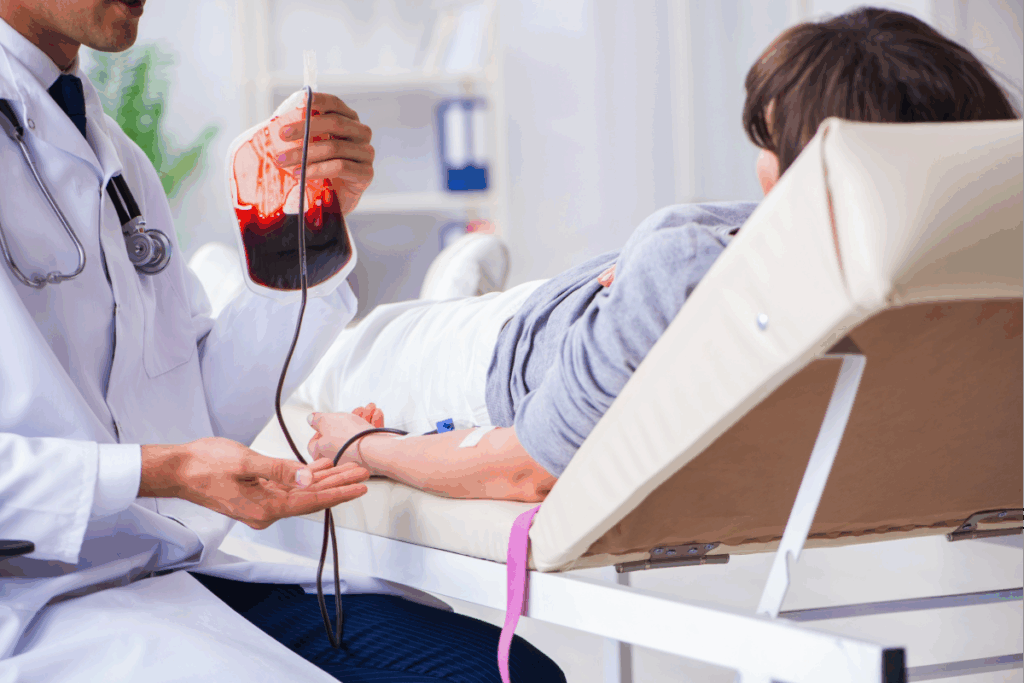
Getting a blood transfusion can save lives. But, it also makes people wonder about their hospital stay. How long you stay in the hospital after a transfusion depends on a few things. These include why you needed the transfusion and your overall health. Explaining the typical monitoring period and patient discharge timeline following a routine Blood transfusion procedure.
Having a transfusion can be scary. Patients often ask what happens next. The time you spend in the hospital after a transfusion depends on how complex your situation is. It also depends on how closely you need to be watched.
Key Takeaways
- The length of hospital stay after a blood transfusion varies based on individual patient needs.
- Patients undergoing major surgery may require longer hospital stays due to possible complications.
- Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication of major surgery that can affect how long you stay in the hospital.
- Knowing what affects your hospital stay can help manage your expectations.
- Close monitoring and proper care are key for a smooth recovery after a transfusion.
Understanding Blood Transfusions
A blood transfusion is a medical process where blood or blood parts are given to someone. It’s done to replace lost blood or to improve blood quality. This is key for treating many health issues, like those from surgeries, injuries, or blood diseases.
Doctors carefully think about whether a blood transfusion is right for a patient.
“Most patients with von Willebrand’s disease (VWD) have reduced plasma levels of antihemophilic factor procoagulant activity (VIIIAHF), antigen (VIIIAGN), and von Willebrand factor activity (VIIIvwF),”
This shows how complex some conditions are that might need blood transfusions.
What is a Blood Transfusion?
A blood transfusion is when blood or blood products are given to a patient. This can be whole blood, red blood cells, plasma, or platelets. It aims to fix the patient’s blood count, help tissues get oxygen, or fix blood clotting problems.
This happens in a hospital where doctors can watch the patient closely. The blood is given through an IV, and how fast it’s given is carefully watched to avoid bad reactions.
Reasons for Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are needed for many health issues. These include severe anemia, big blood loss from surgery or injury, bleeding disorders like hemophilia, and some cancers or treatments that harm the bone marrow. Also, patients with chronic blood cell problems might need transfusions.
There are many reasons for blood transfusions, and doctors decide based on a full check-up of the patient. Knowing why a transfusion is needed helps patients understand its importance.
The Procedure of Blood Transfusion
Getting a blood transfusion is more than just the transfusion itself. It includes careful preparation and monitoring. We make sure every step is taken to keep patients safe and the procedure effective.
Steps Involved in a Blood Transfusion
The blood transfusion process has several key steps:
- Pre-transfusion testing to ensure compatibility between the donor’s blood and the recipient’s blood.
- Administration of the blood product through an intravenous (IV) line.
- Monitoring the patient during the transfusion for any signs of adverse reactions.
Before starting, we do thorough checks. We verify the patient’s identity and the blood product details to avoid mismatches. The transfusion usually takes 1 to 4 hours, depending on the blood type and amount.
Monitoring During the Transfusion
We watch the patient’s vital signs closely during the transfusion. This includes heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature. We do this to quickly spot any issues.
| Monitoring Aspect | Description | Frequency |
| Vital Signs | Checking heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature. | Every 15-30 minutes |
| Adverse Reactions | Watching for signs of allergic reactions or other complications. | Continuously |
| Blood Component | Verifying the blood product being transfused. | At the start and end |
By managing each stage of the blood transfusion carefully, we reduce risks. This ensures the best outcomes for our patients.
Factors Affecting Hospital Stay
Your stay in the hospital after a blood transfusion depends on several factors. We know it can be tough, both physically and emotionally. Our aim is to give you the care and support you need during this time.
Type of Blood Transfusion Required
The type of blood transfusion you get affects how long you’ll stay in the hospital. Each transfusion has its own level of complexity. For example, a simple red blood cell transfusion might need less watching than a more complex one.
We customize our care to fit your specific transfusion needs. This way, we can manage any complications early and effectively. This helps in shortening your stay.
Underlying Health Conditions
Any health issues you have can also impact your hospital stay. Conditions like heart disease or kidney disease need careful attention. They can make the transfusion and recovery more complicated.
For instance, patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) might stay longer. AKI is a risk for those having major surgery. It can lead to short-term and long-term problems. We consider these conditions when planning your care, aiming to prevent complications.
By understanding and managing these factors, we can better predict and prepare for your recovery. This helps us aim for a smoother and more efficient hospital stay.
Immediate Effects of Blood Transfusion
It’s important to know the immediate effects of blood transfusions for better patient care. Blood transfusions are usually safe but can cause reactions. These can range from mild to severe.
Common Reactions to Expect
Most people getting a blood transfusion may feel some common reactions. These include:
- Mild Fever: A slight increase in body temperature is common. It’s often treated with medication.
- Chills: Some patients might feel cold. This can be fixed with warming blankets.
- Itching or Rash: Mild allergic reactions can cause itching or a rash.
These reactions are usually mild and can be handled by medical staff.>
Serious Side Effects to Watch For
While rare, serious side effects can happen. It’s key for patients to know about these possible issues:
- Anaphylaxis: A severe, life-threatening allergic reaction that needs immediate medical help.
- Hemolytic Acute Reaction: This happens when the blood given isn’t compatible with the patient’s. It leads to the destruction of red blood cells.
- Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI): A serious condition marked by sudden non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Spotting the signs of these serious side effects early can greatly improve outcomes. Patients should watch for unusual symptoms and tell their healthcare providers right away.
Knowing both common reactions and serious side effects helps patients navigate their treatment journey. They’ll know what to expect and when to ask for help.
Recovery Process Post-Transfusion
The journey to recovery after a blood transfusion is all about careful monitoring and care. As we move the patient from the transfusion to recovery, our main goal is their safety and stability.
Initial Recovery Period
We watch the patient’s vital signs closely during the initial recovery. This includes heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. This watchful eye helps us spot any issues, like an adverse reaction to the blood. Our medical team is ready to act fast to ensure the best results for our patients.
We also check if the patient is getting better or worse. This helps us see if the blood transfusion is working, like for anemia or blood loss.
Criteria for Discharge
Before a patient can go home after a blood transfusion, we check a few important things. We look at their vital signs, if they had any bad reactions, and if they’re getting better. Our aim is to make sure each patient is stable enough to recover safely at home.
We also teach patients and their caregivers about post-transfusion care. They learn about signs of trouble and when to get help. This knowledge is key for their recovery at home.
“The care received during and after a blood transfusion is just as important as the transfusion itself. Ensuring that patients are well-informed and supported throughout the recovery process is key to achieving the best outcomes.”
— Transfusion Medicine Specialist
By managing the recovery process well, we can lower the risk of problems. This helps our patients recover fully and quickly.
Average Hospital Stay Duration
Knowing how long you’ll stay in the hospital after a blood transfusion is important. The time you spend can change based on why you got the transfusion, your health, and if any problems come up.
Typical Timeline for Patients
The time in the hospital after a blood transfusion can be a few hours or a few days. Some patients get discharged quickly after the transfusion. Others, if they have a serious condition, might stay longer. Usually, patients stay for at least 24 to 48 hours to check for any bad reactions and make sure they’re okay.
Variations Based on Individual Cases
The time you stay in the hospital can differ based on your needs. For example, surgery patients might need more time to heal. Those getting transfusions for ongoing health issues might have a different recovery pace. Things that can affect how long you stay include the type of transfusion, any health problems you have, and how well you react to the treatment. We keep a close eye on you to adjust your care as needed.
In some cases, you might go home sooner if your health allows it, with plans for follow-up care. But, if problems come up, you might need to stay longer. It’s key to follow your doctor’s advice for a smooth recovery.
Follow-Up After Blood Transfusion
The time after a blood transfusion is very important. We stress the need for good post-transfusion care. Getting the right follow-up care is key for a safe recovery and to catch any problems early.
Importance of Post-Transfusion Care
Post-transfusion care is a big part of treatment. It means watching the patient, handling side effects, and making sure the transfusion worked. Following the doctor’s instructions is very important to avoid and fix any issues.
Key aspects of post-transfusion care include:
- Monitoring for signs of complications
- Managing any side effects or reactions
- Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers
- Adherence to medication regimens as prescribed
Signs to Watch for After Discharge
After leaving the hospital after a blood transfusion, it’s important to watch for signs of trouble. Look out for fever, chills, shortness of breath, tiredness, or any other strange feelings. If you notice any of these, call your doctor right away.
| Signs to Watch For | Description | Action to Take |
| Fever | Elevated body temperature | Contact healthcare provider if fever exceeds 100.4°F (38°C) |
| Shortness of Breath | Difficulty breathing or feeling winded | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Unusual or Severe Symptoms | Any unusual or severe symptoms | Contact healthcare provider for guidance |
Knowing these signs and acting fast can help you recover safely.
Potential Complications
While rare, complications can happen after a blood transfusion. We watch patients closely during and after the transfusion. This helps us spot and handle any bad reactions quickly.
Serious but Rare Complications
Some complications are rare but serious. These include:
- Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI): a condition that can cause breathing difficulties due to inflammation in the lungs.
- Transfusion-Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO): a condition where the circulatory system is overloaded, potentially leading to heart failure.
- Hemolytic Reactions: severe reactions that occur when the transfused blood is not compatible with the patient’s blood type.
- Anaphylactic Reactions: severe allergic reactions that can be life-threatening.
These complications show why it’s so important to watch patients closely during and after transfusions.
How to Handle Complications
If complications happen, we act fast. Here’s what we do:
- Stopping the Transfusion: we stop the transfusion right away to prevent more reactions.
- Medical Evaluation: we quickly check the patient’s condition to find out what’s causing the problem.
- Supportive Care: we give care to help manage symptoms and support the patient’s recovery.
- Monitoring: we keep a close eye on the patient’s condition for any further changes.
We also try to prevent complications by being careful with blood typing and matching. And we watch patients closely during the transfusion.
For patients with complex conditions, like type A aortic dissection and lower-extremity malperfusion, managing blood transfusions is more complex. Research shows these patients have a lower survival rate. This shows how challenging their care is.
By knowing about the possible complications of blood transfusions and how to handle them, we can give our patients the best care possible.
The Importance of Blood Type Matching
Ensuring the right blood type match is key in blood transfusions. It’s not just a rule; it’s a lifesaver. Blood type matching prevents bad reactions.
Understanding Blood Compatibility
Knowing blood types is vital. There are four main types: A, B, AB, and O. Each has different antigens on red blood cells. The Rh system adds another layer, classifying blood as Rh-positive or Rh-negative.
When we give blood, it must match the recipient’s type. This prevents an immune reaction. The wrong blood can cause a severe reaction.
Risks of Mismatched Blood Transfusions
Mismatched blood can be very dangerous. The main risk is a hemolytic transfusion reaction. This can lead to fever, chills, and even death.
To show why blood type matching is so important, here’s a table of compatible blood types:
| Blood Type | Can Receive Blood From | Can Donate Blood To |
| A+ | A+, A-, O+, O- | A+, AB+ |
| O- | O- | O-, O+, A-, A+, B-, B+, AB-, AB+ |
| B+ | B+, B-, O+, O- | B+, AB+ |
| AB+ | AB+, AB-, A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O- | AB+ |
Accurate blood type matching is essential for safe transfusions. Understanding blood compatibility and the risks of mismatched transfusions is key. It shows the care in matching blood types for patients.
Support and Resources
The journey after a blood transfusion is just starting. It’s a time that needs lots of support and resources. Getting a blood transfusion can be tough, not just for the person getting it but also for their family. So, having good support is key for getting better and feeling well again.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Emotional and psychological support are very important after a blood transfusion. Patients might feel many emotions, like relief or worry. Our healthcare team is here to help with both medical care and emotional support.
We offer support groups, counseling, and educational materials. These help patients deal with their feelings and understand their treatment. As one patient said,
“The support group was a lifeline for me; it helped me understand I wasn’t alone in this journey.”
We aim to support the whole person, not just their medical issue.
Resources for Blood Donors
Blood donation is vital, and we support our donors. We give them resources to know how their donation helps and what to expect next. Our help includes post-donation care, nutrition tips, and contact info for any questions.
- Post-donation care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery
- Nutritional guidance to help replenish blood components
- Contact details for donor support services
We also show our thanks to blood donors. We have recognition programs and educational materials to highlight their importance.
FAQs About Blood Transfusions
Patients often have many questions about blood transfusions. They want to know about the procedure and what happens after. We make sure to answer these questions to help patients feel informed and comfortable.
Common Questions Addressed
People often ask about the safety of the blood, the transfusion process, and what to expect after. We aim to clear up these concerns and offer reassurance.
- Is the blood supply safe? Yes, we take many steps to ensure it is. This includes screening donors and testing the blood thoroughly.
- How long does a blood transfusion take? It can last from 1 to 4 hours. This depends on the type of transfusion and the patient’s needs.
- Will I experience any side effects? Most patients don’t have big problems. But, some might get a rash or a fever. Serious side effects are very rare.
Answers to Patient Concerns
We know patients have unique worries based on their health and situations. We offer personalized care and answer specific questions.
Some worry about allergic reactions or getting sick from the blood. We assure patients we follow strict rules to lower these risks. This includes careful screening and testing.
- Pre-transfusion testing checks if the donor’s blood matches the patient’s.
- Monitoring during the transfusion helps spot and handle any bad reactions quickly.
- Post-transfusion care watches for complications and guides the patient on recovery.
We hope answering these FAQs and concerns helps patients understand blood transfusions better. This should reduce any anxiety they might have.
Conclusion
It’s important for patients to understand blood transfusions. We’ve talked about what affects how long you stay in the hospital after one. This includes the type of transfusion and your health.
A summary of key points shows why safe blood donation and transfusion are critical. Healthcare providers must check for compatibility and watch patients closely. This helps reduce risks and ensures treatment works well.
Keeping the blood supply safe is key. We urge patients and donors to know about the process and possible issues. This teamwork is essential for good healthcare.
Our talk on safe practices in blood donation ends with a call for more education. This helps us offer top-notch healthcare to everyone, including international patients.
FAQ
What is a blood transfusion?
A blood transfusion is when blood or blood parts are given to someone. It’s to replace lost blood or to make the blood better.
Why do people need blood transfusions?
People might need blood transfusions after surgeries, injuries, or if their blood isn’t working right.
How long does a blood transfusion take?
A blood transfusion can take a few hours to finish.
What are the common reactions to a blood transfusion?
Common reactions include fever, chills, and mild allergies.
What are the serious side effects of a blood transfusion?
Severe side effects can be anaphylaxis, hemolysis, and acute kidney injury.
How long do you stay in the hospital after a blood transfusion?
How long you stay in the hospital depends on why you got the transfusion and your health.
What is the importance of blood type matching?
Matching the donor’s blood with the recipient’s is key for a safe transfusion. Mismatched blood can cause serious problems.
What are the signs to watch for after a blood transfusion?
Watch for fever, chills, or trouble breathing after a transfusion.
Are blood transfusions safe?
Mostly, blood transfusions are safe. But, it’s good to know about possible reactions and symptoms.
Why is follow-up care important after a blood transfusion?
Follow-up care is vital for a safe recovery. It helps catch any problems early.
What kind of support is available to patients after a blood transfusion?
Patients can get emotional and psychological support. There are also resources for blood donors.
How long does it take to recover from a blood transfusion?
Recovery involves watching for reactions, checking vital signs, and making sure the patient is okay.
Can underlying health conditions affect the length of hospital stay after a blood transfusion?
Yes, conditions like heart or kidney disease can affect how long you stay in the hospital.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8233480/
JAMA Network. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamasurgery/fullarticle/2814272
































