Coronary artery disease is a big problem worldwide. Millions of people get checked with angiography to see how their arteries are doing. Angiography is a key tool for doctors to see the heart’s blood vessels and find blockages. Do they stent during angioplasty? Yes. Get the best immediate fix for blockages. Learn how this vital procedure restores amazing blood flow.
If a blockage is found during angiography, the next step is often angioplasty. This is when the blocked artery is widened, and a stent is put in to keep it open. This method is very common for treating coronary artery disease.
Key Takeaways
- Angiography is used to diagnose coronary artery disease by visualizing the heart’s blood vessels.
- A blockage found during angiography may lead to an immediate angioplasty.
- Stenting is often performed during angioplasty to keep the artery open.
- The combined procedure of angiography and angioplasty with stenting is a common treatment approach.
- Understanding the role of each procedure can help patients better navigate their treatment options.
Understanding Angiography and Angioplasty
Angiography and angioplasty are key in diagnosing and treating heart issues. They are vital for both patients and doctors to understand in cardiology.
Definition of Angiography
Angiography uses X-rays and a contrast agent to see inside blood vessels. It helps find blockages or problems. This lets cardiologists check arteries and decide on treatment.
It gives a clear view of blood vessel health. This helps doctors find and fix issues that need more action.
Overview of Angioplasty
Angioplasty is a treatment to open narrowed or blocked arteries. A cardiologist uses a balloon catheter to inflate the area. This improves blood flow.
Often, a stent is placed to keep the artery open. This method is key in treating heart disease and has changed cardiology.
How They Are Related
Angiography and angioplasty work together in treating heart diseases. First, angiography finds blockages. Then, angioplasty treats them.
This smooth transition shows how these procedures are connected. It highlights the success of modern cardiology.
Understanding these procedures is essential for those pursuing a career in cardiology. Cardiology fellowships offer advanced training. Understanding what is cardiologist means seeing their role in these critical steps.
Becoming a cardiologist takes years of schooling and residency. This includes training in angiography and angioplasty.
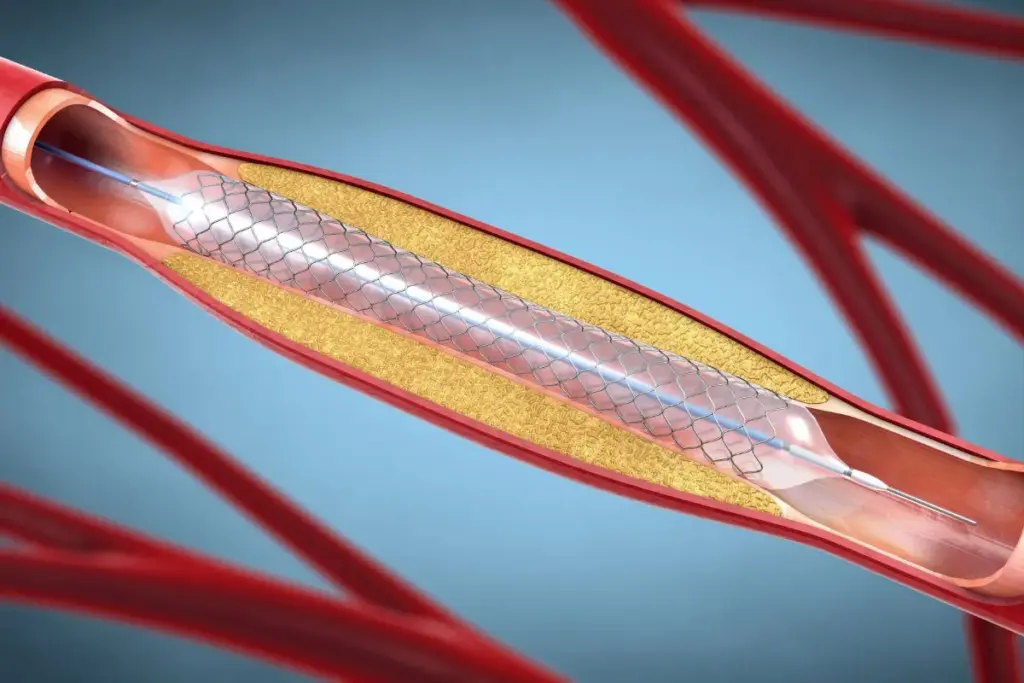
What is a Stent?
Stents are key in keeping arteries open for heart health. They can seem complex, but we’ll explain them simply.
Definition and Purpose
A stent is a small mesh device designed to keep arteries open. This improves blood flow to the heart. Its main job is to stop the artery from getting narrow again after an angioplasty.
Think of stents as tiny scaffolds for artery walls. They help keep the artery open and working well. This is very important for people who have had angioplasty.
Types of Stents
There are many stent types, each for different needs. Here are the most common:
- Bare-metal stents: These are the first stents made from metal mesh. They work well but might cause the artery to narrow again.
- Drug-eluting stents: These stents have medicine that stops the artery from narrowing. They are used more today because they work better.
- Bioresorbable stents: These stents are made from materials that the body can break down over time. They are a new idea and might offer better long-term results.
|
Type of Stent |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Bare-metal |
Made from metal mesh |
Effective, simple design |
|
Drug-eluting |
Coated with medication to prevent re-narrowing |
Reduced risk of artery re-narrowing |
|
Bioresorbable |
Made from absorbable materials |
Potential for improved long-term outcomes |
Evolution of Stent Technology
Stent technology has grown a lot over time. The goal is to make patient care better. Drug-eluting stents, for example, have greatly reduced artery narrowing risks.
The future of stent technology is exciting. There’s ongoing research into bioresorbable stents and new materials. We’re always looking to improve care for our patients.
The Angioplasty Procedure Explained
Learning about angioplasty can ease worries for those facing it. It’s a treatment to open narrowed arteries and boost blood flow to the heart. We’ll explain the steps, what to expect, and how to recover.
Pre-Procedure Preparations
Before angioplasty, several steps are taken to ensure success and safety. Our team reviews your medical history and performs tests like blood work and electrocardiograms. It’s important to tell us about any medications you’re taking.
On the day of the procedure, arrive with an empty stomach. Angioplasty is done under local anesthesia. Also, arrange for someone to drive you home as you might feel groggy.
Steps of the Angioplasty Procedure
The procedure involves several steps. First, you’ll be positioned on a table, and the area will be cleaned and numbed. A small incision is made to insert a catheter with a balloon tip.
The balloon is then inflated to widen the artery. A stent is often placed to keep it open. This requires precision and is done by experienced cardiologists.
The procedure can take 30 minutes to a few hours. The time depends on the blockage’s complexity and your condition.
Post-Procedure Recovery
After angioplasty, you’ll be monitored for a few hours. We watch for any complications and ensure you’re stable before discharge. You might feel sore at the catheter site, but this usually goes away in a few days.
Follow our instructions for post-procedure care, including medication and follow-up appointments. For those interested in becoming cardiologists, it takes many years of education and training.
In summary, angioplasty is a complex procedure that requires careful preparation and precise execution. Understanding the process and the expertise of medical professionals can help patients feel more confident and prepared.
When is a Stent Placed?
Cardiologists use several factors to decide if a stent is needed. They look at how bad the heart disease is, the patient’s health, and the blockage’s details.
Criteria for Stent Insertion
There are many things cardiologists check before placing a stent. They look for big blockages in the heart’s arteries, usually over 70% blocked. They also consider where and how long the blockage is.
They also think about the patient’s symptoms and health history. For example, those with chest pain or who’ve had a heart attack might need a stent. They also look at risk factors like diabetes and smoking.
Types of Conditions Requiring Stenting
Stents are often used for coronary artery disease (CAD). Acute coronary syndrome (ACS), like heart attacks, also needs stenting right away.
Other reasons for stenting include blocked arteries and stents that get blocked again. The type of stent depends on the problem.
Risks of Not Using a Stent
Not getting a stent when needed can be risky. It can lead to heart attacks, worse chest pain, and a lower quality of life. Without a stent, big blockages can cause more heart damage.
Not every patient is a good candidate for stenting. The choice is made carefully, considering each person’s health and situation.
Differences Between Angioplasty and Angiography
Angioplasty and angiography are used in heart care but for different reasons. Angiography is for looking inside blood vessels. Angioplasty is for opening up blocked or narrowed blood vessels.
Purpose of Each Procedure
Angiography uses a contrast agent to see blockages in blood vessels with X-ray imaging. It helps doctors find where and how bad the blockages are. Angioplasty, on the other hand, uses a balloon to widen arteries and improve blood flow to the heart.
Key differences in purpose:
- Angiography is for looking at blood vessels to find problems.
- Angioplasty is for treating narrowed arteries by using a balloon and sometimes a stent.
Risks and Benefits
Both procedures have risks and benefits. Angiography is mostly safe but can cause bleeding or an allergic reaction. Angioplasty is generally safe but can lead to artery damage, bleeding, or blood clots.
|
Procedure |
Risks |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Angiography |
Bleeding, allergic reactions to contrast dye |
Detailed visualization of blood vessels, diagnostic accuracy |
|
Angioplasty |
Artery damage, bleeding, blood clots |
Improved blood flow, relief from symptoms, prevention of heart attack |
Diagnostic vs. Treatment Focus
Angiography focuses on finding problems in blood vessels. Angioplasty aims to fix these problems by opening up blocked areas.
To be an interventional cardiologist, one needs a lot of training. This includes a cardiology fellowship program. The field of cardiology is complex and competitive, so cardiologists must keep learning and stay current with new techniques.
Benefits of Using a Stent with Angioplasty
Stenting with angioplasty has changed how we treat heart disease. It makes patients’ lives better by improving blood flow and reducing blockages. Let’s look at how this combo helps patients.
Improved Blood Flow
Stents help keep arteries open during angioplasty. This ensures blood reaches the heart muscle well. It cuts down on chest pain and shortness of breath, making life better for patients.
Reduced Risk of Future Blockages
Stenting also lowers the risk of arteries narrowing again. Drug-eluting stents prevent this narrowing, known as restenosis. This means fewer repeat procedures for patients.
A doctor, with over 10 years of experience, says, “New stent tech has cut down restenosis a lot. Angioplasty is now a more lasting fix for patients.”
- Improved blood flow to the heart muscle
- Reduced risk of future blockages
- Enhanced patient outcomes and quality of life
Patient Outcomes and Statistics
Research shows stenting with angioplasty boosts patient results. A big study found stenting cut down on heart problems more than angioplasty alone. Becoming a cardiologist takes a lot of work, but it’s worth it. They are among the highest-paid doctors, thanks to their skill.
Cardiology has made huge strides, with stenting being key. As we keep getting better, stenting will keep making patients’ lives better.
Risks and Considerations of Stenting
Stenting is a common treatment, but it comes with risks. It’s important to know these risks before deciding on stenting. A cardiologist will carefully evaluate you. They have many years of schooling and know a lot about heart health.
Potential Complications
Stenting can lead to complications. One big risk is restenosis, when the artery narrows again. Even with new stent technology, restenosis is a concern (Source: [14], [22]).
Other risks include bleeding, allergic reactions, and stent thrombosis. Knowing these risks helps patients make better choices.
Long-Term Considerations
Several factors influence the success of stenting. Your health, medicine, and lifestyle are key. A cardiologist, with education required for cardiologist and experience, helps a lot. They learn for years to manage heart problems.
Thinking about the future, you might need more treatments. Seeing your doctor regularly is important. This helps keep the stented artery healthy.
Importance of Follow-Up Care
Follow-up care is vital after stenting. Regular visits with a cardiologist are important. They check how the stent is doing and your heart health. Becoming a cardiologist takes a lot of work, education, and dedication.
Living a healthy lifestyle is also key. Eating right, exercising, and not smoking can help a lot. These actions can improve your health and lower the chance of future heart problems.
In summary, stenting is a good option for many heart issues. But, knowing the risks and long-term needs is important. With the right care and follow-up, patients can do well.
Patient Experience and What to Expect
Undergoing angioplasty and stenting can be intimidating. We want to make sure you know what to expect. We aim to ease your worries and support you every step of the way.
Pre-Procedure Anxiety and Preparations
Many patients feel nervous before these procedures. We know this and want to help. We tell you all about the procedure, its benefits, and what to expect. Here’s what you might need to do:
- Get the tests and exams needed for the procedure
- Talk about your medications and allergies with your team
- Follow instructions on fasting or other special steps
- Plan for someone to take you home after
During the Procedure
You’ll get local anesthesia to numb the area. A team of skilled cardiologists and staff will watch over you. We use the latest technology to make sure you’re comfortable.
Cardiologists in the U.S. are very well-paid and experienced. This means you get the best care from top experts. The field is competitive, but it’s worth it for your health.
Post-Procedure Care and Lifestyle Changes
After the procedure, we keep an eye on you to make sure everything goes smoothly. We’ll tell you how to take care of yourself, including:
- Managing any pain or discomfort
- Watching the insertion site for infection signs
- Slowly getting back to normal activities
- Making lifestyle changes to keep your heart healthy
Knowing what to expect and getting good care helps you feel more confident. Our team is here to support you, from start to finish.
Advances in Angioplasty Techniques
Medical technology keeps getting better, making angioplasty more effective. Cardiology is always changing, with new tools and methods coming out. These advancements contribute significantly to enhancing patient care.
Innovations in Stenting
Stenting has seen big improvements in angioplasty. Stents are key in keeping arteries open and improving blood flow. New stents include:
- Drug-Eluting Stents: These stents release medicine to stop cell growth, cutting down on restenosis risk.
- Bioresorbable Stents: These stents dissolve over time, providing temporary support for the artery and possibly reducing complications.
These new stents have made angioplasty safer and more effective. A study found drug-eluting stents cut restenosis rates by up to 70% compared to old stents.
“The development of drug-eluting stents has been a game-changer in the field of interventional cardiology, significantly reducing the need for repeat procedures.”
A leading cardiologist in the field
The Role of Technology
Technology is key in improving angioplasty. It includes imaging for clear artery views and robotic systems for precise stent placement. These advancements are changing the game.
|
Technology |
Application in Angioplasty |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) |
Used to assess the size of the artery and guide stent placement. |
Improves accuracy of stent deployment. |
|
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) |
Provides high-resolution images of the coronary arteries. |
Enhances visualization of stent apposition and artery wall. |
|
Robotic-Assisted Angioplasty |
Enables precise control over catheter and stent placement. |
Reduces radiation exposure to operators and improves procedural accuracy. |
Future Directions in Cardiovascular Interventions
The future of cardiovascular interventions looks bright. New technologies and methods will keep improving patient care. This is exciting for both patients and doctors.
For those wanting to be cardiologists, knowing the path is key. It involves medical school, internal medicine residency, and a cardiology fellowship. This can take 3 to 4 years. Cardiologists do a lot, from diagnosing to treating patients.
As we explore new possibilities in cardiovascular care, the future is full of hope. It’s a great time to be in this field.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways on Angioplasty and Stenting
Understanding angioplasty and stenting is complex. To become a cardiologist surgeon, you need a lot of education and training. This includes finishing cardiologist education and a cardiology residency.
It takes over a decade after medical school to become a cardiologist surgeon. Knowing about angioplasty and stenting helps patients make better choices for their health.
Summary of Key Points
We have examined the interplay between angiography and angioplasty. We also talked about stenting for coronary artery disease. Knowing the benefits and risks is key for patients.
Importance of Informed Decisions
Patients should talk to doctors to understand their needs. This way, they can make smart choices about their care. It’s important to know about the time and effort needed to become a cardiologist.
Encouragement to Consult Healthcare Professionals
We urge patients to get advice from skilled healthcare professionals. Cardiologists, after a lot of education and training, can help a lot. Together, patients can get the best care and results.
FAQ
What is angiography and how is it related to stenting?
Angiography is a way to see inside blood vessels. It helps doctors find problems like blockages. After finding a blockage, doctors might use angioplasty and stenting to fix it.
How long does it take to become a cardiologist?
Becoming a cardiologist takes about 11-12 years after high school. You need four years of college, four years of medical school, and three to four years of residency. Then, you do three years of cardiology fellowship.
What is the difference between angioplasty and angiography?
Angiography is for looking inside blood vessels. Angioplasty is for fixing narrowed or blocked ones. Doctors often do angioplasty right after angiography if they find a blockage.
What are the benefits of using a stent with angioplasty?
Stents help keep blood flowing well. They also lower the chance of future blockages. This can make patients feel better and live longer.
What are the possible risks and complications of stenting?
Risks include bleeding, infection, and blockages coming back. You might need to keep an eye on things long-term and possibly have more procedures.
What can I expect during the angioplasty procedure?
You’ll get local anesthesia and maybe sedation. The doctor will use a catheter to open the blockage. They might put in a stent to keep it open.
How long is the recovery time after angioplasty and stenting?
Recovery time varies, but most people can get back to normal in a week or so. You should avoid heavy lifting and bending for a bit.
What are the latest advances in angioplasty techniques?
New stent technologies and imaging tools are improving angioplasty. These advancements help doctors do the procedure better and with less risk.
How can I become a cardiologist?
First, get a medical degree. Then, do internal medicine residency and cardiology fellowship. You’ll also need to get certified and licensed.
What is the role of technology in cardiovascular interventions?
Technology is key in heart treatments. It includes new stents, imaging, and less invasive methods. These help patients recover faster and live better.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26409835/





