Last Updated on October 31, 2025 by Saadet Demir

A bulging eardrum happens when the tympanic membrane pushes out. This is due to too much pressure or fluid in the middle ear. It usually means there’s a problem that needs a doctor’s help.
The tympanic membrane, or eardrum, is key for hearing. It vibrates when sound waves hit it. Then, it sends these vibrations to the tiny bones in the middle ear.
Spotting a bulging eardrum is important for finding ear problems. At Liv Hospital, we use advanced tools to check and fix this issue.
How to recognize a bulging eardrum, a sign of pressure buildup and fluid (otitis media) that requires medical attention.
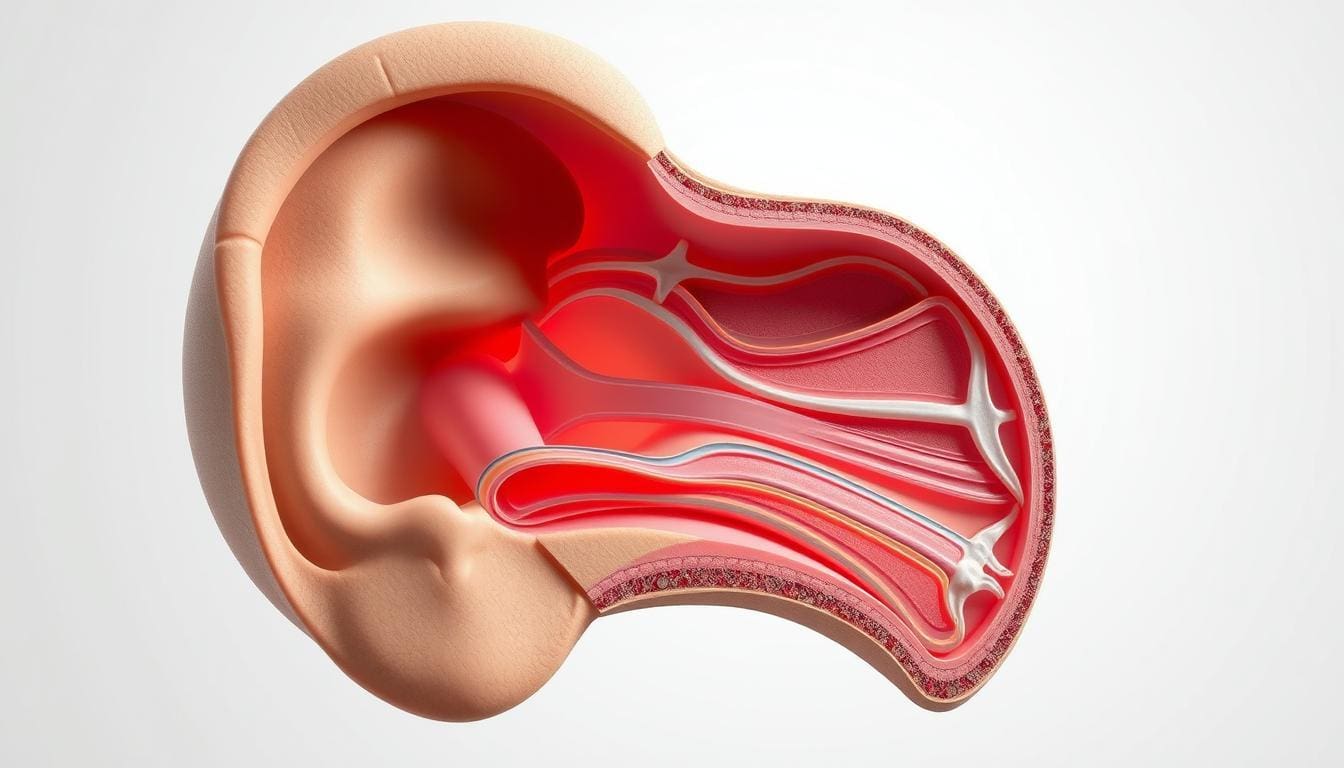
Knowing how the eardrum works is key to spotting problems and keeping ears healthy. The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is a thin, semi-transparent layer. It separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear. It vibrates with sound waves and sends these vibrations to the ossicles in the middle ear.
The eardrum has three layers: an outer layer, a middle layer, and an inner layer. The outer epithelial layer connects with the ear canal’s skin. The inner mucosal layer links with the middle ear’s mucous membrane. The middle fibrous layer gives the eardrum its strength and flexibility.
The eardrum’s job is to send sound vibrations to the ossicles. The ossicles then send these vibrations to the inner ear. This is how we hear normally. Any problem with the eardrum can affect our hearing.
A healthy eardrum is thin, clear, and whole, with a normal light reflex. The light reflex is a light reflection that looks like a cone pointing to the eardrum’s center. A normal eardrum is also slightly concave and angled in the ear canal.
To understand a healthy eardrum better, let’s look at its details:
Characteristic | Normal Appearance |
Color | Pearl-gray or light gray |
Transparency | Translucent |
Light Reflex | Cone-shaped reflection |
Position | Slightly concave |
Otolaryngologists say, “A normal eardrum is vital for sound wave transmission. Any change in its appearance can signal a problem.”
“The normal tympanic membrane is a delicate structure that requires precise examination to diagnose any abnormalities.”
Knowing the eardrum’s normal anatomy and look is key for diagnosing and treating ear issues. Next, we’ll look at what makes a bulging eardrum and its implications.
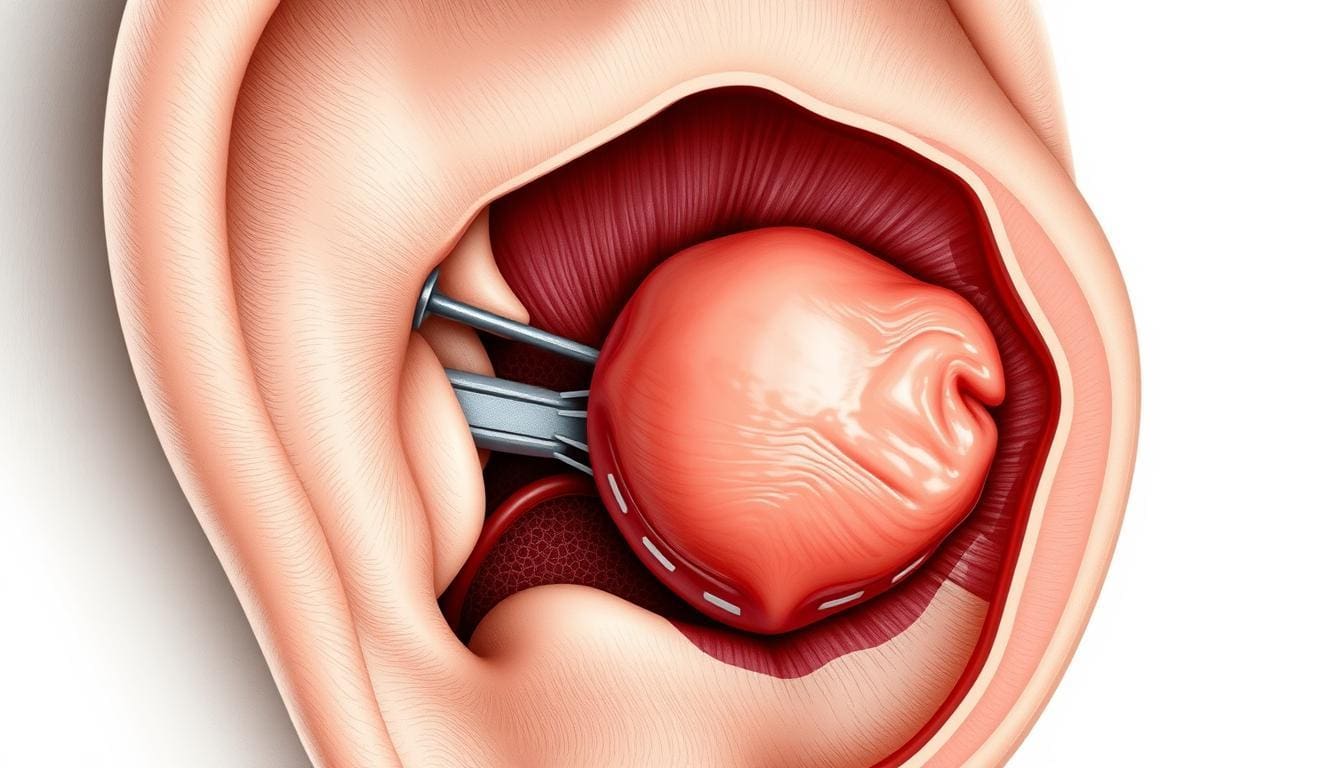
A bulging eardrum happens when the tympanic membrane pushes outwards. This is due to too much pressure or fluid in the middle ear. It can be caused by infections, problems with the Eustachian tube, or barotrauma.
The tympanic membrane, or eardrum, is a thin layer between the outer ear and the middle ear. It keeps a certain tension under normal conditions. But, if middle ear pressure gets out of balance, the eardrum can bulge.
Otolaryngologists say the eardrum’s position and how it moves are key to middle ear health. A bulging eardrum usually means there’s a problem with middle ear pressure. This can be due to issues with the Eustachian tube or fluid buildup.
Changes in middle ear pressure can really affect the eardrum. If the Eustachian tube is blocked or not working right, pressure or fluid can build up. This pushes the eardrum out, making it bulge.
This can hurt and might make it hard to hear. Things like middle ear infections, allergies, or changes in air pressure can cause these problems. It’s important to know about these causes and effects to get the right treatment.
By understanding what causes a bulging eardrum, people can get help sooner. This can help avoid more serious issues.
Many things can cause a bulging eardrum. This includes middle ear infections and problems with the Eustachian tube. Knowing what causes it helps in treating it.
Middle ear infections, or otitis media, often cause a bulging eardrum, mainly in kids. Fluid buildup behind the eardrum is a sign of infection. Symptoms include ear pain, fever, and hearing loss.
Key factors contributing to otitis media include:
The Eustachian tube helps balance air pressure in the middle ear. If it doesn’t work right, the eardrum can bulge. This can happen due to allergies, colds, or sinus infections.
Symptoms associated with Eustachian tube dysfunction include:
Barotrauma happens when there’s a big pressure difference between the outside and the middle ear. This can occur during flying, diving, or driving through mountains. The pressure change can damage the eardrum.
Prevention strategies for barotrauma include:
Knowing the common causes of a bulging eardrum helps prevent them. It also helps find the right medical care when needed.
It’s important to know the signs of a bulging eardrum to get the right treatment. You might see or feel different symptoms. These need to be watched closely.
A bulging eardrum can cause ear pain, fullness or pressure, and hearing loss. These happen because of the extra pressure on the eardrum. This is often from middle ear infections or problems with the Eustachian tube.
You might also feel discomfort or unease in your ear. This feeling can stay the same or change with the environment’s pressure.
Doctors look for signs like a bulging or erythematous tympanic membrane during exams. This means the eardrum is inflamed or infected. It might look retracted or bulging because of the pressure.
They also check the eardrum’s color and mobility with an otoscope. A bulging eardrum might move less because of the pressure.
People with a bulging eardrum might also have fever if it’s caused by an infection. They could see discharge or fluid leakage from their ear if it’s perforated.
Some might hear tinnitus or ringing in the ears. This can be very upsetting. If these symptoms don’t go away or get worse, you should see a doctor.
We find certain groups are more likely to have bulging eardrums. Knowing who these groups are helps us catch and treat the problem early.
Children are more likely to get ear infections because their Eustachian tubes are smaller. This makes them at risk for bulging eardrums. Ear infections are common in young children, and if not treated, can cause serious problems.
Infants are extra vulnerable because their Eustachian tubes are even narrower and less effective. This makes them more likely to get middle ear infections and related issues.
Those who keep getting ear infections or have chronic Eustachian tube issues are at higher risk. Recurring ear problems suggest a deeper issue that might need medical help to avoid worse problems.
These people should get regular check-ups from doctors to keep their condition under control and prevent a bulging eardrum.
People with weak immune systems, like those with immunodeficiency or on immunosuppressive drugs, are more prone to infections. A weakened immune system can make infections worse or last longer, raising the risk of complications like a bulging eardrum.
It’s key for these individuals to stay in close touch with their healthcare team. This helps manage their immune status and prevent infections that could harm their ears.
Diagnosing a bulging eardrum involves several steps. We use otoscopic examination, tympanometry, and clinical evaluation. Getting the diagnosis right is key to treating it well.
Otoscopic examination is the main way to spot a bulging eardrum. We use an otoscope to look at the eardrum. We check for bulging, color changes, and light reflexes.
The otoscope helps us see the eardrum’s position, color, and how it moves.
Tympanometry is a key tool for diagnosing. It checks the eardrum’s movement and middle ear reflexes. It tells us about the eardrum’s mobility and middle ear function.
We also use audiometry to check for hearing loss. Tympanocentesis helps relieve pressure.
Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Information Gained |
Otoscopic Examination | Visual inspection of the eardrum | Eardrum position, color, and mobility |
Tympanometry | Measure eardrum mobility and middle ear function | Eardrum compliance and middle ear pressure |
Audiometry | Assess hearing loss | Degree and type of hearing loss |
It’s important to tell a bulging eardrum from other ear issues. We look at conditions like otitis media with effusion, tympanic membrane perforation, and cholesteatoma. A detailed check and tests help us get it right.
By combining what we see with otoscopy, tympanometry, and other tests, we can accurately diagnose a bulging eardrum. Then, we can plan the best treatment.
It’s important to know the differences between a bulging eardrum and a normal one. A bulging eardrum can be a sign of middle ear infections or Eustachian tube problems. It looks different from a healthy eardrum.
Looking at a bulging eardrum and a normal one, you can spot some key differences. A normal eardrum looks clear and shiny, showing light well because it’s thin. A bulging eardrum, though, looks more rounded and might stick out because of pressure.
The color of the eardrum also tells us a lot. A healthy eardrum is usually a pearly gray. But, a bulging eardrum might look red because of infection or inflammation. This color change is a big clue for doctors.
The way the eardrum sits and moves is also telling. A normal eardrum bends a bit and moves with air pressure changes. But, a bulging eardrum is stiffer and might not move at all because of pressure or fluid.
Doctors use a test called tympanometry to check how well the eardrum moves. A bulging eardrum usually doesn’t move as much as a healthy one.
Managing a bulging eardrum needs a detailed plan. It focuses on the cause and easing symptoms. Each plan is made for the person, aiming for relief and avoiding problems.
Medical treatments are key for a bulging eardrum, mainly for infections or Eustachian tube issues. Antibiotics treat middle ear infections. Decongestants help with Eustachian tube problems by easing nasal congestion.
Other treatments might include:
Home remedies can also help with a bulging eardrum. These include:
Always talk to a doctor before trying home remedies, if symptoms don’t get better or get worse.
Surgery might be needed for a bulging eardrum in some cases. This is true for ongoing fluid, infections, or hearing loss.
Surgical Procedure | Description | Indications |
Myringotomy | A surgical incision in the eardrum to drain fluid | Persistent fluid buildup, recurring infections |
Tympanostomy Tube Insertion | Insertion of tubes to ventilate the middle ear | Recurring ear infections, persistent fluid buildup |
Adenoidectomy | Removal of adenoids to reduce infection risk | Recurring infections, Eustachian tube dysfunction |
We decide on surgery based on the severity of symptoms and other treatments’ success.
Knowing about treatment options helps those with a bulging eardrum make informed choices. Working with healthcare professionals leads to the best results.
Knowing when to see a doctor for a bulging eardrum is very important. If you have severe ear pain, can’t hear well, or symptoms get worse, get help fast. It’s key to understand the difference between a bulging eardrum and a normal one. This helps you find the right treatment for ear infections.
We talked about why a bulging eardrum happens, like with middle ear infections. These can cause a lot of pain and serious problems if not treated. Knowing the symptoms and treatment options helps you act quickly.
Seeing a doctor early can prevent serious damage and ensure you get the right treatment. If you’re worried about your symptoms, don’t wait. A doctor can diagnose and suggest the best treatment, helping you feel better and avoid serious issues.
A bulging eardrum happens when pressure or fluid builds up behind it. This makes the eardrum bulge outward. It’s often a sign of a middle ear infection or Eustachian tube problems.
Common causes include middle ear infections and Eustachian tube issues. Barotrauma, or pressure changes, can also cause it. Knowing these causes helps in treating it right.
Symptoms include discomfort and hearing changes. You might also feel pain or a fullness in your ear.
Doctors use otoscopy and tympanometry to diagnose it. These tests help find the problem accurately.
Treatments include medical care and home remedies. Sometimes, surgery is needed to fix the cause.
Kids, people with ear problems, and those with weak immune systems are at risk. They might need more treatment.
Yes, it can mean a serious issue like a middle ear infection. Seeing a doctor is important if symptoms don’t get better.
A bulging eardrum looks swollen and might be red. It moves less than a normal eardrum, which is thin and clear.
The Eustachian tube keeps air pressure in the middle ear balanced. If it doesn’t work right, the eardrum can bulge.
See a doctor for persistent or severe symptoms like pain or hearing loss. Early treatment can help a lot.
Tympanometry tests the eardrum’s function and middle ear reflexes. It helps diagnose issues like a bulging eardrum.
Yes, it can happen without an infection. For example, Eustachian tube problems or barotrauma can also cause it.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023, September 25). Sinus Infection (Sinusitis). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/sinus-infection.html
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us