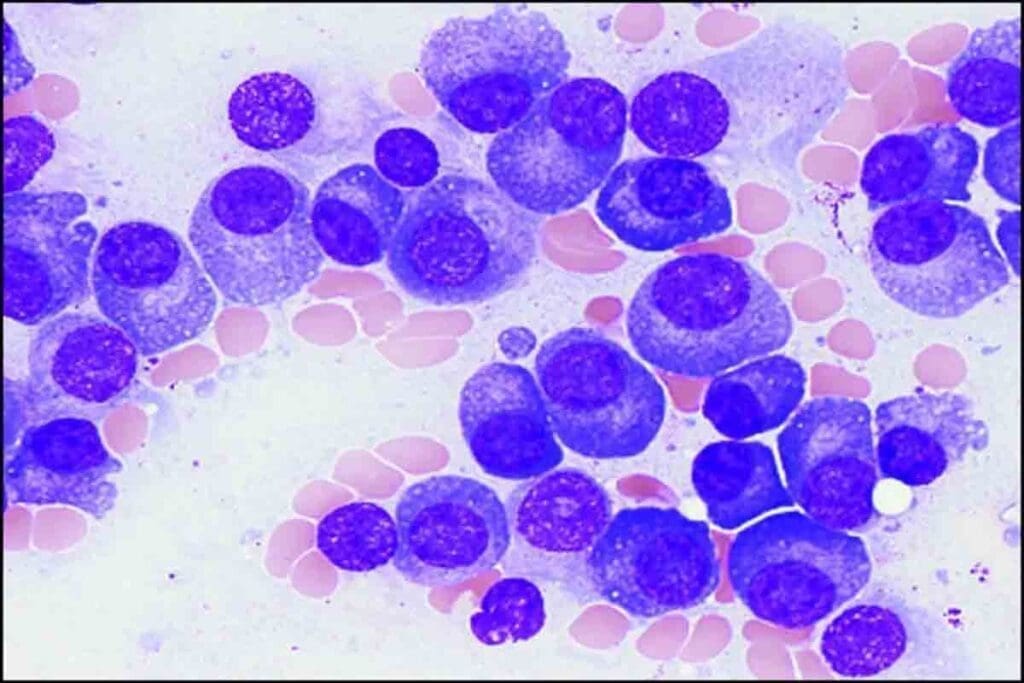
When a child develops persistent fatigue, frequent bruising, or repeated infections, it may signal an underlying bone marrow disorder. At Liv Hospital, we are dedicated to providing patient-centered, innovative care to families facing concerns about these symptoms.
Understanding the signs of bone marrow disease symptoms in child is key for timely medical intervention. Common signs include fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, unexplained fevers, and pallor due to blood cell production issues. We will dive into these symptoms, shedding light on their causes and why early diagnosis matters.
Key Takeaways
- Recognizing bone marrow disorder symptoms is vital for early diagnosis and treatment.
- Common symptoms include fatigue, frequent infections, and easy bruising.
- Disruptions in blood cell production can lead to various health issues.
- Timely medical intervention is essential for managing bone marrow disorders.
- Liv Hospital provides thorough care for families dealing with these concerns.
Fatigue and Weakness: Primary Signs of Bone Marrow Disease
Bone marrow disease often shows up with symptoms that are not very specific. Fatigue and weakness are common. It’s important to understand how bone marrow works and its role in health.
What is Bone Marrow and How it Functions
Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones like hips and thighbones. It makes red blood cells for oxygen, white blood cells to fight infections, and platelets to stop bleeding. When it’s healthy, it makes the right amount of blood cells.
But, when it’s sick, it can’t do this right. This can lead to problems.
How Bone Marrow Disease Causes Extreme Tiredness
Leukemia and other bone marrow diseases can lower healthy blood cells. This leads to fatigue and weakness. When bone marrow is sick, it might not make enough red blood cells.
Or, the cells it makes might not work well. This means less oxygen for tissues and organs. This can make you feel very tired and weak.
Distinguishing Normal Childhood Fatigue from Disease-Related Exhaustion
It’s normal for kids to feel tired after playing or growing. But, if they’re always tired and it doesn’t get better, it could be a problem. We need to tell normal tiredness from tiredness caused by bone marrow disease.
If your child is always tired and doesn’t get better with rest, or has pale skin or gets sick a lot, see a doctor. It’s very important.
Frequent Infections and Compromised Immunity

One key sign of bone marrow disease in kids is getting sick often. This is because their immune system is weak. The bone marrow makes immune cells, like white blood cells, which fight off germs. When it’s sick, it can’t make enough cells, leaving kids open to infections.
The Connection Between Immune Function and Bone Marrow
The bone marrow makes blood cells, including immune cells. These cells help keep us safe from germs. In kids with bone marrow problems, making these cells can be hard, weakening their immune system.
Impaired immune function in kids with bone marrow disease can come from the disease itself or treatments like chemo. This makes them more likely to get sick, which can be very serious.
Types of Recurring Infections Common in Children with Bone Marrow Disorders
Kids with bone marrow disorders often get different kinds of infections. Some common ones are:
- Bacterial infections, like pneumonia or sepsis, which need quick medical help.
- Viral infections, such as the flu or RSV, which can make immunocompromised kids very sick.
- Fungal infections, which are hard to treat and might need special medicine.
When to Worry About Your Child’s Infection Frequency
While getting sick sometimes is normal, kids with bone marrow disorders are at higher risk. Parents should worry if their child:
- Gets sick often or has severe infections.
- Needs to stay in the hospital or gets antibiotics through a vein.
- Takes a long time to get better or doesn’t respond to treatment.
If you see these signs, talk to your child’s doctor right away. Catching and treating infections early can help kids with bone marrow disease a lot.
Easy Bruising and Unusual Bleeding Episodes
Easy bruising and unusual bleeding can be signs of bone marrow disease in kids. This happens because the bone marrow doesn’t make enough platelets. Platelets are key for blood to clot.
When there aren’t enough platelets, kids might bruise and bleed more than usual. This can be hard to stop.
Why Platelet Deficiencies Lead to Bruising
Platelets are small blood cells that help stop bleeding when a blood vessel gets hurt. In kids with bone marrow disease, making platelets can be tough. This leads to a low platelet count, or thrombocytopenia.
With fewer platelets, blood can’t clot well. This means kids might bruise easily and bleed for a long time.
Recognizing Abnormal Bruising Patterns
Parents should know the difference between normal and abnormal bruising in kids. Normal bruises usually show up on the knees, elbows, or shins. But, if a child bruises in places like the torso, face, or arms without reason, it might be a sign of something serious.
Prolonged Bleeding as a Warning Sign
Bleeding that lasts a long time after a small injury or happens on its own is a big warning sign. Kids with bone marrow disease might bleed more or for longer than others. This needs to be checked by a doctor right away.
| Symptom | Normal in Children | Possible Bone Marrow Disease Indicator |
| Bruising Location | Knees, elbows, shins | Torso, face, arms without apparent cause |
| Bleeding Duration | Stops within a few minutes | Prolonged or spontaneous |
| Frequency of Bruising | Occasional | Frequent or unexplained |
Bone Marrow Disease Symptoms in Children: Unexplained Fevers
Bone marrow disease in kids can show many symptoms, with unexplained fevers being a big warning sign. These fevers often happen in diseases like leukemia. They are the body’s way of reacting to the disease.
Fever as an Inflammatory Response in Bone Marrow Disorders
Fever is how our body fights off infections or inflammation. In bone marrow disorders, fever means the body is battling something. Bone marrow diseases can disrupt normal immune function, leading to fevers that may not be directly related to typical infections.
When a child has a bone marrow disorder, their immune system may be weakened. This makes them more likely to get infections and fevers. It’s important for parents to watch these fevers closely and know when they might be serious.
Pattern of Fevers in Various Bone Marrow Diseases
Different bone marrow diseases can cause fevers in different ways. For example, in leukemia, fevers can keep coming back and not go away with usual treatments. Knowing these patterns can help doctors figure out what’s wrong.
| Disease | Fever Pattern | Other Symptoms |
| Leukemia | Recurrent, persistent | Fatigue, weight loss, bruising |
| Aplastic Anemia | Intermittent, related to infections | Fatigue, infections, bleeding |
| Myelodysplastic Syndromes | Variable, sometimes low-grade | Anemia, infections, bruising |
When Fevers Should Prompt Medical Evaluation
While fevers are common in kids, some signs need a doctor’s check-up. Fevers that are persistent, recurrent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms need to be looked at closely.
Parents should watch for fevers that:
- Last more than 3-4 days
- Are accompanied by other symptoms like bruising, bleeding, or significant fatigue
- Do not respond to typical fever-reducing medications
If a child has any of these fever patterns, it’s important to talk to a doctor. This helps find out what’s wrong and how to treat it.
Pallor and Significant Skin Changes
Children with bone marrow disease often show significant skin changes. One common sign is pallor, caused by anemia. Anemia happens when the body makes fewer red blood cells, which carry oxygen.
We’ll look at how anemia affects skin color. We’ll also talk about other skin signs that can show bone marrow failure.
Understanding Anemia’s Effect on Skin Color
Anemia can make skin appear pale because of fewer red blood cells. Red blood cells carry hemoglobin, which brings oxygen to the body. If there are fewer red blood cells, the skin looks pale or washed out.
This is because there’s less hemoglobin to give the skin its usual color.Symptoms of bone marrow disease like anemia can be an early sign of trouble.
In children, anemia from bone marrow disease can show in different ways. Some might look generally pale, while others might have more noticeable pallor around the eyes or mucous membranes. It’s important for parents to watch their child’s skin color and overall health. These can be signs of deeper issues.
Other Skin Manifestations of Bone Marrow Failure
Beyond pallor, bone marrow failure can cause other skin signs. For example, not enough platelets can lead to easy bruising or petechiae (small spots on the skin). Platelets help blood clot, so without enough, even small injuries can cause big bruises.
| Skin Manifestation | Cause | Characteristics |
| Pallor | Anemia due to reduced red blood cell production | Pale skin, often more noticeable around the eyes and mucous membranes |
| Easy Bruising | Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) | Bruises appear with minimal trauma, can be large or small |
| Petechiae | Thrombocytopenia | Small, pinpoint spots on the skin, often on the legs or areas under pressure |
Spotting these skin changes early is key to catching bone marrow disease early. If you see persistent or severe skin signs, see a healthcare professional right away. They can evaluate and treat your child properly.
Bone Pain and Skeletal Abnormalities
Bone marrow disease can cause bone pain and skeletal issues in kids. It’s important for parents to know why. Bone pain can really hurt a child’s life, making it hard to do normal things.
We’ll look at how bone marrow problems can cause pain and skeletal issues. This helps parents and caregivers know if their child has more than just growing pains.
How Bone Marrow Problems Affect the Skeletal System
Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones like hips and thighbones. It makes blood cells. Diseases here can cause pain and skeletal problems because the marrow is surrounded by bone.
Bone marrow disorders can weaken or deform bones. This leads to pain and might affect how a child moves.
Common Locations of Bone Pain in Children
Bone pain from bone marrow disease can happen in different places. Common spots include:
- The arms and legs, mainly in long bones
- The back, ribs, and pelvis
- The sternum and clavicles
These areas have a lot of bone marrow. Disease here can cause a lot of pain.
| Location | Possible Causes | Symptoms |
| Arms and Legs | Bone marrow expansion or infiltration | Pain, swelling |
| Back, Ribs, Pelvis | Bone marrow disease affecting bone structure | Pain, tenderness |
Distinguishing Growing Pains from Bone Marrow Disorder Symptoms
Growing pains are common in kids, usually in the legs. But, bone marrow disorder symptoms can also cause limb pain. It’s key to tell them apart.
Growing pains happen at night, affect both sides, and don’t have other symptoms like fever or swelling. Bone marrow disease pain is often constant, in one spot, and can have other symptoms like tiredness, fever, or bruising.
If your child has ongoing or severe bone pain, see a doctor. They can find out why.
Petechiae and Purpura: Signs of Bone Marrow Issues
Petechiae and purpura are skin signs that can point to bone marrow problems in kids. They often show up when there’s a low platelet count. This is a common issue with bone marrow disorders.
Identifying These Distinctive Skin Manifestations
Petechiae are small spots on the skin from tiny blood vessel breaks. They are usually red or purple and can group together. Purpura are bigger, purple patches from bleeding under the skin.
To spot these signs, look for skin that’s discolored or bruised without a clear reason. Watching these spots is key, as they can point to serious health issues, like bone marrow disease.
What Causes Petechiae in Bone Marrow Disorders
Petechiae and purpura often come from low platelet counts in bone marrow disorders. Platelets help blood clot, and low numbers can cause easy bruising and bleeding.
When the bone marrow can’t make enough platelets, it can be due to diseases like aplastic anemia and leukemia. This failure can lead to a drop in platelet production, making spots more likely.
When Skin Spots Require Immediate Medical Attention
While petechiae and purpura might hint at bone marrow problems, not all cases are serious. Yet, it’s important to see a doctor if you notice:
- Rapid growth of petechiae or purpura
- Other symptoms like fever, tiredness, or bleeding
- Petechiae or purpura in a child, as they can signal serious issues
If you’re worried about your child’s skin or think spots might be from bone marrow issues, get medical help fast. Early treatment can make a big difference in managing bone marrow diseases.
Recurrent Nosebleeds and Bleeding Gums
Children with frequent nosebleeds and bleeding gums might have a bone marrow disorder. This disorder affects their body’s ability to make enough platelets. Platelets are key for blood to clot, and not having enough can cause bleeding problems.
The Connection Between Platelet Production and Bleeding
Platelets are made in the bone marrow. When the bone marrow is sick, it can’t make enough platelets. This leads to thrombocytopenia, or low platelet counts. Low platelet counts cause nosebleeds and bleeding gums because the body can’t clot blood well.
“The link between platelet count and bleeding risk is clear,” says a hematologist. “Kids with low platelet counts bleed more often. This can be scary and needs quick help.”
Normal vs. Abnormal Bleeding in Children
It’s important to tell normal from abnormal bleeding in kids. Sometimes, kids get nosebleeds from dry air or minor bumps. But frequent or long-lasting bleeding is not normal and might mean something serious is wrong.
Bleeding gums can be from bad oral hygiene, but if it happens a lot with nosebleeds, it could mean a bigger problem with the bone marrow.
- Frequent or severe nosebleeds
- Bleeding gums without apparent cause
- Petechiae or purpura on the skin
Seeing a doctor is important to figure out why these signs are happening.
Managing Bleeding Episodes at Home
While waiting for a doctor, parents can help at home. For nosebleeds, gently press the nostrils and keep the head up. For bleeding gums, clean teeth well and avoid hard foods.
Parents should stay calm and follow these steps to help their child. But if bleeding doesn’t stop or gets worse, they need to get medical help right away.
Growth Delays and Developmental Issues
Bone marrow disease can greatly affect a child’s growth and development. It can cause many health problems that impact a child’s overall well-being.
Impact on Physical Growth
Bone marrow disease can slow down physical growth in several ways. Anemia and other complications can make a child very tired. This can stop them from doing normal activities, which can slow growth.
Also, treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can affect growth hormones. It’s important for parents to keep a close eye on their child’s growth and talk to their healthcare team about any concerns.
Developmental Delays Associated with Bone Marrow Disorders
Children with bone marrow disease may also face developmental delays. These can include slow speech, motor skill problems, and cognitive issues. The reasons for these delays can be many, including the disease itself, treatment side effects, and the emotional toll of being sick all the time.
For example, a child who is in the hospital a lot may miss out on important learning experiences. It’s key for parents to seek help for their child, like physical and speech therapy, to help them catch up.
Monitoring Your Child’s Growth and Development
Keeping a close eye on a child’s growth and development is vital. Parents should work with their child’s healthcare team to track progress and catch any delays early.
By staying in touch with healthcare professionals and being proactive, parents can help their child get the support they need. This way, their child can thrive despite the challenges of bone marrow disease.
“Early intervention and thorough care can greatly improve the future for children with bone marrow disorders.”
Breathing Difficulties and Reduced Exercise Tolerance
Bone marrow disease can cause anemia in children, leading to breathing problems. Anemia happens when there’s not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. These are key for carrying oxygen to our tissues.
When the bone marrow can’t make enough red blood cells, our body doesn’t get enough oxygen. This can cause symptoms like shortness of breath.
The Relationship Between Red Blood Cells and Oxygen
Red blood cells are vital for carrying oxygen from our lungs to our body’s tissues. Inside these cells, a protein called hemoglobin binds to oxygen. This helps deliver oxygen to where it’s needed.
In bone marrow disease, making red blood cells can be a problem. This means less oxygen gets delivered. Children might feel tired, weak, and have trouble breathing.
Recognizing Symptoms of Bone Marrow Failure in Breathing
Symptoms of bone marrow failure that affect breathing include shortness of breath and rapid breathing. In severe cases, the skin might turn blue (cyanosis). Children may also get tired easily or have trouble playing.
It’s important to notice these symptoms early. This helps get medical help quickly.
When to Seek Emergency Care for Breathing Problems
If a child has severe breathing trouble, shows cyanosis, or seems confused and tired, get help right away. These signs mean they might not be getting enough oxygen. Quick medical care can make a big difference.
| Symptom | Description | Action |
| Shortness of Breath | Difficulty breathing or feeling winded even at rest | Monitor closely, consult a doctor if persistent |
| Rapid Breathing Rate | Breathing faster than normal | Seek medical evaluation |
| Cyanosis | Blue discoloration of the skin | Emergency medical care |
Enlarged Liver or Spleen: Visible Signs of Bone Marrow Problems
The liver and spleen are key to our body’s health. They filter blood, store red blood cells, and help fight off infections. When bone marrow diseases disrupt blood cell production, these organs can swell up.
Why Organ Enlargement Occurs
When bone marrow diseases spread, they can fill the liver and spleen with bad cells. This makes these organs grow bigger. For example, leukemia can cause the liver and spleen to swell up with cancer cells.
This swelling is not just a simple growth. It’s a sign of a serious problem that needs to be fixed. How much they swell depends on the disease’s severity and type.
Recognizing Abdominal Changes
Spotting changes in the belly can be tricky at first. But as the problem gets worse, kids might feel pain or discomfort in the upper belly. Sometimes, the swelling is big enough to see or feel.
Common signs to look out for include:
- Abdominal distension or swelling
- Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen
- Early satiety or loss of appetite
- Fatigue due to anemia or other related conditions
Complications of Enlarged Organs
An enlarged liver or spleen isn’t a disease itself. But it can cause big problems if not treated. For example, a big spleen can trap blood cells, leading to anemia, infections, or bleeding issues.
Also, a very big spleen can hurt, cause pain, or even burst. This is a serious emergency. So, it’s important for parents to watch for these signs and get medical help if they see them in their child.
Conclusion: Recognizing and Responding to Bone Marrow Disease Symptoms
It’s key to spot the signs of bone marrow disease in kids early. We’ve talked about bone marrow symptoms like tiredness and getting sick a lot. Also, signs like easy bruising and unexplained fevers are important.
Knowing these symptoms of bone marrow disorders helps parents act fast. This quick action is vital for kids to get the right care. Early treatment can really help kids get better.
Being on the lookout for bone marrow disease symptoms in child is a must. If you see anything odd, get medical help right away. This way, your child can get the help they need quickly.
We stress how important it is to know and act on bone marrow problems and symptoms. With the help of doctors, you and your child can face bone marrow disease together.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of bone marrow disease in children?
Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and frequent infections. Easy bruising and unexplained fevers are also common. Other signs are pallor, bone pain, and breathing difficulties.
How does bone marrow disease cause extreme tiredness in children?
It reduces red blood cell production. Red blood cells carry oxygen. Without enough, tissues don’t get enough oxygen, leading to fatigue and weakness.
What is the connection between immune function and bone marrow?
Bone marrow makes white blood cells. These cells fight infections. A disease here can weaken the immune system.
Why do children with bone marrow disease experience easy bruising and unusual bleeding episodes?
It’s because of platelet deficiencies. Platelets help blood clot. Without enough, bleeding and bruising happen more easily.
When should parents be concerned about their child’s infection frequency?
If your child gets infections often, it’s a worry sign. It might mean their white blood cells aren’t being made right.
How can anemia resulting from bone marrow disease affect a child’s skin color?
Anemia makes skin pale. This is because red blood cells carry oxygen. Without enough, tissues don’t get enough oxygen.
What are petechiae and purpura, and how are they related to bone marrow issues?
These are skin spots that show low platelet counts. It’s a sign of bone marrow problems.
How does bone marrow disease affect a child’s physical growth and development?
It can slow growth and development. This is because it affects blood cell production, leading to complications.
What is the relationship between red blood cells and oxygen delivery, and how does it relate to breathing difficulties?
Red blood cells carry oxygen. Without enough, tissues don’t get enough oxygen. This can cause breathing problems and make it hard to exercise.
Why does organ enlargement occur in bone marrow diseases?
It happens when abnormal cells build up. Or when the body tries to make up for the bone marrow’s reduced function.
What are the possible complications of enlarged organs in bone marrow disease?
Enlarged organs can cause discomfort and pain. They can also make organ function worse.
How can parents manage bleeding episodes at home?
Apply gentle pressure to the area. Elevate the affected limb. Seek medical help if bleeding doesn’t stop.
When should parents seek emergency care for their child’s breathing problems?
Get emergency help for severe breathing issues. This includes rapid breathing, shortness of breath, or blue-tinged lips.
References
- Vissers, L. T. W., et al. (2023). Pediatric bone marrow failure: A broad landscape in hematology. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, Article 883826. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2022.883826/full
- Leng, Y. L., et al. (2025). Differentiating primary bone marrow failure syndromes in children: Early clinical features and predictive factors for diagnosis. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 13, Article 11550. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12176817/




































