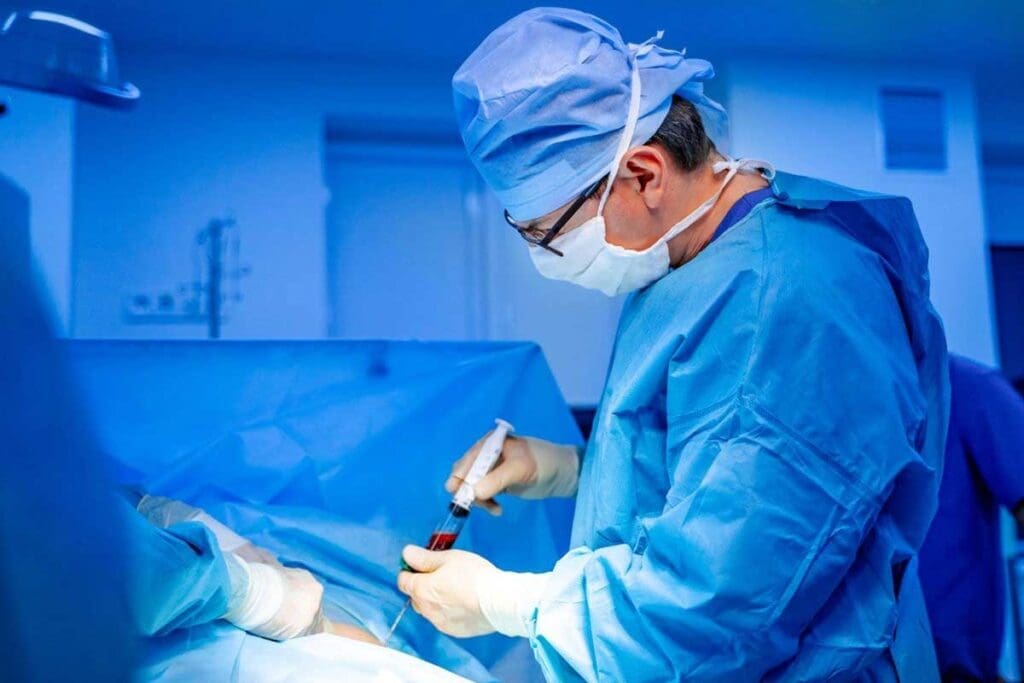
At Liv Hospital, we tackle the challenges of rare blood disorders like aplastic anemia. This serious issue happens when the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. A bone marrow transplant brings hope by adding healthy donor stem cells to make blood cells again. Learn how BMTaplastic anemia transplant works for treatment. Find out if this serious condition is considered cancer in this powerful guide.
We’ll look into how this treatment works. And we’ll answer a big question: Is aplastic anemia considered cancer? Even though it’s treated like cancer, aplastic anemia is different.
Key Takeaways
- A bone marrow transplant is a viable treatment option for severe aplastic anemia.
- The procedure involves infusing healthy stem cells to restore blood cell production.
- Aplastic anemia is a serious condition, but it is not classified as cancer.
- Treatment approaches may overlap with those used in cancer therapy.
- Liv Hospital provides expert, patient-centered care for rare blood disorders.
Understanding Aplastic Anemia: A Rare Blood Disorder

Aplastic anemia is a rare condition where the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells. This leads to a lack of red, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells are key to carrying oxygen, fighting infections, and stopping bleeding.
Definition and Pathophysiology
Aplastic anemia happens when the bone marrow fails to make blood cells. The exact reason is not known, but it is thought to be linked to the immune system attacking the bone marrow’s stem cells. This can be caused by toxins, certain drugs, viruses, and autoimmune diseases.
The immune system and bone marrow have a complex relationship in aplastic anemia. Normally, the bone marrow makes stem cells that turn into different blood cells. But in this condition, this process is disrupted, leading to a severe lack of blood cells.
“The diagnosis of aplastic anemia requires a thorough check-up, including blood tests and a bone marrow biopsy. This helps see how bad the bone marrow failure is and rules out other conditions.”
Common Symptoms and Presentation
The symptoms of aplastic anemia come from the lack of blood cells. Common signs include:
- Fatigue and weakness from not enough red blood cells
- Frequent infections due to not enough white blood cells
- Bleeding or bruising easily from not enough platelets
Patients can have mild to severe symptoms, depending on how bad the bone marrow failure is. Doctors usually diagnose it when a patient shows these symptoms, leading to a detailed check-up.
| Symptom | Cause | Clinical Implication |
| Fatigue and weakness | Anemia (low red blood cell count) | May need blood transfusions to help with oxygen delivery |
| Frequent infections | Neutropenia (low white blood cell count) | Higher risk of serious infections, might need antibiotics to prevent |
| Bleeding or bruising easily | Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) | May need platelet transfusions to stop or treat bleeding |
Knowing about aplastic anemia’s definition, how it works, and its symptoms is key to early diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing these signs helps doctors start the right treatment quickly, improving patient outcomes.
Is Aplastic Anemia Cancer? Clearing the Confusion
It’s important to know the difference between aplastic anemia and cancer. Both affect the bone marrow but in different ways. This knowledge helps in getting the right treatment.
Key Differences Between Aplastic Anemia and Cancer
Aplastic anemia is a rare blood disorder where the bone marrow can’t make blood cells. Cancer, on the other hand, is when abnormal cells grow out of control. The main difference is how the bone marrow works.
In aplastic anemia, the marrow can’t make cells. But in cancer, it makes bad cells that take over.
Aplastic anemia is not cancer. But it can look like cancer because both can cause a lack of blood cells.
Why the Confusion Exists
There are a few reasons why people get confused. Both can make you feel tired, get sick easily, and bleed a lot. They also both need bone marrow tests to diagnose.
Also, some treatments for aplastic anemia are similar to cancer treatments. This adds to the confusion.
But plastic anemia is a different condition from cancer. Getting a proper diagnosis is key to the right treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors of Aplastic Anemia
Knowing the causes and risk factors of aplastic anemia is key foto timelyreatment. This condition can come from many sources, including both inherited and acquired factors.
Acquired Aplastic Anemia
Acquired aplastic anemia is the most common type. It’s not passed down through genes but develops over time. Exposure to certain chemicals and toxins is a big risk factor. Pesticides, insecticides, and some industrial chemicals can increase the risk.
ExpoRadiation exposure is also a major concern. High levels of radiation, like from nuclear accidents or some medical treatments, can harm the bone marrow. Viral infections, like hepatitis and Epstein-Barr virus, can also lead to acquired aplastic anemia.
Some medications can cause aplastic anemia as a rare side effect. This includes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and some chemotherapy drugs. It’s important to talk about these risks with your doctor.
Inherited Forms of Aplastic Anemia
Inherited aplastic anemia is less common but important, mainly in younger people. Fanconi anemia is a well-known inherited form. It’s caused by a genetic problem that can lead to bone marrow failure and cancer risk.
Other inherited conditions, like Dyskeratosis congenita, also raise the risk of aplastic anemia. These conditions often involve genetic mutations that affect the bone marrow’s ability to make blood cells.
Knowing if aplastic anemia is inherited or acquired is critical. It helps determine the right treatment and assess family risks.
Diagnosing Aplastic Anemia: The Path to Proper Treatment
Diagnosing aplastic anemia is a detailed process. It includes blood tests, a bone marrow biopsy, and other tests. We’ll explain each step and why they’re important for a correct diagnosis.
Blood Tests and Initial Evaluation
The first step is blood tests. These tests check the levels of different blood cells.
Blood tests for aplastic anemia include:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check red, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Reticulocyte count to see how new red blood cells are made.
These tests help spot problems in blood cell counts that might show aplastic anemia.
| Test | Purpose | Expected Result in Aplastic Anemia |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Measures levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. | Low counts of one or more cell types. |
| Reticulocyte Count | Evaluates the production of new red blood cells. | Low reticulocyte count indicates inadequate bone marrow response. |
Bone Marrow Biopsy and Specialized Testing
A bone marrow biopsy is key to diagnosing aplastic anemia. It takes a small bone marrow sample for examination.
During the biopsy, we check the bone marrow’s cell count and look for any issues. This helps confirm the diagnosis and see how severe the bone marrow failure is.
“The diagnosis of aplastic anemia is mainly based on the bone marrow biopsy findings. It shows the bone marrow’s condition directly.”
Other tests might be done to rule out other conditions and find aplastic anemia.
Treatment Options for Aplastic Anemia
Managing aplastic anemia involves different approaches. These include supportive care, immunosuppressive therapy, and bone marrow transplantation. The right treatment depends on how severe the condition is, the patient’s age, and their health.
Supportive Care Measures
Supportive care is key in treating aplastic anemia. It aims to ease symptoms and prevent complications. This includes:
- Blood transfusions to increase red blood cell, white blood cell, and platelet counts.
- Antibiotics to treat infections.
- Growth factors stimulate the production of blood cells.
These steps help until a more lasting treatment, like a bone marrow transplant, is possible.
Immunosuppressive Therapy
For those not ready for a bone marrow transplant, immunosuppressive therapy is an option. This treatment uses drugs to weaken the immune system. This might help the bone marrow recover. Drugs like antithymocyte globulin (ATG) and cyclosporine are used.
When BMT Is Recommended
Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT) is a main treatment for aplastic anemia. It’s best for younger patients and those with severe disease. BMT replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy marrow from a donor. The decision to do BMT depends on several factors, including disease severity, age, and donor availability. For many, BMT is a chance for a cure, making it a key treatment option.
In conclusion, treating aplastic anemia is tailored to each patient. Supportive care and immunosuppressive therapy are important. But bone marrow transplantation is a potentially curative option for many.
BMT for Aplastic Anemia: The Definitive Treatment
BMT is a cure for aplastic anemia by fixing the bone marrow problem. Aplastic anemia makes it hard for the bone marrow to make blood cells. This leads to tiredness, infections, and bleeding.
By using healthy donor stem cells, BMT can fix this problem. It can make the bone marrow work right again, possibly curing the disease.
How BMT Addresses the Root Cause
BMT fixes aplastic anemia by replacing bad bone marrow with good donor stem cells. Here’s how it works:
- Eliminating the faulty bone marrow: The old bone marrow is removed with special treatments.
- Infusing healthy stem cells: New stem cells from a donor are put into the patient’s blood. They go to the bone marrow and start making healthy blood cells.
- Restoring bone marrow function: The new stem cells start making blood cells. This can cure the patient of aplastic anemia.
Advantages of BMT Over Other Treatments
BMT has big advantages over other treatments for aplastic anemia:
- Potential for cure: BMT can cure the disease by replacing the bad bone marrow. Other treatments just manage symptoms.
- Long-term solution: BMT can solve the problem for a long time. Patients don’t need to keep getting treatments.
- Reduced risk of relapse: BMT lowers the chance of the disease coming back. This is better than other treatments.
Even though BMT is a big procedure with risks, new medical tech and care have made it safer. This has helped many patients with aplastic anemia.
The Bone Marrow Transplant Process for Aplastic Anemia Patients
For those with aplastic anemia, a bone marrow transplant is a detailed process. It needs careful planning and preparation. This process has several key steps that are vital for success.
Finding a Suitable Donor
Finding a donor is the first step. This involves human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing to find a compatible donor. This is usually a sibling or an unrelated donor from registries. Finding a compatible donor is key to avoiding graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), a major risk of bone marrow transplantation.
- Family members are usually the first to be tested for compatibility.
- If no family member is a match, an unrelated donor is sought through international registries.
- The donor’s health and compatibility are thoroughly assessed.
Pre-Transplant Evaluation and Preparation
After finding a donor, the patient goes through a detailed pre-transplant evaluation. This checks the patient’s health, the severity of aplastic anemia, and prepares them physically and emotionally for the transplant.
- Detailed medical history and physical examination.
- Laboratory tests, including blood counts and biochemical profiles.
- Cardiac and pulmonary function tests to assess the patient’s ability to tolerate the conditioning regimen.
Conditioning Regimens for Aplastic Anemia
Conditioning regimens are key in preparing the body for the transplant. These regimens use immunosuppressive therapy to get rid of the current bone marrow and prevent the new marrow from being rejected. The goal is to make room for the donor’s bone marrow to engraft and produce healthy blood cells.
- Chemotherapy is commonly used to suppress the immune system.
- In some cases, total body irradiation (TBI) may be used in conjunction with chemotherapy.
- The intensity of the conditioning regimen is tailored to the individual patient’s condition and the specific protocol of the treatment center.
Understanding these steps helps patients and their families better understand the bone marrow transplantation process for aplastic anemia.
The Transplantation Procedure and Immediate Aftercare
The bone marrow transplant procedure is a key step in treating aplastic anemia. It offers a chance for a cure for this rare blood disorder. Understanding the details of the transplant process is vital for a successful outcome.
The Day of Transplant: What Happens
On transplant day, patients get healthy donor stem cells infused into their bodies. This is like a blood transfusion, but through a central line. The stem cells start to repopulate the bone marrow, helping to restore blood cell production.
Pre-transplant preparation is key to getting the patient’s body ready. This includes treatments like chemotherapy and radiation to weaken the immune system. This makes room for the new stem cells.
Early Post-Transplant Management
Early care after transplant focuses on managing risks and supporting recovery. Close monitoring is critical to catch and treat problems like GVHD, infections, or graft failure quickly.
Post-transplant care includes medicines to prevent GVHD and infections. Regular blood tests check the patient’s health and blood counts. The medical team also advises on lifestyle changes to help recovery.
Knowing the aplastic anemia cure rate after BMT is important. While results vary, BMT is a highly effective treatment. It offers a high chance of cure for many patients.
Recovery After BMT for Aplastic Anemia
When patients get BMT for aplastic anemia, knowing about recovery is key. The recovery time is filled with watching for signs, dealing with possible issues, and ongoing care.
Timeline for Blood Count Recovery
Getting healthy blood cells back is a big part of recovery. How long it takes can differ for each person. But, here are some general times:
- Neutrophil recovery: Usually happens in 2-4 weeks after the transplant.
- Platelet recovery: Takes longer, often 3-6 months or more.
- Red blood cell recovery: Can take months, sometimes up to a year or more.
Potential Complications and Management
BMT can cure aplastic anemia, but it comes with risks. Some possible problems include:
| Complication | Description | Management |
| Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) | A condition where donor cells attack the recipient’s body. | Immunosuppressive medications, close monitoring. |
| Infections | Patients are at risk due to immunosuppression. | Prophylactic antibiotics, isolation precautions. |
| Organ toxicity | Chemotherapy and radiation can affect organ function. | Supportive care, monitoring of organ function. |
Long-term Follow-up Care
Long-term care is vital for keeping an eye on health and managing transplant effects. It includes regular visits, watching for GVHD, and helping with ongoing health problems.
Knowing about recovery and possible issues helps patients and their families. It makes the journey after BMT better for those with aplastic anemia.
Success Rates and Outcomes of BMT Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Bone marrow transplant (BMT) for aplastic anemia has shown great promise. It’s a key treatment for severe cases that haven’t responded to other treatments. It offers a chance for a cure.
Recent studies show a five-year survival rate of 70 to 80 percent after BMT for severe aplastic anemia. This is a big jump from before. It’s thanks to better transplant techniques, donor matching, and care after the transplant.
Survival Statistics and Quality of Life
Survival rates for BMT in aplastic anemia have greatly improved. A big reason is the better quality of life after BMT. Many patients see a big boost in their health and happiness.
One study found that most patients who live more than two years after BMT have a good life. They can do normal things and live long lives. This shows BMT’s success in saving lives and improving the quality of life.
Factors Affecting Transplant Success
Several things can affect how well BMT works for aplastic anemia. These include:
- Age of the patient at the time of transplant
- Donor match quality
- Pre-transplant health status of the patient
- Conditioning regimen used before transplant
- Post-transplant care and management
Experts say the success of BMT depends on careful patient selection, precise donor matching, and detailed post-transplant care. By focusing on these areas, doctors can improve BMT outcomes for aplastic anemia patients.
In summary, BMT is a very effective treatment for aplastic anemia. Success rates and survival statistics are getting better. Understanding what affects transplant success helps improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Managing aplastic anemia well needs a team effort. It’s a complex condition that requires many medical experts working together. They aim to give the best care possible.
At the core of treating aplastic anemia is a team. This team includes hematologists, oncologists, immunologists, and more. They create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
The Role of Specialized Treatment Centers
Specialized treatment centers are key in managing aplastic anemia. They have the latest technology and staff who know the newest treatments. Specialized centers offer many benefits. They provide:
- Advanced treatments, like bone marrow transplants
- A team of experts working together
- Support for patients and their families
- Opportunities to join clinical trials
Liv Hospital’s Evidence-Based Approach
Liv Hospital focuses on evidence-based treatment for aplastic anemia. Our team is committed to quality care that follows the latest research and guidelines.
Our approach includes:
- Thorough tests to find the cause of aplastic anemia
- Creating a treatment plan that fits the patient
- Access to the latest treatments, like immunosuppressive therapy
- Support for patients and their families
Conclusion: The Future of Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Aplastic anemia is a rare and serious blood disorder. It needs quick and effective treatment. Even though it’s not cancer, it can severely affect the body, requiring detailed care.
Thanks to advances in bone marrow transplant (BMT) and immunosuppressive therapy, survival rates have improved. The future of treating aplastic anemia looks bright. Ongoing research and new BMT techniques are on the horizon.
At Liv Hospital, we’re all about top-notch healthcare. We use a team approach to make sure our patients get the best care. We’re excited about the role BMT will play in treating aplastic anemia, bringing hope to patients everywhere.
The outlook for aplastic anemia treatment is optimistic. We’re focused on bettering patient outcomes and improving their quality of life. We’re committed to supporting international patients seeking advanced medical care.
FAQ
What is aplastic anemia, and how does it affect the body?
Aplastic anemia is a rare blood disorder. It happens when the bone marrow can’t make enough blood cells. This leads to fatigue, infections, and bleeding problems. Our team is here to help with all aspects of care.
Is aplastic anemia considered a form of cancer?
No, aplastic anemia is not cancer. It’s a different condition that affects the bone marrow. We help clear up any confusion and ease worries.
What are the causes and risk factors of developing aplastic anemia?
Several things can cause aplastic anemia, like toxins, certain drugs, viruses, and genetics. We find out what’s causing it to plan the best treatment.
How is aplastic anemia diagnosed?
Doctors use blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and other checks to diagnose it. Our diagnosis is detailed and accurate, helping us choose the right treatment.
What treatment options are available for aplastic anemia?
Treatments include supportive care, drugs to calm the immune system, and bone marrow transplant. We pick the best treatment based on the patient’s needs.
When is a bone marrow transplant recommended for aplastic anemia?
BMT is considered for severe cases when other treatments don’t work. We look at the patient’s health and donor availability.
What is the bone marrow transplant process like for aplastic anemia patients?
Finding a donor, pre-transplant checks, conditioning, and the transplant itself are part of the process. We support patients every step of the way.
What are the success rates and outcomes of BMT for aplastic anemia?
BMT is very effective for severe aplastic anemia, improving survival and quality of life. We focus on personalized care to ensure the best results.
How does Liv Hospital approach the treatment of aplastic anemia?
Liv Hospital uses a team approach, combining treatments with support services. Our specialists work together to provide top-notch care for international patients.
Can aplastic anemia be cured?
Yes, with the right treatment, like BMT, aplastic anemia can be cured. We aim to give our patients the best chance of recovery.
What is the role of immunosuppressive therapy in treating aplastic anemia?
This therapy helps by reducing the immune system’s attack on the bone marrow. It’s an option when BMT isn’t right away or suitable.
How long does it take to recover from a bone marrow transplant for aplastic anemia?
Recovery times vary, but blood counts start to improve a few weeks after the transplant. We’re here to support patients through the recovery.
Reference:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2018). Severe aplastic anemia: allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Retrieved from , https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6093726



































