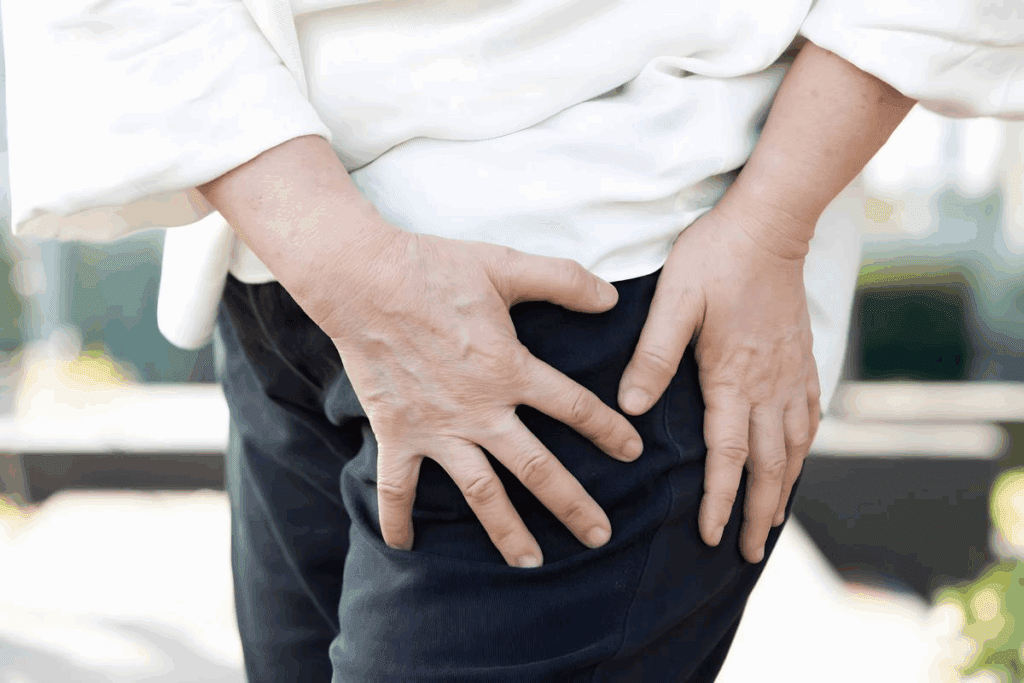
Many people suffer from hip pain because of wrong diagnoses. Often, what seems like tendonitis is really bursitis. This is a condition that makes the fluid-filled sacs around joints and tissues swell.
It’s important to know the difference between tendonitis vs bursitis. Both can make your hip hurt and swell, but they need different treatments. If you’re not diagnosed right, you might suffer for a long time without getting better.
Key Takeaways
- Distinguishing between bursitis and tendonitis is essential for effective treatment.
- Bursitis causes inflammation in the fluid-filled sacs around joints.
- Misdiagnosis can lead to prolonged hip pain and ineffective treatments.
- Understanding the differences between bursitis and tendonitis can improve diagnosis.
- Proper diagnosis is key to easing hip inflammation and pain.
Understanding Tendonitis: Causes and Symptoms

Tendonitis is when tendons, which connect muscles to bones, get inflamed. It’s important to know what causes it, its symptoms, and how it’s different from bursitis.
What Happens in Tendonitis?
Tendonitis happens when tendons get irritated or inflamed. This can be from doing the same thing over and over or from a sudden injury. It leads to pain, stiffness, and less mobility in the affected area.
Key symptoms of tendonitis include:
- Pain or tenderness near a joint
- Stiffness, mostly after resting
- Swelling or redness around the tendon
- A grating feeling when moving the tendon
Common Locations for Tendonitis
Tendonitis can happen in any tendon, but some areas get it more often. The most common spots are:
- The shoulders (rotator cuff tendonitis)
- The elbows (tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis)
- The wrists (De Quervain’s tenosynovitis)
- The knees (patellar tendonitis or jumper’s knee)
- The heels (Achilles tendonitis)
Risk Factors for Developing Tendonitis
There are several things that can make you more likely to get tendonitis. These include:
- Age: Tendons get less flexible and more likely to get hurt as you get older.
- Repetitive motions: Doing the same thing over and over can strain tendons.
- Poor biomechanics or technique during sports or work
- Previous injuries or conditions that affect tendon health
Knowing these risk factors and taking steps to prevent them can help avoid tendonitis.
Bursitis in Hip Symptoms: A Common Misdiagnosis
Understanding hip bursitis is key to correct diagnosis and treatment of hip pain. Hip bursitis is when the bursae in the hip area get inflamed. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints and reduce friction.
Recognizing Hip Bursitis
Hip bursitis can take two main forms: trochanteric and iliopsoas bursitis. Spotting the symptoms is the first step to figuring out what’s wrong. Common signs include pain on the outer hip, groin pain, and pain when lying on the affected side or getting up from sitting.
The pain from hip bursitis can be sharp or a dull ache. It often gets worse with activities like climbing stairs, running, or even simple actions like standing up from sitting.
Trochanteric Bursitis vs. Iliopsoas Bursitis
Trochanteric bursitis hits the bursa near the greater trochanter of the femur, causing pain on the outer hip. Iliopsoas bursitis affects the bursa near the iliopsoas muscle, leading to groin pain or pain in the front of the hip.
| Characteristics | Trochanteric Bursitis | Iliopsoas Bursitis |
| Location of Pain | Outer hip | Groin or front of the hip |
| Activities Exacerbating Pain | Running, climbing stairs | Hip flexion activities |
Hip Pain Patterns and Management
Managing hip bursitis means knowing the pain patterns and using the right strategies. This can include physical therapy, anti-inflammatory meds, and sometimes corticosteroid injections.
- Rest and ice to reduce inflammation
- Physical therapy to strengthen the hip muscles
- Avoiding activities that make the condition worse
Getting the right diagnosis and treatment plan is vital for easing symptoms and improving life for those with hip bursitis.
Tendonitis vs. Bursitis: Key Differences
Tendonitis and bursitis often look similar, which can confuse people. Both affect the musculoskeletal system and cause pain. But they involve different parts and have unique traits.
Anatomical Differences Between Tendons and Bursae
Tendons and bursae are key parts of our musculoskeletal system. Tendons are strong cords that link muscles to bones, helping us move. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones, tendons, and muscles, making movement smooth.
Key anatomical differences include:
- Tendons are dense tissue, while bursae are fluid-filled sacs.
- Tendons connect muscles to bones, and bursae are between bones, tendons, and muscles or skin.
- Tendons handle tensile forces, and bursae reduce friction and absorb compressive forces.
Symptom Comparison and Overlap
Tendonitis and bursitis have different structures, but their symptoms can be similar. Both can cause pain, swelling, and limited movement. The location and nature of the pain can help tell them apart.
Common symptoms of tendonitis include:
- Pain that gets worse with activity
- Tenderness and swelling along the tendon
- Crepitus or a grating sensation when moving the affected tendon
Bursitis symptoms may include:
- Pain that is typically more localized to the area of the bursa
- Swelling and redness over the bursa
- Increased pain when pressing on the affected area or moving the adjacent joint
Pain Patterns and Triggers
Understanding pain patterns and triggers can help tell tendonitis from bursitis. Tendonitis pain often follows a pattern related to the activity that stresses the tendon. Bursitis pain can be constant and worsens with direct pressure on the bursa.
“Accurate diagnosis is key for effective management of both tendonitis and bursitis. Knowing the unique traits of each condition helps healthcare providers create targeted treatment plans.” –
Orthopedic Expert
By recognizing the differences in anatomy, symptoms, and pain patterns, healthcare professionals can make accurate diagnoses. This leads to better treatment and outcomes for patients.
What Can Be Mistaken for Tendonitis?
Tendonitis symptoms can be tricky to spot, as other issues look similar. Knowing these conditions helps get the right diagnosis and treatment.
Muscle Strains and Tears
Muscle strains happen when muscles stretch or tear. This can be due to overstretching or sudden muscle contraction. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and trouble moving. Muscle strains are common in athletes and those with hard jobs.
Unlike tendonitis, muscle strains affect the muscle itself. Treatment usually involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Physical therapy is also used to make the muscle stronger.
Ligament Sprains
Ligament sprains occur when ligaments stretch or tear. This can lead to pain and joint instability, sometimes mistaken for tendonitis. Ligament sprains can range from mild to severe.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and bruising. A doctor will often do a physical exam and use X-rays or MRI for diagnosis. Treatment may include rest, physical therapy, or surgery for severe cases.
Nerve Compression Syndromes
Nerve compression happens when a nerve is pinched. This can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness. It can look like tendonitis. Common examples are carpal tunnel syndrome and sciatica.
Nerve compression syndromes need a different treatment than tendonitis. This may include physical therapy, changing how you work, and sometimes injections or surgery to ease nerve pressure.
Arthritis Conditions That Mimic Tendonitis
Arthritis conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and gout can look like tendonitis. This makes it hard to tell what’s wrong. Knowing about these conditions is key to getting the right treatment.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Tendon Symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that mainly hits joints but can affect tendons too. The inflammation from RA can cause pain and stiffness, often in the hands and feet.
Key symptoms of RA that may be mistaken for tendonitis include:
- Pain and stiffness in the hands and feet
- Swelling and redness around the affected joints
- Morning stiffness that lasts for hours
Gout and Pseudogout
Gout and pseudogout are types of arthritis that cause sudden, severe joint pain. Gout is from urate crystals, and pseudogout is from calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals. Both can cause intense pain and swelling near joints, like tendonitis.
Distinguishing features include:
- Sudden onset of severe pain
- Redness and swelling around the affected joint
- Warmth to the touch
Osteoarthritis vs. Tendon Pain
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease that can cause pain and stiffness, often mistaken for tendonitis. OA happens when joints wear out, leading to cartilage breakdown.
Differentiating OA from tendonitis involves:
- Assessing the location and nature of the pain
- Evaluating joint mobility and stiffness
- Imaging studies to visualize joint damage
Shoulder Pain: Bursitis or Tendonitis?
Figuring out what causes shoulder pain is key. It could be bursitis or tendonitis, each needing its own treatment. Shoulder pain affects people of all ages and activity levels.
Characteristics of Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis happens when the bursae in the shoulder joint get inflamed. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints and reduce friction. Symptoms of shoulder bursitis include:
- Pain on the outside of the shoulder or upper arm
- Swelling or redness in the affected area
- Increased pain when lying on the affected side
- Limited mobility and stiffness
Rotator Cuff Tendonitis
Rotator cuff tendonitis is when the tendons in the rotator cuff get inflamed. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons around the shoulder joint. Common symptoms include:
- Pain when reaching overhead or lifting
- Weakness in the shoulder or arm
- Pain when sleeping on the affected side
- A clicking or catching sensation in the shoulder
When Both Conditions Coexist in the Shoulder
Sometimes, both bursitis and tendonitis can happen together in the shoulder. This makes diagnosis and treatment harder. Key factors to consider include:
- The presence of both inflammatory and degenerative changes
- More complex treatment plans that may include a combination of conservative management and interventional procedures
- The importance of a thorough diagnosis to address both conditions effectively
Knowing if shoulder pain is from bursitis, tendonitis, or both is vital for treatment. Accurate diagnosis and proper management can greatly improve outcomes. It helps avoid chronic pain and disability.
Elbow Conditions: Beyond Tennis Elbow
Many elbow conditions exist beyond tennis elbow. These can cause pain and make daily tasks hard. Knowing about these conditions helps in getting the right treatment.
Olecranon Bursitis vs. Lateral Epicondylitis
Olecranon bursitis and lateral epicondylitis are two elbow issues. Olecranon bursitis is inflammation at the elbow’s back, causing swelling and pain when bent. Lateral epicondylitis, or tennis elbow, affects the outside tendons, leading to pain when gripping or twisting.
The main differences are:
- Location of pain: Olecranon bursitis hurts the back of the elbow, while lateral epicondylitis hurts the outside.
- Nature of pain: Bursitis causes swelling and pain at rest, while tendonitis pain is action-triggered.
Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow)
Medial epicondylitis, or golfer’s elbow, affects the inside tendons. It causes pain and stiffness, mainly when flexing the wrist or gripping. It’s common in golfers but can happen to anyone doing repetitive wrist and forearm actions.
Symptoms include:
- Pain and stiffness on the inside of the elbow
- Weakness in the hands and wrists
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers
Forearm Pain: Bursitis or Tendonitis?
Forearm pain can be from bursitis or tendonitis. Bursitis in the forearm is rare but can happen from repetitive motion or trauma. Tendonitis is more common and often from overuse or strain.
To tell them apart, look at:
- Location and nature of pain
- Triggers that make pain worse
- Presence of swelling or redness
Knee Pain: Differentiating Bursitis and Tendonitis
Knee pain can come from many sources, like bursitis and tendonitis. Knowing what causes knee pain is key to treating it right.
Prepatellar Bursitis (Housemaid’s Knee)
Prepatellar bursitis, or housemaid’s knee, is when the bursa in front of the knee gets inflamed. It’s usually from kneeling a lot, causing pain and swelling.
Symptoms include swelling, redness, and tenderness. In bad cases, the swelling can be big, and the area might feel warm.
Patellar Tendonitis (Jumper’s Knee)
Patellar tendonitis, or jumper’s knee, is when the tendon from the kneecap to the shinbone gets inflamed. It’s common in athletes who jump a lot.
Common symptoms are pain and tenderness below the kneecap, worse when jumping, landing, or climbing stairs.
Pes Anserine Bursitis and Goosefoot Tendonitis
Pes anserine bursitis is when the bursa on the lower inner knee gets inflamed. Goosefoot tendonitis is when the tendons in this area get inflamed.
Symptoms of pes anserine bursitis include pain on the lower inner knee, getting worse with activities like climbing stairs or standing up from sitting.
| Condition | Common Cause | Primary Symptoms |
| Prepatellar Bursitis | Repetitive kneeling | Swelling, pain at the front of the knee |
| Patellar Tendonitis | Jumping sports | Pain below the kneecap, tenderness |
| Pes Anserine Bursitis | Overuse, direct blow | Pain on the lower inner knee |
Ankle and Foot Conditions: Complex Diagnoses
Conditions affecting the ankle and foot are tricky to diagnose. This is because of their complex anatomy.
The ankle and foot can face many issues. These problems can really affect how we move and feel. Getting the right diagnosis is key to treating these issues well.
Retrocalcaneal Bursitis vs. Achilles Tendonitis
Retrocalcaneal bursitis and Achilles tendonitis often cause pain in the back of the ankle. Retrocalcaneal bursitis is when the bursa between the Achilles tendon and the heel gets inflamed. Achilles tendonitis is when the tendon gets inflamed or wears down.
The main difference is where and how the pain feels. Pain from retrocalcaneal bursitis is deeper and higher than from Achilles tendonitis.
| Condition | Pain Location | Nature of Pain |
| Retrocalcaneal Bursitis | Upper posterior ankle | Deep, often associated with swelling |
| Achilles Tendonitis | Lower posterior ankle, along the tendon | Sharp, specially with activity |
Medial and Lateral Ankle Bursitis
Ankle bursitis can happen on either side, often from too much motion or direct hits.
It shows as pain and swelling in one spot, getting worse with more activity.
“Understanding the specific location and triggers of ankle pain is key to diagnosing bursitis and telling it apart from other issues.”
Bursitis in the Toes and Forefoot
Bursitis can also hit the toes and forefoot. This usually comes from shoes that don’t fit right or from constant pressure.
To treat it, we need to ease the pressure, wear the right shoes, and sometimes, use corticosteroid shots.
Wrist and Hand: Tendonitis Mimickers
Wrist and hand pain can be caused by many things. It’s important to know what’s causing it to get the right treatment. The wrist and hand have many parts that can get hurt.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a problem with the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist. It happens when these tendons get irritated or squeezed. You might feel pain and tenderness, like when you make a fist or turn your wrist.
Key features of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis:
- Pain on the thumb side of the wrist
- Swelling or tenderness near the thumb
- Difficulty moving the thumb or wrist
Wrist Bursitis and Tendonitis
Wrist bursitis is when the bursae in the wrist get inflamed. Tendonitis is when the tendons get inflamed. Both can make your wrist hurt and move less easily. Bursitis often comes from doing the same thing over and over, or getting hit. Tendonitis can happen from too much use or getting older.
Nighttime Wrist Pain: Causes and Significance
Pain in your wrist at night can really mess up your sleep. It might mean there’s something wrong that needs to be fixed. Possible reasons include:
- Repetitive strain injuries
- Wrist ganglion cysts
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Tendonitis or bursitis
Figuring out why your wrist hurts at night is key to feeling better. If the pain doesn’t go away or is really bad, see a doctor. They can help find out what’s wrong and how to fix it.
Diagnostic Methods: Identifying the True Condition
To diagnose bursitis and tendonitis, doctors use a mix of clinical checks and imaging tests. They aim to find the real cause and plan the best treatment.
Physical Examination and Bursa Tests
First, doctors do a detailed physical check. They look for signs of swelling, tenderness, and stiffness in the affected area. Special tests, like the “bursitis test,” help spot bursitis. This test involves moving the hip in a certain way to see if it hurts.
Key signs of bursitis include:
- Tenderness when touching the bursa
- Swelling or redness
- Pain with certain movements
- Less range of motion
Does Bursitis Show Up on X-ray?
X-rays aren’t the main tool for diagnosing bursitis. But, they can rule out other issues like fractures. Sometimes, an X-ray might show calcium in the bursa, hinting at chronic bursitis. Yet, X-rays can’t see the bursa itself well.
“X-rays are useful for excluding other causes of pain, but they are not the primary diagnostic tool for bursitis.”
MRI and Ultrasound Findings in Bursitis and Tendonitis
MRI and ultrasound are key for checking bursitis and tendonitis. MRI shows detailed images of soft tissues like tendons and bursae. It can spot inflammation, fluid, and damage.
Ultrasound is also great for looking at tendons and bursae in real-time. It can find fluid, thickened tendons, and other signs of bursitis and tendonitis.
- Fluid in the bursa
- Thickened or torn tendons
- Inflammation and swelling around the area
- Calcifications or degenerative changes
By using both clinical checks and imaging, doctors can accurately diagnose bursitis and tendonitis. This leads to better treatment plans.
“The combination of clinical assessment and imaging modalities like MRI and ultrasound enhances diagnostic accuracy and guides targeted treatment for bursitis and tendonitis.”
Intermittent Symptoms: When Conditions Come and Go
Bursitis and tendonitis symptoms can change a lot. This makes it hard for patients and doctors to figure out what’s going on. Both conditions have symptoms that come and go, making it tough to diagnose and treat.
Why Does Bursitis Come and Go?
Bursitis symptoms can change for many reasons. Things like how much you move and pressure on the bursa can affect it. When the bursa gets inflamed, it hurts and makes moving hard. But, resting or avoiding certain activities can help the symptoms go away.
Factors contributing to bursitis flare-ups include:
- Repetitive motion or overuse
- Direct blows or trauma to the affected area
- Infection or underlying inflammatory conditions
Tendonitis Flare-ups and Nighttime Pain
Tendonitis symptoms can also change, with flare-ups happening when you do certain things. Many people with tendonitis hurt at night because their tendons get inflamed and irritated, even when they’re not moving.
Understanding the causes of nighttime pain is key:
- Increased tendon inflammation when in a resting position
- Poor sleeping posture or ergonomics
- Inadequate management of daytime activities
Tracking Symptom Patterns for Better Diagnosis
Keeping a symptom journal is very helpful. It helps find patterns and triggers for bursitis and tendonitis. By tracking symptoms, patients can give doctors the info they need for a correct diagnosis and treatment plan.
Key elements to track include:
- Activities or events that precede symptom flare-ups
- The severity and duration of symptoms
- Any measures that provide relief or exacerbate the condition
Treatment Approaches: Targeting the Right Condition
It’s important to know the difference between bursitis and tendonitis to choose the right treatment. Both have similar symptoms but need different treatments.
Conservative Management Strategies
For both bursitis and tendonitis, the first step is usually conservative management. This includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). It also includes physical therapy to keep the joint moving and strengthen muscles.
Key components of conservative management:
- Rest and activity modification
- Physical therapy
- Use of orthotics or assistive devices
- Stretching and strengthening exercises
A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy showed physical therapy helps. It reduces pain and improves function in hip bursitis patients.
Medication Options for Bursitis and Tendonitis
Medicine is key in managing bursitis and tendonitis symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers like NSAIDs help reduce inflammation and pain.
| Medication Type | Use in Bursitis | Use in Tendonitis |
| NSAIDs | Reduces inflammation and pain | Reduces pain and inflammation |
| Corticosteroid injections | Effective for reducing severe inflammation | Used cautiously due to risk of tendon rupture |
An orthopedic specialist, says corticosteroid injections are effective for acute bursitis. But, they must be used carefully in tendonitis due to risks.
“The goal of treatment is not just to alleviate symptoms but to address the underlying cause, whether it’s bursitis or tendonitis, to prevent recurrence and promote long-term recovery.”
Orthopedic Specialist
Interventional Procedures and When They’re Needed
When conservative management and medication don’t work, interventional procedures might be needed. These include corticosteroid injections, PRP therapy, or sometimes surgery.
PRP therapy involves injecting platelet-rich plasma into the affected area. It’s a promising treatment for cases that don’t respond to other treatments.
The right treatment depends on the diagnosis, symptom severity, and patient factors. A healthcare professional can guide the best treatment plan.
Prevention Strategies for Bursitis and Tendonitis
To prevent bursitis and tendonitis, we need to use several strategies. These include proper body mechanics, regular exercise, and supportive equipment. By following these steps, we can lower our risk of getting these conditions.
Proper Body Mechanics
Keeping a good posture is key to avoiding bursitis and tendonitis. This means being careful with how we move and stand. For example, lifting heavy things right by bending at the knees helps avoid tendon and bursae strain.
It’s also important to stretch and move around when doing the same thing over and over. Changing how we sleep or sit can help prevent these issues too.
Exercise Modifications and Strengthening
Exercise modifications and strengthening are important. Start with a warm-up, then slowly increase the intensity and time. Also, do exercises that make the muscles around joints stronger.
For instance, exercises for the rotator cuff can prevent shoulder tendonitis. Changing how we run or adding cross-training can also help avoid tendonitis in our legs.
Supportive Equipment and Ergonomics
Supportive equipment and ergonomic changes are also key. Use ergonomic furniture, wear supportive shoes, and wear protective gear when needed.
Make sure your workspace supports good posture. This means having your computer at eye level and using a chair with back support. Using knee pads for kneeling can also help.
By using proper body mechanics, modifying exercises, and using supportive equipment, we can prevent bursitis and tendonitis. This keeps our joints healthy and working well.
Conclusion: Ensuring Accurate Diagnosis and Effective Treatment
Getting a correct diagnosis is key to treating bursitis and tendonitis well. Knowing what causes these issues and their symptoms helps in making a good treatment plan. Tests like X-rays and MRI scans are important for confirming the diagnosis and checking for other problems.
Treatment for bursitis and tendonitis often includes rest, physical therapy, and managing pain. Sometimes, surgery is needed to fix deeper problems. For more details on hip bursitis, its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Getting a proper diagnosis and following a treatment plan can help ease symptoms and prevent future problems. It’s important to work with doctors to find the best treatment for your condition.
FAQ
What is the difference between bursitis and tendonitis?
Bursitis is when the bursae, fluid-filled sacs, get inflamed. These sacs cushion joints and reduce friction. Tendonitis is when the tendons, which connect muscles to bones, get inflamed. Both can cause pain and stiffness but affect different parts of the body.
Can bursitis and tendonitis occur at the same time?
Yes, it’s possible to have both bursitis and tendonitis at once. This is common in areas like the shoulder or hip. It makes diagnosing and treating them harder.
How is bursitis diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam, medical history, and imaging like X-ray, MRI, or ultrasound to diagnose bursitis. They might also do a bursa test to check for tenderness and swelling.
Does bursitis show up on X-ray?
X-rays might not show bursitis because they mainly show bones. But, an X-ray can rule out other issues like fractures or osteoarthritis. Ultrasound or MRI are better for seeing bursitis.
What are the symptoms of hip bursitis?
Hip bursitis causes pain on the outside of the hip, thigh, or buttock. It gets worse with activities like walking or climbing stairs. You might also see swelling, redness, and tenderness.
Can bursitis come and go?
Yes, bursitis symptoms can come and go. They can get worse or better based on how active you are, your posture, and any underlying health issues.
How is tendonitis treated?
Tendonitis treatment includes rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). It also includes physical therapy and medication to help with pain and swelling.
What is the difference between trochanteric and iliopsoas bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis is on the outside of the hip, causing pain and tenderness. Iliopsoas bursitis is in the groin area, leading to pain and stiffness in the front of the hip.
Can arthritis be mistaken for tendonitis?
Yes, arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or osteoarthritis can seem like tendonitis. It’s important to get an accurate diagnosis.
How can I prevent bursitis and tendonitis?
To prevent these conditions, keep your body mechanics right, avoid repetitive strain, and use supportive gear. Also, use ergonomic techniques to reduce risk.
References
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2021). Soft Tissue Rheumatic Disorders. Retrieved October 2025, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK585754/?report=reader

































