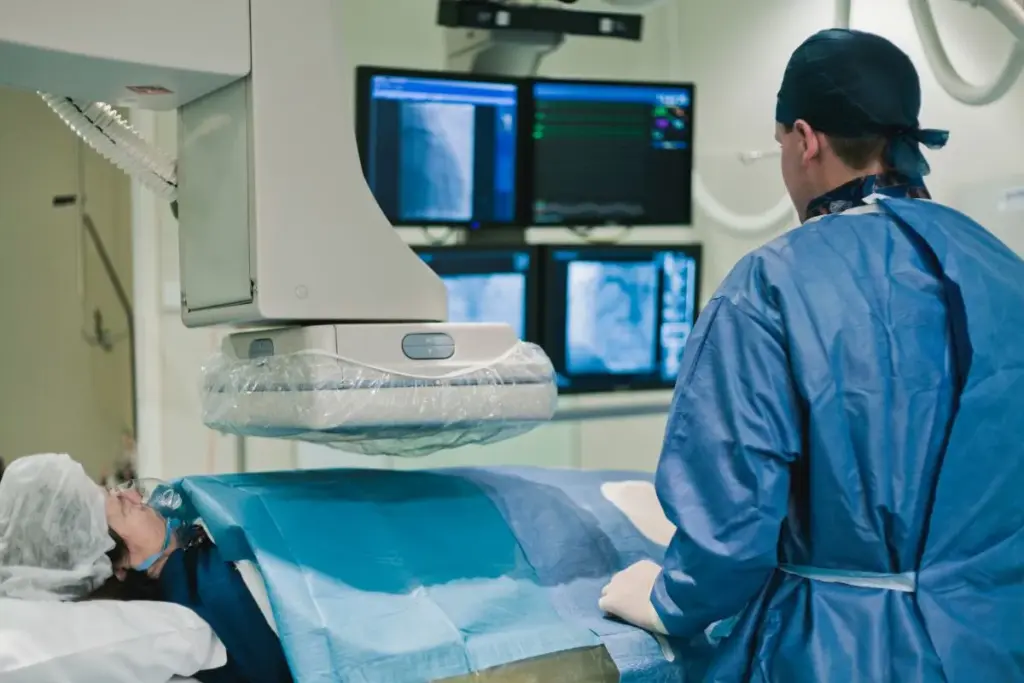
Heart disease is a big problem worldwide, with clogged arteries being a major concern. In the United States, heart disease kills over 650,000 people every year.
It’s very important to diagnose heart conditions correctly to treat them well. Two common tests used are coronary angiogram and cardiac catheterization. Even though they’re related, they have different roles in checking heart health.
We’ll look at the differences and similarities between these tests. This will help you know what to expect when you get checked for heart issues.
Key Takeaways
- Coronary angiogram and cardiac catheterization are medical procedures used to diagnose heart conditions.
- Understanding the difference between these procedures is key for effective treatment.
- Both procedures help find clogged arteries and check overall heart health.
- Cardiac catheterization is a wider procedure that can include coronary angiogram.
- These tests are vital for figuring out the best treatment for heart disease.
Understanding Coronary Angiogram
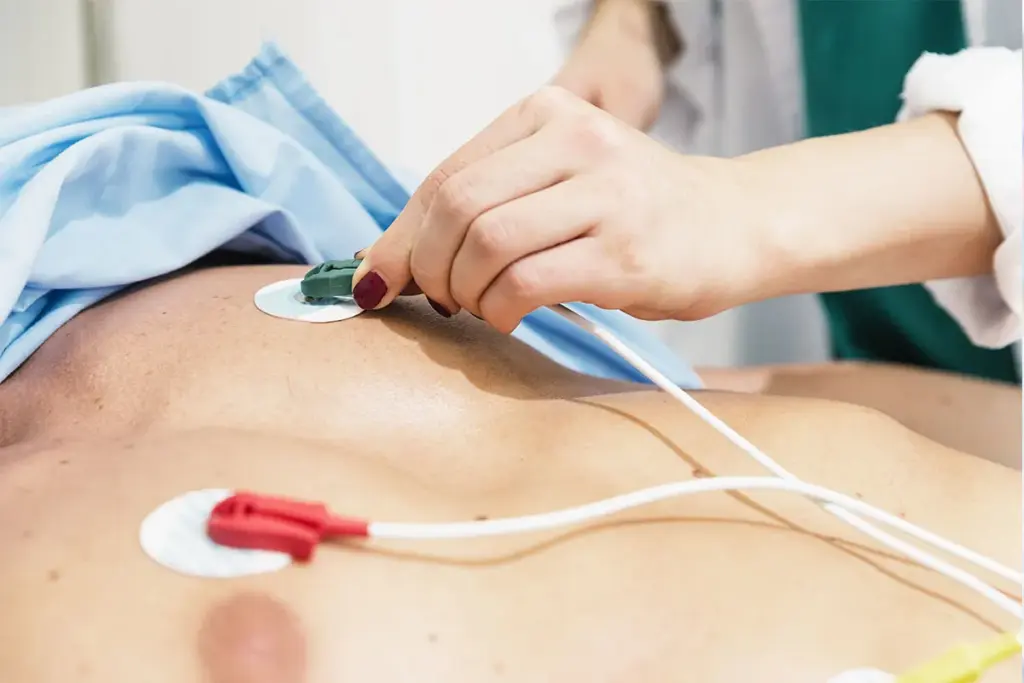
The coronary angiogram is a key test for doctors to check the heart’s arteries. It helps find out if there’s a blockage that could lead to heart attacks. This test is very important for heart health.
Definition of Coronary Angiogram
A coronary angiogram uses X-rays to see the heart’s arteries. A dye is injected through a catheter to make the arteries show up on the X-rays. This lets doctors spot any problems in the arteries.
Purpose of Coronary Angiogram
The primary objective of a coronary angiogram is to identify and evaluate the severity of coronary artery disease. It shows if the arteries are blocked or narrowed, which can stop blood from reaching the heart. Doctors use this info to choose the best treatment, like medicine or surgery.
Knowing about coronary angiograms helps patients understand their heart health. It shows how important this test is in finding and treating clogged arteries.
What is Cardiac Catheterization?
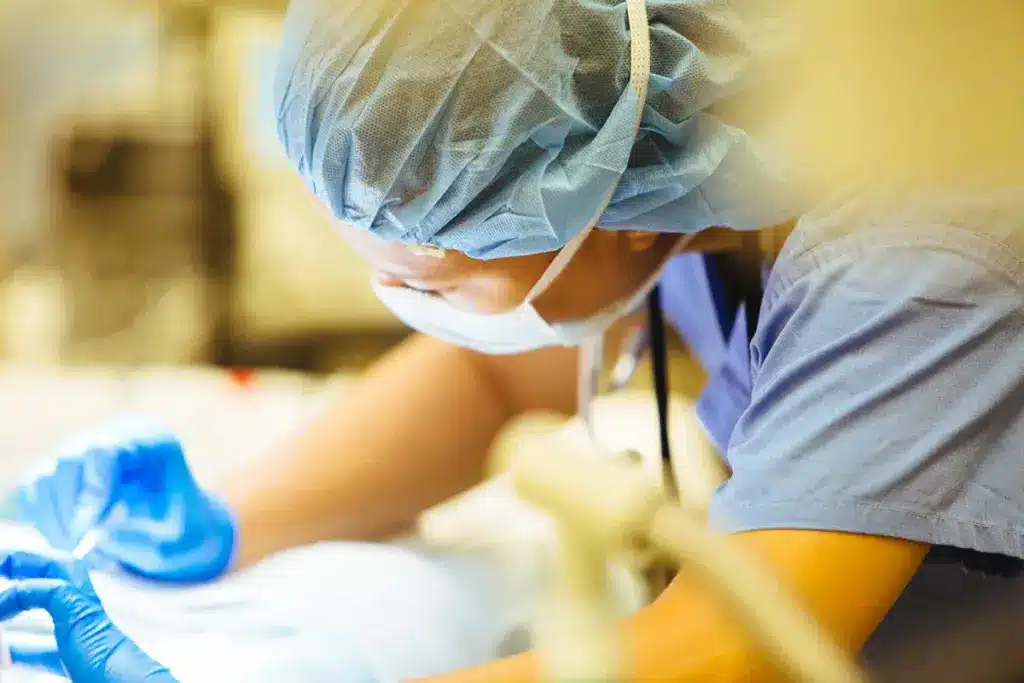
Cardiac catheterization is a key medical procedure for heart issues. It involves putting a thin, flexible tube called a catheter into an artery. This tube is guided to the heart from the leg or arm.
Overview of Cardiac Catheterization
During this procedure, we can see the coronary arteries and check the heart’s function. A contrast agent is injected through the catheter. This lets us take detailed X-ray images.
The info from this procedure helps diagnose issues like clogged arteries. It also helps decide the best treatment.
The procedure happens in a special lab by a team of skilled cardiologists and technicians. Patients get local anesthesia to numb the area. They might also get sedation to relax.
Indications for Cardiac Catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is used for many heart conditions, including:
- Diagnosing coronary artery disease
- Checking how bad coronary artery blockages are
- Looking at heart valve function
- Finding out why patients have symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath
In some cases, it’s not just for diagnosis. It’s also for treatment. For example, angioplasty and stenting can open blocked arteries. This helps blood flow to the heart.
Key Differences Between Angiogram and Catheterization
Coronary angiogram and cardiac catheterization are two different tests for the heart. They help doctors find and fix heart problems. Knowing the difference helps patients and doctors make better choices for heart health.
Purpose and Goals
A coronary angiogram shows the heart’s arteries to find blockages. Cardiac catheterization is more flexible. It can check the heart and fix problems like angioplasty and stenting.
Angiography checks for artery disease. Catheterization treats the heart directly.
Procedure Variations
Both tests use a catheter in the heart. But, they differ in how they’re done. Angiograms mainly look at the arteries. Catheterizations can also check blood pressure and do treatments.
|
Procedure |
Primary Focus |
Common Additional Steps |
|---|---|---|
|
Coronary Angiogram |
Imaging coronary arteries |
None |
|
Cardiac Catheterization |
Diagnostic and therapeutic interventions |
Angioplasty, stenting, measuring heart chamber pressures |
Risks and Complications
Both tests have risks, but they’re different. Angiograms might cause bleeding or dye allergies. Catheterizations have these risks too. But, it also has more serious problems like artery damage.
- Bleeding or hematoma at the catheter site
- Allergic reactions to contrast dye
- Coronary artery dissection or perforation (more common in cardiac catheterization)
How is a Coronary Angiogram Performed?
A coronary angiogram is a key test for heart health. It lets doctors see the coronary arteries and find any blockages or issues.
Step-by-Step Process
The first step is to numb the area where the catheter will go. This is usually in the groin or arm. Then, a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into the artery.
Next, the catheter is guided to the coronary arteries using X-ray images. A contrast dye is then injected to make the arteries visible on the X-ray. This dye helps doctors see any blockages or narrowing.
The whole process happens in a special lab. A team of skilled cardiologists and technicians work together to perform the angiogram.
Tools and Technologies Used
Several tools and technologies are used in a coronary angiogram. The main one is X-ray angiography, which gives real-time images of the arteries. Advanced catheter systems and guidewires help navigate the arteries precisely.
The contrast dye used is safe and effective. It provides clear images of the arteries. Some places might also use fractional flow reserve (FFR) measurement to check blockage severity and decide treatment.
Key technologies used include:
- X-ray angiography
- Advanced catheter systems
- Guidewires
- Contrast dye
- Fractional flow reserve (FFR) measurement
Recovery After a Coronary Angiogram
Understanding the recovery after a coronary angiogram is key for a smooth recovery. We’ll walk you through the typical recovery time and share tips on managing symptoms. This will help you navigate this important phase.
Typical Recovery Timeline
The recovery time after a coronary angiogram varies. It depends on your health and the procedure details. Most people can get back to normal in a few days.
Immediate Recovery (First 24 hours): Rest is vital right after the procedure. You should avoid heavy lifting, bending, or hard activities.
Short-Term Recovery (2-3 days): You can start with light activities in a couple of days. But, always follow your doctor’s specific instructions.
Managing Post-Procedure Symptoms
Some symptoms like bruising or discomfort at the catheter site are common after a coronary angiogram. Applying gentle pressure or using cold compresses can help ease these symptoms.
- Watch the catheter site for signs of infection, like redness, swelling, or more pain.
- Take your doctor’s advice on medication, including blood thinners.
- Drink plenty of water and eat well to support your recovery.
“Following the procedure, my doctor’s clear instructions on post-procedure care made a significant difference in my recovery.”
Knowing how to recover after a coronary angiogram is important. It helps avoid complications and ensures a healthy recovery. By following the advice above and keeping in touch with your healthcare provider, you can get through this period confidently.
Risks Involved in Angiography
It’s important for patients to know the risks of coronary angiography. This test is key for diagnosing heart issues but comes with some dangers.
Common Risks
Some common risks include bleeding or bruising at the catheter site. Allergic reactions to the dye used and damage to blood vessels are also possible. Knowing these risks helps patients make better choices about their health.
- Bleeding or bruising at the catheter site
- Allergic reactions to the contrast dye
- Damage to the blood vessels
- Infection
Rare Complications
Though rare, serious complications like heart attack, stroke, or death can happen. These risks highlight the need for skilled professionals and a well-equipped place for the procedure. Talking to your doctor about your risks is key.
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Death
- Kidney damage due to contrast dye
To lower risks, follow all instructions before and after the test. Tell your doctor about any health issues or medicines you’re on. By understanding and managing these risks, patients can make better choices about coronary angiography.
Benefits of Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography offers many benefits. It helps doctors diagnose and plan treatments. This tool is key in cardiology, showing the coronary arteries in detail. It aids in managing heart disease well.
Diagnostic Advantages
Coronary angiography has several benefits for diagnosis:
- It shows coronary artery disease accurately
- It finds blockages and narrow spots in arteries
- It checks how severe the disease is
A leading cardiologist says, “Coronary angiography gives us a clear view of the heart’s arteries. This helps us create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.”
“Coronary angiography is a critical diagnostic tool that has revolutionized the management of coronary artery disease.”
|
Diagnostic Feature |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Accurate Visualization |
Helps in precise diagnosis of coronary artery disease |
|
Identification of Blockages |
Enables targeted interventions such as angioplasty |
|
Assessment of Disease Severity |
Informs treatment decisions and prognosis |
Treatment Planning
Coronary angiography is key for planning treatments. It helps doctors choose the best treatment, like medicine, angioplasty, or CABG.
Key aspects of treatment planning include:
- Determining the need for revascularization procedures
- Selecting the most suitable revascularization method
- Planning the procedural details, such as access site and stent selection
Coronary angiography gives detailed insights into the heart’s anatomy. This leads to personalized treatment plans that improve patient results.
Alternatives to Coronary Angiography
There’s a growing need for less invasive ways to check the heart. Coronary angiography is key for diagnosing heart disease. But, not everyone can have this test. We’ll look at other ways to check the heart and when to use them.
Non-Invasive Imaging Techniques
There are new ways to see the heart without surgery. These include:
- Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA): This uses CT scans to see the heart’s arteries.
- Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI shows the heart’s details without radiation.
- Myocardial Perfusion Imaging: This test checks blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Stress Echocardiography: It uses ultrasound to see how the heart works under stress.
These tests help doctors understand heart health and decide on treatments.
When to Consider Alternatives
Doctors might choose other tests in certain situations:
|
Clinical Scenario |
Preferred Alternative |
|---|---|
|
Patients with severe kidney disease |
Cardiac MRI or Stress Echocardiography |
|
Patients with allergy to contrast dye |
CCTA or Cardiac MRI |
|
Patients who are pregnant or at risk of radiation exposure |
Cardiac MRI |
|
Initial assessment of coronary artery disease risk |
CCTA or Myocardial Perfusion Imaging |
Using these alternatives helps doctors find the best test for each patient. This way, they can avoid risks and get better results.
Costs of Coronary Angiograms
Knowing the cost of a coronary angiogram is key to smart healthcare choices. This test can be pricey, with many factors affecting the final cost.
Average Cost Breakdown
The price of a coronary angiogram changes based on who does it, where, and where you have it done. It can be in a hospital or an outpatient clinic.
The total cost includes the test itself, any hospital stay, doctor fees, and extra tests or meds. Costs can range from $5,000 to $20,000 or more.
Insurance Coverage Considerations
Insurance is a big factor in what you pay for a coronary angiogram.
Most insurance plans cover this test if it’s needed. But, how much they cover can differ. It’s important to check your policy to see what’s included and what’s not.
|
Cost Component |
Average Cost |
|---|---|
|
Procedure |
$3,000 – $10,000 |
|
Hospital Stay |
$1,000 – $5,000 |
|
Doctor’s Fees |
$500 – $2,000 |
|
Additional Tests/Medications |
$500 – $1,000 |
|
Total |
$5,000 – $18,000 |
Talking to your healthcare provider about costs is vital. They can help you understand the total cost and plan your finances.
Importance of Discussing Options with Your Doctor
Talking about your heart health with your doctor is very important. When you have a heart condition, it’s key to talk openly with your doctor. This way, you can make the best choices for your care.
Key Questions to Ask
There are important questions to ask your doctor. These include:
- What are the possible reasons for my heart condition?
- What tests do I need to understand my condition?
- What treatment options are there, and which one is best for me?
- What are the risks and benefits of each treatment?
- How will my condition be managed in the long run?
Asking these questions helps you understand your condition and the options available. This way, you can make informed choices about your care.
Understanding the Risks and Benefits
Every test and treatment has its own risks and benefits. Knowing these is key to making good choices for your heart health.
|
Procedure |
Risks |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Coronary Angiogram |
Bleeding, infection, reaction to contrast dye |
Detailed imaging of coronary arteries, guides treatment decisions |
|
Cardiac Catheterization |
Bleeding, infection, artery damage |
Diagnostic and potentially therapeutic, allows for interventions like angioplasty |
By knowing the risks and benefits, you and your doctor can create a treatment plan that fits your needs. This plan aims to minimize complications.
Talking well with your healthcare provider is essential for managing your heart health. By asking the right questions and understanding the risks and benefits, you can make choices that improve your health.
Patient Experiences and Testimonials
Listening to patients who have had coronary angiogram and cardiac catheterization is very helpful. Their stories give a personal view of the procedures. This helps others know what to expect and make smart choices about their heart health.
Real Stories from Patients
Many patients have shared their experiences. For example, one patient said, “I was nervous but the team was reassuring. They explained everything clearly, and it was over before I knew it.” These firsthand accounts show how caring doctors and nurses make patients feel safe and comfortable.
Recovery times vary. Some patients were back to normal in a few days, while others took a week. For instance, one patient said, “I was back to my routine in 48 hours, but I was told to take it easy for a week.” These stories show the importance of care tailored to each person’s needs.
Importance of Shared Experiences
Sharing experiences is key for those considering coronary angiogram and cardiac catheterization. Hearing from others helps people understand what to expect. This makes them more confident in their choices.
Testimonials also highlight the diagnostic advantages and treatment planning benefits of these procedures. Patients often thank these tests for the clarity and reassurance they provided. This allows them to move forward with effective treatment plans for their heart health.
|
Aspect |
Coronary Angiogram |
Cardiac Catheterization |
|---|---|---|
|
Purpose |
Diagnose clogged arteries |
Diagnose and treat heart conditions |
|
Procedure |
Minimally invasive, uses dye to visualize arteries |
Minimally invasive, can include angioplasty or stenting |
|
Recovery |
Typically quick, with most patients resuming normal activities within a few days |
Recovery time varies, but generally similar to coronary angiogram |
By sharing their stories, patients help others and improve our understanding of heart health. We encourage patients to talk about their experiences with their healthcare providers. This helps make informed decisions about their care.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
It’s important to know the difference between a coronary angiogram and cardiac catheterization for your heart health. We’ve looked at what each is, why they’re used, and how they work.
Talking to healthcare providers is key when dealing with clogged arteries. They can figure out the best plan for you. This way, you understand your condition and the treatment options better.
Key Considerations
Let’s review the main points. Coronary angiograms and cardiac catheterizations are different but related. Angiograms mainly show the coronary arteries. Catheterizations can do more, like treating problems.
Next Steps
To make a smart choice about your heart, talk to healthcare providers. They offer tailored advice and support. Together, you can create a plan that fits your needs and improves your heart health.
FAQ
Is a coronary angiogram the same as cardiac catheterization?
A coronary angiogram and cardiac catheterization are related but different. A coronary angiogram uses dye and X-rays to see the heart’s arteries. Cardiac catheterization is a broader procedure that involves a catheter in the heart for diagnosis and treatment.
What is the purpose of a coronary angiogram?
A coronary angiogram is used to find blockages in the heart’s arteries. It helps doctors see how severe the disease is and plan treatment.
How is a coronary angiogram performed?
To perform a coronary angiogram, a catheter is inserted into an artery. Then, contrast dye is injected, and X-rays are taken to see the arteries.
What are the risks associated with coronary angiography?
Risks include bleeding, allergic reactions, and kidney damage. Rarely, it can cause heart attack, stroke, or arrhythmias.
How long does it take to recover from a coronary angiogram?
Recovery time is a few hours to a day. Patients are watched for complications. Most can go back to normal activities in a day or two.
Are there alternatives to coronary angiography?
Yes, tests like CT angiography, MRI, or stress tests can diagnose heart disease. These are options for those not suited for invasive procedures.
How much does a coronary angiogram cost?
The cost varies by location, insurance, and facility. It can range from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars.
Does insurance cover coronary angiograms?
Many insurance plans cover coronary angiograms when needed. But, coverage and costs vary. Check with your provider for details.
Can I have a coronary angiogram if I have kidney disease?
Those with kidney disease face higher risks from the dye used in angiograms. Doctors might choose other tests or take extra precautions.
How do I prepare for a coronary angiogram?
Preparation includes fasting, disclosing allergies, and following your doctor’s instructions on medications and preparations.
Can atherosclerosis cause high blood pressure?
Atherosclerosis can lead to high blood pressure. It narrows and stiffens arteries, making it harder for the heart to pump blood.
How do clogged arteries affect blood pressure?
Clogged arteries make the heart work harder to pump blood. This can increase blood pressure.
Can you have good blood pressure with clogged arteries?
Yes, you can have normal blood pressure with clogged arteries. But, clogged arteries increase the risk of heart problems, even with normal blood pressure.
Reference
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3525492/)