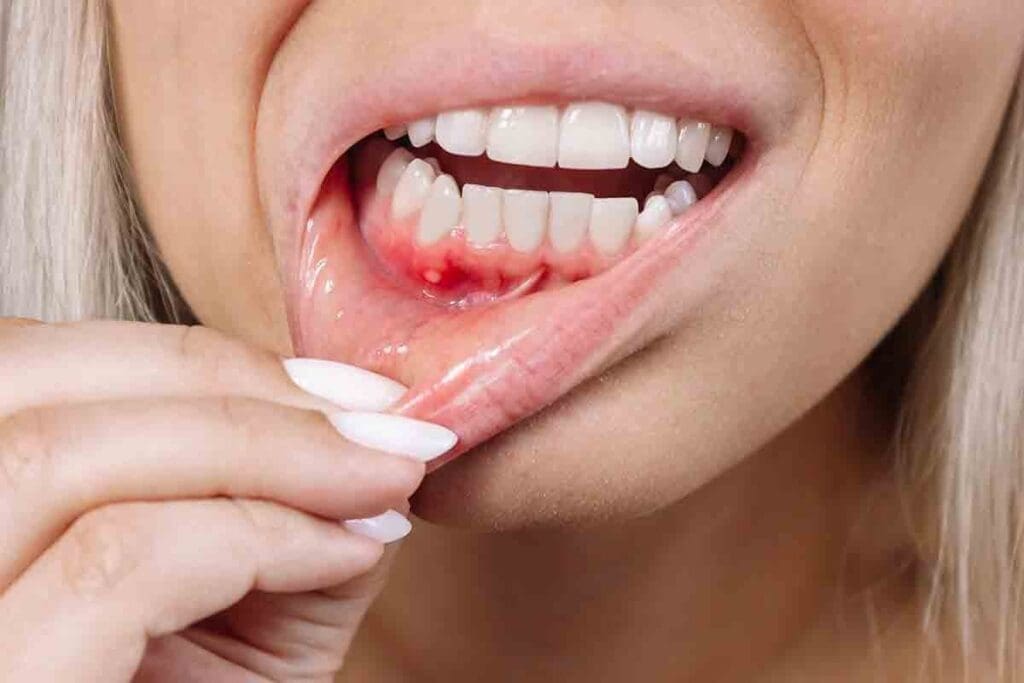
Bleeding disorders are conditions that make it hard for the body to clot blood. This can cause abnormal or uncontrollable bleeding after injuries, surgeries, or even without any reason.Learn bleeding disorder signs, effects on clotting, and key causes.
Usually, when a blood vessel gets hurt, platelets stick together to form a plug. Clotting factors then work together to make a fibrin clot. But, people with bleeding disorders might not have enough or normal platelets. They might also have low levels of clotting proteins, making it hard to stop bleeding.
Key Takeaways
- Bleeding disorders affect the body’s ability to clot blood.
- These conditions can lead to heavy and prolonged bleeding.
- Symptoms include easy bruising, bleeding gums, and unexplained nosebleeds.
- Bleeding disorders can be inherited or acquired.
- Proper diagnosis and treatment are key to managing bleeding disorders.
Understanding Blood Clotting and Haemostatic Disorders
It’s important to know how blood clotting works to understand bleeding and haemostatic disorders. Blood clotting, or coagulation, is a complex process. It involves platelets and many plasma proteins, called clotting or coagulation factors.
The Normal Blood Clotting Process
The blood clotting process starts when there’s an injury to blood vessels. It involves several steps, like vascular spasm and platelet plug formation. Platelets are key in the early stages, forming a plug at the injury site.
Then, coagulation factors take over, leading to a fibrin clot. This clot stabilizes the platelet plug.
- Platelet activation and aggregation
- Coagulation cascade involving various clotting factors
- Fibrin clot formation
How Bleeding Disorders Disrupt Hemostasis
Bleeding disorders make it hard for the body to form blood clots. This can happen because of problems with platelets or coagulation factors. For example, von Willebrand disease, hemophilia A and B, and rare factor deficiencies are blood not clotting conditions.
Some common issues with bleeding disorders include:
- Low platelet count or dysfunctional platelets
- Deficiencies in specific coagulation factors
- Inherited or acquired conditions affecting hemostasis
Understanding these disruptions is key to diagnosing and managing bleeding disorders.
What Are Bleeding Disorders: Definition and Overview

Bleeding disorders are conditions where blood can’t clot right. This leads to bleeding that doesn’t stop or happens on its own. These issues can really affect someone’s life, causing symptoms that range from mild to severe.
Medical Definition of Bleeding Disorders
Bleeding disorders are health issues that make it hard for blood to clot. Hemostasis is a complex process involving multiple factors and pathways that work together to stop bleeding when a blood vessel is injured. These disorders can be caused by a lack or problem with these clotting factors.
Primary vs. Secondary Hemostasis Defects
Hemostasis is split into primary and secondary parts. Primary involves the formation of a platelet plug. Secondary is the coagulation cascade, leading to a fibrin clot. Bleeding disorders can result from defects in either primary or secondary hemostasis, or both. For example, von Willebrand disease affects primary hemostasis, while hemophilia A and B are related to secondary hemostasis issues.
Global Prevalence and Epidemiology
Bleeding disorders can be inherited or caused by other factors like liver disease or certain medications. Millions worldwide are affected, with many cases not yet diagnosed. The prevalence of specific bleeding disorders varies; for example, von Willebrand disease is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. Understanding the epidemiology of bleeding disorders is key for diagnosis, treatment, and management.
Symptoms of bleeding disorders include bleeding into joints or muscles, easy bruising, heavy menstrual bleeding, and persistent nosebleeds. Spotting these symptoms is important for diagnosing and managing bleeding disorders effectively.
Types of Bleeding Disorders
It’s important to know about the different bleeding disorders. They affect how the body makes blood clots. This can lead to bleeding that doesn’t stop or happens on its own.
Von Willebrand Disease: The Most Common Bleeding Disorder
Von Willebrand disease is the most common bleeding disorder globally. It’s a lifelong issue caused by a lack or problem with von Willebrand factor. This protein is key for blood to clot. People with it might bruise easily, get nosebleeds, or have heavy periods.
Hemophilia A and B
Hemophilia A and B are genetic conditions. They happen when there’s not enough clotting factor VIII or IX. Hemophilia A is more common. Both can cause bleeding in joints and muscles, leading to pain and disability if not treated.
Rare Factor Deficiencies
Rare factor deficiencies include issues with factors II, V, VII, X, XI, and XIII. These are less common than hemophilia and von Willebrand disease. They can cause serious bleeding problems. Finding the right factor deficiency often needs special lab tests.
In summary, knowing about bleeding disorders like von Willebrand disease, hemophilia A and B, and rare factor deficiencies is key. Each has its own signs and treatment options.
Bleeding Disorder Symptoms and Warning Signs
It’s important to know the signs of bleeding disorders early. These disorders can show up in different ways, affecting people differently. Spotting these symptoms early can help get the right treatment fast.
Easy Bruising and Prolonged Bleeding
Easy bruising is a common sign of bleeding disorders. People with these disorders might bruise easily, even from small bumps. Bleeding that lasts a long time after injuries or surgeries is another key symptom.
Spontaneous Bleeding Episodes
Some bleeding disorders cause bleeding without any reason. These sudden episodes can be scary and need quick medical help.
Joint and Muscle Bleeding
Bleeding into joints or muscles is a sign of certain bleeding disorders, like hemophilia. It can cause pain, swelling, and make it hard to move.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding and Nosebleeds
Women with bleeding disorders might have very heavy periods. They might also get nosebleeds that last a long time.
The table below lists common symptoms of bleeding disorders:
| Symptom | Description |
| Easy Bruising | Bruising easily with minor trauma |
| Prolonged Bleeding | Bleeding that continues after injuries or surgeries |
| Spontaneous Bleeding | Bleeding episodes without apparent cause |
| Joint and Muscle Bleeding | Bleeding into joints or muscles, causing pain and swelling |
| Heavy Menstrual Bleeding | Excessive bleeding during menstruation |
| Nosebleeds | Frequent or prolonged nosebleeds |
Knowing these symptoms is key to getting the right treatment for bleeding disorders. If you or someone you know shows these signs, seeing a doctor is very important.
Causes of Blood Not Clotting Conditions
It’s important to know why bleeding disorders happen. They can come from inherited or acquired causes. Knowing this helps in treating them better.
Inherited Genetic Causes
Bleeding disorders passed down through genes are inherited. Von Willebrand disease and Hemophilia A and B are examples. These conditions affect blood clotting because of missing or faulty clotting factors.
Hemophilia A is caused by a lack of factor VIII. Hemophilia B is due to a deficiency of factor IX. The severity of these conditions varies, depending on the blood’s clotting factor levels.
Acquired Causes: Liver Disease and Vitamin K Deficiency
Acquired bleeding disorders develop over time. Liver disease is a major cause. The liver makes proteins needed for blood clotting. Diseases like cirrhosis can stop the liver from doing this.
Vitamin K deficiency is another cause. Vitamin K is needed for clotting factors. A lack of it can happen due to diet, malabsorption, or certain medications.
| Cause | Description | Impact on Clotting |
| Liver Disease | Impaired liver function due to disease or damage | Reduced production of clotting factors |
| Vitamin K Deficiency | Lack of vitamin K due to diet or malabsorption | Impaired production of clotting factors |
Blood Thinning Disease: Medication-Induced Bleeding Disorders
Some medications can cause bleeding disorders. Anticoagulant drugs, like warfarin, are meant to prevent clots but can cause bleeding. It’s important to manage them carefully.
Other drugs, like antibiotics and antiplatelet drugs, can also affect clotting. Patients on these should be closely watched by their doctors to avoid bleeding.
In conclusion, bleeding disorders come from genetic, acquired, and medication-induced factors. Understanding these causes is key to diagnosing and managing bleeding conditions effectively.
Diagnosing and Evaluating Bleeding Disorders
Diagnosing bleeding disorders is complex. It involves both clinical checks and lab tests. Getting the diagnosis right is key for good treatment.
Initial Evaluation and Medical History
The first step is a detailed medical history and physical check. This helps spot signs like easy bruising or long bleeding times. It also looks for sudden bleeding episodes.
Laboratory Tests for Coagulation Disorders
Labs are essential for finding coagulation disorders. Tests include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check platelet numbers
- Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT) for the intrinsic clotting pathway
- Prothrombin Time (PT) for the extrinsic pathway
- Thrombin Time to see fibrinogen to fibrin conversion
- Platelet Aggregation Tests for platelet function
These tests find clotting factor issues or other problems.
Specialized Testing for Specific Disorders
Some bleeding disorders need special tests. For instance, von Willebrand disease tests von Willebrand factor levels. Hemophilia A and B tests factor VIII and IX levels.
Treatment Approaches for Hemorrhagic Disorders
Managing bleeding disorders requires a mix of treatments. This includes replacing missing clotting factors and using medications to help blood clot. Each treatment plan is made to fit the disorder type, its severity, and the patient’s needs.
Replacement Therapy and Factor Concentrates
Replacement therapy is key for some bleeding disorders, like hemophilia A and B. It involves giving the missing clotting factor to the blood. Clotting factor concentrates are used for this, and they can be given to prevent or treat bleeding.
Recombinant clotting factors are now more common. They are safer and work well. These products are made to act like natural clotting factors, lowering the risk of complications.
Medications to Promote Clotting
Medications also help with clotting and managing bleeding disorders. Desmopressin is a hormone that helps release clotting factors. It’s good for mild hemophilia A and some von Willebrand disease.
Antifibrinolytics help keep clots stable. They are often used with other treatments to improve their effect.
Management of “Can’t Stop Bleeding” Emergencies
Severe bleeding needs quick action to stop it. This might include clotting factor concentrates, fresh frozen plasma, or platelets. The choice depends on the bleeding cause.
Emergency management plans are vital for bleeding disorder patients. They should be made to fit the patient’s needs and medical history.
Surgical Considerations for Patients with Bleeding Disorders
Surgery for patients with bleeding disorders needs careful planning. Preoperative assessment helps figure out the best treatments to reduce bleeding risks.
Using clotting factor concentrates and other agents can make surgery safer. Post-surgery, it’s important to watch for any signs of bleeding or clotting problems.
Living with a Bleeding Disorder
Managing a bleeding disorder requires medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and support. People with these disorders can live active lives by taking precautions and understanding their condition.
Lifestyle Modifications and Precautions
Those with bleeding disorders must make big lifestyle changes to avoid bleeding. This means avoiding sports, wearing protective gear, and being careful every day.
Managing Bleeding Risks in Daily Activities
Even simple tasks can be hard with a bleeding disorder. Using sharp objects or doing activities that might hurt needs extra care. Changing daily routines and using protective gear can help.
| Activity | Precaution | Benefit |
| Cooking | Use blunt knives or protective gloves | Reduces risk of cuts |
| Gardening | Wear protective gloves and clothing | Minimizes risk of injury |
| Sports | Avoid contact sports; use protective gear | Decreases risk of bleeding episodes |
Support Resources and Patient Organizations
Support from patient groups and communities is key for those with bleeding disorders. These resources offer important info, emotional support, and advocacy.
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
Living with a bleeding disorder can affect your mind, causing anxiety and stress. Using strategies like mindfulness and getting professional help can help your mental health.
Key Coping Strategies:
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques
- Seeking support from mental health professionals
- Connecting with support groups
By using these strategies and making smart lifestyle choices, people with bleeding disorders can have fulfilling lives.
Conclusion
It’s important to understand bleeding disorders early. These conditions make it hard for the body to stop bleeding. This can lead to bleeding that doesn’t stop on its own.
With the right diagnosis and treatment, people with bleeding disorders can live full lives. Knowing the symptoms and causes is key. Also, finding the right treatment is important.
Managing bleeding disorders requires a detailed plan. This includes making lifestyle changes and taking steps to avoid bleeding. It also means having access to support and resources.
In conclusion, knowing about bleeding disorders can greatly improve life for those affected. With good management, people can do all they want without worrying about bleeding. This makes life better and safer.
FAQ
What is a bleeding disorder?
A bleeding disorder makes it hard for the body to stop bleeding. This leads to bleeding that lasts too long or is too much.
What are the most common types of bleeding disorders?
The most common types include von Willebrand disease, hemophilia A and B, and rare factor deficiencies.
What are the symptoms of a bleeding disorder?
Symptoms include easy bruising and bleeding that doesn’t stop. You might also have spontaneous bleeding, bleeding in joints and muscles, and heavy periods.
How are bleeding disorders diagnosed?
Doctors use a medical history, physical exam, and lab tests to diagnose. These tests include coagulation studies and tests for specific disorders.
What are the causes of bleeding disorders?
Causes include inherited genetic factors, conditions like liver disease, and vitamin K deficiency. Medications can also cause bleeding disorders.
How are bleeding disorders treated?
Treatment includes replacement therapy and clotting medications. It also covers managing bleeding emergencies and surgical considerations.
Can bleeding disorders be managed?
Yes, with the right treatment and lifestyle changes, people with bleeding disorders can manage their condition. They can lead active lives.
What lifestyle changes can help manage bleeding disorders?
Changes include avoiding injuries, staying healthy, and being careful with medications. These steps help manage bleeding disorders.
Are there support resources available for individuals with bleeding disorders?
Yes, there are support groups and patient organizations. They offer information, guidance, and emotional support.
How can I find a specialist to diagnose and treat bleeding disorders?
Ask your primary care doctor for a referral. Or contact a local hospital or medical center with a hematology or coagulation department.
Reference
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2023, August 3). Bleeding disorders: What are bleeding disorders? U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/bleeding-disorders




































