Hemolytic anemia happens when red blood cells are destroyed faster than they’re made. This leads to serious symptoms.
At Liv Hospital, we use advanced tests to find out can anemia cause fever and how hemolytic anemia leads to jaundice and yellow eyes.
Can anemia cause fever? Anemia means not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. It can cause tiredness and trouble breathing. In some cases, anemia—especially when linked to infections or inflammation—may also be associated with fever.
Key Takeaways
- Hemolytic anemia is a condition where red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be made.
- Common symptoms include fever, jaundice, and yellowing of the eyes.
- Advanced diagnostics are key to understanding the link between hemolytic anemia and its symptoms.
- Liv Hospital is dedicated to giving full care to patients with hemolytic anemia.
- Good management and treatment of hemolytic anemia depend on accurate diagnosis.
Understanding Hemolytic Anemia: A Comprehensive Overview

Hemolytic anemia happens when the body gets rid of red blood cells too quickly. This makes it hard for the body to get enough oxygen. It can cause many health problems because of the lack of red blood cells.
Definition and Hemolytic Meaning
The word “hemolytic” means the breakdown of red blood cells. Hemolytic anemia occurs when the body gets rid of too many red blood cells. This happens faster than the bone marrow can make new ones.
This breakdown can happen inside or outside the blood vessels. It often happens in the spleen or liver. The hemolytic meaning also includes the release of hemoglobin into the blood. This can cause jaundice because of the buildup of bilirubin.
The Impact of Excessive Destruction of Red Blood Cells
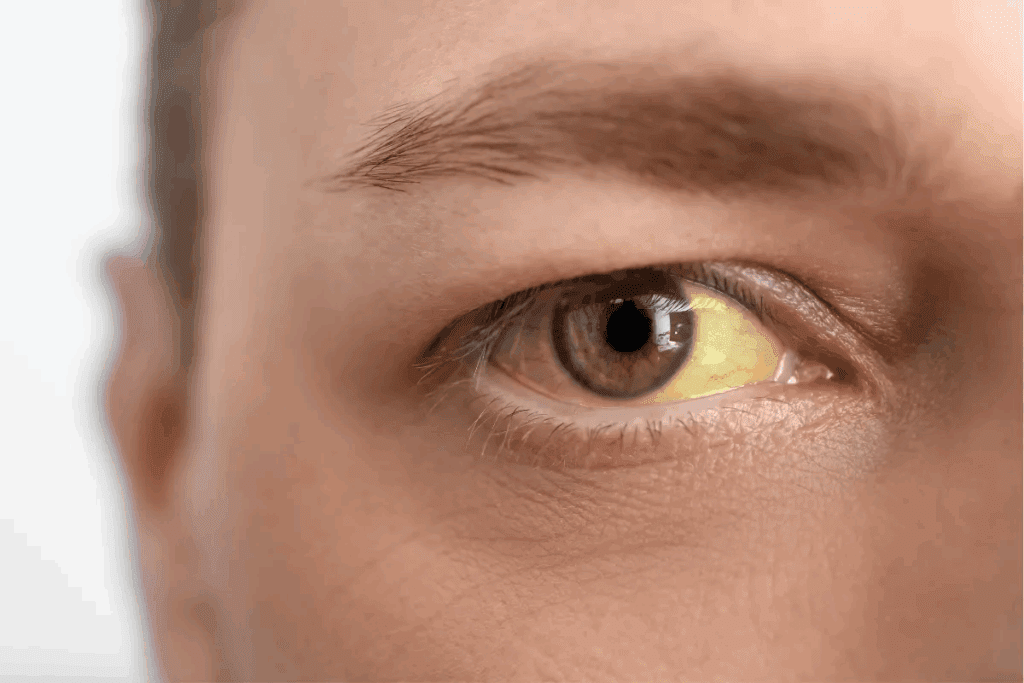
When too many red blood cells are destroyed, bilirubin levels go up. This leads to jaundice and yellow eyes. The body doesn’t have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to tissues and organs.
This problem can come from many things, like genetic disorders, infections, or some medicines. Knowing what causes and affects hemolytic anemia is key to treating it.
The Mechanism Behind Erythrocyte Hemolysis
Understanding erythrocyte hemolysis is key to diagnosing and managing hemolytic anemia. This condition is when too many red blood cells are destroyed. It can cause anemia, jaundice, and other health issues.
Normal Red Blood Cell Lifecycle
Red blood cells (RBCs) live about 120 days. They go through changes that lead to their removal. The process of making, maturing, and destroying RBCs is carefully controlled. Any imbalance can cause hemolytic anemia.
Destruction of RBCs is Called Hemolysis
Hemolysis is when RBCs are destroyed. This can happen inside or outside blood vessels. It’s caused by autoimmune disorders, infections, and certain medications. The breakdown of RBCs can release hemoglobin into the blood, leading to hemoglobin fever and other issues.
Intravascular vs. Extravascular Hemolysis
Intravascular hemolysis happens inside blood vessels. It’s linked to paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and mechanical heart valves. Extravascular hemolysis occurs outside blood vessels, mainly in the spleen. It’s seen in hereditary spherocytosis and autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Knowing the difference is vital for correct diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, erythrocyte hemolysis is a complex issue that can cause health problems. Understanding the lifecycle of RBCs and the differences between intravascular and extravascular hemolysis is key to managing hemolytic anemia well.
Can Anemia Cause Fever? Exploring the Connection
Hemolytic anemia occurs when the body breaks down red blood cells too fast. This can start an inflammatory response, leading to fever. It happens when the body can’t make new red blood cells fast enough.
The Inflammatory Response to Destroyed Red Blood Cells
When red blood cells break down, they release hemoglobin into the blood. This can start an inflammatory response. The body’s defense mechanism is at work.
The inflammatory response is caused by cytokines and other substances. These can make you feel feverish by affecting your body’s temperature control.
The process involves several key steps:
- Red blood cells are destroyed, releasing hemoglobin into the bloodstream.
- The free hemoglobin can bind to haptoglobin, forming a complex that is removed by the liver.
- If the capacity of haptoglobin is exceeded, free hemoglobin can cause oxidative stress and inflammation.
- The inflammatory response is triggered, leading to the production of cytokines and other mediators that can cause fever.
Hemoglobin Fever: Mechanisms and Manifestations
Fever from hemolytic anemia, known as “hemoglobin fever,” is complex. It’s not just the free hemoglobin that causes fever. It’s how the body reacts to it.
The severity of the fever can vary. Some people might just have a mild fever. Others might have a more serious reaction.
The factors that affect how severe the fever is include:
- The rate and extent of red blood cell destruction.
- The body’s ability to clear free hemoglobin and other debris from the bloodstream.
- The presence of underlying conditions may affect the inflammatory response.
In conclusion, anemia and fever are mainly linked in cases of hemolytic anemia. Understanding this connection is key to diagnosing and treating patients with fever.
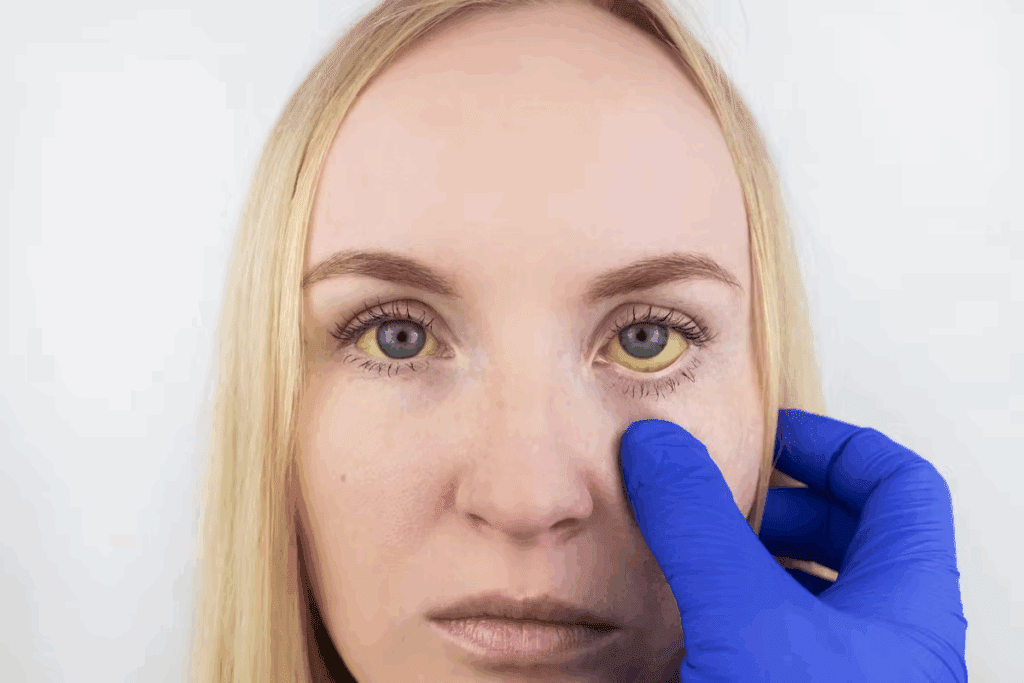
Jaundice and Yellow Eyes: Visible Signs of Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolytic anemia shows itself in many ways, like jaundice and yellow eyes. This happens because too many red blood cells are destroyed. The body can’t make enough new ones, so bilirubin builds up.
How Bilirubin Accumulation Leads to Jaundice Anemia
When red blood cells break down too fast in hemolytic anemia, more bilirubin is made. The liver usually gets rid of bilirubin through bile. But if too much is made, the liver can’t keep up.
This leads to bilirubin building up in the blood. It makes the skin and eyes turn yellow, known as jaundice. Jaundice anemia is when someone with anemia also has jaundice, showing they are connected.
Can Anemia Cause Yellow Eyes? Understanding the Connection
Yes, anemia can cause yellow eyes, mainly in hemolytic anemia. The breakdown of red blood cells increases bilirubin, turning the yes yellow.
Not all anemia causes yellow eyes. But, in hemolytic anemia, it’s a common sign. Knowing the link between anemia and yellow eyes helps in diagnosing and treating hemolytic anemia.
To figure out why eyes turn yellow, doctors do blood tests. They check bilirubin levels and red blood cell health. Understanding the connection between hemolytic anemia and its symptoms is key to good care.
Types and Causes of Hemolytic Anemia
It’s important to know the types and causes of hemolytic anemia for proper treatment. This condition can be inherited or acquired, each with its own causes and effects.
Inherited Hemolytic Anemias
Inherited hemolytic anemias come from genetic mutations. These affect how red blood cells are made or work. Sickle cell disease and thalassemia are examples. These conditions lead to ongoing red blood cell breakdown, needing constant care.
Acquired Hemolytic Anemia: Autoimmune and Drug-Induced
Acquired hemolytic anemia can come from autoimmune disorders or certain drugs. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia happens when the body attacks its own red blood cells. Drug-induced hemolytic anemia occurs when some medications destroy red blood cells.
Drugs like some antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medicines can cause this. Finding the cause is key to diagnosing acquired hemolytic anemia.
Chronic Hemolysis: Long-term Implications
Chronic hemolysis, whether inherited or acquired, has serious long-term effects. It can cause jaundice, anemia, and gallstones. Managing it requires careful monitoring, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Knowing the causes and types of hemolytic anemia helps in creating effective treatment plans. Healthcare providers can then tailor treatments to manage the condition better and improve patient outcomes.
How to Diagnose Hemolytic Anemia: Clinical Approaches
To diagnose hemolytic anemia, doctors use several steps. These include blood tests, looking at your medical history, and a physical check-up. Lab tests are key in confirming the diagnosis.
Tests like hemoglobin levels, blood smears, and the Coombs test are used. A doctor will look at these results to find out why you have hemolytic anemia.
Knowing how to diagnose hemolytic anemia is important. It helps doctors create a treatment plan that works for you. This plan combines what they find in your tests and your overall health.
Getting the right diagnosis is vital for treating hemolytic anemia. By learning how to diagnose it, doctors can help patients live better lives. This improves their health and happiness.
FAQ
What is hemolytic anemia?
Hemolytic anemia happens when red blood cells are destroyed too quickly. This leads to a shortage of these cells.
What are the symptoms of hemolytic anemia?
Symptoms include feeling very tired, short of breath, and jaundice. You might also notice yellow eyes.
Can anemia cause fever?
Yes, fever can occur in hemolytic anemia. It’s due to the body’s reaction to the destruction of red blood cells.
What is the connection between jaundice and anemia?
Jaundice is a sign of hemolytic anemia. It happens when too many red blood cells are broken down, causing bilirubin to build up.
How is hemolytic anemia diagnosed?
Doctors use blood tests, medical history, and physical exams to diagnose it. It’s a thorough process.
What is the difference between intravascular and extravascular hemolysis?
Intravascular hemolysis happens inside blood vessels. Extravascular hemolysis occurs outside, like in the spleen.
What are the causes of hemolytic anemia?
It can be caused by genetic disorders, infections, certain medicines, and autoimmune diseases.
Can anemia cause yellow eyes?
Yes, yellow eyes can happen in hemolytic anemia. It’s because of the buildup of bilirubin.
What is chronic hemolysis?
Chronic hemolysis is when red blood cells are destroyed over a long time. It can cause ongoing anemia and other issues.
How is acquired hemolytic anemia treated?
Treatment varies based on the cause. It might include medicines, transfusions, or other interventions.
What is erythrocyte hemolysis?
Erythrocyte hemolysis is when red blood cells are destroyed. It can be due to genetic disorders or infections.
Is hemolytic anemia a genetic disorder?
Some types are inherited. Others are caused by infections or medicines.
Reference:
National Institutes of Health, PMC. (n.d.). Hemolytic anemia. Retrieved from
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5586889




































