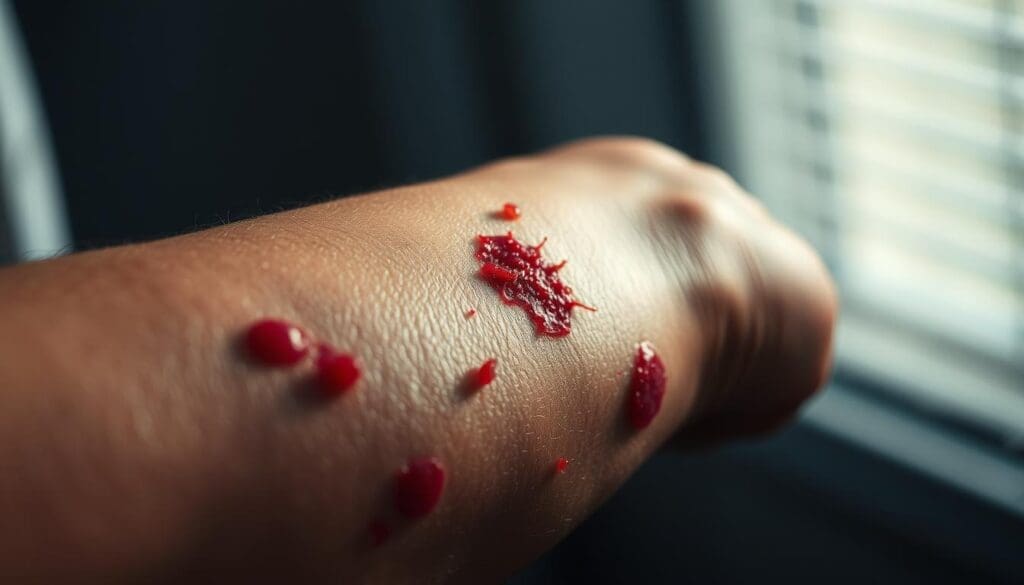
Ever seen tiny red or purple spots on your skin? Or felt itching and bruising without knowing why? Skin changes like these can be puzzling and sometimes concerning. At Liv Hospital, we know how important it is to understand these symptoms. Discover can petechiae be itchy, their link to bruising, and what skin rashes may indicate for your health.
Petechiae are small, flat spots on the skin from capillary bleeding. They can be linked to many health issues, some causing itching and bruising. It’s key for both patients and doctors to grasp this connection.
We aim to help by looking into the reasons behind these symptoms. Our goal is to give you the knowledge to get the right medical help. We want to explain these symptoms clearly and how they relate to each other.
Key Takeaways
- Petechiae are tiny spots on the skin caused by capillary bleeding.
- They can be associated with various medical conditions that cause itching and bruising.
- Understanding the link between petechiae, itching, and bruising is key for proper diagnosis.
- At Liv Hospital, we focus on patient-centered care and evidence-based treatment.
- Getting medical help is vital for dealing with unexplained skin changes.
What Are Petechiae? Characteristics and Appearance
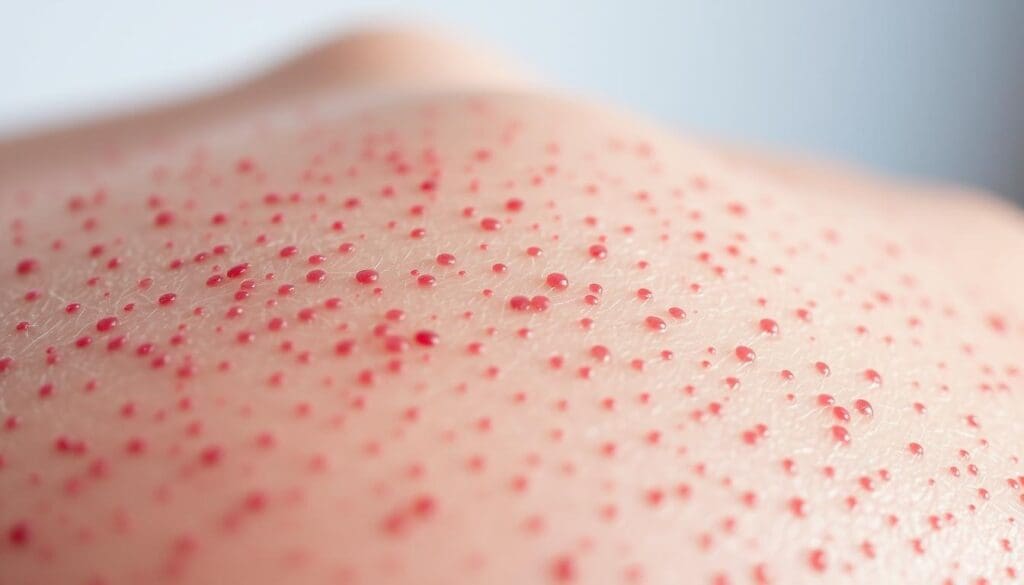
Petechiae are small, flat spots on the skin from minor bleeding. They are less than 2mm across and can be red, purple, or brown. Knowing about petechiae helps us understand their role in health.
Definition and Physical Appearance
Petechiae are small and don’t fade when pressed. This makes them different from other skin rashes. They often show up in groups on the arms, legs, and face.
Key characteristics of petechiae include:
- Tiny, flat spots less than 2mm across
- Red, purple, or brown in color
- Non-blanching when pressed
- Often appear in clusters
How Petechiae Differ from Other Skin Conditions
Petechiae stand out because of their small size and non-blanching nature. They are not itchy or painful, unlike many rashes. They also differ from purpura, which are larger bruises.
The Non-Blanching Nature of Petechiae
The non-blanching nature of petechiae is key to diagnosis. When pressed, petechiae remain visible, showing they are not just on the surface. This helps doctors tell them apart from other skin issues.
Understanding petechiae helps us find the cause and treatment. Their presence, with or without itching or bruising, needs a doctor’s check-up.
The Physiological Mechanism Behind Petechiae
Petechiae form through a mix of capillary bleeding, platelet function, and blood clotting. To grasp how petechiae appear, we must explore the physiological processes behind them.
How Capillary Bleeding Creates Petechiae
Capillary bleeding is the main reason for petechiae. When capillaries get damaged, they spill blood into the skin, causing small spots. This bleeding is usually minor but can spread a lot, depending on the cause. Capillary fragility is key, as fragile capillaries are more likely to leak.
The Role of Platelets and Blood Clotting
Platelets help stop bleeding by forming clots. If there are too few platelets or they don’t work right, the body can’t stop bleeding as well. This can lead to more bleeding, including petechiae. Blood clotting factors also play a part in stopping bleeding, and problems with these can cause petechiae too.
Blood clotting is a complex process with many steps and factors. Any problem in this process can cause bleeding, like petechiae. Knowing how platelets and blood clotting work in petechiae is important for finding the cause.
Why Petechiae Appear in Specific Patterns and Locations
Petechiae show up in certain patterns and places because of things like gravity and pressure. For example, they might be more common on the lower legs because of more venous pressure. Some conditions make petechiae appear in specific ways, which helps doctors diagnose.
Seeing these patterns helps doctors figure out what’s going on and how to test for it. It’s important to look at where the petechiae are and any other symptoms when checking patients.
Common Causes of Petechiae
Many things can cause petechiae, from thrombocytopenia to physical injury. Knowing what causes them helps doctors diagnose and treat the problem.
Thrombocytopenia and Low Platelet Counts
Thrombocytopenia means you have too few platelets. Platelets help blood clot. Without enough, you might see petechiae, which are small spots under the skin. We’ll look into how doctors find thrombocytopenia and what it means for your health.
Medication-Induced Petechiae
Some medicines can cause petechiae as a side effect. This includes drugs that prevent blood clotting and some antibiotics. We’ll talk about how these drugs affect your blood and lead to petechiae.
Infections That Can Trigger Petechiae
Infections often cause petechiae too. This can be from bacteria, viruses, or fungi. We’ll see how infections can lead to petechiae and point out specific ones that might cause it.
Physical Trauma and Pressure-Related Causes
Physical injuries and pressure can also cause petechiae. This includes getting hurt, straining hard, or putting too much pressure on your skin. We’ll explain how these factors can lead to petechiae and give examples of when they might happen.
Can Petechiae Be Itchy? Examining the Evidence
Petechiae are usually not itchy, but some conditions can make them itchy. We need to look at what petechiae are and when they might itch.
The Typical Non-Itchy Nature of Petechiae
Petechiae are small spots on the skin from tiny blood vessel breaks. They are not itchy because they come from bleeding, not from inflammation or allergies. This makes them different from many other skin rashes.
When Petechiae Might Be Associated with Itching
Even though petechiae are not itchy, they can be in some cases. For example, conditions like vasculitis or infections can cause itching. Also, if petechiae happen with other skin issues, like eczema, the itching from those conditions can be present too.
Key scenarios where petechiae might be associated with itching include:
- Underlying inflammatory or infectious conditions
- Co-existing skin conditions like eczema or dermatitis
- Allergic reactions that cause both petechiae and itching
Distinguishing Between Petechiae and Itchy Rashes
Telling petechiae apart from itchy rashes is important for the right treatment. Petechiae are not raised or scaly and don’t change color when pressed. If a rash is itchy and doesn’t look like petechiae, it might be something else like an allergy or eczema.
Medical evaluation is essential to figure out what’s causing skin symptoms. A doctor can check you thoroughly, ask about your health history, and run tests to find the cause.
The Connection Between Bruising and Petechiae
Bruising and petechiae share common causes and mechanisms. Healthcare professionals need to understand this. They are both signs of bleeding into the skin but look and mean different things.
Shared Mechanisms and Causes
Bleeding into the skin causes both bruising and petechiae. Bleeding disorders like hemophilia or von Willebrand disease can cause them. Also, conditions that affect platelet count or function, like thrombocytopenia, can lead to these symptoms.
Another key factor is blood vessel health. Conditions that harm blood vessels can cause both bruising and petechiae. For example, vasculitis, an inflammation of blood vessels, can lead to these symptoms.
Differences in Presentation
Bruises are larger and more spread out, often from trauma or a lot of bleeding. Petechiae, on the other hand, are small, pinpoint spots that don’t always come from trauma.
Easy Bruising as a Related Symptom
Easy bruising is often linked to petechiae. Together, they can show problems like bleeding disorders or low platelet counts. It’s important to look at easy bruising with petechiae to find the cause.
| Symptom | Bruising | Petechiae |
| Appearance | Larger, diffuse areas | Small, pinpoint spots |
| Common Causes | Trauma, bleeding disorders | Low platelet count, vasculitis |
| Associated Symptoms | Easy bruising, petechiae | Purpura, easy bruising |
It’s key to understand the link between bruising and petechiae for diagnosis and treatment. By knowing the shared causes and differences, healthcare providers can give better care.
Itchy Skin and Bruising: When They Occur Together
When you have itchy skin and bruising at the same time, it’s a sign of something complex. It can be hard for both patients and doctors to figure out what’s going on. This mix of symptoms might point to many different health issues.
Common Conditions Causing Both Symptoms
Many health problems can make your skin itch and cause bruises. Autoimmune disorders like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can do this. They cause inflammation that leads to itching and bruising.
Certain infections, like hepatitis or HIV, can also cause these symptoms. This happens through immune complex deposition and vasculitis.
Blood disorders, including thrombocytopenia or platelet dysfunction, can cause bruising. Conditions like lymphoma can make your skin itch. Liver diseases, such as cirrhosis, can cause itching and bruising. This is because of bile salt buildup and less clotting factor production.
The Role of Inflammation in Itching and Bruising
Inflammation is key in both itching and bruising. It leads to the release of chemicals that cause itching. It also makes blood vessels more likely to leak, causing bruises.
In conditions like vasculitis, inflammation damages blood vessel walls. This can lead to both bruising and itching. Knowing how inflammation works helps doctors find the root cause and treat it.
Distinguishing Between Causation and Correlation
It’s important to tell if itchy skin and bruising are caused by the same thing or just happen together. Sometimes, one condition can cause both symptoms. Other times, they might happen for different reasons.
For example, dry skin (xerosis) can make you itch, leading to scratching and bruising. Here, itching causes the bruising. But in some diseases, both symptoms can happen on their own.
To find out what’s causing these symptoms, doctors need to look at your medical history, do a physical exam, and sometimes run tests.
Medical Conditions That Can Cause Both Petechiae and Itching
Itching and petechiae are more than just skin issues. They can show serious health problems. Knowing what causes these symptoms is key to treating them right.
Blood Disorders: Anemia, Leukemia, and Platelet Dysfunction
Blood disorders can lead to itching and petechiae. Anemia happens when there’s not enough red blood cells or hemoglobin. This makes it hard for the body to carry oxygen and nutrients.
Leukemia is a blood or bone marrow cancer. It can cause petechiae by affecting platelet production. Platelet dysfunction also leads to bleeding signs like petechiae.
Some important blood disorders include:
- Anemia
- Leukemia
- Platelet dysfunction
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms
Autoimmune Conditions and Their Skin Manifestations
Autoimmune diseases happen when the body attacks itself. Conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can cause skin problems. These include petechiae and itching.
Common autoimmune conditions that may cause these symptoms include:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriasis
Liver and Kidney Diseases That Affect Skin
Liver and kidney diseases can harm the skin, causing itching and petechiae. Liver cirrhosis and chronic kidney disease can lead to toxin buildup. This affects the skin.
Some liver and kidney diseases that can affect the skin include:
- Liver cirrhosis
- Chronic kidney disease
- Hepatitis
Allergic Reactions and Vasculitis
Allergic reactions can cause itching and petechiae. Vasculitis is inflammation of blood vessels. It can damage vessels and cause bleeding.
It’s important to know the medical conditions that cause itching and petechiae. This helps healthcare providers treat these symptoms effectively. They can improve patients’ lives by addressing the root causes.
Unexplained Bruising and Itching on Legs: Specific Concerns
Seeing unexplained bruises and itching on your legs can be a sign of health problems. These signs might point to vascular or skin issues that need a doctor’s help.
Vascular Issues Affecting the Lower Extremities
Vascular problems are a big worry when you see bruises and itching on your legs. Issues like poor blood flow, varicose veins, and deep vein thrombosis can cause these symptoms. Poor circulation can lead to bruises because of less blood and oxygen to the skin. Varicose veins can make your skin itch and hurt because of blood pooling and skin pressure.
- Varicose veins
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Poor circulation
It’s important to deal with these vascular problems quickly to avoid worse issues. For example, not treating deep vein thrombosis can lead to a serious lung problem called pulmonary embolism.
Dermatological Conditions Common in Leg Areas
Many skin problems can show up in your legs and cause bruises and itching. Eczema, psoriasis, and contact dermatitis can make your skin itchy and inflamed. This can make your skin bruise easily because of the inflammation and scratching.
“Dermatological conditions can significantly impact the quality of life, causing discomfort and distress. Proper diagnosis and treatment are critical to manage these conditions effectively.”
These skin issues need special treatments, like creams, pills, and changes in your daily life. These can help control symptoms and stop them from getting worse.
When Leg Symptoms Signal Systemic Problems
Sometimes, bruises and itching in your legs can mean there’s a bigger problem inside your body. For example, liver or kidney disease can make you itch because of toxins. Blood disorders like leukemia or lymphoma can also cause these symptoms because of abnormal blood cells.
| Systemic Condition | Possible Symptoms |
| Liver Disease | Itching, jaundice |
| Kidney Disease | Itching, swelling |
| Blood Disorders | Bruising, itching |
It’s very important to see a doctor to check if your symptoms are from a bigger problem. Finding and treating these problems early can really help your health.
Diagnostic Approach to Petechiae, Bruising, and Itching
To diagnose petechiae, bruising, and itching, we use a few key steps. These include a physical check-up, lab tests, and sometimes imaging studies. This helps us find out what’s causing the problem.
Physical Examination Techniques
Checking a patient thoroughly is key when they have petechiae, bruising, and itching. We start by looking at the skin lesions. We note their size, color, and if they change color when pressed.
We also check the patient’s overall health. This helps us see if there’s a bigger issue that’s causing the skin problems.
Laboratory Tests and Blood Work
Lab tests are very important in figuring out what’s behind petechiae, bruising, and itching. First, we do a complete blood count (CBC). This checks the platelet count, hemoglobin, and white blood cell count.
Depending on what we find, we might do more tests. These could include clotting studies, liver function tests, or tests for infections or autoimmune diseases.
| Laboratory Test | Purpose |
| Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Evaluate platelet count, hemoglobin, and white blood cell count |
| Clotting Studies | Assess coagulation disorders |
| Liver Function Tests | Evaluate liver health and its impact on skin symptoms |
Imaging and Specialized Testing
Sometimes, we need imaging like ultrasound or CT scans. This helps us see what’s going on inside the body.
We might also do skin biopsies. This is to find out more about specific skin conditions.
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
When we’re figuring out what’s causing the symptoms, we think about many possibilities. This is called differential diagnosis.
We look at both common and serious conditions. We use what we learn from the physical exam, lab tests, and imaging to narrow down the list.
By taking a detailed approach, we can find the real cause of petechiae, bruising, and itching. This helps us choose the right treatment.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Managing petechiae, bruising, and itching needs a full plan. This plan should tackle both symptoms and their causes. We’ll look at the different treatments and strategies for these symptoms.
Addressing Underlying Causes
Finding and fixing the root cause is the first step. This might mean treating conditions like thrombocytopenia, infections, or autoimmune diseases. For example, if a drug is causing the problem, we might change or stop it.
When we find the cause, treating it is key. For instance, if a platelet disorder is the issue, we might use drugs to boost platelet count or function.
Managing Itching Symptoms
It’s important to ease itching to improve life quality. We use creams and pills to help. Antihistamines and corticosteroids are often used to cut down itching and swelling.
Keeping the skin clean and using moisturizers can also help. Sometimes, we suggest special skincare products or treatments based on the patient’s needs.
Treatments for Associated Bruising
We use different methods to treat bruising linked to petechiae. These aim to lessen bruising severity and frequency. We focus on improving blood vessel health and clotting.
We might suggest vitamin C or K supplements for better vascular health. For serious bruising, we might need to use specific drugs or therapies.
When to Consider Emergency Treatment
It’s vital to know when to get emergency help. Severe bruising, heavy bleeding, or signs of infection need quick medical care. We watch for signs of serious conditions that might show up with petechiae, bruising, and itching.
If symptoms suddenly get worse, breathing is hard, or other serious signs appear, get emergency help fast. Quick action can make a big difference in serious cases.
Conclusion: Understanding the Complex Relationship Between Skin Symptoms
We’ve looked into how petechiae, bruising, and itching are connected. These signs can point to serious health issues. They often work together, showing different health problems.
Petechiae don’t fade when pressed, and they might mean you have low platelets or blood vessel problems. Bruising can happen from injuries, blood clotting issues, or side effects of drugs. Itching can be a sign of skin problems, diseases, or allergies. When all these happen together, it might mean you need to see a doctor.
It’s key to understand how these symptoms are linked. This helps doctors find the real cause and treat it right. By seeing how petechiae, bruising, and itching are connected, doctors can give better care.
Dealing with these symptoms in a full way can really help people get better. We stress the need to see a doctor if these signs don’t go away or get worse. This way, you get the help you need quickly.
FAQ
Can petechiae be itchy?
Usually, petechiae don’t itch. But sometimes, they can be itchy if there’s another skin issue or condition.
What causes itchy skin and bruising?
Itchy skin and bruising can come from many things. This includes blood problems, autoimmune diseases, and liver or kidney issues. Allergic reactions can also cause it.
Are petechiae a sign of a serious medical condition?
Yes, petechiae can mean a serious problem. This includes blood disorders, leukemia, or vasculitis. Always see a doctor if you notice them.
How are petechiae diagnosed?
Doctors check for petechiae by looking and doing tests. They might also use imaging to find the cause.
Can certain medications cause petechiae and itching?
Yes, some medicines can make you itch and get petechiae. Always talk to your doctor about your meds.
What is the connection between bruising and petechiae?
Bruising and petechiae both happen when blood leaks under the skin. They often have the same causes, like low platelets or bleeding disorders.
How can itchy skin and bruising on the legs be treated?
Treatment for itchy skin and bruising on the legs depends on the cause. It might involve fixing vascular issues, skin problems, or other health issues.
When should I seek medical attention for petechiae, bruising, or itching?
See a doctor if you have unexplained or severe petechiae, bruising, or itching. This is true if you have other symptoms too.
Can petechiae be a symptom of an underlying infection?
Yes, petechiae can be a sign of some infections. It’s important to find and treat the infection.
How can I manage itching associated with petechiae or other skin conditions?
To manage itching, treat the cause, use creams or ointments, and avoid scratching. Scratching can hurt your skin more.
References
National Health Service. (2023, November 28). Rash. nhs.uk.https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/rash/
Sahu, K. K., & Mishra, A. K. (2021). Skin manifestations in leukemia. Bloodline, 3(2), 54–57.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9338601/


































