Acute appendicitis is a serious condition that needs quick action. The first sign is usually a pain in the belly that moves to the right lower area.
Appendicitis symptoms gets worse fast, often from symptom onset to possible rupture within 36 to 72 hours. Without treatment, it can cause serious problems. At livhospital.com, we stress the need for fast medical help to improve patient results and lower risks.
Key Takeaways
- Acute appendicitis is a rapidly progressing condition.
- Symptoms typically start as diffuse abdominal pain.
- Prompt medical attention is critical to avoid complications.
- The risk of rupture increases significantly after 36 hours.
- Timely intervention is key to optimizing patient outcomes.
Understanding Appendicitis: An Overview
To understand appendicitis, we need to know its causes and where the appendix is. Appendicitis happens when the appendix gets blocked, causing inflammation. This blockage can be due to many things, like fecaliths, lymphoid hyperplasia, or other foreign objects.
What Causes Appendicitis
Appendicitis can have many causes. The main one is when the appendix gets blocked, leading to too many bacteria and inflammation. People usually get it around 28 years old. The risk is higher for men than women, at 8.6% versus 6.7%.
Genetics, diet, and infections can also play a part. Even though we don’t know all the details, it’s clear that appendicitis is complex. It needs a thorough medical check-up.
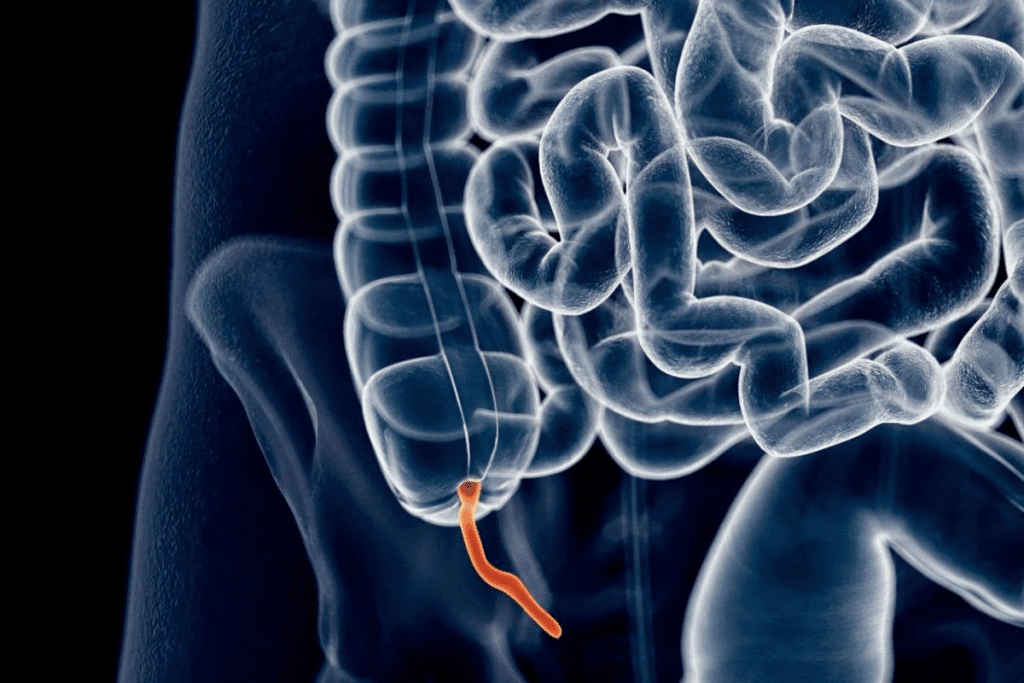
Anatomical Location: What Side is the Appendix On
The appendix is a small, tube-like organ near the large intestine. It’s usually found on the lower right side of the abdomen. Knowing where the appendix is helps doctors diagnose appendicitis faster.
Why Timing is Critical in Appendicitis Cases
Getting treatment for appendicitis quickly is very important. Waiting too long can cause serious problems like perforation and peritonitis. The risk of these complications grows after 36 hours of symptoms starting.
So, recognizing symptoms early and getting medical help fast is key. This can greatly improve a patient’s chances of recovery.
In summary, understanding appendicitis means knowing its causes, where it is, and why quick treatment is essential. By grasping these points, people can better handle this condition and get the right medical care.
The 4 Stages of Appendicitis
Appendicitis goes through four stages, from mild inflammation to serious complications. Knowing these stages helps us understand how severe it is and when to get medical help.
Stage 1: Early Inflammation (0-12 Hours)
The first stage of appendicitis starts with blockage and swelling. People might feel mild pain first near the belly button and then in the lower right side. It’s hard to diagnose early because the symptoms are not clear.
Stage 2: Acute Appendicitis (12-24 Hours)
In the second stage, the inflammation gets worse, and the pain gets stronger. Symptoms include loss of appetite, nausea, and a slight fever. It’s important to act fast because waiting can make things worse.
Stage 3: Suppurative Appendicitis (24-36 Hours)
By the third stage, the appendix is filled with pus. Symptoms get worse, with more pain, higher fever, and vomiting. Surgery is often needed to stop things from getting worse.
Stage 4: Gangrenous and Perforated Appendicitis (36+ Hours)
The last stage is the most serious. The appendix can turn gangrenous and even burst. This can cause peritonitis, a very dangerous condition. Signs of a burst appendix include severe pain and high fever. It’s a medical emergency.
Appendicitis quickly moves through its four stages, each with its own symptoms and severity. It’s important to know these stages to get help fast and avoid serious problems.
- Early detection is key: Spotting the first signs of appendicitis can lead to quick treatment.
- Progression is rapid: The condition can quickly go from mild to severe.
- Complications are serious: If not treated, appendicitis can lead to life-threatening conditions like peritonitis.
Appendicitis Symptoms Timeline
Appendicitis symptoms change over time. Knowing these changes helps patients get medical help faster. It’s important to understand how symptoms progress for timely treatment.
Initial Warning Signs (First 12 Hours)
Appendicitis starts with vague pain in the belly, often near the navel. This pain is usually mild and may make you lose your appetite. As time goes on, the pain moves to the lower right side of the abdomen.
Nausea and vomiting can start too, but they’re often mild at first.
Developing Symptoms (12-24 Hours)
After 12 hours, the pain gets more focused and intense in the lower right. It can hurt more when you move, cough, or sneeze. Fever may start, usually under 101 °F (38.3 °C).
Some people might also notice changes in their bowel movements, like constipation or diarrhea.
Severe Symptoms (24-36 Hours)
Between 24 to 36 hours, symptoms can get worse. The pain becomes more constant and intense. You might feel a higher fever and chills.
The abdomen may feel more sensitive to touch, and you might eat less.
Ruptured Appendix Symptoms (After 36 Hours)
If the appendix ruptures after 36 hours, symptoms can change a lot. At first, the pain might seem to lessen. But then, it gets much worse.
You might feel severe abdominal pain, high fever, and peritonitis, which is very dangerous. The abdomen becomes very tender and stiff.
It’s key to recognize these symptoms and seek medical help quickly. Appendicitis is a serious emergency that needs fast treatment to avoid serious problems.
Demographic Patterns and Risk Assessment
Appendicitis rates and lifetime risk are linked to age and gender. It can happen at any age but is most common in those 5 to 45 years old.
Age and Gender Distribution
The average age when people get appendicitis is about 28 years. Research shows that the lifetime risk of getting it is 8.6% for males and 6.7% for females. Males are slightly more affected than females, with a ratio that changes with age.
Incidence Rates in the United States
In the U.S., the rate of new appendicitis cases is between 100 and 223 per 100,000 people each year. Studies show that rates have stayed mostly the same, with some differences in groups.
Lifetime Risk Factors
Knowing the lifetime risk factors for appendicitis is key for early detection and prevention. Age, gender, and possibly genetics affect risk. Healthcare providers use this info to assess patient risk and guide treatment.
Appendicitis is a complex issue influenced by many factors. By grasping these patterns and risks, we can enhance diagnosis, treatment, and care for patients.
Complications of Delayed Treatment
Getting treatment quickly is key for those with appendicitis. Waiting too long can lead to serious and even deadly problems. Ignoring appendicitis can greatly increase the risk of severe health issues.
Perforation Risk: The 36-Hour Threshold
One big risk of waiting too long is perforation, where the appendix bursts. This usually happens within 36 hours of symptoms starting. Spotting appendicitis signs early is key to avoiding perforation.
Abscess Formation and Management
A burst appendix can sometimes cause an abscess. We treat abscesses by draining them, either surgically or through a needle. Quick action is needed to stop things from getting worse.
Peritonitis: A Life-Threatening Complication
Peritonitis, or inflammation of the peritoneum, is a serious problem. It happens when bacteria from a burst appendix spread in the belly. We treat it with antibiotics and surgery to clean the belly.
Long-term Health Consequences
Waiting too long to treat appendicitis can also cause long-term health issues. For example, a burst appendix can cause adhesions and bowel obstruction. We stress the need for quick medical care to avoid these problems.
In summary, the dangers of delayed treatment for appendicitis highlight the importance of seeking medical help fast. Understanding these risks helps us see why early treatment is so critical.
Diagnostic and Treatment Timeline
Understanding the timeline for diagnosing and treating appendicitis is key. Quick action is vital to avoid serious problems and ensure the best results for patients.
Optimal Diagnostic Window
Diagnosing appendicitis involves a patient’s history, physical exam, and tests like ultrasound or CT scans. The best time to diagnose is within 12 to 24 hours after symptoms start. Waiting too long can lead to serious issues.
Key diagnostic factors include:
- Clinical presentation: severity of pain, location, and progression
- Laboratory tests: white blood cell count, C-reactive protein levels
- Imaging studies: ultrasound, CT scans to visualize the appendix
Surgical Intervention Timing
Surgery to remove the appendix is usually needed. We aim to operate as soon as we can after finding out it’s appendicitis. This is to prevent serious problems. The risk of the appendix bursting increases after 36 hours.
Non-Surgical Management Options
In some cases, not needing surgery is considered. This might be for early cases or those who can’t have surgery. This usually means antibiotics and watching closely. But, surgery is the best way to treat appendicitis.
Non-surgical management may include:
- Antibiotic therapy to treat infection
- Monitoring for signs of improvement or complications
- Dietary adjustments and supportive care
Recovery Timeline After Appendectomy
Recovery time after an appendectomy varies. It depends on the surgery type and the patient’s health. Most people can get back to normal in a few weeks. We give detailed instructions to help with recovery.
Typical recovery milestones:
- Hospital stay: usually 1-3 days
- Return to light activities: within 1-2 weeks
- Full recovery: within 4-6 weeks
Conclusion: The Importance of Prompt Medical Attention
Appendicitis is a serious condition that needs quick action. Getting treatment fast is key to avoiding serious problems. Knowing the signs, like stomach pain and feeling sick, helps catch it early.
It’s important for people to know the symptoms of appendicitis. This way, they can get help right away. Waiting too long can cause serious issues, like holes in the stomach lining and infection in the belly.
We talked about how fast action is needed in appendicitis cases. This is why seeing a doctor quickly is so important. By acting fast, patients can avoid long-term health problems.
FAQ
What is appendicitis and what causes it?
Appendicitis is when the appendix gets inflamed. This usually happens when something blocks the appendix. Things like fecaliths, lymphoid hyperplasia, or other debris can cause this blockage.
Where is the appendix located?
The appendix is found on the lower right side of the abdomen. Knowing where it is helps doctors diagnose appendicitis.
What are the 4 stages of appendicitis?
Appendicitis has four stages. Stage 1 is early inflammation, lasting 0-12 hours. Stage 2 is acute appendicitis, lasting 12-24 hours. Stage 3 is suppurative appendicitis, lasting 24-36 hours. Stage 4 is gangrenous and perforated appendicitis, lasting 36+ hours.
What are the initial symptoms of appendicitis?
Early signs of appendicitis include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. These symptoms can get worse if not treated.
How long does it take for appendicitis symptoms to develop?
Symptoms of appendicitis can appear quickly, often in 12-24 hours. Getting medical help fast is important to avoid serious problems.
Can appendicitis occur at any age?
Yes, appendicitis can happen at any age. But some people are at higher risk due to certain factors.
What are the complications of delayed treatment for appendicitis?
Waiting too long to treat appendicitis can cause serious problems. These include perforation, abscesses, peritonitis, and long-term health issues.
What is the optimal diagnostic window for appendicitis?
The best time to diagnose appendicitis is within 24-48 hours after symptoms start. Quick diagnosis and treatment are key to avoiding serious issues.
What is the treatment for appendicitis?
The main treatment for appendicitis is surgery, called an appendectomy. Sometimes, doctors might not recommend surgery.
How long does it take to recover from an appendectomy?
Recovery from an appendectomy varies. But most people can get back to normal in a few weeks.
What are the symptoms of a ruptured appendix?
A ruptured appendix can cause severe stomach pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness. Quick medical care is vital to prevent more problems.
Can appendicitis be prevented?
There’s no sure way to prevent appendicitis. But eating well and staying healthy might lower your risk.
References:
Cleveland Clinic. (2025). Appendectomy (Appendix Removal): Surgery & Recovery. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/procedures/21922-appendectomy
Lotfollahzadeh, S. (2024). Appendicitis – StatPearls. NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493193/
Kollias, T. F., & et al. (2024). Sex Differences in Appendicitis: A Systematic Review. PMC. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11162818/
Li, J., & et al. (2021). Revisiting delayed appendectomy in patients with acute appendicitis. PMC. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8281431/
Crocker, C., & et al. (2020). Ultrasound and CT in the Diagnosis of Appendicitis: Accuracy. AJR. https://ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.19.22370