Sleep apnea is a big health worry with serious heart risks. Studies show it ups the chance of heart failure by 140%, stroke by 60%, and coronary heart disease by 30%. Can sleep apnea cause heart problems? Learn the definitive link between untreated sleep apnea and increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention say heart disease is the top killer in the U.S. and worldwide. Sleep apnea raises the risk of heart issues like coronary disease, heart failure, and stroke. At Liv Hospital, we stress finding sleep apnea early and treating it fully to avoid heart problems.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep apnea greatly ups the risk of heart failure, stroke, and coronary heart disease.
- Many with heart disease don’t know they have sleep apnea.
- Spotting and treating sleep apnea early can stop heart problems.
- Liv Hospital’s care focuses on each patient’s needs for sleep apnea.
- Heart disease is the biggest killer worldwide, and sleep apnea plays a big part.
Understanding Sleep Apnea: Types and Prevalence

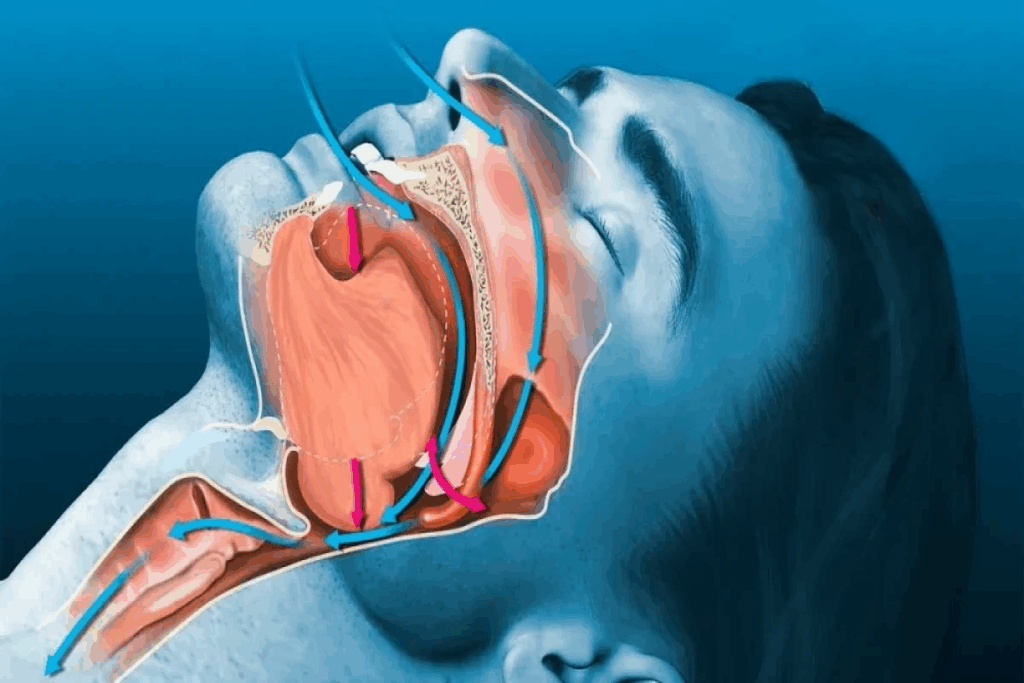
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder. It happens when a person’s breathing stops during sleep. These stops can happen many times a night because of a blockage in the airway.
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea means breathing stops or gets shallow during sleep. It can cause poor sleep and low oxygen levels. Sleep apnea is not just a simple sleep disorder; it’s a condition that can have significant implications for overall health, including cardiovascular problems.
Types of Sleep Apnea: Obstructive, Central, and Complex
There are three main types of sleep apnea: obstructive, central, and complex. Obstructive sleep apnea happens when the throat muscles relax, blocking the airway. Central sleep apnea occurs when the brain doesn’t send signals to breathe. Complex sleep apnea syndrome is a mix of both obstructive and central sleep apnea.
Prevalence Statistics: 34% of Middle-Aged Men and 17% of Women
Sleep apnea is more common than people think. About 34% of middle-aged men and 17% of middle-aged women have it. These numbers show why it’s key to know about it and get it treated right.
The Sleep Apnea-Cardiovascular Connection

The link between sleep apnea and heart health is complex. Sleep apnea causes breathing pauses during sleep. This can harm the heart and the cardiovascular system.
How Disrupted Breathing Affects Your Heart
When breathing stops in sleep apnea, the body’s oxygen levels drop. This can raise blood pressure. The body’s stress response is triggered, releasing hormones like adrenaline.
The heart faces repeated strain from these interruptions. Studies show sleep apnea’s severity is linked to heart disease risk.
“For every measure of reduced blood oxygen levels during sleep, individuals face a 45% increased risk for primary cardiovascular events.”
Oxygen Desaturation and Cardiovascular Strain
Oxygen levels in the blood drop during sleep apnea. This makes the heart work harder. It leads to strain on the cardiovascular system.
Oxygen Desaturation Level | Cardiovascular Impact |
Mild | Increased blood pressure |
Moderate | Cardiovascular strain, possible arrhythmias |
Severe | High cardiovascular risk, heart failure possible |
The Role of Sympathetic Nervous System Activation
The “fight or flight” response is triggered in sleep apnea. This response releases stress hormones. It can increase heart rate and blood pressure.
The constant activation of the sympathetic nervous system can harm heart health. It may lead to high blood pressure and heart disease.
It’s important to understand how sleep apnea affects the heart. This knowledge helps create better treatments for both conditions.
Can Sleep Apnea Cause Heart Problems? The Research Evidence
A lot of research shows sleep apnea can raise heart disease risk. We’ll look at key studies and NIH research to get a clearer picture.
Clinical Studies Linking Sleep Apnea to Heart Disease
Many studies have linked sleep apnea to heart disease. They found sleep apnea increases the chance of heart attacks, strokes, and arrhythmias.
Recent research has uncovered how sleep apnea harms the heart. It found low blood oxygen levels during sleep cause inflammation and damage the heart.
The NIH Research on Blood Oxygen Levels and Cardiovascular Risk
The NIH has done a lot of research on sleep apnea and heart disease. A key study found low blood oxygen levels during sleep raise heart disease risk.
Every drop in blood oxygen levels during sleep increases heart disease risk. This shows why treating sleep apnea is key for heart health.
The 45% Increased Risk for Primary Cardiovascular Events
A major NIH study found sleep apnea raises 45% risk for heart problems. This study shows how important it is to diagnose and treat sleep apnea early.
Study | Findings | Implications |
NIH-funded research on sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease | 45% increased risk for primary cardiovascular events | Underscores the need for early diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea |
Clinical studies on sleep apnea and heart disease | Association between sleep apnea and increased cardiovascular risk | Highlights the importance of addressing sleep apnea for cardiovascular health |
Understanding the research helps us see how sleep apnea affects heart health. It’s vital to know the risks and take steps to manage sleep apnea to avoid heart problems.
Sleep Apnea and Heart Failure
It’s important to understand how sleep apnea and heart failure are connected. Sleep apnea, mainly obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), is a big risk for heart failure.
How Sleep Apnea Contributes to Heart Failure Development
Sleep apnea can harm the heart in several ways. Low oxygen levels during sleep make the heart work harder. This can damage the heart over time, leading to heart failure.
Key factors in the development of heart failure due to sleep apnea include:
- Increased sympathetic nervous system activity
- Intermittent hypoxia leading to oxidative stress
- Inflammation and endothelial dysfunction
The 140% Increased Risk Factor
Untreated sleep apnea greatly raises the risk of heart failure. A study found that severe OSA increases the risk by 140%. This shows why treating sleep apnea is so important.
Condition | Increased Risk of Heart Failure |
Severe OSA | 140% |
Mild OSA | Moderate increase |
Recognizing the Warning Signs
Knowing the signs of heart failure is key. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling, and irregular heartbeats. If you see these, get medical help right away.
“Early diagnosis and treatment of sleep apnea can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart failure and improve overall cardiovascular health.”
Sleep Apnea and Coronary Artery Disease
Research shows sleep apnea raises the risk of coronary heart disease. This link is key to grasp, as both affect heart health a lot.
The Connection Between OSA and Coronary Heart Disease
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is tied to heart diseases like coronary artery disease. The breathing stops and starts during sleep. This causes blood oxygen levels to change, putting stress on the heart.
The reasons for this link include inflammation, oxidative stress, and damage to the blood vessel lining. These issues help coronary artery disease grow and get worse.
The 30% Increased Risk for Coronary Heart Disease
People with sleep apnea face a much higher risk of getting coronary heart disease. Research points to a 30% increase in risk.
This higher risk comes from the chronic low oxygen levels in sleep apnea. It causes blood vessel damage and hardening of arteries.
Mechanisms of Arterial Damage
The damage to arteries in sleep apnea comes from several sources:
- Inflammation: Sleep apnea patients have higher levels of inflammatory markers.
- Oxidative Stress: The constant low and high oxygen levels during sleep damage the blood vessel lining.
- Endothelial Dysfunction: The blood vessel lining gets damaged. This makes it hard for blood vessels to widen and can lead to hardening of arteries.
Knowing how these mechanisms work is key to finding treatments. Treatments should tackle both sleep apnea and its effects on heart disease.
Sleep Apnea’s Impact on Stroke Risk
Research shows sleep apnea raises stroke risk, making it key to manage. Sleep apnea causes breathing pauses or shallow breathing during sleep. This affects heart health.
Understanding the 60% Increased Stroke Risk
People with sleep apnea face a 60% higher stroke risk. This is due to breathing pauses that lower blood oxygen, cause inflammation, and strain the heart.
The reasons for this increased risk include:
- Oxygen desaturation: Low oxygen harms the brain and other tissues.
- Inflammation: It can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
- Cardiovascular strain: The heart works harder, risking heart failure or arrhythmias.
Sleep Apnea as a Silent Contributor to Cerebrovascular Events
Sleep apnea often goes unnoticed, with symptoms mistaken for other issues. It silently raises the risk of strokes. Knowing the signs, like loud snoring and morning headaches, is key for early action.
Post-Stroke Sleep Apnea Management
Managing sleep apnea is vital after a stroke. Untreated sleep apnea can worsen recovery and increase stroke risk. CPAP therapy can help manage it and improve outcomes for stroke survivors.
Those who have had a stroke or are at risk should talk to their doctor about sleep apnea. This ensures they get the best care.
Atrial Fibrillation and Sleep Apnea: A Dangerous Duo
Sleep apnea and atrial fibrillation affect each other. Atrial fibrillation causes irregular heartbeats. This can lead to heart failure and stroke risk.
Sleep apnea, like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), can cause atrial fibrillation. The lack of oxygen and poor sleep can damage the heart. This damage can lead to atrial fibrillation.
How Sleep Apnea Triggers Atrial Fibrillation
Sleep apnea can start atrial fibrillation in several ways. The lack of oxygen can cause heart damage. The heart’s electrical pathways can be affected.
The heart’s structure and function can also change. This makes it easier for atrial fibrillation to start and stay.
The Cycle of Worsening Symptoms
Having both sleep apnea and atrial fibrillation makes things worse. Atrial fibrillation can make the heart work less well. This can make sleep apnea worse.
Untreated sleep apnea can also make atrial fibrillation harder to manage. Treating both conditions together is key to improving symptoms.
Treatment Approaches for Patients with Both Conditions
Dealing with both sleep apnea and atrial fibrillation needs a full plan. CPAP therapy is often used for sleep apnea. It helps improve sleep and reduce heart problems.
Other treatments include:
- Anti-arrhythmic medications to control atrial fibrillation
- Catheter ablation to restore a normal heart rhythm
- Lifestyle changes like losing weight, exercising, and quitting smoking
With a detailed treatment plan, doctors can better manage both conditions. This improves patients’ lives and outcomes.
The Economic and Healthcare Impact of Untreated Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea, if not treated, can cause big problems. It affects not just the person’s health but also the whole healthcare system.
38,000 Cardiovascular Deaths Annually
The National Commission on Sleep Disorders Research found a shocking fact. Sleep apnea leads to about 38,000 heart-related deaths each year. This shows how serious untreated sleep apnea is for heart health.
$42 Million in Related Hospitalization Costs
Untreated sleep apnea also has a big financial cost. It costs around $42 million each year for hospital stays. This is a big financial problem for healthcare systems.
The Problem of Underdiagnosis: 40-80% of Cardiac Patients
Another big problem is that many cases of sleep apnea go undiagnosed. Studies say 40% to 80% of heart patients have it without knowing. This not only hurts their health but also adds to the financial burden.
To understand the effects of untreated sleep apnea better, let’s look at the numbers:
Category | Statistic | Impact |
Cardiovascular Deaths | 38,000 annually | Significant mortality risk |
Hospitalization Costs | $42 million | Economic burden on healthcare |
Underdiagnosis in Cardiac Patients | 40-80% | Compromised health outcomes and increased costs |
We need to tackle untreated sleep apnea to lessen its economic and healthcare effects. Raising awareness and getting more people diagnosed is key to reducing its impact.
Treatment Options That Protect Your Heart
We now have many ways to treat sleep apnea that also help your heart. Treating sleep apnea is key for keeping your heart healthy. There are several effective ways to do this.
CPAP Therapy and Cardiovascular Benefits
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is a common and effective treatment for sleep apnea. It delivers a steady stream of air through a mask, keeping the airway open. Studies have shown that CPAP therapy can have significant cardiovascular benefits, including reduced blood pressure and improved heart function.
CPAP therapy has been shown to decrease the risk of heart problems in patients with sleep apnea. It improves oxygen levels and reduces heart strain, helping to lower the risks of sleep apnea on the heart.
Alternative Treatments for Sleep Apnea
While CPAP therapy is highly effective, there are other treatments for those who may not tolerate it or prefer other options. Oral appliance therapy is one such alternative. It involves a custom-made mouthpiece that advances the lower jaw to keep the airway open.
- Oral appliance therapy for mild to moderate sleep apnea
- Surgical options for severe cases or when other treatments fail
- Upper airway stimulation therapy for moderate to severe sleep apnea
Lifestyle Modifications for Heart Health and Better Sleep
Lifestyle changes are also important in managing sleep apnea and improving heart health. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can greatly reduce sleep apnea severity. Avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed can also improve sleep quality.
Other beneficial lifestyle changes include:
- Regular physical activity to improve cardiovascular health
- Quitting smoking to reduce cardiovascular risk factors
- Sleeping on your side to reduce apnea episodes
By combining these lifestyle changes with the right medical treatments, patients can manage sleep apnea and protect their heart health.
Conclusion: Taking Action for Heart and Sleep Health
It’s important to know how sleep apnea affects your heart. Sleep apnea can increase the risk of heart disease. But, treating it can help keep your heart healthy and lower the risk of heart problems.
Recognizing the signs of sleep apnea and getting medical help is key. This can protect your sleep and heart health. Treatments like CPAP therapy and making lifestyle changes can greatly improve sleep quality and heart health.
Protecting your heart and sleep is vital for your overall health. We urge people to see a doctor if they think they have sleep apnea. Talking to a healthcare professional can help find the best treatment and improve heart health.
FAQ
Does sleep apnea directly cause heart problems?
Sleep apnea is a big risk for heart issues like heart failure and coronary artery disease. It might not directly cause heart problems. But, it can make existing heart conditions worse and raise the risk of heart events.
Can untreated sleep apnea lead to heart failure?
Yes, untreated sleep apnea can raise the risk of heart failure by 140%. The breathing pauses during sleep can strain the heart, cause inflammation, and stress. This can lead to heart failure.
How does sleep apnea affect the heart?
Sleep apnea can harm the heart by causing low oxygen levels, heart strain, and stress. These issues can lead to high blood pressure, heart changes, and irregular heartbeats. This increases the risk of heart problems.
Is sleep apnea linked to coronary artery disease?
Yes, sleep apnea is linked to a higher risk of coronary artery disease. Studies show that obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) can increase the risk of heart disease by 30%.
Can sleep apnea increase the risk of stroke?
Yes, sleep apnea can raise the risk of stroke by 60%. The breathing pauses during sleep can cause heart strain, inflammation, and stress. This can lead to stroke.
How is sleep apnea related to atrial fibrillation?
Sleep apnea can trigger atrial fibrillation by changing the heart’s electrical activity and causing inflammation. Treating sleep apnea can help lower the risk of atrial fibrillation coming back.
What are the treatment options for sleep apnea?
Treatments for sleep apnea include CPAP therapy, oral appliances, and positional therapy. Lifestyle changes like losing weight and exercising are also helpful. These treatments can reduce heart risks and improve health.
Can lifestyle changes help manage sleep apnea?
Yes, lifestyle changes like losing weight, exercising, and avoiding sleeping on your back can help manage sleep apnea. These changes can also improve heart health and lower heart risks.
What is the economic impact of untreated sleep apnea?
Untreated sleep apnea leads to 38,000 cardiovascular deaths a year and $42 million in hospital costs. Awareness and diagnosis are key to reducing the economic burden of sleep apnea.
References
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). Can Sleep Apnea Cause Heart Problems What You. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34797460/

































