in complex aneurysms | Enhances coil stability, improves outcomes |
| Flow Diversion Devices | Redirecting blood flow away from the aneurysm | Promotes clotting, useful for large or complex aneurysms |
Liquid Embolic Agents
Liquid embolic agents block blood vessels or malformations with a solidifying liquid. They’re great for treating arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) and other vascular issues.
Advantages: These agents can be precisely delivered. This gives a high level of control over the embolization process.
How Brain Embolization Is Performed: Step-by-Step
Brain embolization is a detailed procedure that needs careful planning and execution. We know patients and their families want to know more about it.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before starting, we do a lot of preparation. We look at the patient’s medical history and current health. We also study imaging like angiograms and MRI scans to plan the best approach.
Patients must stop certain medicines that could affect the procedure or increase bleeding risks.
Anesthesia and Vascular Access
On the day of the procedure, patients get anesthesia to stay comfortable. General anesthesia is used to keep the patient calm and steady. A small incision in the groin allows us to insert a catheter into the femoral artery.
This catheter is how we deliver embolic materials to the treatment site.
Catheter Navigation to the Treatment Site
We use advanced imaging like fluoroscopy to guide the catheter to the brain. This step needs a lot of precision. The catheter must reach the aneurysm or AVM without harming nearby tissues.
Our neurointerventionalists are experts at navigating the catheter to the right spot.
Deployment of Embolic Materials
With the catheter in place, we release embolic materials like coils or liquids into the aneurysm or AVM. The type of material used depends on the lesion and the patient’s health. Our goal is to block the aneurysm or AVM to prevent bleeding.
We watch the patient closely and adjust as needed to get the best results.
Understanding brain embolization helps patients see the skill and care involved. Our team is dedicated to providing top-notch care for each patient.
Embolization for Different Vascular Conditions
Embolization is used for many vascular conditions. It works differently for each condition. Our team is skilled in using these techniques to get the best results.
Cerebral Aneurysm Embolization Techniques
Embolization is a top choice for treating aneurysms that could burst. We use coil embolization and stent-assisted coiling. These methods block the aneurysm to stop bleeding.
Coil embolization fills the aneurysm with coils to stop blood flow. For wider-necked aneurysms, we use stent-assisted coiling. This method places a stent to hold the coils in place.
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) Embolization
AVMs are abnormal connections between arteries and veins. They can cause seizures, headaches, and bleeding. Embolization is a key treatment to block these abnormal vessels.
We use liquid embolic agents like Onyx or n-BCA for AVMs. These agents are pushed through microcatheters to the AVM’s center. They solidify and block the abnormal vessels.
| Vascular Condition | Embolization Technique | Embolic Material |
| Cerebral Aneurysm | Coil Embolization | Coils |
| Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) | Liquid Embolization | Onyx or n-BCA |
| Arteriovenous Fistula | Coil or Liquid Embolization | Coils or Onyx |
Other Vascular Abnormalities Treated with Endovascular Embolization
Embolization is also used for other vascular issues. This includes arteriovenous fistulas, tumors, and vascular malformations.
It can help reduce blood flow to tumors, making them easier to remove or treat with radiation. It’s also used to treat vascular malformations and arteriovenous fistulas.
“Embolization has revolutionized the treatment of vascular conditions, making it a minimally invasive and highly effective option.”
Understanding the many conditions treated with embolization shows its versatility and effectiveness. This approach is a big step forward in treating vascular issues.
Recovery and Post-Procedure Care
Knowing what to expect after an aneurysm embolization is key. We help our patients through every step for a smooth recovery.
Immediate Post-Procedure Monitoring
Patients are watched closely in a recovery area for hours after the procedure. We look for any immediate problems and manage pain. This early watch is important for catching issues fast.
Hospital Stay Duration
The time in the hospital varies based on the patient’s health and the procedure’s complexity. Most stay overnight for observation. Sometimes, the procedure is done on an outpatient basis, and patients go home the same day. We talk about the expected stay with each patient based on their needs.
Activity Restrictions and Return to Normal Life
We advise patients on what activities to avoid for a few weeks. This includes heavy lifting, bending, and strenuous activities. Most can get back to normal in a few days to a week. We give personalized advice based on the patient’s situation and procedure details.
Follow-up Imaging and Appointments
Follow-up care is vital for recovery. We schedule imaging appointments to check the treated aneurysm. These visits help us see if the embolization worked and address any concerns. We adjust the follow-up schedule for each patient’s needs.
By following our care instructions and attending follow-up appointments, patients can recover well and avoid complications. We’re dedicated to supporting our patients, giving them the care and guidance for the best outcomes.
Comparing Embolization to Traditional Brain Surgery
When treating cerebral aneurysms, we have two main options: embolization and traditional brain surgery. Embolization is a minimally invasive method. It offers many benefits over traditional surgery.
Minimally Invasive vs. Open Surgical Approaches
Embolization uses small incisions in the groin. A catheter is guided to the aneurysm. This method causes less tissue trauma and lowers the risk of infection. Open surgery, with a larger skull incision, is more invasive.
Traditional brain surgery has a bigger incision and more tissue disruption. It can lead to longer recovery times and more complications.
Recovery Time and Hospital Stay Differences
Embolization offers a shorter recovery time. Patients feel less pain and can get back to normal activities faster. This is unlike traditional brain surgery.
Embolization also means a shorter hospital stay. Many patients are discharged within a day or two. Traditional brain surgery requires a longer stay due to its invasive nature.
Success Rates and Long-term Outcomes
Embolization and traditional brain surgery both have success rates. Embolization works well for certain aneurysms, with lasting results. The procedure’s success depends on the aneurysm’s size and location.
Traditional brain surgery, though more invasive, has a proven track record. The choice between the two depends on the aneurysm’s specifics and the patient’s health.
Risk Profiles of Each Approach
Each method has its risks. Embolization risks include stroke or aneurysm rupture. Traditional brain surgery risks include infection and brain damage.
It’s important to understand these risks when choosing between embolization and traditional surgery. We help patients decide based on their needs and condition.
Conclusion: Advances and Future Directions in Brain Embolization
The field of brain embolization is growing fast. This is thanks to new technology and techniques. We’ve seen big improvements in how safe and effective these procedures are.
Flow diversion devices and liquid embolic agents have been key. They’ve made a big difference in treating cerebral aneurysms and other vascular issues.
Looking ahead, brain embolization will keep being a key treatment. New research and development will bring even better materials and methods. This will make these procedures even more effective.
We’re excited about the future of brain embolization. It could help treat more vascular conditions. As technology gets better, patients will see better results. This will improve their quality of life.
FAQ
What is aneurysm embolization?
Aneurysm embolization is a procedure to treat cerebral aneurysms. It blocks blood flow into the aneurysm. This prevents it from rupturing.
What is the difference between an aneurysm and an embolism?
An aneurysm is a bulge in an artery’s wall. An embolism is when a blood clot blocks a vessel. This blocks blood flow.
What are the risk factors for aneurysm rupture?
High blood pressure, smoking, and family history increase the risk of aneurysm rupture.
What are the signs and symptoms of a brain aneurysm?
Symptoms include headaches, nausea, and neurological deficits.
How is brain embolization performed?
It involves deploying coils into the aneurysm through a catheter. The catheter is guided by images.
What are the different types of brain embolization procedures?
Types include coil embolization, stent-assisted coiling, and flow diversion devices. Liquid embolic agents are also used.
What is the recovery process like after aneurysm embolization?
Recovery involves monitoring, a short hospital stay, and activity restrictions. Follow-up imaging and appointments are also needed.
How does embolization compare to traditional brain surgery?
Embolization is less invasive. It causes less pain and has a shorter recovery time than open surgery.
What is the success rate of aneurysm embolization?
Success rates vary. It can offer durable results for certain conditions.
What are the possible complications of brain embolization?
Complications include bleeding or clotting during the procedure. Issues with the embolic materials used can also occur.
What is cerebral embolisation?
Cerebral embolisation is another name for brain embolization. It refers to the minimally invasive treatment of brain vascular conditions.
What is endovascular embolization?
Endovascular embolization includes various minimally invasive procedures. It treats vascular conditions throughout the body.
What is coil embolization for aneurysm?
Coil embolization involves deploying coils into the aneurysm. This blocks blood flow and prevents rupture.
What is arteriovenous malformation embolization?
Arteriovenous malformation embolization treats AVMs. It uses liquid embolic agents to occlude abnormal connections between arteries and veins.
References:
- Molyneux, A. J., Kerr, R. S. C., Yu, L. M., Clarke, M., Sneade, M., Yarnold, J. A., Campbell, M. K., Rischmiller, J., Stratton, I. M., & Sandercock, P. (2005). International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2,143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: A randomized comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. The Lancet, 366(9488), 809–817.








