Osteoporosis is a common condition that affects millions globally. It raises the risk of fractures and can lower quality of life. Effective management is key to avoiding serious issues.
Osteoporosis treatment includes medications and lifestyle changes. Bisphosphonates and denosumab are often given to make bones stronger.
Finding the best osteoporosis treatment is important for patients. It depends on the severity of osteoporosis, the patient’s health, and the side effects of medications.
Key Takeaways
- Osteoporosis treatment combines medications and lifestyle changes.
- Medications like bisphosphonates are used to strengthen bones.
- The best treatment approach depends on the severity of osteoporosis and patient health.
- Lifestyle changes play a key role in managing osteoporosis.
- Effective treatment can greatly reduce the risk of fractures.
Understanding Osteoporosis and Treatment Goals
Understanding osteoporosis is key to managing its impact on bone health and reducing the risk of fractures. Osteoporosis is a condition where bones are weakened, making them more prone to fractures.
Definition and Prevalence of Osteoporosis
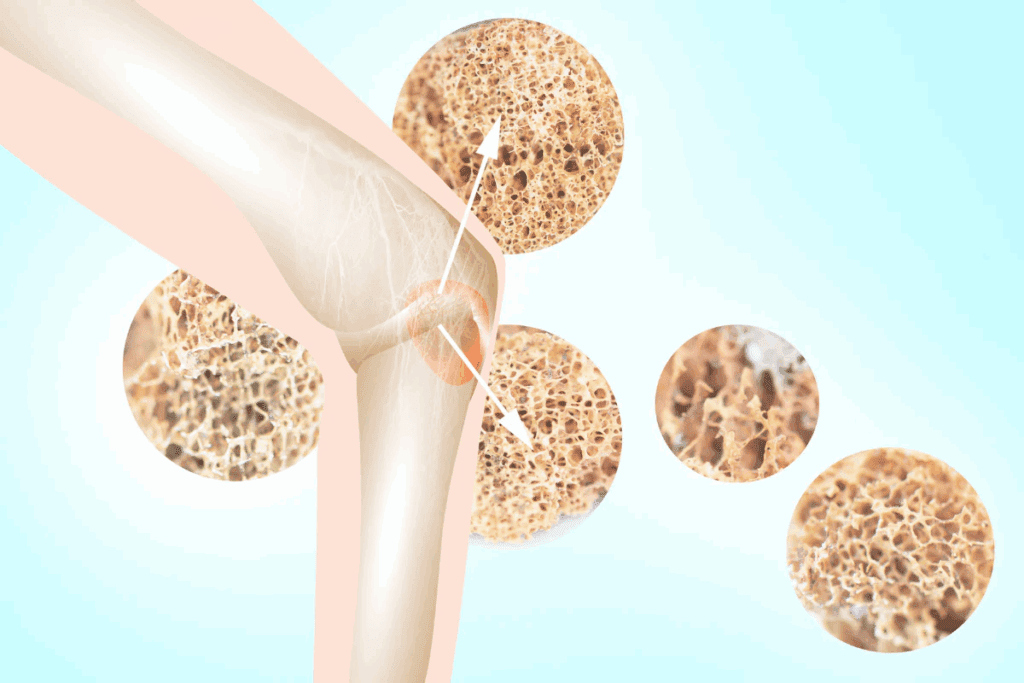
Osteoporosis is a bone disease caused by low bone density, increasing the risk of fractures. The National Osteoporosis Foundation says about 10 million Americans have osteoporosis. Another 44 million have low bone density, which also raises their risk.
The risk of osteoporosis grows with age, hitting a big part of the elderly. It’s estimated that half of women and a quarter of men over 50 will have an osteoporotic fracture in their lifetime.
How Osteoporosis Affects Bone Health
Osteoporosis harms bone health by lowering bone density and messing with the bone’s structure. This increases the risk of fractures. Bones are always being remade, but in osteoporosis, this process is out of balance, leading to bone loss.
| Aspect of Bone Health | Normal Bone | Osteoporotic Bone |
| Bone Density | High | Low |
| Microarchitecture | Intact | Disrupted |
| Fracture Risk | Low | High |
Treatment Objectives and Outcome Measures
The main goals of treating osteoporosis are to lower fracture risk, slow disease progress, and improve life quality. Doctors check bone mineral density (BMD) changes, monitor fractures, and look at overall health.
Bisphosphonate drugs are a common treatment for osteoporosis. They aim to reduce bone loss and boost BMD. Other options include lifestyle changes, supplements, and other medications.
Diagnosing Osteoporosis: The First Step to Treatment
Getting a correct diagnosis of osteoporosis is key to managing it well. It involves a doctor’s evaluation, looking at your medical history, and certain tests.
Bone Mineral Density Testing
Bone Mineral Density (BMD) tests are vital for spotting osteoporosis. They check the minerals in your bones, like calcium, to see how healthy they are. Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) is the main method used.
DXA scans are non-invasive and quickly check bone density. They help not just in diagnosing but also in tracking how well treatments work.
FRAX Score and Fracture Risk Assessment
The FRAX score is a tool for figuring out fracture risk. It looks at age, sex, weight, height, past fractures, family history, and BMD.
“The FRAX tool has been shown to improve the prediction of fracture risk and guide treatment decisions in patients with osteoporosis.”
It calculates the chance of a major osteoporotic fracture in 10 years. Doctors use this score to decide if treatment is needed and how strong it should be.
When to Begin Treatment
Deciding when to start treatment for osteoporosis depends on several things. These include BMD test results, FRAX score, and personal risk factors.
- Those who have had osteoporotic fractures usually start treatment right away.
- People with a high FRAX score, showing a high fracture risk, might also start treatment early.
- Postmenopausal women and men over 50 are at high risk and often need early treatment.
Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly lower fracture risk. It also improves life quality for those with osteoporosis.
First-Line Pharmaceutical Treatment: Bisphosphonates
Bisphosphonates are seen as the first choice for treating osteoporosis. They help by stopping bone loss, which increases bone density. This makes bones stronger and less likely to break.
Alendronate Weekly Pill (Fosamax)
Alendronate, or Fosamax, is a common bisphosphonate. It’s taken once a week. Studies show it lowers the risk of fractures in the spine, hips, and other areas.
Risedronate Oral Treatment (Actonel)
Risedronate, or Actonel, is another bisphosphonate for osteoporosis. It comes in weekly or monthly pills. It helps prevent spine fractures and is safe to use.
Zoledronic Acid Infusion (Reclast)
Zoledronic acid, or Reclast, is given yearly through an IV. It’s good for those who can’t take pills or have stomach problems. It helps prevent fractures and boosts bone density in women after menopause.
Efficacy and Safety Profile
Bisphosphonates are known for their effectiveness and safety. But, they can cause stomach problems, muscle pain, and, very rarely, jaw damage. It’s important to watch for these side effects and choose the right patient for treatment.
| Bisphosphonate | Dosing Frequency | Fracture Risk Reduction |
| Alendronate (Fosamax) | Weekly | Significant reduction in vertebral, non-vertebral, and hip fractures |
| Risedronate (Actonel) | Weekly or Monthly | Reduces risk of vertebral fractures |
| Zoledronic Acid (Reclast) | Annual Infusion | Reduces risk of vertebral, non-vertebral, and hip fractures |
RANK Ligand Inhibitors: Denosumab Injection Therapy
RANK ligand inhibitors, like denosumab, are key in fighting osteoporosis. Denosumab is a special antibody that targets the RANK ligand. This protein helps in the growth and survival of osteoclasts, the bone-resorbing cells.
Mechanism of Action
Denosumab binds to the RANK ligand, stopping it from working. This action reduces the number and activity of osteoclasts. As a result, bone resorption goes down, and bone density increases.
Administration and Dosing Schedule

Denosumab is given as a subcutaneous injection every six months. This schedule helps keep bone resorption under control between doses. It’s a convenient option for patients.
Benefits and Possible Side Effects
Denosumab greatly lowers the risk of fractures in osteoporosis patients. But, it can cause side effects like low calcium levels, serious infections, skin issues, and rare fractures in the thigh.
Comparison with Bisphosphonates
Denosumab is an alternative to bisphosphonates, the usual first choice for osteoporosis. Both treatments reduce fracture risk, but denosumab works differently. It might be better for those who can’t take bisphosphonates or have certain health issues.
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action | Dosing Schedule | Fracture Risk Reduction |
| Denosumab | RANK ligand inhibition | Every 6 months | Significant reduction in vertebral, non-vertebral, and hip fractures |
| Bisphosphonates | Inhibition of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption | Weekly or monthly oral; yearly IV infusion | Reduces risk of vertebral, non-vertebral, and hip fractures |
Anabolic Agents for Severe Osteoporosis
Anabolic agents are a new hope for those with severe osteoporosis. They help grow bone by boosting bone formation. This makes bones stronger and less likely to break.
Teriparatide Daily Injection (Forteo)
Teriparatide, known as Forteo, is a daily injection. It makes bones denser by mimicking parathyroid hormone. This leads to new bone growth.
Key benefits of teriparatide include its ability to reduce vertebral and non-vertebral fractures in patients with severe osteoporosis.
Abaloparatide Osteoporosis Treatment (Tymlos)
Abaloparatide, or Tymlos, is another treatment for osteoporosis. It’s a protein that helps bones grow.
Studies show abaloparatide cuts down vertebral fractures and boosts bone density in postmenopausal women.
Romosozumab Bone Therapy (Evenity)
Romosozumab, or Evenity, is a new therapy. It targets the sclerostin pathway to grow bones and reduce bone loss. It’s shown to lower vertebral fracture risk.
Notably, romosozumab is given monthly. It quickly increases bone density.
Comparing Efficacy of Anabolic Treatments
It’s important to compare these treatments. Look at how they affect bone density, fracture risk, and safety. Each has its own schedule, side effects, and best patients.
- Teriparatide and abaloparatide are both parathyroid hormone analogs with daily injection schedules.
- Romosozumab offers a monthly dosing regimen and acts through a different mechanism.
Choosing a treatment depends on the patient’s needs and health history.
Hormone Replacement Therapy for Osteoporosis
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is often talked about for managing osteoporosis. It has benefits and risks that need careful thought. Osteoporosis weakens bones, a big worry for women after menopause because estrogen levels drop.
Benefits for Postmenopausal Women
HRT can help manage osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. It adds estrogen, which their bodies don’t make enough of anymore. The main advantage of HRT is that it helps keep or even increase bone mineral density. This lowers the chance of bone fractures.
- Reduces the risk of osteoporotic fractures
- Helps in maintaining bone density
- Can alleviate menopausal symptoms
Risks and Contraindications
Even though HRT has benefits, it also has risks. It can increase the risk of breast cancer, heart problems, and blood clots. It’s important to think about these risks and how they compare to the benefits for each person.
- Assess the risk of breast cancer and cardiovascular diseases
- Consider family medical history
- Evaluate the presence of other health conditions
Current Recommendations and Guidelines
Experts say HRT might be a good choice for postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, if they’re at high risk of breaking bones. The choice to start HRT should be based on a detailed look at the patient’s risk factors, medical history, and what they prefer.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) and other guidelines suggest using the lowest dose of HRT for the shortest time needed. It’s important to keep an eye on how the treatment is working and make changes as needed.
Essential Supplements for Bone Health
Supplements are key for keeping bones strong and preventing osteoporosis. As we get older, our bones naturally lose density and strength. This makes taking supplements important for bone health.
Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
Calcium and vitamin D are vital for bones. Calcium helps build and keep bones strong. Vitamin D makes sure the body absorbs calcium well. Studies show that enough calcium and vitamin D can lower the risk of fractures in older people.
Adults need about 1,000 mg of calcium daily, more for women over 50. Vitamin D intake should be 600-800 IU each day. Always talk to a doctor about the right supplements for you.
Vitamin K2 Supplements for Bone Strength
Vitamin K2 is important for bone health. It helps direct calcium to bones, not soft tissues. Research shows vitamin K2 can boost bone density and lower fracture risk. The right dose varies based on individual needs and health.
Magnesium Bone Support
Magnesium is vital for bone health. It helps manage calcium and bone mineralization. Enough magnesium is linked to higher bone density and less osteoporosis risk. Men need about 400-420 mg, and women need 310-320 mg daily.
Proper Dosing and Timing
Getting the right amount and timing of supplements is key. It’s best to take calcium and magnesium in divided doses to improve absorption. Vitamin D works best with a fatty meal. A doctor can help figure out the best schedule for you.
Knowing how these supplements work and following the right dosing can help keep bones healthy. This reduces the chance of osteoporosis.
The Best Osteoporosis Treatment Approaches by Patient Profile
When it comes to osteoporosis, the right treatment depends on who you are. Different people need different plans to manage their condition well.
Treatment for Postmenopausal Women
Women after menopause often face osteoporosis due to lower estrogen levels. Estrogen replacement therapy and bisphosphonates are common treatments. The choice depends on the patient’s health history and risk factors.
A study showed both treatments can lower fracture risk in postmenopausal women. But, the best choice should match the patient’s unique needs and health.
Men with Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis in men is often missed and not treated enough. Bisphosphonates are the main treatment for men, just like for women after menopause. Teriparatide might be an option for those at high risk of fractures.
Before starting treatment, it’s important to check fracture risk and bone density. Diet and exercise are also key in managing osteoporosis in men.
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Long-term use of glucocorticoids can cause osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates are the first choice to prevent and treat this type of osteoporosis. People on long-term glucocorticoids should be checked for fracture risk and considered for preventive therapy.
| Treatment | Patient Group | Efficacy |
| Bisphosphonates | Postmenopausal Women, Men | High |
| Teriparatide | Men, High-Risk Patients | High |
| Estrogen Replacement | Postmenopausal Women | Moderate |
Young Adults with Osteoporosis
Young adults with osteoporosis need a special approach. It’s about finding and treating the underlying causes. This might include hormonal imbalances, lifestyle factors, or genetic conditions.
In some cases, bisphosphonates might be used, but with careful thought due to long-term effects on bones.
Treatment for young adults should be very personalized. It should consider the specific cause of osteoporosis and the patient’s overall health.
Exercise Regimens for Strengthening Bones
Regular physical activity is key for strong bones and preventing fractures. It boosts bone density and improves physical function. This reduces the risk of falls and fractures. A good exercise plan should mix resistance training, weight-bearing exercises, and balance training.
Resistance and Strength Training Benefits
Resistance and strength training are vital for bone health. They make muscles and bones work harder, leading to bone growth and density. Activities like weight lifting, resistance bands, and bodyweight exercises are great. Regular resistance training boosts bone health and muscle strength.
Weight-Bearing Exercise Recommendations
Weight-bearing exercises strengthen bones by working against gravity. Walking, hiking, jogging, climbing stairs, and dancing are good examples. These activities can be adjusted for any fitness level and improve bone density. Weight-bearing exercises are great for the hips and lower spine.
Balance Training for Fall Prevention
Balance training is key to prevent falls, a major risk for fractures in osteoporosis patients. Tai chi, single-leg stands, and heel-to-toe walks challenge balance. They improve stability and reduce fall risk. Adding balance training to your routine boosts physical function and confidence.
Creating an Effective Exercise Routine
To build a good exercise routine for bone health, mix different exercises. Aim for 30 minutes of exercise daily, including resistance training, weight-bearing activities, and balance exercises. Always consult a healthcare provider or fitness expert to create a routine that fits your needs. Consistency and progression are essential for bone health benefits.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Bone Health
Changing your lifestyle can help a lot with bone health. Making these changes can make your bones stronger and lower the chance of breaking them.
Dietary Considerations
Eating foods rich in calcium and vitamin D is key for strong bones. Dairy, leafy greens, and fortified cereals are good choices. A top osteoporosis expert says, “A diet full of calcium and vitamin D is very important for bones.”
But, don’t overdo it with caffeine and sodium. They can block calcium from being absorbed. Drinking enough water is also important for bone health.
Smoking Cessation and Alcohol Moderation
Stopping smoking is a big step for bone health. Smoking harms bone cells and lowers bone density, making breaks more likely. Quitting can greatly improve your health and bone strength.
Drinking alcohol in moderation is also key. Too much alcohol can hurt bone health by slowing down bone growth and speeding up bone loss. Drinking in small amounts can help avoid these problems.
“Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake are among the most effective lifestyle changes for supporting bone health and reducing fracture risk.”
Fall Prevention Strategies at Home
Stopping falls is very important, even more so for those with osteoporosis. Making a few changes at home can help a lot. Remove things that could trip you up, make sure the lights are good, and put up handrails where needed.
Also, doing exercises that improve balance and strength can help you stay steady. A healthcare expert notes, “Preventing falls is key to staying independent and avoiding fractures.”
By making these lifestyle changes, you can help keep your bones strong and improve your overall health.
Fracture Risk Reduction Strategies
Managing osteoporosis means finding ways to lower the risk of fractures. This involves a mix of strategies to tackle different factors that lead to fractures.
Assessing and Addressing Fall Risk
Checking for fall risk is key to preventing fractures. Doctors use tools to see who’s at risk. They look at age, medical history, and physical health.
- Reviewing medications that may affect balance or blood pressure
- Assessing vision and hearing impairments
- Evaluating muscle strength and balance
Fixing these risks might mean physical therapy, better vision care, or changing meds.
Home Safety Modifications
Changing your home to make it safer is another important step. Simple changes can make a big difference.
- Removing tripping hazards such as loose rugs or cords
- Improving lighting, specially in stairways and hallways
- Installing handrails in key spots
These changes can make your home safer.
Protective Equipment and Assistive Devices
Wearing protective gear and using assistive devices can also help. Hip protectors, for example, can help prevent hip fractures if you fall.
“The use of hip protectors has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of hip fractures among older adults at high risk of falling.”
– Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma
Other devices, like canes or walkers, can also help keep you stable and reduce falls.
Post-Fracture Care and Prevention
After a fracture, it’s vital to take steps to prevent more. This might mean better osteoporosis treatment, safer home, and better physical health.
Post-fracture care should also tackle any conditions that led to the fracture.
Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
It’s important to check how well osteoporosis treatment is working. This helps doctors make changes to help patients get better. Regular checks and updates to treatment plans are key.
Bone Density Monitoring Schedule
Checking bone density regularly is a big part of seeing if treatment is working. How often depends on the patient’s bone health, risk factors, and treatment.
Initial Assessment: The first bone density test sets a baseline at the start of treatment.
Follow-Up: Tests are usually done every 1-2 years. But, this can change based on what each patient needs.
Biochemical Markers of Bone Turnover
Biochemical markers also help see if treatment is working. They show how fast bones are being made or broken down.
- N-Telopeptide (NTX): Shows bone breakdown.
- C-Telopeptide (CTX): Also checks bone breakdown.
- Procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (P1NP): Measures bone formation.
When to Consider Treatment Changes
Changing treatment might be needed if the current one isn’t working well. This includes if there’s a lot of bone loss or a higher risk of fractures. Doctors also adjust plans if patients can’t tolerate side effects or if their health changes.
Indicators for Change: A big drop in bone density, fractures, or bad side effects mean it’s time to think about changing treatment.
Managing Side Effects of Osteoporosis Medications
Managing side effects is key to osteoporosis treatment. It lets patients stick to their medication plans. Osteoporosis drugs are vital for bone health but can have side effects. Knowing these and how to handle them is vital for good treatment.
Common Side Effects and Mitigation Strategies
Osteoporosis drugs can cause side effects like stomach issues. Bisphosphonates, a common type, can lead to stomach pain and esophagus problems. To avoid these, patients should drink a full glass of water and stay upright for 30 minutes after taking the drug.
Denosumab, another drug, can cause low calcium levels. Eating enough calcium and vitamin D can help prevent this. If patients feel muscle cramps or tingling, they should tell their doctor right away.
| Medication Class | Common Side Effects | Mitigation Strategies |
| Bisphosphonates | Gastrointestinal issues | Take with water, remain upright |
| RANK Ligand Inhibitors | Hypocalcemia | Ensure adequate calcium and vitamin D intake |
Rare but Serious Complications
Some osteoporosis drugs can lead to serious problems. Bisphosphonates, for example, can cause jaw problems and bone fractures. To avoid jaw issues, keep teeth clean, avoid dental work, and tell dentists about drug use.
Patients on bisphosphonates for a long time should watch for thigh or groin pain. Regular checks with doctors can help prevent these risks.
Drug Holidays: When and Why
Drug holidays are a strategy to reduce risks from osteoporosis drugs. After 3 to 5 years, patients at low risk might stop treatment. This decision depends on how likely they are to break a bone.
During a drug holiday, patients are watched closely for bone density changes. This approach balances risk and bone health.
Comprehensive Osteoporosis Patient Care
Osteoporosis care has changed a lot. Now, it includes a team effort, teaching patients, and support groups. This new way of caring is key to managing osteoporosis well and helping patients get better.
Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach
A team of doctors works together to treat osteoporosis. This team includes primary care doctors, endocrinologists, orthopedic specialists, and physical therapists. This teamwork makes sure patients get care that fits their needs.
The benefits of this team effort are many:
- It helps find and treat problems better.
- Patients learn more and get more support.
- It also helps manage other health issues and side effects of medicine.
Patient Education and Self-Management
Teaching patients is a big part of osteoporosis care. When patients know how to manage their condition, they can stick to their treatment plans. They can also make lifestyle changes that help their bones.
Important things to teach patients include:
| Topic | Description | Benefits |
| Medication adherence | Understanding the importance of taking medications as prescribed | Improved treatment outcomes |
| Lifestyle modifications | Making changes to diet, exercise, and smoking habits | Enhanced bone health |
| Fall prevention | Strategies for reducing fall risk at home | Reduced fracture risk |
Support Resources and Services
Support groups and services are very important for osteoporosis care. These can include:
- Patient support groups
- Online educational resources
- Home safety assessments
Healthcare providers offer these resources to help patients manage their condition. This improves their quality of life.
Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials
Osteoporosis treatment is changing fast with new therapies and trials. Research is finding new ways to help bone health. This means better care for those with osteoporosis.
New Medications in Development
New medicines are being made to treat osteoporosis. These include:
- Sclerostin inhibitors: Drugs that help bones grow by blocking sclerostin.
- Cathepsin K inhibitors: Medicines that stop cathepsin K, helping bones stay strong.
- Novel bisphosphonates: New ways to make bisphosphonates to help bones and reduce side effects.
These new medicines could lead to better treatments with fewer side effects.
Novel Treatment Approaches
Researchers are also looking at new ways to treat osteoporosis. Some ideas include:
- Personalized medicine: Treating each patient based on their genes and body chemistry.
- Combination therapies: Using more than one treatment at a time for better results.
- Stem cell therapies: Studying how stem cells can help grow new bone.
These new ideas aim to improve current treatments and help patients more.
Participating in Clinical Trials
Some patients can try new treatments in clinical trials. These trials test if new medicines are safe and work well. Talking to a doctor about the risks and benefits is important.
As osteoporosis treatment keeps getting better, knowing about new treatments and trials is key. It helps both patients and doctors make the best choices for care.
Conclusion: Creating a Personalized Long-Term Osteoporosis Management Plan
Managing osteoporosis well means having a plan that fits you. This plan should include treatments and lifestyle changes. Knowing about osteoporosis and its goals helps you and your doctor make a plan just for you.
A good osteoporosis care plan has medicines like bisphosphonates and RANK ligand inhibitors. It also includes calcium and vitamin D supplements. Exercise and diet changes are key to keeping bones strong.
For a plan to work, you need to check in regularly. This means checking bone density, looking at fracture risk, and handling medicine side effects. A team effort in osteoporosis care can lower fracture risk and keep bones healthy.
Having a plan that’s just for you is key to caring for osteoporosis. It helps you manage your condition and live better.
FAQ
What is the most effective treatment for osteoporosis?
Treating osteoporosis often means using a mix of medicines, lifestyle changes, and supplements. Bisphosphonates, like alendronate and risedronate, are usually the first choice.
How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
Doctors use bone mineral density tests, like DXA, to find osteoporosis. They also use the FRAX score to check fracture risk.
What are the benefits of denosumab injection therapy?
Denosumab injections help grow bone density. They also lower the chance of fractures in people with osteoporosis.
What are the possible side effects of bisphosphonates?
Bisphosphonates can cause stomach problems, like esophagitis and dyspepsia. But, they can also lead to rare but serious issues like jaw osteonecrosis and atypical femoral fractures.
How can I support bone health through diet and supplements?
For strong bones, take calcium, vitamin D, vitamin K2, and magnesium. Eating fruits, veggies, and whole grains also helps.
What exercises are best for strengthening bones?
Doing resistance training, weight-bearing exercises, and balance training can make bones stronger. This reduces fracture risk.
How can I reduce my risk of falls and fractures?
To avoid falls and fractures, check your fall risk, make your home safer, and use protective gear and devices.
How often should I have my bone density monitored?
How often you need bone density checks depends on your osteoporosis level and treatment success. Usually, it’s every 1-2 years.
What are the benefits of hormone replacement therapy for osteoporosis?
Hormone therapy can ease menopause symptoms and help bones in postmenopausal women. But, it’s important to consider the risks and when it’s not safe.
Can I participate in clinical trials for new osteoporosis treatments?
Yes, people with osteoporosis might join clinical trials for new treatments. This can give them access to new therapies and help research.
How can I manage side effects of osteoporosis medications?
To handle side effects, know the common and rare issues, use strategies to lessen them, and consider drug breaks when needed.
What is the role of a multidisciplinary treatment approach in osteoporosis care?
A team of healthcare experts working together is key in osteoporosis care. They offer education, self-care tips, and support resources.
References
- Zhao, J. G., et al. (2023). Plant-derived natural medicines for the management of osteoporosis. Phytomedicine, 110, 154286.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2225411023000846























