Can an ear infection cause hearing loss? Learn about the temporary conductive hearing loss caused by fluid buildup behind the eardrum.
Ear infections are common, hitting kids hard, and can mess with hearing. Fluid and swelling in the middle ear might cause hearing problems. We’ll look into how ear infections and hearing loss are linked, and the risks of lasting damage.
Most people with middle ear infections or fluid buildup face some hearing loss. While ear infections are more common in kids, they can hit anyone. Knowing how ear infections affect hearing is key to treating them right.
Key Takeaways
- Ear infections can cause temporary or permanent hearing loss.
- Fluid and inflammation in the middle ear can lead to hearing loss.
- Ear infections are more common in children but can occur at any age.
- Understanding the causes and effects of ear infections is key for effective management.
- Early intervention can help prevent long-term hearing damage.
Understanding Ear Infections and Their Prevalence

Ear infections, or otitis media, are common and affect people of all ages. They are most common in children. These infections happen when bacteria or viruses infect the middle ear, causing inflammation and fluid buildup.
Types of Ear Infections
There are different types of ear infections. Acute otitis media is the most common, with a sudden onset. Otitis media with effusion is when fluid builds up in the middle ear without an acute infection. Chronic suppurative otitis media is a long-lasting infection that can cause the eardrum to perforate and discharge.
Who Is Most Susceptible to Ear Infections
Ear infections are more common in babies and young children. Their Eustachian tubes are smaller, making it harder for fluid to drain. The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communications Disorders says 5 out of 6 children will get an ear infection by 3 years old. Adults with allergies, colds, or sinus infections are also at risk.
Statistics on Ear Infection Occurrence in the United States
Ear infections are a big health issue in the United States. They lead to many doctor visits and sometimes surgery. Most people with middle ear infections or fluid experience some hearing loss. This shows why quick treatment is important.
The Connection Between Ear Infections and Hearing Loss
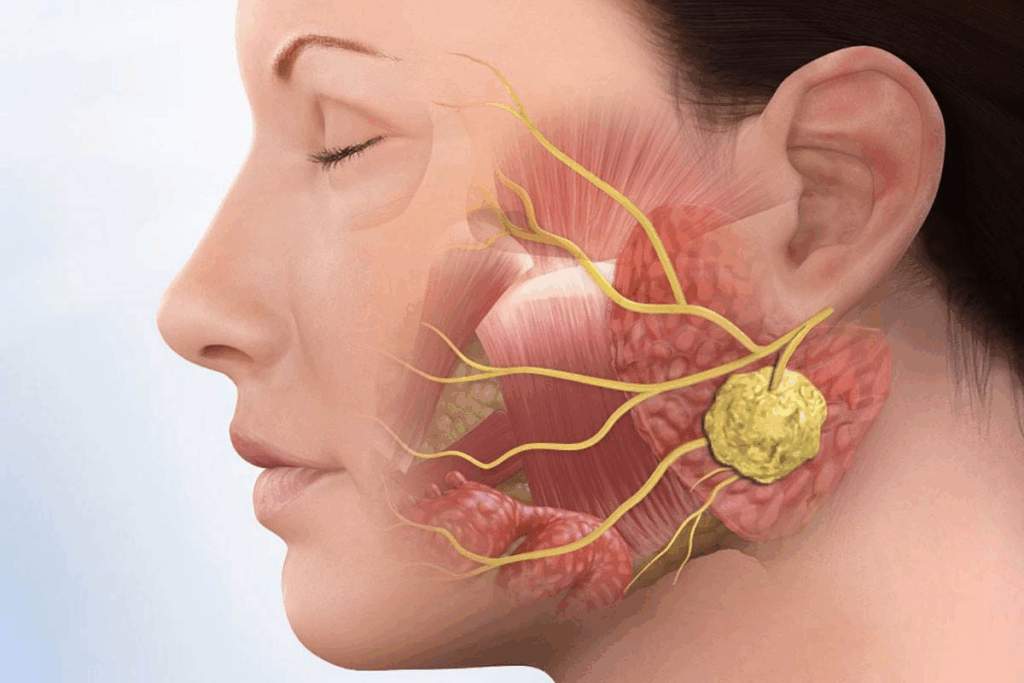
It’s important to know how ear infections can lead to hearing problems. Ear infections, like otitis media, can cause hearing loss. This happens when fluid builds up in the middle ear, blocking sound.
Research Findings on Hearing Loss and Ear Infections
Studies have found that ear infections can cause hearing loss. The fluid buildup in otitis media leads to conductive hearing loss. This type of loss is usually temporary but can be severe, making it hard to hear.
Key findings include:
- The average hearing loss from ear infections is about 24 decibels.
- Around 15 percent of teens with otitis media have hearing over 25 dB.
How Common Is Hearing Loss with Ear Infections
Hearing loss is a common problem with ear infections. It’s a big worry, mainly for kids and teens.
The impact on daily life can be big. Even a small hearing loss can make talking and learning hard.
The 24-Decibel Impact: What It Means for Everyday Hearing
A 24-decibel hearing loss is like wearing earplugs. It makes it hard to hear speech and other sounds clearly. It can cause problems with:
- Understanding conversations, which gets harder in loud places.
- Noticing certain sounds, which can make things sound unclear.
Knowing about this level of hearing loss is key. It helps manage the condition and prevent more problems.
How Do Ear Infections Cause Hearing Loss?
Ear infections can cause hearing loss by affecting the middle ear. They do this by disrupting how sound is conducted to the inner ear.
The Mechanism of Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss happens when sound can’t reach the inner ear properly. During an ear infection, fluid builds up in the middle ear. This fluid blocks sound vibrations, causing hearing loss. The middle ear’s role in sound conduction is key, and any problem can affect hearing a lot.
Fluid Buildup and Sound Wave Transmission
Fluid in the middle ear slows down or distorts sound waves. Normally, sound waves hit the eardrum and make the ossicles vibrate. These vibrations then go to the inner ear. But with fluid, these vibrations are dampened, leading to hearing loss. This condition is usually temporary and gets better once the infection is treated.
Inflammation’s Effect on Eardrum Mobility
Inflammation from an ear infection can make the eardrum and ossicles less mobile. When the eardrum gets inflamed, it can’t respond well to sound waves. This makes hearing worse. The inflammation can also make the eardrum stiff or perforated, leading to more hearing loss. It can also affect the ossicles, making them less effective at transmitting sound.
Key factors that contribute to hearing loss during an ear infection include:
- Fluid buildup in the middle ear
- Inflammation of the eardrum and ossicles
- Disruption of sound wave transmission
Understanding these mechanisms is key to treating ear infections effectively. By addressing the root causes of hearing loss, we can prevent long-term damage.
Temporary vs. Permanent Hearing Loss from Ear Infections
It’s important to know the difference between temporary and permanent hearing loss from ear infections. Ear infections can cause fluid buildup in the middle ear. This fluid can block sound waves, leading to hearing loss. Most of the time, this loss is temporary and goes away once the infection clears.
But, long-lasting or repeated infections can cause serious problems. This includes the risk of permanent hearing loss from ear infection. Knowing the difference between temporary and permanent loss helps you get the right medical care.
Characteristics of Temporary Hearing Loss
Temporary hearing loss from ear infections is usually conductive. This means fluid or inflammation in the middle ear stops sound waves from getting through. Once the infection is treated and the fluid goes away, hearing usually comes back.
The signs of temporary hearing loss include:
- Fluctuating hearing levels
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Muffled or distorted sound perception
When and How Hearing Loss Becomes Permanent
Ear infection permanent hearing loss happens when the infection damages the inner ear or hearing nerves. This is often sensorineural and can last forever. Risks include repeated infections, delayed treatment, and existing ear or hearing problems.
Recovery Timeline for Temporary Hearing Loss
The time it takes for temporary hearing loss to recover varies. It depends on the person and how bad the infection is. Usually, hearing starts to get better a few days to weeks after treatment. It can take up to several months for full recovery in some cases.
Recovery Stage | Timeline | Characteristics |
Initial Improvement | 1-4 weeks | Hearing starts to return as infection clears |
Significant Recovery | 1-3 months | Most individuals notice significant improvement |
Full Recovery | Up to 6 months | Hearing returns to normal or near-normal levels |
Understanding how ear infections can affect hearing is key. It helps manage expectations and seek timely medical help. If you or a loved one has hearing loss from an ear infection, seeing a healthcare professional is essential.
Recognizing the Signs of Hearing Loss During an Ear Infection
Hearing loss can happen from ear infections. Knowing the signs can help avoid lasting damage. We’ll look at the signs in adults and kids, and when to get medical help right away.
Symptoms in Adults
Adults with ear infection hearing loss might notice a few things. These include:
- Muffled or distorted hearing
- Difficulty understanding speech, specially in noisy places
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears
Adults should watch for these signs. Getting medical help early can stop hearing loss from getting worse.
Symptoms in Children
Young kids might not say what’s wrong. But, there are signs parents and caregivers can spot:
- Pulling or tugging on the ear
- Fussiness or irritability, which can mean ear pain
- Fever, as ear infections often come with a high temperature
- Discharge or fluid leaking from the ear
- Difficulty responding to sounds or their name being called
- Unsteadiness or balance problems
Watching for these signs can help catch hearing loss early in kids.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Some symptoms need quick medical help. These include:
- Severe ear pain
- High fever
- Discharge or fluid leaking from the ear
- Hearing loss that is sudden or severe
- Dizziness or loss of balance
If you or your child has these symptoms, get medical help fast. Early action can greatly improve outcomes.
Symptom | Adults | Children |
Muffled or distorted hearing | Common | Difficult to diagnose |
Ear pain | Present | Often indicated by fussiness |
Fever | Possible | Common |
Discharge or fluid leaking | Rare | Possible |
The table shows some symptoms are common in both adults and kids. But, how they show up can be very different.
“The key to managing hearing loss from ear infections is catching it early and treating it right. Knowing the signs helps people get medical help when it’s most important.”
— Medical Expert, ENT Specialist
Risk Factors for Severe Complications and Permanent Damage
It’s important to know the risk factors for severe complications from ear infections. Some people are more likely to face serious issues because of certain factors.
Recurrent Ear Infections
Having ear infections often can lead to serious problems. This includes permanent hearing loss. Frequent infections cause long-term inflammation and harm to the middle ear.
Table: Complications Associated with Recurrent Ear Infections
Complication | Description | Potential Outcome |
Chronic Inflammation | Ongoing inflammation of the middle ear | Permanent damage to the eardrum and ossicles |
Eardrum Perforation | Perforation or rupture of the eardrum | Hearing loss and increased risk of infections |
Mastoiditis | Infection of the mastoid bone | Serious complications, including meningitis |
Delayed or Inadequate Treatment
Not treating ear infections quickly or properly can cause serious problems. It’s key to get medical help right away to avoid lasting damage.
Pre-existing Conditions That Increase Risk
Some health issues can make ear infections worse. This includes allergies, colds, and sinus infections. These can make ear infections more severe.
Knowing these risk factors helps us take steps to prevent serious problems. We can focus on those at higher risk. This way, we can offer better care to avoid severe outcomes.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss Related to Ear Infections
Diagnosing hearing loss from ear infections involves several steps. It’s important to find the cause for the right treatment. Ear infections can cause hearing problems, and we need to know why.
Physical Examination Procedures
A physical exam is the first step. A healthcare professional looks at the ear canal and eardrum with an otoscope. They check for signs of infection like redness or fluid.
Key components of the physical examination include:
- Visual inspection of the ear canal and eardrum
- Assessment of eardrum mobility using pneumatic otoscopy
- Examination of the nasal passages and throat
Hearing Tests and Evaluations
Hearing tests are key to understanding the hearing loss. Audiometry checks how well you can hear different sounds. Tympanometry looks at the middle ear’s function.
Hearing tests may include:
- Pure-tone audiometry to assess hearing thresholds
- Speech audiometry to evaluate speech recognition
- Tympanometry to assess middle ear function
Imaging Studies for Middle and Inner Ear Assessment
Imaging studies are sometimes needed for the middle and inner ear. CT scans or MRI can show structural issues or complications from the infection.
We use imaging studies to:
- Assess the extent of infection or inflammation
- Identify any structural damage to the ear
- Guide treatment decisions
Healthcare professionals use physical exams, hearing tests, and imaging to diagnose ear infection-related hearing loss. This helps them create a good treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Ear Infections to Prevent Hearing Loss
To prevent hearing loss from ear infections, several treatments are available. The right treatment depends on the infection’s severity and cause.
Medical Interventions
For bacterial ear infections, antibiotics are often prescribed. It’s key to finish the antibiotics as directed to clear the infection. Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can also help manage pain and fever.
Decongestants and antihistamines may be used to reduce nasal congestion. This can help prevent further infections.
Surgical Options for Chronic Cases
In cases of recurring or chronic infections, surgical intervention might be needed. Tympanostomy tubes, or ear tubes, are inserted to drain fluid and ventilate the middle ear. This can prevent future infections and hearing loss.
Adenoidectomy, the removal of adenoids, may also be considered. This is if enlarged adenoids are causing the infections.
Home Remedies and Pain Management
Medical treatment is key for ear infections, but home remedies can also help. A warm compress on the ear can ease pain. Sleeping with the head elevated can also help with congestion.
Good hygiene and avoiding irritants like smoke are also important. These steps can help manage symptoms and prevent post ear infection hearing loss.
Long-term Management for Those with Permanent Hearing Loss
For those with permanent hearing loss from ear infections, long-term management is key. Adapting to hearing loss can be tough. But, with the right strategies and support, you can live a fulfilling life.
Hearing Aids and Assistive Devices
Hearing aids and assistive devices are vital for managing permanent hearing loss. They help you better engage with your surroundings and talk to others. It’s important to talk to an audiologist to find the best device for you.
Hearing aids come in different styles, like behind-the-ear or in-the-ear. The right choice depends on your hearing loss and what you prefer. Assistive devices like FM systems can also help in certain situations.
Rehabilitation Therapies
Rehabilitation therapies are key to adapting to hearing loss. Auditory therapy can improve your communication skills. Speech therapy helps with any changes in how you speak.
Counseling is also important for emotional support. It helps you cope with the emotional side of hearing loss. Our team creates a personalized plan for you.
Coping Strategies for Daily Life
It’s important to find ways to manage daily life with hearing loss. Simple changes, like facing the speaker, can help a lot. Using visual cues and reducing noise also makes a difference.
Exploring communication strategies like lip-reading can also help. Staying connected with loved ones and joining support groups is important too. We encourage you to find what works best for you.
Preventing Ear Infections and Associated Hearing Loss
It’s important to know how to stop ear infections to protect your hearing. By taking certain steps, you can lower your chance of getting ear infections and hearing loss.
Lifestyle and Environmental Modifications
Changing your lifestyle and environment can help prevent ear infections. For example, staying away from secondhand smoke is key, as it increases the risk of ear infections. Also, washing your hands often can stop infections that might cause ear infections.
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who have colds or other infections
- Keeping immunizations up to date
- Breastfeeding infants, as it has been shown to reduce the risk of ear infections
By doing these things, you can make your environment healthier and lower the risk of ear infections.
Vaccination and Preventive Healthcare
Vaccines are very important in stopping infections that can lead to ear infections. Making sure you’re up to date on flu and pneumococcal disease vaccines can greatly lower your risk of ear infections.
- Getting vaccinated against flu annually
- Receiving pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) as recommended
- Staying informed about other recommended vaccinations
Regular health check-ups are also important. They help catch and treat problems early, before they lead to ear infections.
Early Intervention Strategies
Acting fast when you notice signs of an ear infection is critical. It can prevent hearing loss. Knowing the signs, like ear pain and fever, and getting help right away is very important.
- Being aware of the symptoms of ear infections, such as ear pain and fever
- Seeking medical care if symptoms persist or worsen
- Following treatment plans as directed by healthcare professionals
By using these prevention strategies, you can lower your risk of hearing loss from ear infections.
Conclusion: Understanding the Impact of Ear Infections on Hearing Health
It’s important to know how ear infections can harm our hearing. These infections can lead to hearing loss if they keep coming back or are not treated. By taking steps to prevent them and getting help when needed, we can keep our hearing safe.
We’ve looked into how ear infections can cause hearing loss. We’ve also talked about the different kinds of ear infections and how they affect our hearing. It’s key to watch for signs like trouble hearing or feeling like your ear is full. If these signs don’t go away, see a doctor.
There are ways to prevent ear infections and the hearing loss they can cause. Making healthy lifestyle choices and getting vaccinated can help. For those who lose hearing permanently, there are treatments like hearing aids and therapy to help improve life.
Knowing how ear infections and hearing loss are connected helps us manage and prevent problems. If you’re having ear infection or hearing loss symptoms, talk to a healthcare expert. They can help figure out what’s going on and find the right treatment.
FAQ
Can an ear infection cause permanent hearing loss?
Yes, an ear infection can cause permanent hearing loss. This is more likely if it’s not treated or if treatment is delayed.
What is the average hearing loss associated with ear infections?
Ear infections can cause an average hearing loss of 24 decibels. This can make it hard to communicate every day.
How do ear infections cause hearing loss?
Ear infections lead to hearing loss by causing fluid buildup and inflammation. This blocks sound waves from passing through the middle ear.
What are the symptoms of hearing loss associated with ear infections in adults?
Adults might notice muffled hearing and trouble understanding speech. They may also feel like their ears are full or have pressure.
What are the symptoms of hearing loss associated with ear infections in children?
Kids might have delayed speech, not respond to sounds, or be very irritable. This is because they can’t tell you they’re having trouble hearing.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for hearing loss associated with an ear infection?
Seek medical help right away if you or your child has severe ear pain, fever, ear discharge, or significant hearing loss.
Can recurrent ear infections lead to permanent hearing loss?
Yes, having ear infections over and over again can increase the risk of permanent hearing loss. This is because repeated inflammation and fluid buildup can damage the middle ear.
How are ear infections diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose ear infections through physical exams, like otoscopy and tympanometry. They also do hearing tests to check for loss.
What are the treatment options for ear infections to prevent hearing loss?
Treatments include antibiotics, surgery for chronic cases, and home remedies for pain. These help manage the infection and prevent hearing loss.
Can hearing aids help with permanent hearing loss due to ear infections?
Yes, hearing aids and assistive devices can greatly improve communication and life quality for those with permanent hearing loss.
How can ear infections and associated hearing loss be prevented?
Preventing ear infections involves making lifestyle changes, getting vaccinated, and treating infections early. These steps help manage ear infections effectively.
Does ear infection cause deafness?
While rare, severe or recurring ear infections can lead to significant hearing loss or even deafness if not managed well.
Can a ear infection cause hearing loss in one ear?
Yes, an ear infection can cause hearing loss in one ear. It depends on which ear is affected.
Is hearing loss after an ear infection temporary?
Hearing loss after an ear infection is often temporary and gets better once the infection is treated. But sometimes, it can be permanent.
Can an ear infection lead to long-term hearing loss?
Yes, if not treated properly, an ear infection can cause long-term or permanent hearing loss.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). Can an Ear Infection Cause Hearing Loss Ear. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9419542/



































