
Bladder cancer is a big health issue worldwide, hitting many people, mostly older adults. It’s when cells in the bladder grow out of control. Many things can affect how common it is, like smoking, chemicals, and genes.
View 7 types of bladder lesions with pictures. Learn the key visual differences between benign conditions and cancerous tumors.
Bladder cancer rates differ around the globe, with more cases in developed countries. In the U.S., it’s the fourth most common cancer in men.
Things that increase your risk include smoking, family history, and chemicals. Smoking is the biggest risk, causing about half of all cases.
Knowing how bladder cancer spreads helps us find better ways to stop it and treat it. We need more research to find the causes and ways to lower its impact.
By understanding the many factors that lead to bladder cancer, we can aim to lower its numbers. This will help improve the lives of those dealing with it.
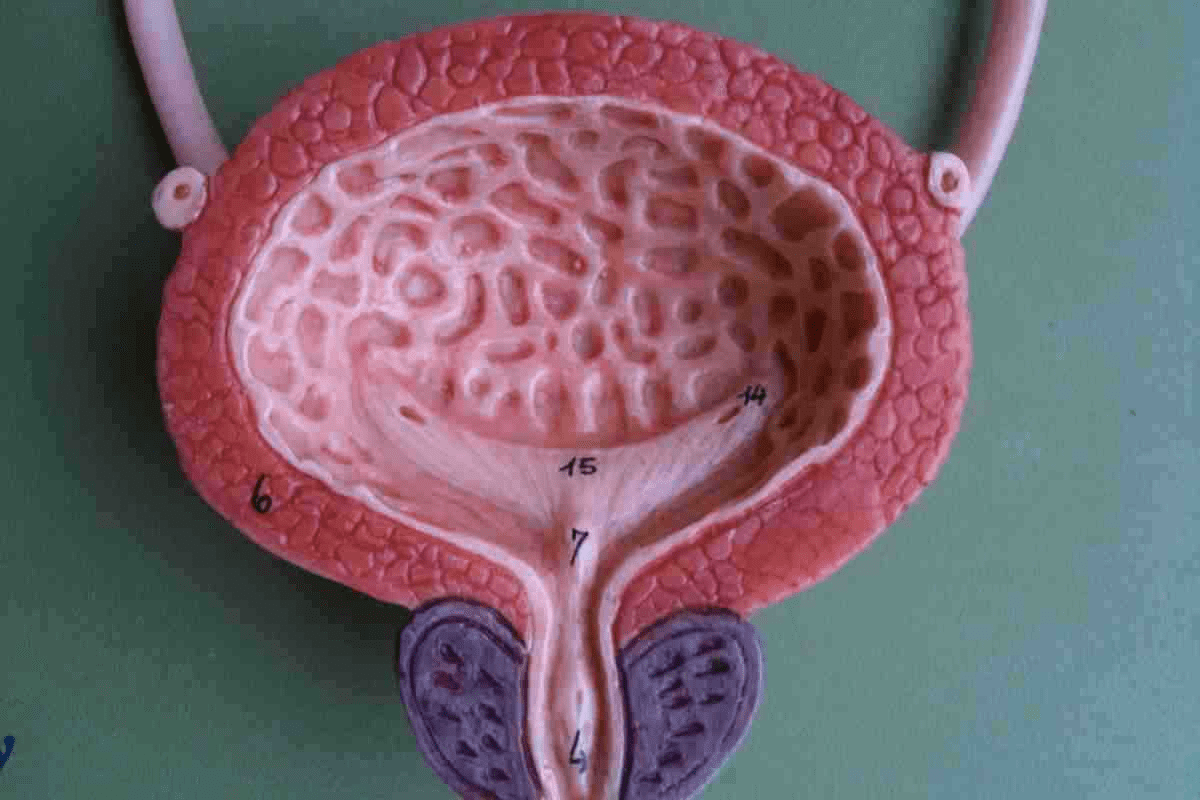
Knowing the bladder’s anatomy is key to finding and treating bladder lesions. The bladder is a complex organ. Its structure is important for spotting and diagnosing lesions.
The bladder trigone, or the bladder’s trigone, is a vital spot. It’s a triangle at the bladder’s base, marked by the two ureteric openings and the internal urethral opening. This area is often where bladder lesions appear.
The bladder trigone is a key spot for lesions. Its special shape and location make it more likely to have growths, both good and bad.
Other parts of the bladder can also get lesions. These include the bladder walls, the dome, and the areas around the ureteric openings. Knowing these areas well is important for treating bladder problems.
Lesions in these spots can affect a patient’s health a lot. Getting the right diagnosis is key for the right treatment. We’ll look at the different kinds of lesions and why they matter.
Bladder lesions can come from genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Smoking is a big risk because it harms the bladder lining and raises cancer risk. Jobs in dye, rubber, and textile industries also up the risk. Chronic inflammation, from infections or other causes, can lead to bladder lesions too.
Knowing these risks helps in prevention and early detection. Avoiding smoking, managing work exposures, and lowering chronic inflammation can help. This way, people can lower their risk of getting bladder lesions.
Urothelial carcinoma is a type of cancer that affects the bladder. It is the most common type of bladder cancer.
Symptoms include blood in the urine, frequent need to urinate, and pain while urinating. Doctors use imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans for diagnosis. Sometimes, a biopsy is needed.
Treatment options vary based on the cancer’s stage and grade. For early-stage cancer, surgery is often the choice. More advanced cases might need chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Squamous cell carcinoma starts in squamous cells. It’s not as common as other bladder cancers but is very aggressive.
To diagnose squamous cell carcinoma, doctors look at risk factors, symptoms, and cell structure. Chronic irritation or infection increases the risk.
Diagnosis relies on cell examination. Treatment choices depend on the cancer’s stage and spread.
Adenocarcinoma of the bladder is a rare and aggressive cancer. It comes from glandular cells and makes up a small part of bladder cancer cases.Visual CharacteristicsIt’s hard to spot adenocarcinoma because its symptoms are not clear.
But, some signs can help doctors find it. On scans like CT or MRI, it looks like a mass or thickening in the bladder wall.Histological FeaturesThe cells in adenocarcinoma form gland-like structures. They might look like acini or tubules. The tissue can also have a cribriform pattern.Key Distinguishing FactorsAdenocarcinoma is different from other bladder cancers because it grows fast. It’s more likely to spread and invade other parts of the body.Treatment Options
Doctors use a mix of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation to treat adenocarcinoma. The treatment plan depends on how far the cancer has spread.
Knowing about adenocarcinoma helps doctors give better care to patients. This rare and aggressive bladder cancer needs a careful approach.
Urothelial papilloma is a rare, benign tumor found in the bladder. It shows up as a small, solitary growth on the bladder wall. The exact cause is not known, but it might be linked to chronic irritation or other factors.
To diagnose urothelial papilloma, doctors use cystoscopy and biopsy. Treatment often involves surgically removing the tumor. Sometimes, more steps are needed to stop it from coming back.
It’s important to tell urothelial papilloma apart from other bladder issues, like cancer. A detailed check-up and diagnosis by a healthcare expert are key. This ensures the right treatment and management.
Nephrogenic adenoma is a rare, benign lesion. It often occurs due to chronic irritation or injury in the urinary tract. Doctors diagnose it through a detailed examination of tissue samples.
The main goal of treatment is to fix the issue that caused the lesion. This approach helps in managing and possibly curing the condition.
Cystitis cystica and glandularis are bladder conditions. They cause symptoms and need the right diagnosis and treatment. Knowing about these conditions helps manage them better.
We’ve looked at the different kinds of bladder lesions, both good and bad. Knowing the differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer and other issues.
Spotting the signs of bladder lesions early can make a big difference. Doctors can then create specific plans to help patients with bladder cancer.
Managing bladder lesions well means understanding risks like smoking and certain jobs. It also means knowing about the various types of lesions.
By focusing on education and awareness, we can help people stay healthy. We urge patients and doctors to keep up with new diagnosis and treatment methods.
Common bladder lesions include urothelial carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Adenocarcinoma is also common. Urothelial papilloma and inverted papilloma are benign types. Nephrogenic adenoma and cystitis cystica and glandularis are also seen.
The bladder trigone is a key area for lesions. Its anatomy helps us understand and manage bladder lesions.
Pictures of benign tumors like urothelial papilloma help doctors. They help tell benign from malignant lesions, ensuring the right treatment.
Smoking and work exposures are big risks. Chronic inflammation also increases the risk.
Smoking is a major risk for bladder cancer. Quitting can lower this risk.
Pictures show urothelial carcinoma’s look. This helps doctors diagnose and differentiate it from other cancers.
Adenocarcinoma is diagnosed by its look, histology, and images. These help doctors tell it apart from other cancers.
Cystitis cystica and glandularis are benign but can look like cancer. Pictures and histology help tell them apart from cancer.
Yes, some bladder lesions are benign. Urothelial papilloma and inverted papilloma are examples. Pictures and histology help tell them from cancer.
Knowing the types of bladder lesions is key for right diagnosis and treatment. It helps doctors give better care to patients.
Types of bladder cancer – https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/bladder-cancer/types-stages-grades/types
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us