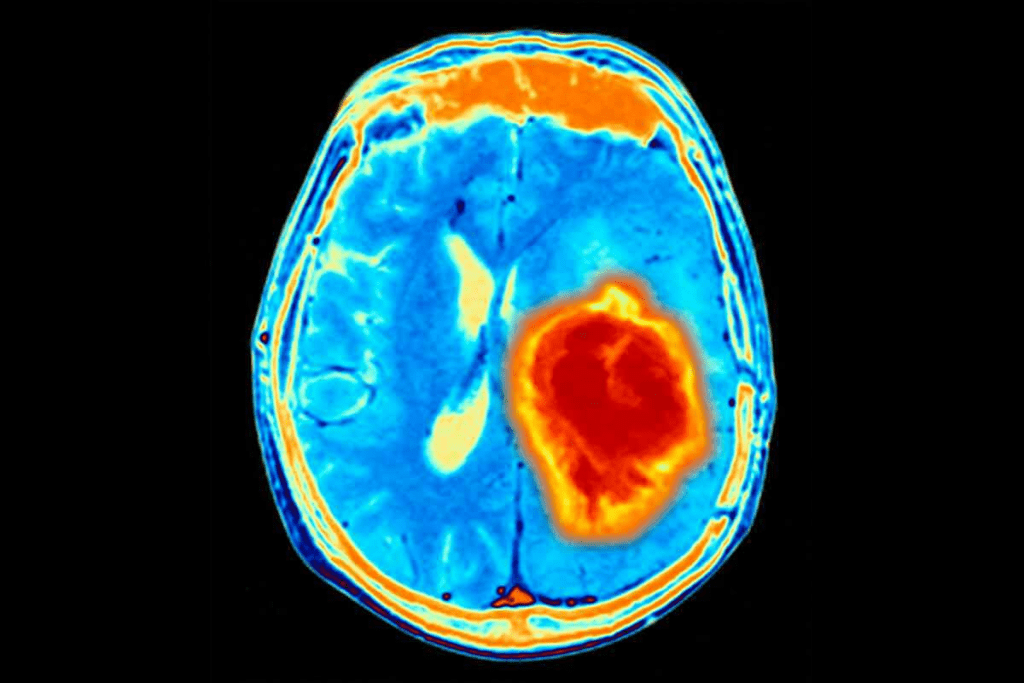
Modern medicine has made big steps in finding brain tumors. A key tool is the MRI scan, which has changed medical imaging a lot.
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan uses strong magnets to show detailed pictures of inside the body. It does this without using harmful radiation. This makes it great for checking sensitive areas.
Liv Hospital is all about the latest in medical tests and caring for patients. They show how MRI scans can spot tumors very well. In some cases, MRI’s accuracy is over 97%. This makes MRI a top choice for finding tumors.
Key Takeaways
- MRIs are a critical diagnostic tool for detecting brain tumors.
- Modern MRI scans achieve high diagnostic accuracy.
- MRI technology uses strong magnets, not radiation.
- Liv Hospital is at the forefront of diagnostic care.
- Understanding MRI scans is essential for informed health decisions.
The Science Behind Brain Cancer MRI Technology
MRI technology uses strong magnetic forces and radio waves to create detailed brain images. It’s great for finding and understanding brain tumors. This tech is key for doctors to see what’s going on inside the brain.
How MRI Creates Detailed Brain Images
MRI works by using nuclear magnetic resonance. When you get an MRI, a strong magnetic field aligns hydrogen atoms in your body. Then, radio waves disturb these atoms, causing them to send signals. The MRI machine catches these signals to make detailed images.
The steps are:
- Alignment of hydrogen atoms using a strong magnetic field
- Disturbing these atoms with radiofrequency waves
- Capturing the emitted signals
- Reconstructing these signals into detailed images
This tech helps doctors see soft tissues in the brain. It’s very useful for finding brain tumors.
Why MRI Outperforms CT and Other Imaging Methods
MRI is better than CT scans and other methods in many ways. It gives clear images of soft tissues without using harmful radiation. A study inPLOS ONE shows MRI is more sensitive in finding brain tumors. This makes MRI the top choice for diagnosing brain cancer.
Here are some reasons why MRI is better:
- High-resolution imaging of soft tissues
- No ionizing radiation, making it safer for patients
- Ability to detect a wide range of tumor types and characteristics
These benefits make MRI essential for diagnosing and planning treatment for brain cancer.
Remarkable Accuracy: Modern MRI Brain Tumor Detection Rates
Modern MRI technology has greatly improved in detecting brain tumors. It uses deep learning models to create detailed images. These images help doctors find tumors accurately.
Studies show MRI is very good at spotting certain cancers. Doctors can even tell if a tumor is cancerous just by looking at the MRI images.
Deep Learning Models Achieving 97%+ Diagnostic Accuracy
Deep learning models have made MRI scans much better. They can spot complex patterns in images, reaching accuracy rates over 97%.Research studies show MRI and deep learning together improve brain tumor detection.
Using deep learning in MRI analysis is a big step forward in neuro-oncology. It helps doctors make better decisions for their patients.
Sensitivity and Specificity for Different Tumor Types
How well MRI detects brain tumors depends on the tumor type. For example, MRI is great at spotting mri benign brain tumor cases. It gives detailed info about the tumor.
When it comes to benign vs malignant brain tumor mri images, MRI is very helpful. But sometimes, more tests are needed to be sure.
It’s important to know what MRI can and can’t do for different brain tumors. The answer to can MRI detect brain tumor is usually yes. But, it depends on the tumor’s size, location, and type.
Can MRI Detect Brain Tumor? Capabilities and Limitations
Detecting brain tumors with MRI is complex. It’s important to know what MRI can and can’t do. MRI is key in brain tumor imaging because it’s very sensitive and shows soft tissues well.
MRI’s Role in Brain Tumor Detection
MRI is great at finding many brain tumors. It helps doctors spot both cancerous and non-cancerous growths. It uses strong magnets and radio waves to show brain details, making tumors visible that other methods miss.
Detection Thresholds for Various Tumor Types
Each brain tumor type has its own MRI visibility level. High-grade gliomas are usually easy to spot because they stand out with contrast and size. Low-grade gliomas, on the other hand, might be harder to see and need a closer look.
- High-grade gliomas: Show strong contrast and big size.
- Low-grade gliomas: Look like non-enhancing or slightly enhanced spots.
- Meningiomas: Appear as clear, outside-the-brain masses with strong contrast.
When Additional Imaging Techniques May Be Necessary
Even though MRI is very good, sometimes more tests are needed. If a tumor isn’t clear on MRI or if doctors want to see how active it is, they might use PET or CT scans along with MRI.
Complementary Imaging Techniques
Using MRI with other tests can give a fuller picture of the tumor. This is helpful for:
- Seeing how aggressive the tumor is
- Planning surgery
- Tracking how well treatment is working
Knowing what MRI can and can’t do helps doctors make better choices for their patients.
What Do Tumors Look Like on MRI? Visual Characteristics
On MRI, tumors show unique patterns and abnormalities. MRI technology gives detailed views of soft body tissues. It’s key for spotting tumors.
Signal Intensity Patterns and Abnormal Masses
Tumors on MRI look like distinct masses with odd signal intensity. The intensity changes based on the tumor type, grade, and makeup. For example, some tumors look bright on T2-weighted images because they have lots of water. Others look dark on T1-weighted images.
A study on theNational Center for Biotechnology Information shows MRI has greatly helped find and understand brain tumors.
Edema, Enhancement, and Other Visual Markers
Swelling, or edema, around tumors is common on MRI. It shows up as a bright area on T2-weighted images. Tumors also show contrast material uptake, which helps figure out their nature and grade.
Other signs include the tumor’s shape, its position, and any effects it has on nearby areas. These details help doctors decide if the tumor can be removed and plan treatment.
Case Examples of Different Tumor Appearances
Different tumors look different on MRI. For instance, glioblastomas are irregular and enhance with contrast, surrounded by swelling. Meningiomas, on the other hand, are well-defined and enhance near the brain’s surface.
Studies show MRI can tell apart various brain tumors by their looks. This info is essential for making treatment plans and predicting how patients will do.
Benign vs. Malignant Brain Tumor MRI: Critical Differences
It’s important to know the difference between benign and malignant brain tumors on MRI. MRI scans help doctors tell these tumors apart. They look at specific signs in the images.
Well-Defined Borders vs. Invasive Patterns
Benign tumors have well-defined borders. They look like clear, round shapes that stand out from the brain. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, have invasive patterns. Their edges are not clear and blend into the brain.
“Benign tumors have clear edges, while malignant ones don’t,” a study on brain tumors says.
Contrast Enhancement Characteristics
How tumors look with contrast on MRI is key. Malignant tumors show heterogeneous enhancement. They have spots of dead tissue and uneven brightness. Benign tumors, by contrast, look homogeneous. They are evenly bright and uniform.
- Malignant tumors: heterogeneous enhancement, necrosis, irregular patterns
- Benign tumors: homogeneous enhancement, uniform patterns
Growth Patterns and Surrounding Tissue Effects
The way a tumor grows and affects the brain is also telling. Malignant tumors infiltrate the brain, causing swelling and pressure. Benign tumors can also cause swelling but tend to displace brain structures instead of spreading into them.
A top neuroradiologist says, “MRI shows how aggressive a tumor is. It helps doctors decide the best treatment.”
In summary, MRI is key in telling benign from malignant brain tumors. By looking at the tumor’s edges, how it looks with contrast, and how it grows, doctors can make better diagnoses and plans.
Advanced Brain Cancer MRI Techniques Revolutionizing Diagnosis
Advanced MRI techniques are changing how we diagnose brain cancer. These new methods give us detailed information for planning treatments. They help us understand brain tumors better.
Contrast-Enhanced Sequences and Their Benefits
Contrast-enhanced MRI uses a special agent to show brain areas. It’s great for finding brain tumors because they often show up with this agent. This method helps see tumor edges, spot small tumors, and tell different tumors apart.
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Functional MRI (fMRI) and Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) give us more than just pictures. fMRI shows how brain areas work, which is key for surgery planning. DTI maps out brain paths, helping surgeons avoid damage during operations.
Spectroscopy and Perfusion Studies
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) and perfusion studies are also used. MRS tells us about tumor metabolism, helping identify tumor types and grades. Perfusion studies show how fast blood flows to the tumor, showing its aggressiveness.
Together, these MRI techniques lead to better brain cancer diagnosis. They give detailed info for making treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
Common Brain Tumors and Their Distinctive MRI Signatures
Advanced MRI techniques have greatly improved how we detect and understand brain tumors. This has led to better care for patients. MRI scans help identify and tell apart different brain tumors by their unique signs. Studies show MRI’s accuracy in diagnosing brain tumors is very high, with some models over 97% accurate.
Gliomas: High-Grade vs. Low-Grade Appearance
Gliomas are common primary brain tumors, divided into grades based on how aggressive they are. High-grade gliomas show up on MRI as messy masses with irregular edges, necrosis, and a lot of swelling. Low-grade gliomas look more uniform, with less swelling and clearer edges.
An Expert explains, “Knowing the difference between high-grade and low-grade gliomas on MRI is key for choosing the right treatment.”
“The use of advanced MRI sequences, such as diffusion-weighted imaging and perfusion-weighted imaging, has greatly enhanced our ability to characterize gliomas and predict their grade.” – An Expert Neuro-Oncologist
Meningiomas: Typical Presentation and Variants
Meningiomas are usually benign tumors from the meninges, the brain’s protective membranes. On MRI, they look like clear, extra-axial masses that are the same or a bit brighter than gray matter on T1-weighted images. They enhance strongly after contrast. But, atypical or malignant meningiomas might look more aggressive, with irregular edges and brain invasion.
- Typical meningioma characteristics on MRI:
- Well-defined borders
- Isointense or slightly hyperintense on T1-weighted images
- Strong homogeneous enhancement
- Atypical features:
- Irregular borders
- Heterogeneous enhancement
- Brain invasion
Metastatic Tumors: Identifying Secondary Brain Cancer
Metastatic brain tumors are cancers that have spread to the brain from other places. On MRI, they look like clear, defined lesions at the gray-white junction, with a lot of swelling around them. Contrast-enhanced MRI is key for spotting these, as they show strong ring enhancement. A study in the Journal of Neuro-Oncology found MRI’s sensitivity for brain metastases is over 90%.
| Tumor Type | Typical MRI Features |
| High-Grade Gliomas | Heterogeneous appearance, necrosis, significant edema |
| Low-Grade Gliomas | Homogeneous appearance, less edema, defined border |
| Meningiomas | Well-defined, extra-axial, strong homogeneous enhancement |
| Metastatic Tumors | Multiple lesions, gray-white junction, strong ring enhancement |
In conclusion, MRI is essential for diagnosing and understanding brain tumors. By recognizing the unique MRI signs of gliomas, meningiomas, and metastatic tumors, doctors can make more precise diagnoses and plan better treatments.
Preparing for a Brain Cancer MRI: Patient Experience Guide
Getting ready for your brain cancer MRI can make you feel less anxious. It’s a detailed test that shows the brain’s images. This helps doctors find and treat brain tumors well.
Before Your Scan: Preparation and Expectations
There are steps to take before your MRI. Remove any metal objects like jewelry and glasses. You’ll wear a hospital gown to avoid metal on your body.
Tell your doctor about any medical implants or conditions. This includes pacemakers and claustrophobia. It might change your procedure or need special plans.
- Arrive at least 30 minutes before your scheduled appointment time to complete any necessary paperwork.
- Bring any relevant medical records or previous MRI scans.
- Follow any specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider, such as fasting or avoiding certain medications.
During the Procedure: What Happens in the MRI Suite
In the MRI suite, you’ll lie on a table that moves into the machine. The test is usually painless but might feel tight or noisy.
To help you relax, you might get earplugs or headphones. Sometimes, mild sedation is offered if you’re nervous.
After Your Scan: Results Timeline and Next Steps
After the MRI, a radiologist will review the images. Your doctor will then talk to you about the results. You’ll usually hear back within a few hours or the next day.
Your doctor will explain the findings and what to do next. This could include more tests, a biopsy, or treatment plans.
| Result Timeline | Next Steps |
| Within a few hours | Discussion with your doctor |
| The next day | Further testing or treatment planning |
How MRI Findings Guide Brain Tumor Treatment Planning
MRI has changed how we plan treatment for brain tumors. It gives us detailed information about the tumor. This info is key for making treatment plans that work well.
Surgical Navigation and Resection Planning
MRI helps a lot with planning surgery for brain tumors. It shows where the tumor is, how big it is, and how it’s related to other parts of the brain. This helps surgeons plan the best way to remove the tumor safely.
- Precise tumor localization
- Identification of critical surrounding structures
- Planning of optimal surgical approach
A study onNature.com shows MRI makes surgery better for patients.
Radiation Therapy Targeting Precision
MRI is also key for making radiation therapy more precise. It shows the tumor’s edges and how it’s near other tissues. This helps doctors aim radiation therapy better, protecting healthy brain areas.
Using MRI for radiation planning helps patients get better results and fewer side effects.
Monitoring Treatment Response and Recurrence
MRI is important not just for planning treatment but also for checking how well it’s working. Regular scans help doctors see if the tumor is responding to treatment. They can also spot if the tumor comes back early.
- Regular MRI scans for treatment response assessment
- Early detection of recurrence
- Adjustment of treatment plans as necessary
MRI gives insights into how the tumor behaves and how it’s responding to treatment. This helps doctors make changes to treatment plans. It ensures patients get the best care possible.
Conclusion: The Evolving Future of Brain Cancer MRI
The future of brain cancer MRI is changing fast. New tech is making it better for finding and treating brain tumors. MRI is getting more accurate at spotting and understanding brain cancers.
New methods and uses are coming for MRI in brain cancer care. These include better imaging, functional MRI, and diffusion tensor imaging. They help doctors learn more about tumors and the brain around them.
Brain cancer MRI’s role is set to grow, with hopes for personalized treatments. As MRI tech gets better, it will help more in treating brain cancer patients.
FAQ
Can MRI detect brain tumors?
Yes, MRI is very good at finding brain tumors. It shows the brain in detail and spots tumors accurately.
What do tumors look like on MRI?
Tumors on MRI look like odd masses. They have special signal patterns. They might show up more with contrast agents and often have swelling around them.
How accurate is MRI in detecting brain tumors?
MRI is very accurate, thanks to new technology and deep learning. It can spot tumors with 97% accuracy or more for some types.
Can MRI distinguish between benign and malignant brain tumors?
Yes, MRI can tell the difference. It looks at how the tumor grows, its edges, and how it reacts to contrast agents.
What are the advantages of MRI over CT scans for brain tumor detection?
MRI is better than CT scans for finding brain tumors. It shows soft tissues better, spots smaller tumors, and doesn’t use harmful radiation.
Are there any limitations to MRI in detecting brain tumors?
MRI is very good, but it has limits. It can miss some tumors, and sometimes, other tests are needed too.
How do advanced MRI techniques improve brain cancer diagnosis?
New MRI methods give more info. They include contrast-enhanced scans, functional MRI, and others. These help understand tumor behavior and characteristics.
Can MRI be used to monitor treatment response and recurrence?
Yes, MRI is key for tracking treatment and finding tumors again. It helps doctors make better treatment plans.
How do MRI findings guide brain tumor treatment planning?
MRI findings are vital for planning treatment. They help with surgery, radiation, and checking how well treatment works. This ensures treatment is precise and effective.
What should I expect during a brain cancer MRI?
During a brain cancer MRI, you’ll lie on a table that moves into the scanner. You’ll need to stay very quiet and not move during the scan.
How long does it take to get results from a brain cancer MRI?
Getting MRI results can take a few hours or days. A radiologist will look at the images and give a report to your doctor.
Can MRI detect metastatic brain tumors?
Yes, MRI is good at finding tumors that have spread to the brain. These are called metastatic brain tumors.
References
- Abdusalomov, A.B. et al. (2023). Brain tumor detection based on deep learning in MRI images. PMC.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10453020/




































